Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MARKETING RESEARCH Lec08
Uploaded by
Agricultural RahulicOriginal Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
MARKETING RESEARCH Lec08
Uploaded by
Agricultural RahulicCopyright:
lecture AGRI RAHULIC
Lecture 8
MARKETING RESEARCH
Marketing research is the systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data
IC
and findings relevant to a specific marketing situation facing the company. Marketing research
process can be segregated into five major steps, - defining the problem and research objectives,
developing the research plan, collecting the information, analyzing the data and presenting the
findings.
UL
1. Define the Problem and Research Objectives
Some research is exploratory - its goal is to shed light on the real nature of the problem
and to suggest possible solutions or new ideas. Some research is descriptive - it seeks to ascertain
H
certain magnitudes, such as how many people would buy sauce at Rs.180 per Kg. Some research
is causal - its purpose it to test a cause and effect relationship. For example what would happen if
the price of the product is increased, or expenditure on market promotion activities is increased?
RA
2. Develop the research plan
Designing a research plan calls for decisions on the data sources, research approaches,
research instruments, sampling plan, and contact methods.
Data Sources The researcher can gather secondary data, primary data or both. Secondary data
are data that were collected for another purpose and already exist some where eg., data available
RI
from Economic Survey of India. Primary data are data gathered for a specific research project.
Research Approaches - It refers to methods of collecting data. Primary data can be collected in
five ways: observation, focus groups, surveys, behavioral data, and experiments.
Research Instruments It refers to means of collecting data. Marketing researchers have a choice
AG
of two main research instruments in collecting primary data: questionnaires and mechanical
devices.
Sampling Plan After deciding on the research approach and instruments, the marketing research
must design a sampling plan. This plan calls for three decision.
a) Sampling unit: Who is to be surveyed? The marketing researcher must define the target
population that will be sampled.
youtube- AGRI RAHULIC 1 insta- @AGRI RAHULIC
lecture AGRI RAHULIC
b) Sample size: How many people should be surveyed?
c) Sampling procedure: How should the respondents be chosen?
Contact Methods Once the sampling plan has been determined, the marketing research must
IC
decide how the subject should be contacted: mail, telephone, personal, or on-line interviews.
3. Collect the Information
The data collection phase of marketing research is generally the most expensive and the
UL
most prone to error. In the case of surveys, four major problems arise. Some respondents will
not be at home and must be contacted again or replaced. Other respondents will refuse to
cooperate. Still others will give biased or dishonest answers. Finally, some interviewers will be
biased or dishonest.
4. Analyze the data
H
The next-to-last step in the marketing research process is to extract findings from the
RA
collected data. The researcher tabulates the data and develops frequency distributions. Averages
and measures of dispersion are computed for the major variables. The researcher will also apply
some advanced statistical techniques and decision models in the hope of discovering additional
findings.
5. Present the Findings
RI
As the last step, the research presents the findings to the relevant parties. The research
should present major findings that are relevant to the major marketing decisions facing
management.
