Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lupuli Flos
Uploaded by
Artem KulikovOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lupuli Flos
Uploaded by
Artem KulikovCopyright:
Available Formats
Hop strobile EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 10.
Results : see below the sequence of zones present in the CHARACTERS
chromatograms obtained with the reference solution and the
test solution. Furthermore, other fluorescent zones may be Characteristic, aromatic odour.
present in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution.
Top of the plate
_______ _______ IDENTIFICATION
A yellowish-green fluorescent zone A. Hop strobiles are generally isolated and 2-5 cm long,
Hyperoside : a yellowish-orange A yellowish-orange fluorescent petiolate, ovoid, made up of many oval, greenish-yellow,
fluorescent zone zone (hyperoside) sessile, membranous, overlapping bracts. The external
Chlorogenic acid : a light blue A light blue fluorescent zone bracts are flattened and symmetrical. The internal bracts
fluorescent zone (chlorogenic acid) are longer and asymmetrical at the base because of a fold
A yellowish-green fluorescent zone generally encircling an induviate fruit (achene). The ovary
_______ _______ or rarely the fruit, the base of the bracts and especially the
induvial fold, are covered with small orange-yellow glands.
Reference solution Test solution
TESTS
Ethanol (2.9.10) : 95 per cent V/V to 105 per cent V/V of the
quantity stated on the label.
ASSAY
Stock solution. Dilute about 0.400 g, accurately weighed, in
ethanol (60 per cent V/V) R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the
same solvent.
Test solution. Introduce 5.0 mL of the stock solution into
a round-bottomed flask and evaporate to dryness under
reduced pressure. Take up the residue with 8 mL of a mixture
of 10 volumes of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial acetic
acid R and transfer into a 25 mL volumetric flask. Rinse the
round-bottomed flask with 3 mL of a mixture of 10 volumes
of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial acetic acid R and
transfer into the 25 mL volumetric flask. Add 10.0 mL of a
solution containing 25.0 g/L of boric acid R and 20.0 g/L of
oxalic acid R in anhydrous formic acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL
with anhydrous acetic acid R.
Compensation liquid. Introduce 5.0 mL of the stock solution
into a round-bottomed flask and evaporate to dryness under
reduced pressure. Take up the residue with 8 mL of a mixture
of 10 volumes of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial acetic
acid R and transfer into a 25 mL volumetric flask. Rinse the
round-bottomed flask with 3 mL of a mixture of 10 volumes
of methanol R and 100 volumes of glacial acetic acid R and
transfer into the 25 mL volumetric flask. Add 10.0 mL of
anhydrous formic acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL with anhydrous
acetic acid R.
After 30 min measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of the test
solution at 410 nm.
Calculate the percentage content of total flavonoids, expressed
as hyperoside, from the following expression :
A ´ 1.235
m
i.e. taking the value of the specific absorbance of hyperoside
to be 405. Figure 1222.-1. – Illustration for identification test B of
powdered herbal drug of hop strobile
A = absorbance at 410 nm,
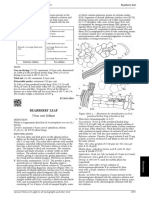
m = mass of the extract to be examined, in grams. B. Microscopic examination (2.8.23). The powder is
greenish-yellow. Examine under a microscope using
chloral hydrate solution R. The powder shows the following
01/2011:1222 diagnostic characters (Figure 1222.-1) : fragments of
bracts and bracteoles covered by polygonal, irregular or
wavy-walled epidermal cells [D, L, M] ; unicellular, conical,
straight or curved covering trichomes with thin, smooth
walls, fragmented [E, G] or attached to an epidermis [A] ;
HOP STROBILE rare anomocytic stomata (2.8.3) [K] ; glandular trichomes,
usually free, with bicellular biseriate stalks and heads
Lupuli flos consisting of 8 small cells [H, N], rarely attached to an
epidermis [La] ; fragments of mesophyll containing small
DEFINITION calcium oxalate cluster crystals [J] ; many characteristic
Dried, generally whole, female inflorescence of Humulus orange-yellow glandular trichomes with short, bicellular
lupulus L. biseriate stalks, bearing a part widening into a cup,
1474 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 10.0 Horse-chestnut
150-250 μm in diameter, made up of a hemispherical layer a water-bath under a reflux condenser. Allow to cool, filter,
of secretory cells with a cuticle that has been detached and and discard the first 10 mL of the filtrate. Evaporate 30.0 mL
distended by the accumulation of oleoresinous secretions of the filtrate to dryness on a water-bath and dry in an oven at
(surface view [B], side view [C]) ; fragments of elongated 100-105 °C for 2 h. The residue weighs a minimum of 0.250 g.
