Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Melissa Leaf
Uploaded by
Artem KulikovOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Melissa Leaf
Uploaded by
Artem KulikovCopyright:
Available Formats
Melissa leaf EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 10.
01/2011:1447 (surface view [Ga]) ; secretory trichomes with unicellular to
tricellular stalks and unicellular or, more rarely, bicellular
heads (surface view [Ba], transverse section [F]).
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution. Place 2.0 g of the powdered herbal drug
MELISSA LEAF (355) (2.9.12) in a 250 mL round-bottomed flask and add
100 mL of water R. Distil for 1 h using the apparatus for the
Melissae folium determination of essential oils in herbal drugs (2.8.12) and
0.5 mL of xylene R in the graduated tube. After distillation
DEFINITION transfer the organic phase to a 1 mL volumetric flask,
Dried leaf of Melissa officinalis L. rinsing the graduated tube of the apparatus with the aid of
a small portion of xylene R, and dilute to 1.0 mL with the
Content : minimum 1.0 per cent of rosmarinic acid (C18H16O8 ; same solvent.
Mr 360.3) (dried drug).
Reference solution. Dissolve 1.0 μL of citronellal R and
CHARACTERS 10.0 μL of citral R (composed of neral and geranial) in
25 mL of xylene R.
Odour reminiscent of lemon.
Plate : TLC silica gel plate R (5-40 μm) [or TLC silica gel
IDENTIFICATION plate R (2-10 μm)].
A. The leaves have a petiole of varying length ; the lamina is Mobile phase : ethyl acetate R, hexane R (10:90 V/V).
broadly ovate, up to about 8 cm long and 5 cm wide, acute Application : 20 μL [or 4 μL] as bands.
at the apex and rounded to cordate at the base ; the margins Development : in an unsaturated tank over a path of 15 cm
are crenate to dentate. The upper surface is intense green, [or 6 cm].
the lower surface is paler green and shows a conspicuous
Drying : in air.
midrib and a raised, reticulate venation ; scattered hairs
occur on the upper surface and along the veins on the lower Detection : spray with anisaldehyde solution R and heat at
surface, which is also finely punctuate. 100-105 °C for 10-15 min ; examine in daylight.
Results : see below the sequence of zones present in the
chromatograms obtained with the reference solution and
the test solution. Furthermore, other zones may be present
in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution.
Top of the plate
_______ _______
Citronellal : a grey or A grey or greyish-violet zone
greyish-violet zone at the border (citronellal) at the border between
between the upper and middle the upper and middle thirds
thirds
A reddish-violet zone
_______ _______
Citral : 2 greyish-violet or 2 greyish-violet or bluish-violet
bluish-violet zones at the border zones (citral) at the border
between the middle and lower between the middle and lower
thirds thirds
Reference solution Test solution
TESTS
Foreign matter (2.8.2) : maximum 10 per cent of stems with a
diameter greater than 1 mm and maximum 2 per cent of other
foreign matter, determined on 20 g.
Loss on drying (2.2.32) : maximum 10.0 per cent, determined
on 1.000 g of the powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12) by
drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
Total ash (2.4.16) : maximum 12.0 per cent.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
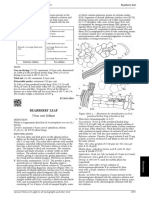
Figure 1447.-1.– Illustration for identification test B of Test solution. Use brown-glass flasks. Disperse 0.100 g of
powdered herbal drug of melissa leaf the powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12) in 90 mL of ethanol
B. Microscopic examination (2.8.23). The powder is greenish. (50 per cent V/V) R. Boil in a water-bath under a reflux
Examine under a microscope using chloral hydrate condenser for 30 min, cool, and filter into a 100 mL volumetric
solution R. The powder shows the following diagnostic flask. Rinse the flask and the filter with 10 mL of ethanol
characters (Figure 1447.-1) : fragments of the upper (50 per cent V/V) R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same
epidermis, in surface view, with sinuous walls [A, B, G], solvent. Filter through a 0.45 μm filter.