AG
youtube- AGRI RAHULIC 2 insta- @AGRI RAHULIC
You might also like
- CHAPTER 3.conducting Marketing ResearchDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 3.conducting Marketing ResearchAngel BenganNo ratings yet
- AMM-Marketing Research (Assignment)Document5 pagesAMM-Marketing Research (Assignment)PRATIKSHA KARNo ratings yet
- Market ResearchDocument25 pagesMarket Researchme youNo ratings yet
- G12 Principles of Marketing W8 LASDocument14 pagesG12 Principles of Marketing W8 LASmaribeldevera razonableNo ratings yet
- The Marketing Research ProcessDocument2 pagesThe Marketing Research ProcessWai Yun MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Marketing Research and Forecasting DemandDocument39 pagesChapter Four: Marketing Research and Forecasting DemandSuLeng LokeNo ratings yet
- Final Document (Principle of Marketing) )Document21 pagesFinal Document (Principle of Marketing) )ASHIMA THAPANo ratings yet
- Mktg671 Ch4 NotesDocument7 pagesMktg671 Ch4 NotesReetu RahmanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter - Week 7 Marketing RevisedDocument7 pages3rd Quarter - Week 7 Marketing RevisedOfelia PedelinoNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Conducting Marketing Research and Forecasting DemandDocument55 pagesMarketing Management: Conducting Marketing Research and Forecasting DemandBilal RajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Zainab GhaddarDocument29 pagesChapter 4 - Zainab GhaddarZainab GhaddarNo ratings yet
- 4Document9 pages4MartaNo ratings yet
- Market Research ProcessDocument17 pagesMarket Research Processpriya balayan100% (2)
- Unit-V: Marketing Information SystemDocument16 pagesUnit-V: Marketing Information SystemLords PorseenaNo ratings yet
- G12 ABM Business Enterprise Simulation Lesson 2Document11 pagesG12 ABM Business Enterprise Simulation Lesson 2Leo Suing100% (2)
- Conducting Marketing Research & Forecasting Demand: Vishnu Parmar, IBA University of Sindh, JamshoroDocument19 pagesConducting Marketing Research & Forecasting Demand: Vishnu Parmar, IBA University of Sindh, Jamshorosumayya84No ratings yet
- American College of Technology: Marketing Research and IntelligenceDocument40 pagesAmerican College of Technology: Marketing Research and IntelligenceTekta MideksaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research: Name-Prativa Kumari SubudhiDocument3 pagesMarketing Research: Name-Prativa Kumari Subudhiprativa subudhiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research Process TOPIC 8Document6 pagesMarketing Research Process TOPIC 8CLEMENCE SANDRANo ratings yet
- Principle Sof Marketi NG: Quarter 1 - Week 6Document10 pagesPrinciple Sof Marketi NG: Quarter 1 - Week 6Lailani MatiasNo ratings yet
- G12 ABM Business Enterprise Simulation-Ppt Lesson 2Document16 pagesG12 ABM Business Enterprise Simulation-Ppt Lesson 2Leo SuingNo ratings yet
- Marketing ResearchDocument21 pagesMarketing ResearchKAIF KHANNo ratings yet
- MP 3Document7 pagesMP 3Pei Xin YauNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Marketing Research: Let's Start!Document14 pagesLesson 6: Marketing Research: Let's Start!Jamaica BuenoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Marketing Research ProcessDocument4 pagesUnit 2 Marketing Research Processrajeev4036No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MarktingDocument65 pagesChapter 3 Marktingmuluken walelgnNo ratings yet
- Q and ADocument11 pagesQ and AVarsha RNo ratings yet
- Market ResearchDocument7 pagesMarket ResearchAzhar DkNo ratings yet
- ch04 Marketing ResearchDocument5 pagesch04 Marketing ResearchSumon Das DasNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research Chapter 3 and 4Document48 pagesMarketing Research Chapter 3 and 4Tina Cuabo CertificoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two The Research Process and Writing Research ProposalDocument17 pagesChapter Two The Research Process and Writing Research ProposalBete AmdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Marketing ResearchDocument19 pagesChapter 2 - Marketing ResearchMelanie Laureano100% (1)
- Advertising StrategyDocument41 pagesAdvertising Strategyvmurali.infoNo ratings yet
- Marketing ResearchDocument38 pagesMarketing ResearchSubhash AroraNo ratings yet
- HaldiramDocument56 pagesHaldiramTrinesh BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research 2Document12 pagesMarketing Research 2Kalkidan TerefeNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research The Research ProcessDocument30 pagesMarketing Research The Research ProcessDhanek NathNo ratings yet
- Topic: Marketing ResearchDocument39 pagesTopic: Marketing ResearchgbgokulNo ratings yet