sclerenchymatous cells of the testa with thick walls showing
Loss on drying (2.2.32) : maximum 10.0 per cent, determined
striations and numerous pits [F].
on 1.000 g of the powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12) by
drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Total ash (2.4.16) : maximum 12.0 per cent.
Test solution. To 1.0 g of the freshly powdered herbal drug
(355) (2.9.12) add 10 mL of a mixture of 3 volumes of
water R and 7 volumes of methanol R ; shake for 15 min
and filter.
Reference solution. Dissolve 1.0 mg of Sudan
orange R, 2.0 mg of curcumin R and 2.0 mg of
dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in 20 mL of methanol R. 01/2017:1830
Plate : TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase : anhydrous acetic acid R, ethyl acetate R,
cyclohexane R (2:38:60 V/V/V).
Application : 20 μL as bands.
HORSE-CHESTNUT
Development : over a path of 15 cm.
Hippocastani semen
Drying : in air.
Detection A : examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
DEFINITION
Results A : the chromatogram obtained with the reference Whole or fragmented, dried, ripe seeds of Aesculus
solution shows 3 quenching zones ; in the lower quarter hippocastanum L.
is the faint zone due to curcumin, somewhat below the
middle is the zone due to dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, and Content : minimum 1.5 per cent of triterpene glycosides,
above, the zone due to Sudan orange. The chromatogram expressed as protoaescigenin (C30H50O6 ; Mr 506.7) (dried
obtained with the test solution shows a number of drug).
quenching zones similar in position to the zones in the
chromatogram obtained with the reference solution : at
about the level of the zone due to curcumin is a faint zone
due to xanthohumol, near the level of the zone due to IDENTIFICATION
dimethylaminobenzaldehyde are zones due to humulones,
and near the level of the zone due to Sudan orange are A. The whole, spherical or oval, slightly flattened seed is
zones due to lupulones. 2-4 cm in diameter. It has a shiny, dark-brown testa with a
broad, round, matt, light-brown spot (hilum) ; particularly
Detection B : examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm. on larger seeds, a short, narrow v-shaped ridge marks the
position of the radicle, with the point terminating close
Results B : in the chromatogram obtained with the test to the hilum.
solution the zones due to lupulones show blue fluorescence,
The fragmented seed occurs as more or less polyhedral
the zones due to humulones show brown fluorescence
and the zone due to xanthohumol shows dark brown pieces, about 1-2 cm in diameter, or as slices. The surfaces
corresponding to the cotyledons are matt, light brown, with
fluorescence.
a clean fracture. Those corresponding to the testa are shiny,
dark brown, except at the hilum, where they are matt, light
Detection C : spray with dilute phosphomolybdotungstic
brown. The testa is weakly bound to the cotyledons and is
reagent R ; expose to ammonia vapour and examine in
often detached.
daylight.
B. Microscopic examination (2.8.23). The powder is
Results C : in the chromatogram obtained with the test yellowish-brown. Examine under a microscope using
solution the zones due to humulones and to lupulones chloral hydrate solution R. The powder shows the following
are bluish-grey and the zone due to xanthohumol is diagnostic characters (Figure 1830.-1): numerous
greenish-grey ; in the chromatogram obtained with different-sized droplets of fatty oil that are either free [D] or
the reference solution the zones are bluish-grey or inside the thin-walled colourless cells of the cotyledons [E,
brownish-grey. G] ; yellowish-brown fragments of the outer testa consisting
of sclerenchymatous cells with thick walls (surface view
[C], transverse section [A]) ; fragments from the inner
TESTS testa consisting of thick-walled, colourless parenchymatous
cells varying in shape [B, H, J] with poorly visible pits and
Matter extractable by ethanol (70 per cent V/V) : minimum occasional annular or spiral vessels [F]. Examine under a
25.0 per cent. microscope using a 50 per cent V/V solution of glycerol R.
