Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reactivity of Metals Notes and Exercises For Secondary 4 (Grade 10)
Uploaded by
Cloudia CloudOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reactivity of Metals Notes and Exercises For Secondary 4 (Grade 10)
Uploaded by
Cloudia CloudCopyright:
Available Formats
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
Unit 11: Reactivity of metals
Gold
Iron
HKDSE Syllabus
Reactivity of metals
Students should learn
- reactions of some common metals(sodium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iron, lead, copper, etc.) with oxygen/air,
water, dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid
- metal reactivity series and the tendency of metals to form positive ions
- displacement reactions and their interpretations based on the reactivity series
- prediction of the occurrence of reactions involving metals using the reactivity series
- relation between the extraction method of a metal and its position in the metal reactivity series
Students should be able to
- describe and compare the reactions of some common metals with oxygen/air, water and dilute acids
- write the word equations for the reactions of metals with oxygen/air, water and dilute acids
- construct a metal reactivity series with reference to their reactions, if any, with oxygen/air, water and dilute acids
- write balanced chemical equations to describe various reactions
- use the state symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) to write chemical equations
- relate the reactivity of metals to the tendency of metals to form positive ions
- describe and explain the displacement reactions involving various metals and metal compounds in aqueous solutions
- deduce the order of reactivity of metals from given information
- write balanced ionic equations
- predict the feasibility of metal reactions based on the metal reactivity series
- relate the extraction method of a metal to its position in the metal reactivity series
___ Points for this unit
1. Reactions between metals with: a)___________ b)___________ c)________ ________
2. Explaining ______________________________(M.R.S.)
3. __________________ reaction (置換反應) and writing _______________ equation
4. _______________ of metal oxide (Extraction)
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 1
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
A. Reactions with Oxygen, Water and acid
1. Metal + Oxygen ________________
Metal Heat needed Observation Word and chemical equations
to start (General: Metal + Oxygen -> Metal oxide)
reaction
1. Burns vigorously with a ________ + ______ ->____________
______flame.
2. _______ powder formed. K(s) + O2(g)
1. Burns vigorously with a Sodium + oxygen -> Sodium oxide
______ _________flame.
Medium 2. _______powder formed Na(s) + O2(g)
1. ________ _______ flame Calcium + Oxygen -> Calcium oxide
2. ___________powder Ca(s) + O2(g)
1. ________ white flame Magnesium + Oxygen -> Magnesium oxide
2. White powder formed Mg(s) + O2(g)
White powder formed Aluminium + Oxygen -> Aluminium oxide
Al(s) + O2(g)
__________ powder when hot, Zinc + Oxygen -> Zinc oxide
__________ powder when cold Zn(s) + O2(g)
Strong Black powder formed Iron+ Oxygen -> Iron(III) oxide
Fe(s) + O2(g)
__________ powder when hot, Lead + Oxygen -> Lead oxide
__________ powder when cold Pb(s) + O2(g) PbO
Black powder formed Copper + Oxygen -> Copper(II) oxide
Cu(s) + O2(g) CuO
Very strong
Red powder formed Mercury + Oxygen -> Mercury(II) oxide
Hg(s) + O2(g) HgO
Do NOT
NO reaction
burn
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 2
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
2. Metal + Water _______________/_________________ + _________
Metal Observation Word and chemical equations
(General: Metal + Oxygen -> Metal oxide)
Metal + Water Metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas
1. _____, _____ into a silvery ball and Potassium +water ->_______ ______+________
darts around.
2. Burns with a _____ flame K(s) + H2O(l)
1. _____, _____ into a silvery ball Sodium +water ->_______ _____+________
and darts around.