sometimes accompanied by palisade parenchyma [Aa] ; Reference solution (a). Dissolve 20.0 mg of rosmarinic
fragments of the lower epidermis [D] with diacytic stomata acid CRS in ethanol (50 per cent V/V) R and dilute to 100.0 mL
(2.8.3) [Db] ; short, straight, unicellular, conical covering with the same solvent. Dilute 20.0 mL of this solution to
trichomes with a finely striated cuticle, free [E] or attached 100.0 mL with ethanol (50 per cent V/V) R.
to an epidermis [Da] ; multicellular, uniseriate covering Reference solution (b). Dissolve 5.0 mg of ferulic acid R in
trichomes with pointed ends and thick, warty cuticles reference solution (a) and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same
[C] ; eight-celled secretory trichomes of lamiaceous type solution.
1536 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 10.0 Melissa leaf dry extract
Column : Test solution. To 0.2 g of the extract to be examined add 5 mL
– size : l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm ; of methanol R. Sonicate for 5 min and filter.
– stationary phase : octadecylsilyl silica gel for Reference solution. Dissolve 1.0 mg of hyperoside R, 1.0 mg
chromatography R (5 μm). of rutoside trihydrate R and 5.0 mg of rosmarinic acid R in
Mobile phase : 10 mL of methanol R.
– mobile phase A : phosphoric acid R, acetonitrile R, water R Plate : TLC silica gel plate R (5-40 μm) [or TLC silica gel plate R
(1:19:80 V/V/V) ; (2-10 μm)].
– mobile phase B : phosphoric acid R, methanol R, acetonitrile R Mobile phase : anhydrous formic acid R, water R, ethyl acetate R
(1:40:59 V/V/V) ; (6:6:90 V/V/V).
Application : 10 μL [or 2 μL] as bands of 15 mm [or 8 mm].
Time Mobile phase A Mobile phase B
(min) (per cent V/V) (per cent V/V) Development : over a path of 8 cm [or 6 cm].
0 - 20 100 → 55 0 → 45 Drying : in air.
20 - 25 55 → 0 45 → 100 Detection : heat at 100 °C for 5 min, spray the plate whilst still
hot with a 5 g/L solution of diphenylboric acid aminoethyl
25 - 30 0 → 100 100 → 0 ester R in ethyl acetate R, and examine in ultraviolet light at
365 nm.
Flow rate : 1.2 mL/min.
Results : see below the sequence of fluorescent zones present
Detection : spectrophotometer at 330 nm. in the chromatograms obtained with the reference solution
Injection : 20 μL. and the test solution. Furthermore, other weaker fluorescent
Relative retention with reference to rosmarinic acid (retention zones may be present in the chromatogram obtained with the
time = about 11 min) : ferulic acid = about 0.8. test solution.
System suitability : reference solution (b) : Top of the plate
– resolution : minimum 4.0 between the peaks due to ferulic
acid and rosmarinic acid.
Calculate the percentage content of rosmarinic acid using the Rosmarinic acid : a light blue An intense light blue fluorescent
fluorescent zone zone (rosmarinic acid)
following expression :
A blue fluorescent zone
A1 ´ m 2 ´ p ´ 0.2 _______ _______
A 2 ´ m1
A blue fluorescent zone
A1 = area of the peak due to rosmarinic acid in the _______ _______
chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
Hyperoside : an orange or
A2 = area of the peak due to rosmarinic acid in greenish-yellow fluorescent
the chromatogram obtained with reference zone
solution (a); A light blue fluorescent zone
m1 = mass of the herbal drug to be examined used to Rutoside : an orange or
prepare the test solution, in grams ; greenish-yellow fluorescent
m2 = mass of rosmarinic acid CRS used to prepare zone
reference solution (a), in grams ; Reference solution Test solution
p = percentage content of rosmarinic acid in rosmarinic
acid CRS. TESTS
Loss on drying (2.8.17) : maximum 6.0 per cent.
