100% found this document useful (1 vote)
4K views25 pagesLesson 13: The Functions and Activities of The Laboratory Sample Reception Area
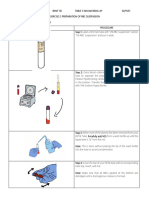
1. The functions of the laboratory sample reception area include receiving various sample types, properly handling samples, and ensuring accurate and timely results and reports.
2. A laboratory assistant called a receptionist is responsible for receiving samples, maintaining logs and tracking systems, communicating with laboratory sections, and performing clerical duties like data entry and filing.
3. Essential information reflected on laboratory request forms includes patient details, requester details, sample details, clinical information, requested examinations, and requester signature to ensure accurate reporting.
Uploaded by
Angel joyce ValenciaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
4K views25 pagesLesson 13: The Functions and Activities of The Laboratory Sample Reception Area
1. The functions of the laboratory sample reception area include receiving various sample types, properly handling samples, and ensuring accurate and timely results and reports.
2. A laboratory assistant called a receptionist is responsible for receiving samples, maintaining logs and tracking systems, communicating with laboratory sections, and performing clerical duties like data entry and filing.
3. Essential information reflected on laboratory request forms includes patient details, requester details, sample details, clinical information, requested examinations, and requester signature to ensure accurate reporting.
Uploaded by
Angel joyce ValenciaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Lesson 13: Introduction
- Learning Outcomes
- Learning Guide
- Information Sheet 13.0