2. _____ flame can be seen. Na(s) + H2O(l)
1. _____ Calcium + Water -> Calcium hydroxide+hydrogen
2. Colourless gas bubbles
3. __________ suspension Ca(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) H2(g)
Metal + Steam Metal oxide + hydrogen gas
Cold water : ____________ Mg(s) + H2O(_)
Hot water : react very slowly
Steam: reacts much faster. Mg(s) + H2O(_)
Same as _____ but less vigorous Al(s) + H2O(_) Al2O3(s)+ H2(g)
Same as _____ but less vigorous Zn(s) + H2O(_) ZnO(s)+ H2(g)
(Remark: colour of oxide:
_____ when hot, _______ when cold)
Same as _____ but less vigorous Fe(s) + H2O(_) Fe2O3(s)+ H2(g)
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 3
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
3. Metals + Acid _____________ + __________
Metal Observation Word and chemical equations
1. Metal dissolves and give out a
lot of heat. Ca(s) + HCl(aq)
(_____________放熱的)
2. Colourless gas bubbles
evolved. Mg(s) + HCl(aq)
(_______________(冒泡))
Al(s) + HCl(aq) AlCl3(aq) + H2(g)
Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Fe(s) + HCl(aq) FeCl3(aq) + H2(g)
Reacts very ____________ Pb(s) + HCl(aq) PbCl2(aq) + H2(g)
1. The oxide of a metal is orange when it is hot but yellow when it is cold. The metal is
A calcium. B lead. C potassium. D zinc.
2. Hydrogen is produced when metal X reacts with water in the set-up shown below:
X could be
A lead.
B magnesium.
C potassium.
D strontium.
3. Which of the following metals can react with cold water readily to give hydrogen?
(1) Calcium (2) Magnesium (3) Zinc
A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 4
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
B. Explaining the Metal reactivity Series
All metals _______ electrons to form positive ions (______) during reaction.
Metal atom Metal ion + electron
Atoms of _______ reactive metals lose outermost shell electrons to form cations _______ readily.
Metal reactivity series Reactivity Tendency of losing electron
Most/least reactive Highest/lowest tendency
Most/least reactive Highest/lowest tendency
Conclusion: More reactive metal is more/less readily to lose electrons.
Factor affecting the tendency of
losing outermost shell electrons
1.____________________
2.____________________
The reactivity of the Group I
metals increases in the order
_______<________<________
while that of Group II metals
increases in the order
_______<________<________
Across the third period, reactivity
decreases in the order
_______>________>________
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 5
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
C. Displacement reaction(置換作用) and ionic equation
A more reactive metal A (Higher in M.R.S.) will displace a less reactive metal B (Lower in M.R.S.) from
a solution of a compound of metal B.
Experiment 1
Add copper to an aqueous solution of silver nitrate.
Chemical equation:
An ionic equation is the equation which ONLY
includes the ions formed or changed in the reaction
Ionic equation
Tips for writing ionic equation:
Observations: 1. Copper __________ Delete the chemical species
2. _________ _____ deposits on the _______ surface which does NOT change in
3. The colour of solution turns from _______ to ___ ___ _______ or _______ after the
reaction.
Experiment 2
Add iron to an aqueous solution of copper(II) nitrate.
Chemical equation:
Ionic equation
Observations: 1. Iron __________
2. ________ _______ _____ deposit on the____ surface
3. The colour of solution turns from ________ to _______
Experiment 3
Add potassium to an aqueous solution of copper (II) nitrate.
Experiment 4
Add lead to an aqueous solution of magnesium nitrate.
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 6
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
D. Reduction of metal oxide
______________(氧化作用): Gain of oxygen to a substance
Metal Metal oxide
______________(還原作用): Loss of oxygen from a substance
Stability of
Reactivity of their Extraction
Metal Chemical equations involved
metal compounds method
(in Ore)
Most/least reactive Most/least stable Example:
NaCl(__)
Al2O3(__)
Heating Step1: ZnS + ____ ____ + ___
with____________ Step2: ____ + C ____ + ___
Examples of FeO + ____ ____ + ____
reducing agent Fe2O3 + ____ ____ + ____
(R.A.):_________ Step1: PbS + ____ ____ + ___
____________
Step2: ____ + C ____ + ___
R.A. can take up
_______ and
_______ the metal CuO + C ___ + _____
oxide back to
_________
CuS + O2 ____ + ____
HgS + O2 ____ + ____
Ag2O ____ + ____
Most/least reactive Most/least stable
Conclusion:
Compounds of a metal _________ in the reactivity series have ___________ stability.
Thus, the reduction of the oxide of the metal is harder.