Starch [K] is present in 3 forms : pyriform or reniform
To 10.0 g of the powdered herbal drug (355) (2.9.12) add simple granules, often with verruciform excrescences,
300 mL of ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R and heat for 10 min on about 15-25 μm in size, sometimes up to 30 μm ;
General Notices (1) apply to all monographs and other texts 1475
You might also like
- BGAS-MCQ-Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesBGAS-MCQ-Exam QuestionsShanmuga Navaneethan100% (5)
- Millefolii HerbaDocument2 pagesMillefolii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Archangelicae RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Archangelicae RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Matricaria Flower: Matricariae OsDocument2 pagesMatricaria Flower: Matricariae OsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Sinensis RadixDocument2 pagesAngelicae Sinensis RadixArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Betulae FoliumDocument3 pagesBetulae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Flos and Fruit PowderDocument46 pagesFlos and Fruit PowderAÏCHA GnosisteNo ratings yet
- Sambuci FlosDocument3 pagesSambuci FlosartemNo ratings yet
- Origani HerbaDocument3 pagesOrigani HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Angelicae Pubescentis RadixDocument3 pagesAngelicae Pubescentis RadixartemNo ratings yet
- Equiseti HerbaDocument3 pagesEquiseti HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- Thymi HerbaDocument3 pagesThymi HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- Ipecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesIpecacuanha Tincture, StandardisedRhosuna AinaNo ratings yet
- Rosmarinus - Farmakope MonografıDocument3 pagesRosmarinus - Farmakope Monografıeylul.irmak.tNo ratings yet
- Hawthorn Berries: Crataegi FructusDocument2 pagesHawthorn Berries: Crataegi FructusartemNo ratings yet
- White Horehound: Marrubii HerbaDocument2 pagesWhite Horehound: Marrubii HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- IPECACUANHADocument3 pagesIPECACUANHALeonardo Henrique SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHDocument4 pagesPharmacopee Francaise - Field Horsetail FHP - Equisetum Arvense PPHValentina MolinaNo ratings yet
- Yarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument4 pagesYarrow For Homoeopathic Preparations Millefolium For Homoeopathic PreparationsHasan Abu AlhabNo ratings yet
- Menthae Piperitae FoliumDocument2 pagesMenthae Piperitae FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Cotton, Absorbent: Lanugo Gossypii AbsorbensDocument2 pagesCotton, Absorbent: Lanugo Gossypii AbsorbensHamed GholamiNo ratings yet
- 6 1 200 Ipecacuanha-Root - (Ipecacuanhae-Radix)Document2 pages6 1 200 Ipecacuanha-Root - (Ipecacuanhae-Radix)Fitry Ana UtamNo ratings yet
- Uvae Ursi FoliumDocument2 pagesUvae Ursi FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Agrimoniae HerbaDocument2 pagesAgrimoniae HerbaartemNo ratings yet
- Senna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentDocument3 pagesSenna Lea Et: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent Mobile Phase B (Per CentartemNo ratings yet
- Aniseed - British Pharmacopoeia 2012 UpdatedDocument3 pagesAniseed - British Pharmacopoeia 2012 UpdatedRoger (Sisfarma)No ratings yet
- Chapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaDocument9 pagesChapter A: New Text of The German PharmacopoeiaAlessandra SeverinoNo ratings yet
- Alfalfa For Homoeopathic Preparations Alfalfa For Homoeopathic PreparationsDocument3 pagesAlfalfa For Homoeopathic Preparations Alfalfa For Homoeopathic PreparationsmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Foeniculi FructusDocument3 pagesFoeniculi FructusHaitao GuanNo ratings yet
- 1847 eDocument3 pages1847 eMiroslav IlicNo ratings yet
- MONOGRAPHIE Purple Cone FlowerDocument3 pagesMONOGRAPHIE Purple Cone Flowerasmae.labindusNo ratings yet
- Bitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureDocument2 pagesBitter-Orange-epicarp and Mesocarp TinctureNikotiano TobacumNo ratings yet
- Melissa LeafDocument2 pagesMelissa LeafArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Tormentillae RhizomaDocument1 pageTormentillae RhizomaartemNo ratings yet
- Belladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesBelladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- Spirulina: Botanical CharacteristicsDocument36 pagesSpirulina: Botanical CharacteristicsWilliams de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Crataegus Oxycanthalinné (Fam - Rosaceae) .It Contains Not Less Than 0.6percent of C-GlycosylatedDocument3 pagesCrataegus Oxycanthalinné (Fam - Rosaceae) .It Contains Not Less Than 0.6percent of C-GlycosylatedcarbouNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Small Scale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 4Th Edition Pavia Kriz Lampman Engel 130525392 Full Chapter PDFDocument25 pagesSolution Manual For Small Scale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 4Th Edition Pavia Kriz Lampman Engel 130525392 Full Chapter PDFmariette.renner827100% (13)
- Willow Bark 1583eDocument2 pagesWillow Bark 1583eBogdan CioroiuNo ratings yet
- Ep6.2 01 100Document2 pagesEp6.2 01 100mehnoor kaurNo ratings yet
- Separation of Plant Pigments PDFDocument3 pagesSeparation of Plant Pigments PDFneelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognostical Evaluation and Tyloses MECHANISM OF Pterocarpus Santalinus LDocument6 pagesPharmacognostical Evaluation and Tyloses MECHANISM OF Pterocarpus Santalinus LwenagoNo ratings yet
- Black Cohosh USP 43 INGLESDocument9 pagesBlack Cohosh USP 43 INGLESAnaly Pocón HernándezNo ratings yet
- APHA 23rd Edition ChlorophyllDocument3 pagesAPHA 23rd Edition ChlorophyllMoutaz AdelNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Beers LawDocument11 pagesLab 4 Beers LawAndrea CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document7 pagesExperiment 1Mhi Ismail0% (1)
- Separation of Plant Pigments by Column ChromatographyDocument17 pagesSeparation of Plant Pigments by Column Chromatographyvishwanathz100% (1)
- AloeDocument2 pagesAloeHage NdoNo ratings yet
- Rumex CrispusDocument2 pagesRumex CrispusLeonardo Henrique SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- Fluocinolone AcetonideDocument2 pagesFluocinolone AcetonideSidahmed SiDo BouchenakNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Photosynthetic Pigments From Isolated ChloroplastDocument32 pagesExtraction of Photosynthetic Pigments From Isolated Chloroplastglorigreiz91% (11)
- Ch311 Organic LabDocument6 pagesCh311 Organic LabSanahKumarNo ratings yet
- 7 ColumnChromDocument7 pages7 ColumnChromfatevilcowNo ratings yet
- BRYONIADocument3 pagesBRYONIALeonardo Henrique SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- Images from Lichenes Australasici Exsiccati and of other characteristic Australasian Lichens. Volume OneFrom EverandImages from Lichenes Australasici Exsiccati and of other characteristic Australasian Lichens. Volume OneNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method Development For Exploring Pharmacokinetic Profile of Ursolic Acid in Rat Tissues by High Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument11 pagesAnalytical Method Development For Exploring Pharmacokinetic Profile of Ursolic Acid in Rat Tissues by High Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Reshma Jain S. J. Rajput Neeraj Kumar Sethiya Sushil K. ChauddharyDocument7 pagesReshma Jain S. J. Rajput Neeraj Kumar Sethiya Sushil K. ChauddharyArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Concurrent quantification of oleanolic acid, β‑sitosterol and lupeol by a validated high‑performance thin‑layer chromatography method in Urginea indica Kunth bulbDocument10 pagesConcurrent quantification of oleanolic acid, β‑sitosterol and lupeol by a validated high‑performance thin‑layer chromatography method in Urginea indica Kunth bulbArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- A Developed High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Method For The Determination of Baicalin in Oroxylum Indicum L. and Its Antioxidant ActivityDocument11 pagesA Developed High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Method For The Determination of Baicalin in Oroxylum Indicum L. and Its Antioxidant ActivityArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- A Validated Method For The Thin Layer Chromatography in Situ Densitometric Quantitation of Capsaicinoids in Habanero Pepper (Capsicum Chinense Jacq.)Document7 pagesA Validated Method For The Thin Layer Chromatography in Situ Densitometric Quantitation of Capsaicinoids in Habanero Pepper (Capsicum Chinense Jacq.)Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- s00764 022 00196 yDocument10 pagess00764 022 00196 yArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Uvae Ursi FoliumDocument2 pagesUvae Ursi FoliumartemNo ratings yet