01/2010:2524 ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution. Use brown glass flasks. To 0.200 g of the extract
to be examined add 50 mL of ethanol (50 per cent V/V) R.
Sonicate for 10 min and dilute to 100.0 mL with ethanol
MELISSA LEAF DRY EXTRACT (50 per cent V/V) R. Filter through a membrane filter (nominal
pore size 0.45 μm).
Melissae folii extractum siccum Reference solution (a). Dissolve 20.0 mg of rosmarinic
acid CRS in ethanol (50 per cent V/V) R and dilute to 100.0 mL
DEFINITION with the same solvent. Dilute 20.0 mL of this solution to
Dry extract produced from Melissa leaf (1447). 100.0 mL with ethanol (50 per cent V/V) R.
Content : minimum 2.0 per cent of rosmarinic acid (C18H16O8 ; Reference solution (b). Dissolve 5 mg of ferulic acid R in
Mr 360.3) (dried extract). reference solution (a) and dilute to 50 mL with reference
solution (a).
PRODUCTION
Column :
The extract is produced from the herbal drug by a suitable
procedure using either hot water (not less than 70 °C) or a – size : l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm ;
hydroalcoholic solvent that is at most equivalent in strength – stationary phase : octadecylsilyl silica gel for
to ethanol (70 per cent V/V). chromatography R (5 μm).
CHARACTERS Mobile phase :
Appearance : brown or greenish-brown, amorphous powder. – mobile phase A : phosphoric acid R, acetonitrile R, water R
(1:19:80 V/V/V) ;
IDENTIFICATION – mobile phase B : phosphoric acid R, methanol R, acetonitrile R
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). (1:40:59 V/V/V) ;
General Notices (1) apply to all monographs and other texts 1537
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rosmarinus - Farmakope MonografıDocument3 pagesRosmarinus - Farmakope Monografıeylul.irmak.tNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Archangelicae RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Archangelicae RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Sambuci FlosDocument3 pagesSambuci FlosartemNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Sinensis RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Sinensis RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- White Horehound: Marrubii HerbaDocument2 pagesWhite Horehound: Marrubii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Willow Bark 1583eDocument2 pagesWillow Bark 1583eBogdan CioroiuNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- Equiseti HerbaDocument3 pagesEquiseti HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Origani HerbaDocument3 pagesOrigani HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Belladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesBelladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- Senna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentDocument3 pagesSenna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentartemNo ratings yet
- Ep6.2 01 100Document2 pagesEp6.2 01 100mehnoor kaurNo ratings yet
- Millefolii HerbaDocument2 pagesMillefolii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Tormentillae RhizomaDocument1 pageTormentillae RhizomaartemNo ratings yet
- Betulae FoliumDocument3 pagesBetulae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Lupuli FlosDocument2 pagesLupuli FlosArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Bitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureDocument2 pagesBitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureNikotiano TobacumNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedRhosuna AinaNo ratings yet
- Menthae Piperitae FoliumDocument2 pagesMenthae Piperitae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Pharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHDocument4 pagesPharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHValentina MolinaNo ratings yet
- Yarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument4 pagesYarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsHasan Abu AlhabNo ratings yet
- Cetirizine DihydrochlorideDocument3 pagesCetirizine DihydrochloridePRADIKA HANDIWIANTANo ratings yet
- Uvae Ursi FoliumDocument2 pagesUvae Ursi FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- BarbitalDocument2 pagesBarbitalOrlando David Medinueta De AvilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaDocument9 pagesChapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaAlessandra SeverinoNo ratings yet