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 7
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
Exercises
91 MC 08
X, Y and Z are metals. Y can displace X from a solution of the nitrate of X. Oxides of X and Y can be
reduced by hydrogen but not the oxide of Z. Which of the following arrangements represents the correct
descending order of reactivity of the metals?
A. Z>Y>X B. X>Y>Z C. Z > X > Y D. X>Z>Y
91 MC 02
Rubidium (Rb) is a group I element below potassium in the Periodic Table. Which of the following
statements about rubidium is correct?
A. Rubidium forms an acidic oxide.
B. Rubidium is more reactive than potassium.
C. Rubidium can be obtained from its oxide by reduction with carbon.
D. The formula for rubidium chloride is RbCl2.
92 MC 31
In the above experiment, a gas is evolved and burns at the jet. Metal X is probably
A. zinc. B. aluminium C. magnesium D. copper
95 MC 18
Metal X reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to liberate hydrogen, but metal Y and metal Z have no
reaction with the dilute acid. The oxide of metal Y decomposes on heating but the oxide of metal Z does
not. Which of the following arrangements represents the order of increasing reactivity of the three
metals?
A. X<Y<Z B. Y<Z<X C. X<Z<Y D. Z<Y<X
89 3(b) The results of experiments with iron and three other metals X, Y, Z and their oxides are
summarized in the following tables:
Metal Iron X Y Z
Experiment
Action of metal on iron(II) No immediate Iron is A gas is
sulphate solution No reaction
reaction deposited evolved
Metal oxide Fe2O3 XO Y2O Z2O
Experiment
Action of heat on metal No reaction No reaction No reaction Metal Z is
oxide formed
(i) What was the gas evolved in the reaction of Y with iron(II) sulphate solution? Write an
equation for the reaction involved. (State symbols should be given.)
(ii) Arrange the four metals in descending order of activity, and briefly explain your answer.
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 8
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
2015 DSE 1A
2016 DSE
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 9
HKDSE Chemistry Topic 3 Metals Unit 11 Reactivity of metals
2018 DSE
Reactivity series of metal
Metals Metals Metals Metals
K 鉀
Na 鈉
Ca 鈣
Mg 鎂
Al 鋁
Zn 鋅
Fe 鐵
Pb 鉛
Cu 銅
Hg 汞
Ag 銀
Au 金
Copyright © 2018 RS Education All rights reserved. www.rse.hk Ron Lam 10
You might also like
- Unit 7: Chemical Equations ChemistryDocument30 pagesUnit 7: Chemical Equations ChemistryAtharvvaNo ratings yet
- NSS Reactivity F3Document8 pagesNSS Reactivity F3Alexander KwongNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical EquationsDocument66 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical EquationsanacercetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Student NotesDocument28 pagesChapter 3 Student Notesapi-497809440100% (1)
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- 4.4 ElectrochemistryDocument20 pages4.4 Electrochemistrygabrielsiema4No ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Document26 pagesIntroductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Ayanthi ShashikalaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionDocument22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemistry: Redox ReactionsDocument16 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry: Redox ReactionsvfdfdNo ratings yet
- OXIDATION NUMBERS AND NAMING CHEMICAL COMPOUNDSDocument6 pagesOXIDATION NUMBERS AND NAMING CHEMICAL COMPOUNDSAnton-ella RosanaNo ratings yet
- Chap-1-Chemical Reaction and EqDocument8 pagesChap-1-Chemical Reaction and Eqapi-400692183No ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument5 pagesStoichiometryZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: All High School Revision Materials Are Available OnDocument50 pagesElectrochemistry: All High School Revision Materials Are Available OnAhmad AlShahrourNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalDocument6 pagesMetals and Non-MetalAansh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument57 pagesMetals and Non MetalsLOLBOINo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument60 pagesMetals and Non MetalslohithreddyjonnakutiNo ratings yet