- Market Research Methods New - 5562f0042194aDocument41 pagesMarket Research Methods New - 5562f0042194aRuwan HerathNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument15 pagesMarketing ManagementSankar RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Scope of MR: Product ResearchDocument53 pagesScope of MR: Product Researchamita_singhNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research SlidesDocument16 pagesMarketing Research SlidesMegha GaurNo ratings yet
- Preface To Marketing Management 14th Edition Peter Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesPreface To Marketing Management 14th Edition Peter Solutions Manualdanielchandlermdfoyjbmkras100% (14)
- ABM PM SLM Week6Document6 pagesABM PM SLM Week6ganda dyosaNo ratings yet
- Chuong 4 - Marketing ResearchDocument72 pagesChuong 4 - Marketing ResearchNguyễn Hữu Hải LuânNo ratings yet
- Marketing ResearchDocument54 pagesMarketing ResearchrajutishwarNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research Management, Unit-2Document3 pagesMarketing Research Management, Unit-2aakarshkapoor81No ratings yet
- Marketing Research Unit - 1Document26 pagesMarketing Research Unit - 1Àñshùl RàñgáríNo ratings yet
- Advertisement Strategy of The Indian Corporate World W:E LG ElectronicsDocument10 pagesAdvertisement Strategy of The Indian Corporate World W:E LG ElectronicsTiwariNo ratings yet
- Ec ReportDocument3 pagesEc ReportmahilomellamaebscaNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument13 pagesPDF DocumentCañada,Renato AyoNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research For Strategic MarketingDocument16 pagesMarketing Research For Strategic MarketingSamah hassanNo ratings yet
- Trial Day-3, Assessment - 1, Bikash SharmaDocument10 pagesTrial Day-3, Assessment - 1, Bikash Sharmabikash sharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Conducting Marketing ResearchDocument22 pagesChapter 4 Conducting Marketing ResearchHeba SamiNo ratings yet
- BBA V Research Methodology PDFDocument12 pagesBBA V Research Methodology PDFPiyush VermaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: B.B.A. V Sem Subject - Research MethodologyDocument26 pagesSyllabus: B.B.A. V Sem Subject - Research MethodologyN. J. DurgeNo ratings yet
- Principle of Marketing-Research MarketDocument21 pagesPrinciple of Marketing-Research MarketAMOS WASIKENo ratings yet
- Brand Research & Analysis: Understand Its Importance & ApplicationFrom EverandBrand Research & Analysis: Understand Its Importance & ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Accounting Concepts and Conventions of AccountingDocument3 pagesAgri Rahulic: Accounting Concepts and Conventions of AccountingAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: National Agricultural PolicyDocument15 pagesAgri Rahulic: National Agricultural PolicyAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Venture Capital Financing - Concept, Purpose and Schemes 1. Venture Capital InstitutionsDocument4 pagesAgri Rahulic: Venture Capital Financing - Concept, Purpose and Schemes 1. Venture Capital InstitutionsAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Principles of Taxation and Tax Structure in IndiaDocument4 pagesAgri Rahulic: Principles of Taxation and Tax Structure in IndiaAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Capital MarketsDocument5 pagesAgri Rahulic: Capital MarketsAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Lec 2021Document34 pagesLec 2021Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Venture Feasibility - Technical and MarketingDocument3 pagesAgri Rahulic: Venture Feasibility - Technical and MarketingAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Business OrganizationDocument22 pagesAgri Rahulic: Business OrganizationAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Venture FeasibilityDocument3 pagesAgri Rahulic: Venture FeasibilityAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Business Environment - Micro Environment Lec09Document2 pagesBusiness Environment - Micro Environment Lec09Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Agri Rahulic: Starting New Business or Buy FirmsDocument8 pagesAgri Rahulic: Starting New Business or Buy FirmsAgricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEUR VS PROFESSIONAL MANAGERS Lec04Document12 pagesENTREPRENEUR VS PROFESSIONAL MANAGERS Lec04Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial - Business - Practices and Policies Lec06Document4 pagesEntrepreneurial - Business - Practices and Policies Lec06Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Sources of Innovative