- Cotton, Absorbent: Lanugo Gossypii AbsorbensDocument2 pagesCotton, Absorbent: Lanugo Gossypii AbsorbensHamed GholamiNo ratings yet
- Lavandulae Flos PH Eur PDFDocument2 pagesLavandulae Flos PH Eur PDFCeangoNo ratings yet
- Papain: ThevohimeofacetoniirlleDocument2 pagesPapain: ThevohimeofacetoniirlleLTV TM DVNo ratings yet
- Ep9.0 03 507Document4 pagesEp9.0 03 507Tiana JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Amisulpride EP 11.0Document2 pagesAmisulpride EP 11.0noschNo ratings yet
- Enrofloxacin For Veterinary UseDocument3 pagesEnrofloxacin For Veterinary Usenguyentuanson167No ratings yet
- 1129 1129 JP Xvii Official Monographs / Labetalol HydrochlorideDocument364 pages1129 1129 JP Xvii Official Monographs / Labetalol HydrochlorideMuhammad Ikhwannasyir100% (1)
- Eucalyptus OilDocument2 pagesEucalyptus Oilsheenali0% (1)
- Hibisci Sabdarifae FlosDocument2 pagesHibisci Sabdarifae FlosInesNo ratings yet
- Matricaria Flower: Matricariae OsDocument2 pagesMatricaria Flower: Matricariae OsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Ambroxol Hydrochloride: Ambroxoli HydrochloridumDocument2 pagesAmbroxol Hydrochloride: Ambroxoli HydrochloridumANDERSON MNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K3Document1 pageVitamin K3firerock07No ratings yet
- 0733E PolyacrilateDocument1 page0733E PolyacrilatenakitaNo ratings yet
- Felodipine: FelodipinumDocument2 pagesFelodipine: FelodipinumIoana-Alexandra Lungu-NastaseNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim: TrimethoprimumDocument3 pagesTrimethoprim: TrimethoprimumLaurențiu Mihai BălanNo ratings yet
- DIPROPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesDIPROPHYLLINEmononoketangqihotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam EP 10Document3 pagesAlprazolam EP 10Erwin FernándezNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Pubescentis RadixDocument3 pagesAngelicae Pubescentis RadixartemNo ratings yet
- Ep7.0 02 1504Document2 pagesEp7.0 02 1504Sidahmed SiDo BouchenakNo ratings yet
- Co Trimoxazole TabletDocument2 pagesCo Trimoxazole TabletYessi LopezNo ratings yet
- 1847 eDocument3 pages1847 eMiroslav IlicNo ratings yet
- Flow Rate: 1.0 Ml/min. Detection: Spectrophotometer at 230 Nm. Injection: 5 L. System Suitability: Reference Solution (A)Document2 pagesFlow Rate: 1.0 Ml/min. Detection: Spectrophotometer at 230 Nm. Injection: 5 L. System Suitability: Reference Solution (A)lee yongqingNo ratings yet
- Prednisone: PrednisonumDocument3 pagesPrednisone: PrednisonumMarcosNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPGuadalupe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- NimesulideDocument2 pagesNimesulideHPLC E77 Quality FarmaNo ratings yet
- Racementhol - British Pharmacopoeia PDFDocument3 pagesRacementhol - British Pharmacopoeia PDFwilNo ratings yet
- Thyme OilDocument9 pagesThyme Oilعبدالعزيز بدرNo ratings yet
- Finasteride: 562 Monographs, Part IDocument2 pagesFinasteride: 562 Monographs, Part ILý TrươngNo ratings yet
- DiacereinDocument3 pagesDiacereinMulayam Singh Yadav0% (2)
- A Validated Method For The Thin Layer Chromatography in Situ Densitometric Quantitation of Capsaicinoids in Habanero Pepper (Capsicum Chinense Jacq.)Document7 pagesA Validated Method For The Thin Layer Chromatography in Situ Densitometric Quantitation of Capsaicinoids in Habanero Pepper (Capsicum Chinense Jacq.)Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method Development For Exploring Pharmacokinetic Profile of Ursolic Acid in Rat Tissues by High Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument11 pagesAnalytical Method Development For Exploring Pharmacokinetic Profile of Ursolic Acid in Rat Tissues by High Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- s00764 022 00196 yDocument10 pagess00764 022 00196 yArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- A Developed High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Method For The Determination of Baicalin in Oroxylum Indicum L. and Its Antioxidant ActivityDocument11 pagesA Developed High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Method For The Determination of Baicalin in Oroxylum Indicum L. and Its Antioxidant ActivityArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Detection