- Activity of MetalsDocument8 pagesActivity of MetalsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- 9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionDocument24 pages9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- 9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionDocument23 pages9.1.1 Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionAlvin LowNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Cbse Class 10 Science Chapter 3Document12 pagesNcert Solution Cbse Class 10 Science Chapter 3Smitha BoseNo ratings yet
- SHS Notes Chemical Equations and ReactionsDocument5 pagesSHS Notes Chemical Equations and ReactionsIMAYOYONo ratings yet
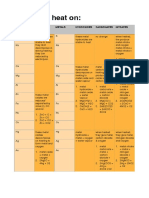
- Actions of Heat On:: Metals Oxides Metals Hydroxides Carbonates NitratesDocument1 pageActions of Heat On:: Metals Oxides Metals Hydroxides Carbonates NitratesKeyur KadiwarNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Chemical equation NotesDocument7 pagesCh1 - Chemical equation Notesਕੇਸ਼ਵ ਗੁਰਜਰNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry calculations and chemical reactionsDocument4 pagesStoichiometry calculations and chemical reactionsLei YinNo ratings yet
- Sharma Science Classes: Science Notes Chapter 1 (Chemical, Reaction and Equations)Document7 pagesSharma Science Classes: Science Notes Chapter 1 (Chemical, Reaction and Equations)Aman YadavNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument56 pagesMetalsTariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument67 pagesREDOXLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry - EquationsDocument5 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry - Equationsgeorge williamson100% (1)
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 1 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 1 2017 PDFKaran Pratap88% (8)
- Synopsis Metals and NonmetalsDocument7 pagesSynopsis Metals and NonmetalsSaumya DhokariyaNo ratings yet
- Anorganic Chemistry: You Want To Gain The "Prize", The B. EngDocument44 pagesAnorganic Chemistry: You Want To Gain The "Prize", The B. EngArinaNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 Chem Summer NoteDocument22 pagesYr 10 Chem Summer NoteTokoni DanielNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument322 pagesScienceIssmeh FatimaNo ratings yet
- EM - 10th Science Notes 2018-19-1Document153 pagesEM - 10th Science Notes 2018-19-1Nagesh EinsteinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter - 1Document8 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter - 1Samradh Singh 9-H DPSKNo ratings yet
- 11 Balancing Equation WorksheetDocument11 pages11 Balancing Equation Worksheeteswong51251200No ratings yet
- Describing Chemical ReactionsDocument42 pagesDescribing Chemical ReactionshypezakramNo ratings yet
- Advanced Material Chemistry Term 1Document74 pagesAdvanced Material Chemistry Term 1Shruti SinghNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document18 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- Oxidation NumberDocument7 pagesOxidation NumberNor Faizahbaizura Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- F5C1 Redox EquilibriumDocument15 pagesF5C1 Redox EquilibriumthilagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Chemical Reactions and EquationsgustafNo ratings yet
- Unit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX OxidationDocument18 pagesUnit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX Oxidationoliver abramsNo ratings yet
- Science Revision STUDY MATERIALDocument94 pagesScience Revision STUDY MATERIALYoNo ratings yet
- Metals Properties Reactions ExtractionDocument0 pagesMetals Properties Reactions ExtractionAdnan Chowdhury100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsDocument18 pagesChemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsproodootNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument17 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- 2.06 RedoxDocument6 pages2.06 RedoxBryan YeohNo ratings yet
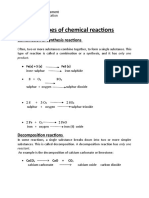
- Different Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination or Synthesis ReactionsDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination or Synthesis ReactionselizabethNo ratings yet
- Batteries & Corrosion Fall 19Document18 pagesBatteries & Corrosion Fall 19Salma SaleemNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth Metals: Properties and UsesDocument20 pagesAlkaline Earth Metals: Properties and UsesMuhammad Saad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-metals GuideDocument12 pagesMetals and Non-metals GuidecharanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8.ABakshDocument10 pagesChemistry Chapter 8.ABakshNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction SPM Form 5Document63 pagesOxidation and Reduction SPM Form 5Azie Nurul Akhtar85% (13)