- Detection of Amitraz, A Formamidine Based Pesticide Using Chromogenic Spray Reagent by Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument4 pagesDetection of Amitraz, A Formamidine Based Pesticide Using Chromogenic Spray Reagent by Thin Layer ChromatographyArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- s00764 022 00203 2Document9 pagess00764 022 00203 2Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2405844019310667 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2405844019310667 MainArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- s00764 022 00164 6Document7 pagess00764 022 00164 6Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0026265X21002733 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0026265X21002733 MainArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Quantification of Piperine in Different Varieties of Piper Nigrum by A Validated High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Densitometry MethodDocument10 pagesQuantification of Piperine in Different Varieties of Piper Nigrum by A Validated High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Densitometry MethodArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Lipophilicity of Chalcones by RP-TLC and Computational MethodsDocument9 pagesEvaluation of The Lipophilicity of Chalcones by RP-TLC and Computational MethodsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S277280992200003X MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S277280992200003X MainArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021967323002261 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0021967323002261 MainArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatographic Method For Determination of AmygdalinDocument32 pagesDevelopment and Validation of High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatographic Method For Determination of AmygdalinArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Sherma 1986Document9 pagesSherma 1986Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 258b759328d95bde1be4ccfae839164bDocument11 pages258b759328d95bde1be4ccfae839164bArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- (20835736 - Acta Chromatographica) BMD-TLC - A Useful Separation Technique For Quantitative Analysis of Arbutin and Hydroquinone in Herbal DrugsDocument10 pages(20835736 - Acta Chromatographica) BMD-TLC - A Useful Separation Technique For Quantitative Analysis of Arbutin and Hydroquinone in Herbal DrugsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Microc 2019 04 079Document8 pages10 1016@j Microc 2019 04 079Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- TLC-densitometricanalysisofallantoininSymphytumofficinaleL RootsDocument11 pagesTLC-densitometricanalysisofallantoininSymphytumofficinaleL RootsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Brimer 1998Document7 pagesBrimer 1998Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix Et RhizomaDocument2 pagesSalviae Miltiorrhizae Radix Et RhizomaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesPROPOFOLArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Rutoside Trihydrate: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent V/V) Mobile Phase B (Per Cent V/V)Document3 pagesRutoside Trihydrate: Time (Min) Mobile Phase A (Per Cent V/V) Mobile Phase B (Per Cent V/V)Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- TLC-densitometric Analysis of Allantoin in Symphytum Officinale L. RootsDocument10 pagesTLC-densitometric Analysis of Allantoin in Symphytum Officinale L. RootsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Abraham 1976Document4 pagesAbraham 1976Artem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Origani HerbaDocument3 pagesOrigani HerbaArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Offshore and Onshore Pipeline SolutionsDocument18 pagesOffshore and Onshore Pipeline SolutionsAshray KvNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Ion Thrusters Xenon Ionized Cathode FilamentDocument2 pagesElectrostatic Ion Thrusters Xenon Ionized Cathode FilamentParama GuruNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 6 Edition: Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides Competition Between Substitution and EliminationDocument65 pagesOrganic Chemistry 6 Edition: Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides Competition Between Substitution and Eliminationpawan kumar guptaNo ratings yet
- Titration - Dry Lab - 2020Document6 pagesTitration - Dry Lab - 2020MariaPaulaGonzalezRojasNo ratings yet
- Nonconventional Methods of Gas LiquefactionDocument45 pagesNonconventional Methods of Gas LiquefactionImtisal E NoorNo ratings yet
- RM Phase - I Test Planner 2023-24Document12 pagesRM Phase - I Test Planner 2023-24arindamgiricontaiNo ratings yet
- MSDS Anhydrous Lanolin 1 PDFDocument6 pagesMSDS Anhydrous Lanolin 1 PDFOm SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Ii (Meng 3306) : Worksheet 1 Chapter1. Potential Flow TheoryDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics Ii (Meng 3306) : Worksheet 1 Chapter1. Potential Flow TheoryAddisu DagneNo ratings yet
- ChlotiahinidinDocument271 pagesChlotiahinidinyanri cahyoNo ratings yet
- Equipment Design Part 1Document50 pagesEquipment Design Part 1Ramzi BEN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- OVAL Corporation: Comblnatlon Alr Ellmlnator-StralnerDocument4 pagesOVAL Corporation: Comblnatlon Alr Ellmlnator-StralnerChuong DongNo ratings yet
- Sinak S-102 Brochure 140401MEDocument2 pagesSinak S-102 Brochure 140401MEAnySikaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesissho 0-MadisonmacdonaldDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesissho 0-Madisonmacdonaldapi-305117392No ratings yet
- Alkane & Alkene MJ 2020Document8 pagesAlkane & Alkene MJ 2020FenNo ratings yet
- Hind Company ProfileDocument8 pagesHind Company ProfileAlok RoyNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: ChemistryDocument25 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: ChemistryMichael OliveraNo ratings yet
- MedPhysTerm-KSMP First Version (200906)Document216 pagesMedPhysTerm-KSMP First Version (200906)Ilkuk EomNo ratings yet
- Components of Solar PanelsDocument2 pagesComponents of Solar PanelsSección Uso CasinoNo ratings yet
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition Volume 14 Issue 11 1975 (Doi 10.1002/anie.197507451) Prof. Dr. Rudolf Criegee - Mechanism of OzonolysisDocument8 pagesAngewandte Chemie International Edition Volume 14 Issue 11 1975 (Doi 10.1002/anie.197507451) Prof. Dr. Rudolf Criegee - Mechanism of OzonolysisSubramanya ByndoorNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Matter Chemical Trends and Bonding Sch3uDocument27 pagesUnit Plan Matter Chemical Trends and Bonding Sch3uapi-350642180No ratings yet
- Worksheet 3: Von Mises Practice Problems: X y XyDocument6 pagesWorksheet 3: Von Mises Practice Problems: X y XyMouad Thf100% (1)
- Test Swab Technical Overview and IFUDocument2 pagesTest Swab Technical Overview and IFUTinnysumardiNo ratings yet
- Compressible Fluid FlowDocument26 pagesCompressible Fluid FlowPradip GuptaNo ratings yet
- Space Product Assurance: Vapour Phase Bioburden Reduction For Flight HardwareDocument24 pagesSpace Product Assurance: Vapour Phase Bioburden Reduction For Flight HardwarejsadachiNo ratings yet
- Petrom OMV Norm B 2001 Rom Eng Rev.1 2006-12-21Document72 pagesPetrom OMV Norm B 2001 Rom Eng Rev.1 2006-12-21lucianduNo ratings yet
- Ann Occup Hyg 2005 Hedmer 629 37Document9 pagesAnn Occup Hyg 2005 Hedmer 629 37Athirah BidinNo ratings yet
- PASTEURISER Holding Section Holding Time CalculationDocument2 pagesPASTEURISER Holding Section Holding Time Calculationarenco100% (2)
- Paints and CoatingsDocument28 pagesPaints and CoatingsMaximiliano MackeviciusNo ratings yet
- Substitution Elimination (Alkilhalides) Bab 5 FessendenDocument113 pagesSubstitution Elimination (Alkilhalides) Bab 5 Fessendenahmad jamalNo ratings yet