0% found this document useful (0 votes)
601 views3 pagesFormula Sheet - Math
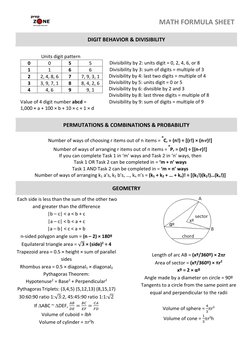
This document provides a summary of various math formulas across several topics:
1) It outlines key number properties including prime numbers, perfect squares, LCM, and GCD.
2) It lists exponent rules and formulas for inequalities, algebra, rates, digit behavior, permutations, combinations, and probability.
3) It includes formulas and rules for geometry, coordinate geometry, trigonometry, statistics, and complex numbers.
Uploaded by
Devansh SharmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
601 views3 pagesFormula Sheet - Math
This document provides a summary of various math formulas across several topics:
1) It outlines key number properties including prime numbers, perfect squares, LCM, and GCD.
2) It lists exponent rules and formulas for inequalities, algebra, rates, digit behavior, permutations, combinations, and probability.
3) It includes formulas and rules for geometry, coordinate geometry, trigonometry, statistics, and complex numbers.
Uploaded by
Devansh SharmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Rates: Describes different rate calculations including work rate, interest rate, and average speed.
- Inequalities and Algebra: Explains methods to solve inequalities and basic algebraic equations.
- Number Properties and Exponents: Covers definitions and lists of prime numbers, perfect squares, and explanations of exponents with examples.
- Geometry: Covers essential geometric formulas and properties including shapes, angles, and areas.
- Permutations, Combinations, and Probability: Explores calculations for selecting items, arranging items, and probability scenarios.
- Digit Behavior and Divisibility: Details digit patterns, rules for divisibility, and applications.
- Coordinate Geometry and Trigonometry: Introduces equations of lines, slopes, and basic trigonometric identities.
- Statistics and Complex Numbers: Reviews statistical measures like mean and introduces complex number operations.