of Amitraz, A Formamidine Based Pesticide Using Chromogenic Spray Reagent by Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument4 pagesDetection of Amitraz, A Formamidine Based Pesticide Using Chromogenic Spray Reagent by Thin Layer ChromatographyArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- s00764 022 00203 2Document9 pagess00764 022 00203 2Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Microc 2019 04 079Document8 pages10 1016@j Microc 2019 04 079Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Concurrent quantification of oleanolic acid, β‑sitosterol and lupeol by a validated high‑performance thin‑layer chromatography method in Urginea indica Kunth bulbDocument10 pagesConcurrent quantification of oleanolic acid, β‑sitosterol and lupeol by a validated high‑performance thin‑layer chromatography method in Urginea indica Kunth bulbArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Reshma Jain S. J. Rajput Neeraj Kumar Sethiya Sushil K. ChauddharyDocument7 pagesReshma Jain S. J. Rajput Neeraj Kumar Sethiya Sushil K. ChauddharyArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- s00764 022 00164 6Document7 pagess00764 022 00164 6Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Quantification of Piperine in Different Varieties of Piper Nigrum by A Validated High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Densitometry MethodDocument10 pagesQuantification of Piperine in Different Varieties of Piper Nigrum by A Validated High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Densitometry MethodArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- DexpanthenolDocument2 pagesDexpanthenolArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatographic Method For Determination of AmygdalinDocument32 pagesDevelopment and Validation of High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatographic Method For Determination of AmygdalinArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021967323002261 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0021967323002261 MainArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Lipophilicity of Chalcones by RP-TLC and Computational MethodsDocument9 pagesEvaluation of The Lipophilicity of Chalcones by RP-TLC and Computational MethodsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S277280992200003X MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S277280992200003X MainArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Abraham 1976Document4 pagesAbraham 1976Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- TLC-densitometric Analysis of Allantoin in Symphytum Officinale L. RootsDocument10 pagesTLC-densitometric Analysis of Allantoin in Symphytum Officinale L. RootsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0026265X21002733 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0026265X21002733 MainArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Origani HerbaDocument3 pagesOrigani HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Brimer 1998Document7 pagesBrimer 1998Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- (20835736 - Acta Chromatographica) BMD-TLC - A Useful Separation Technique For Quantitative Analysis of Arbutin and Hydroquinone in Herbal DrugsDocument10 pages(20835736 - Acta Chromatographica) BMD-TLC - A Useful Separation Technique For Quantitative Analysis of Arbutin and Hydroquinone in Herbal DrugsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- TLC-densitometricanalysisofallantoininSymphytumofficinaleL RootsDocument11 pagesTLC-densitometricanalysisofallantoininSymphytumofficinaleL RootsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 258b759328d95bde1be4ccfae839164bDocument11 pages258b759328d95bde1be4ccfae839164bArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Rutoside Trihydrate: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent V/V) Mobile Phase B (Per Cent V/V)Document3 pagesRutoside Trihydrate: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent V/V) Mobile Phase B (Per Cent V/V)Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- IOHEXOLDocument5 pagesIOHEXOLArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesPROPOFOLArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Lupuli FlosDocument2 pagesLupuli FlosArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Artificial Language Instructions Machine Computer Programs Algorithms Invention of The Computer Jacquard Looms Player PianosDocument13 pagesArtificial Language Instructions Machine Computer Programs Algorithms Invention of The Computer Jacquard Looms Player PianosnervgasNo ratings yet