- Chemical ReactionsDocument37 pagesChemical ReactionsGlydel GealonNo ratings yet
- Combination ReactionsDocument7 pagesCombination Reactionstaurus_nikita4484No ratings yet
- Balancing Redox Reactions Involving Iodine and ManganeseDocument94 pagesBalancing Redox Reactions Involving Iodine and ManganeseKezia MolavinNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mixing Studies of Non-Newtonian Uids in An Anchor Agitated VesselDocument10 pagesMixing Studies of Non-Newtonian Uids in An Anchor Agitated VesselJose Davi Rodrigues Silva UFC100% (1)
- Introduction To Computational ChemistryDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computational ChemistryRicardo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Rucofin Gwe: Composition UsesDocument2 pagesRucofin Gwe: Composition UsesNghia Phan TrungNo ratings yet
- 2023CHE 3241 TEST 2 and ASSIGNMENT 2 - DISTANCEDocument3 pages2023CHE 3241 TEST 2 and ASSIGNMENT 2 - DISTANCEjmbalush74No ratings yet
- MC2 Carbo 2Document7 pagesMC2 Carbo 2Trixie TubogNo ratings yet
- Elephant ToothpasteDocument10 pagesElephant ToothpasteJoseph PendonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Principles for First Year StudentsDocument132 pagesChemical Engineering Principles for First Year StudentsMaui GupitaNo ratings yet
- Technical Catalogue VSF Iec Atex en Rev0 2017 PDFDocument172 pagesTechnical Catalogue VSF Iec Atex en Rev0 2017 PDFshivv230No ratings yet
- Chem-No.-13 2Document5 pagesChem-No.-13 2ho laNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 5, Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 5, Ionic CompoundsAliNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry ReviewDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry ReviewCarlos CabrejosNo ratings yet
- 2.3.02 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 958.01 Phos Pho Rus (To Tal) in Fer Til IzersDocument1 page2.3.02 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 958.01 Phos Pho Rus (To Tal) in Fer Til Izersestefania100% (1)
- Gravimetric Determination of ChlorideDocument8 pagesGravimetric Determination of Chloridejess100% (1)
- College Accounting Chapters 1-30-15th Edition Price Test BankDocument35 pagesCollege Accounting Chapters 1-30-15th Edition Price Test Bankdeemsterazotineaj9ta100% (23)
- Chemistry Check Point RevisionDocument61 pagesChemistry Check Point Revisionsachev.satheeshNo ratings yet
- Henton Et Al. - The Decomposition of Sodium Persulfate in The PresDocument10 pagesHenton Et Al. - The Decomposition of Sodium Persulfate in The PresfuatNo ratings yet
- Electrical Sciences EEE F111Document64 pagesElectrical Sciences EEE F111Kriti TambareNo ratings yet
- Aves - Vitamina e Calidad CarneDocument9 pagesAves - Vitamina e Calidad CarneMarco AsprónNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionsDocument10 pagesReversible ReactionsHamza KhalidNo ratings yet
- Cor 199 Eng DM 160101Document2 pagesCor 199 Eng DM 160101Fraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- DSTI GP Series CatalogDocument30 pagesDSTI GP Series CatalogRasmusKoefoedNo ratings yet
- Protection Repair of ConcreteDocument51 pagesProtection Repair of ConcreteOh No PotatoNo ratings yet
- A262-15 Standard Practices For Detecting Susceptibility To Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless SteelsDocument20 pagesA262-15 Standard Practices For Detecting Susceptibility To Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steelstjt477980% (5)
- Bosch WKD28352GB Washer-DryerDocument56 pagesBosch WKD28352GB Washer-DryerRenz Aldrin EchaoreNo ratings yet
- TAI January 2016Document92 pagesTAI January 2016suresh kumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Minerals Yearbook 2020: (Part-III: Mineral Reviews)Document7 pagesIndian Minerals Yearbook 2020: (Part-III: Mineral Reviews)k_pareshNo ratings yet
- Primocon - Anti FaulingDocument2 pagesPrimocon - Anti FaulingAndri AjaNo ratings yet
- Example Thesis CMGDocument7 pagesExample Thesis CMGneda105No ratings yet
- Mass Transfer 16CE2004 - HandoutDocument80 pagesMass Transfer 16CE2004 - HandoutjAYNo ratings yet
- Wordlywise Book 9 Lesson 9Document1 pageWordlywise Book 9 Lesson 9choiNo ratings yet