Opportunities Lec07Document6 pagesSources of Innovative Opportunities Lec07Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEUR Lec01Document5 pagesENTREPRENEUR Lec01Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP Lec02Document4 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIP Lec02Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFICATION OF ENTREPRENEURS Lec03Document5 pagesCLASSIFICATION OF ENTREPRENEURS Lec03Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURIAL PROCESS AND STRUCTURE, BARRIERS TO ENTREPRENEURSHIP Lec05Document3 pagesENTREPRENEURIAL PROCESS AND STRUCTURE, BARRIERS TO ENTREPRENEURSHIP Lec05Agricultural RahulicNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams: By: Cherides P. MarianoDocument25 pagesPhase Diagrams: By: Cherides P. MarianoWild RiftNo ratings yet
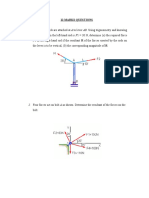
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B.Tech. I - I Sem. L C 4 2 Part-A LABDocument2 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B.Tech. I - I Sem. L C 4 2 Part-A LABHappa1No ratings yet
- MQ SSL/TLS Channels Including V8 ChangesDocument23 pagesMQ SSL/TLS Channels Including V8 ChangesAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bacillariophyceae (Heterokontophyta)Document11 pagesBacillariophyceae (Heterokontophyta)Anjali OjhaNo ratings yet
- 12 MarksDocument23 pages12 Markslakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Automatic Control Systems, 9th Edition: Chapter 9Document50 pagesAutomatic Control Systems, 9th Edition: Chapter 9physisisNo ratings yet
- Jj503 - Mechanical Workshop Practise 4Document2 pagesJj503 - Mechanical Workshop Practise 4jayadarsini2113No ratings yet
- Survey CE1011Document34 pagesSurvey CE1011san htet aung100% (3)
- Reading A Film - Problem of Denotation in Fiction FilmDocument0 pagesReading A Film - Problem of Denotation in Fiction FilmragatasuryaNo ratings yet
- Lista Ejercicios 3 PPEDocument25 pagesLista Ejercicios 3 PPEKarla HermorNo ratings yet
- Mm1 Report Group2 FinalDocument17 pagesMm1 Report Group2 FinalMayumi Atisha KimNo ratings yet
- Bandsaw 7x12 Manual 3410Document30 pagesBandsaw 7x12 Manual 3410sharpxmenNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Modeling of SPT and Grain Size Data in Producing Soil-ProfileDocument5 pagesMATLAB Modeling of SPT and Grain Size Data in Producing Soil-Profileicv.xaviNo ratings yet
- Beckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootDocument56 pagesBeckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootChrisNo ratings yet
- Notes: Edited by William AdkinsDocument6 pagesNotes: Edited by William Adkinsjorge mario durango petroNo ratings yet
- What Is A Philosophical Problem - HackerDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Philosophical Problem - Hackersnain1No ratings yet
- SWT 2 3 101 Brochure.Document8 pagesSWT 2 3 101 Brochure.Uhrin ImreNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT BUCKLING OF STRUTS (Reference)Document13 pagesLAB REPORT BUCKLING OF STRUTS (Reference)jajenNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document8 pagesLab 3TOP 5 GHOSTNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis Genset Dan AtsDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis Genset Dan AtsRamadan yusuf afifNo ratings yet
- Method Comparison Study Report For The ISO 16140-2:2016 Validation of Compact Dry EC, For The Enumeration of ColiformsDocument24 pagesMethod Comparison Study Report For The ISO 16140-2:2016 Validation of Compact Dry EC, For The Enumeration of ColiformsKAREEMNo ratings yet
- Tigear - 2 Gearing: Engineering CatalogDocument292 pagesTigear - 2 Gearing: Engineering Catalogrrobles011No ratings yet
- AutoCAD - Modify ToolbarDocument18 pagesAutoCAD - Modify ToolbarMarcusNo ratings yet
- Reducing Signal NoiseDocument4 pagesReducing Signal NoiseXan OVNo ratings yet
- Luke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesLuke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismseablueNo ratings yet
- Optimal Locations and Sizing of Capacitors For Voltage Stability Enhancement in Distribution SystemsDocument13 pagesOptimal Locations and Sizing of Capacitors For Voltage Stability Enhancement in Distribution Systemsswapna44No ratings yet
- Carpentry 1-2Document16 pagesCarpentry 1-2Zha AgmataNo ratings yet
- IMSO 2008 Short AnswersDocument9 pagesIMSO 2008 Short AnswersWoon Chet ChoonNo ratings yet
- Ash Content PDFDocument4 pagesAsh Content PDFsunniNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of Ship Platform ColissionDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment of Ship Platform Colission123habib123fikriNo ratings yet