- Book Notes - The Story Grid PDF PDFDocument9 pagesBook Notes - The Story Grid PDF PDFRift FeltonNo ratings yet
- Red Leaves FallingDocument1 pageRed Leaves FallingHansel Jake B. Pampilo100% (1)
- LQS ManualDocument38 pagesLQS ManualVindyanchal Kumar100% (1)
- Tort Law SummaryDocument12 pagesTort Law Summarypooh9916100% (1)
- DC20 Adventure - The HuntedDocument12 pagesDC20 Adventure - The HuntedFelix JaegerNo ratings yet
- B Tech Cse With Specialization in Software EngineeringDocument133 pagesB Tech Cse With Specialization in Software EngineeringANo ratings yet
- MKTG Plann Final PageDocument28 pagesMKTG Plann Final Pageacs_89No ratings yet
- ASUG84161 - Road Map The SAP Ariba Supply Chain Collaboration For Buyers Solution and Customer Adoption Update PDFDocument31 pagesASUG84161 - Road Map The SAP Ariba Supply Chain Collaboration For Buyers Solution and Customer Adoption Update PDFshivamdubey12No ratings yet
- IHOP MenuDocument12 pagesIHOP MenuHICHAM AIT ELMAALEMNo ratings yet
- Alphawave IP - Phase I - L2Document12 pagesAlphawave IP - Phase I - L2extortionchloride610No ratings yet
- Ode To LocalizationDocument3 pagesOde To LocalizationArpan DNo ratings yet
- 110-0042313a Datasheet Darps232 Jun23Document2 pages110-0042313a Datasheet Darps232 Jun23chandrahai hrangkhawlNo ratings yet
- Kiem Tra 15 Unit 8Document1 pageKiem Tra 15 Unit 8Văn Nguyễn Thị HồngNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris IIDocument2 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris IIapi-262133173No ratings yet
- Individual Daily Log and Accomplishment ReportDocument3 pagesIndividual Daily Log and Accomplishment ReportmaristellaNo ratings yet
- SoftCam KeyDocument18 pagesSoftCam Keynazri20No ratings yet
- European Parliament: RR/416354EN - Doc PE416.354v02-00Document34 pagesEuropean Parliament: RR/416354EN - Doc PE416.354v02-00eliahmeyerNo ratings yet
- Lenovo Legion 5 15IAH7H: 82RB0000SBDocument2 pagesLenovo Legion 5 15IAH7H: 82RB0000SBVasudev GovindanNo ratings yet
- History Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Notes Amp Study MaterialDocument12 pagesHistory Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Notes Amp Study MaterialAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF of The People A History of The United States Volume 1 To 1877 3rd Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF of The People A History of The United States Volume 1 To 1877 3rd Edition PDFjoanne.hines504100% (39)
- Species Found On Mangrove Ecosystem at Brgy Lasang, Davao CityDocument11 pagesSpecies Found On Mangrove Ecosystem at Brgy Lasang, Davao CityShelby RGNo ratings yet
- History (Living Crafts Tradition of India) PDFDocument124 pagesHistory (Living Crafts Tradition of India) PDFAdms Vakeel Singh100% (2)
- Porcelain VS PolymersDocument6 pagesPorcelain VS PolymersLisa Harrington100% (1)
- MaharudraDocument4 pagesMaharudraabhi kopardeNo ratings yet
- AdaptabilityDocument3 pagesAdaptabilityfarah hanimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ib MCQDocument31 pagesUnit 1 Ib MCQHemant Deshmukh100% (2)
- Case Study AssessmentsDocument8 pagesCase Study AssessmentsntagungiraNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: ESP A.P English MTB Math Filipino MAPEH (Health)Document7 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: ESP A.P English MTB Math Filipino MAPEH (Health)mayann ornedoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9. Amortization of DebtsDocument23 pagesLesson 9. Amortization of DebtsLorenaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationFrom EverandPractical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Dust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesFrom EverandDust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesNo ratings yet
- Lime and Limestone: Chemistry and Technology, Production and UsesFrom EverandLime and Limestone: Chemistry and Technology, Production and UsesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet