Professional Documents
Culture Documents
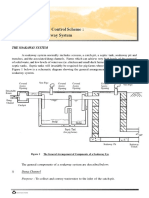
Silo Weights and Measures
Silo Weights and Measures
Uploaded by
Sai Sudheer KattaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Silo Weights and Measures
Silo Weights and Measures
Uploaded by
Sai Sudheer KattaCopyright:
Available Formats
SILO CAPACITIES OF CORNAGE PER FOOT OF HEIGHT
Approximate bushels of dry grain (15.5%)
Kernel Conver-
Moisture sion
Content Factor Inside silo diameter (feet)
8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 30
SHELLED CORN (1.25 cubic feet per bushel at 15.5 per cent moisture)
15.5(*) 1.0 40 63 90 123 160 204 251 304 362 424 640
24 .93 37 58 84 114 148 188 233 281 334 392 592
28 .89 35 56 80 109 142 180 224 270 320 376 568
32 .85 34 53 77 105 136 173 214 258 307 360 543
GROUND EAR CORN (1.94 cubic per bushel at 15.5 percent kernel moisture)
15.5 1.00 26 41 59 80 103 131 162 196 233 274 413
24 .90 23 37 53 72 94 119 148 176 213 250 375
28 .86 22 35 50 69 90 114 141 169 203 238 358
32 .83 21 34 48 66 86 109 134 162 193 227 342
* This first line is for dry grain and can be used to measure capacity of round bins for all small grains.
Conversion Factor – For any size not listed multiply the dry grain capacity of the storage by this factor at listed moisture
content to determine equivalent in dry grain.
Density increases with depth but no allowance was made for compaction in this table. Silos 40 feet or higher may have
10 percent greater capacity then shown in table.
CAPACITIES OF BINS AND CRIBS IN DRY GRAIN
To find the capacities in bushels, first find the volume in cubic feet:
For a crib or cube multiply the length x width x height (all in feet).
For round bins, cribs, or silo multiply the radius (1/2 diameter) x radius x 3.1416 x height.
Then to convert cubic feet to bushels:
Multiply by .8 for small grain or shelled corn.
Multiply by .4 if ear corn.
Multiply by .515 if ground ear corn.
For round bins you may use the top line in Table and multiply by height in feet.
Crib capacities in bushels for ear corn per foot of length:
Width Height in Feet
In feet 8’ 10’ 12’ 14’ 16’
5 16.0 20.0 24.0 28.0 32.0
6 19.2 24.0 28.8 33.6 38.4
STANDARD WEIGHTS OF FARM PRODUCTS PER BUSHEL
lbs. lbs. lbs.
Alfalfa…………………………. 60 Corn (shelled)…... 56 Ryegrass……… 24
Apples(average)…………….. 42 Corn kernel meal.. 50 Rye……………. 56
Barley………………………… 48 Corn (sweet)……. 50 Soybeans……... 60
Beans………………………… 60 Cowpeas………… 60 Spelt…………… 30-40
Bluegrass, (Kentucky)………. 14-28 Flax………………. 56 Sorghum……… 56
Bromegrass, Orchard Grass.. 14 Millet (grain)…….. 50 Sudan Grass…. 40
Buckwheat…………………… 50 Oats……………… 32 Sunflower……... 24
Clover………………………… 60 Onions…………… 52 Timothy……….. 45
Corn (dry ear)………………... 70 Peas……………... 60 Wheat…………. 60
Corn and cob meal………….. 45 Potatoes………… 60 Milk, per gallon.. 8.6
Capacities and Weights, page 1
SILO CAPACITY: TONS OF CORN OR GRASS SILAGE
(68% MOISTURE) IN SETTLED UNOPENED SILOS
RULE OF THUMB ON SILO CAPACITIES:
20’ x 60’ = 500 T. Depth of Inside diameter of silo in feet
20’ x 50’ = 390 T. silage
12’ 14’ 16’ 18’ 20’ 24’ 26’ 30’
20’ x 40’ = 280 T. (in feet)
20’ x 70’ = 575 T.
8 11 15 20 25 31 45 52 70
For any other size silo the radius squared 12 19 25 33 42 52 75 88 117
expressed as a decimal (divided by 100) 16 28 38 49 62 77 111 130 173
times the tonnage of a 20 ft. silo will give 20 38 51 67 85 105 151 177 236
the capacity in tons. 24 49 66 87 110 135 194 228 304
28 61 83 108 137 169 243 286 380
Examples: 32 74 100 131 166 205 295 346 461
30’ x 60’ -– 15 x 15 = 2.25 x 500 or 1145 Tons 36 87 118 155 196 242 348 409 545
16’ x 50’ –- 8 x 8 = .64 x 390 or 250 Tons 40 101 138 180 229 280 403 473 630
30’ x 60’ –- 6 x 6 = .36 x 280 or 101 Tons 44 117 159 207 261 320 461 541 720
50 137 186 248 310 389 560 673 875
TO CONVERT HIGH MOISTURE 55 --- 212 383 365 444 639 750 999
FORAGE TO DRY HAY EQUIVALENT 60 --- --- 319 415 500 720 845 1125
70 --- --- --- --- 574 827 970 1290
Method A – Read the tonnage from the 80 --- --- --- --- 650 1100 1330 1880
Silo Capacity Table. Then divide this 90 --- --- --- --- --- --- --- 2470
figure by 3 to convert to dry hay
equivalent. This will be a close estimate NOTE: When a silo is partially unloaded from the top, the
regardless of the moisture content of the remaining silage is more tightly packed and heavier than the
grass or haylage. same volume in an unopened silo. Therefore, compute the
weight remaining as follows:
Method B – Multiply the tonnage of green
or wet material by the dry hay per ton Example
equivalent in the following table: 1. Use the table to find the 50’ of settled silage in a 20’
original contents before the silo weight 389 T.
Hay or Forage Percent Dry Hay silo was opened.
Moisture Per Ton 2. Estimate depth of silage Weight removed in 32’=205
Green chop 88 .25 tons removed and determine in Tons
Grass silage 70 .34 weight from table.
Grass silage 65 .40 3. Subtract tonnage removed 389 T. (original contents)
Haylage 60 .45 from original contents to find -205 T. (removed in 32’)
Haylage 50 .57 tonnage remaining. 184 T. (remaining in 18’)
Haylage 40 .68
MEASUREMENT STANDARDS, BUNKER SILO – Capacity for Corn Silage, 70
HAY AND STRAW Percent Moisture
Aver- Formula:
age Range Average length x width x settled depth (all in feet) x 40 lbs
Cu.ft./ Cu. Ft./ 2000 lbs.
= Tons
ton ton
Hay, baled 275 250-300
Hay, chopped – field cured 425 400-450 Weight per cu. Ft. will vary by amount of packing, fineness of cut,
Hay, chopped – mow cured 325 300-350 Moisture content, and depth of material. Use the following table to
Hay, long 500 475-525 Estimate pounds per cu. ft. according to depth of pile.
Straw, baled 450 400-500
Straw, chopped 600 575-625
Depth of silage Pounds per cu. ft.
Hay, loose 480 370-390
6 ft. 32 lbs.
Straw, loose 800 750-850
8 36
12 40
20 45
Capacities and Weights, page 2
You might also like
- Beef Cattle Housing and Feedlot FacilitiesDocument23 pagesBeef Cattle Housing and Feedlot FacilitiesCabdalla Niyo100% (1)
- Sepa and PartechDocument5 pagesSepa and Partechdiana bunagan0% (1)
- ANSWERS Preboard Part 1Document12 pagesANSWERS Preboard Part 1Ken Lloyd F. Pabilan100% (4)
- DocxDocument2 pagesDocxDiana BunaganNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2 Sieve Analysis of Coarse Grain SoilDocument3 pagesExperiment No.2 Sieve Analysis of Coarse Grain SoilSajid RazaNo ratings yet
- Comfort Knitting & Crochet: Afghans: More Than 50 Beautiful, Affordable Designs Featuring Berroco's Comfort YarnFrom EverandComfort Knitting & Crochet: Afghans: More Than 50 Beautiful, Affordable Designs Featuring Berroco's Comfort YarnRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Sieve Analysis TestDocument7 pagesSieve Analysis TestamandeepsuperanNo ratings yet
- Planting Guide, Cost and Return Analysis: Per 500 Sq. MeterDocument2 pagesPlanting Guide, Cost and Return Analysis: Per 500 Sq. Meterbharatheeeyudu100% (1)
- A Reassessmment of Sorghum For Lager Beer BrewingDocument9 pagesA Reassessmment of Sorghum For Lager Beer BrewingLaura RondánNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator Excel SheetDocument20 pagesBucket Elevator Excel SheetMaheshNo ratings yet
- Weekend Crochet for Babies: 24 Cute Crochet Designs, From Sweaters and Jackets to Hats and ToysFrom EverandWeekend Crochet for Babies: 24 Cute Crochet Designs, From Sweaters and Jackets to Hats and ToysRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Calculations Screw ConveyorDocument2 pagesCalculations Screw Conveyormashudi_fikriNo ratings yet
- 1990 - Wienese - Mill Setting and ExtractionDocument4 pages1990 - Wienese - Mill Setting and Extractionakshatsabher100% (2)
- Engineering Properties of Agricultural and Food ProductsDocument47 pagesEngineering Properties of Agricultural and Food ProductsBilly Agustin100% (1)
- List of Technically Empanelled Bulk Parties - 1Document12 pagesList of Technically Empanelled Bulk Parties - 1AvijitSinharoy100% (1)
- Belt Speed in M/sec (V) Elevator CalculationsDocument2 pagesBelt Speed in M/sec (V) Elevator CalculationsMashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- Millets NotesDocument17 pagesMillets NotesK bNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator Excel Calculations Bucket Elevator ApplicationsDocument22 pagesBucket Elevator Excel Calculations Bucket Elevator ApplicationsThaigroup CementNo ratings yet
- Using 1,000 Kernel Weight For Calculating Seeding Rates and Harvest LossesDocument5 pagesUsing 1,000 Kernel Weight For Calculating Seeding Rates and Harvest Lossesخير الأنام الحبشىNo ratings yet
- Crop Yields and EstimationsDocument1 pageCrop Yields and EstimationsNeonNo ratings yet
- Dairy Diagnostics Tool BoxDocument8 pagesDairy Diagnostics Tool Boxpavan317No ratings yet
- Managing Tower SilosDocument3 pagesManaging Tower SilosMINA MiladNo ratings yet
- Methods For Calculating Corn Yield: Joe Lauer, AgronomistDocument4 pagesMethods For Calculating Corn Yield: Joe Lauer, AgronomistHuzaifa AhmadNo ratings yet
- .Archivetemptest 3 - Sieve Analysis of SoilDocument11 pages.Archivetemptest 3 - Sieve Analysis of SoilSadon B AsyNo ratings yet
- The University of Toledo Soil Mechanics Laboratory Grain Size Distribution - Sieve AnalysisDocument6 pagesThe University of Toledo Soil Mechanics Laboratory Grain Size Distribution - Sieve AnalysisLeez17No ratings yet
- Papers Traducir CompletoDocument12 pagesPapers Traducir CompletoJuan Jesus Barreda TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Blow Room Production Calculations Formula With ExampleDocument23 pagesBlow Room Production Calculations Formula With ExampleAbel TayeNo ratings yet
- 21 CFR 158-170 Frozen Peas PDFDocument3 pages21 CFR 158-170 Frozen Peas PDFngoc98No ratings yet
- Barley Grass 30ha 40ha: A. For MaizeDocument3 pagesBarley Grass 30ha 40ha: A. For MaizeSergiu ApavaloaeiNo ratings yet
- 2012 Iowa Farm Custom Rate Survey: Ag Decision MakerDocument2 pages2012 Iowa Farm Custom Rate Survey: Ag Decision MakerKyle WilkinsNo ratings yet
- 1964 - Van Hengel - Suggestions For The SettingsDocument4 pages1964 - Van Hengel - Suggestions For The SettingsCecilio Valderrama100% (1)
- Quilt Thread Usage Chart Amann Group MettlerDocument1 pageQuilt Thread Usage Chart Amann Group MettlerAmannGroupMettlerNo ratings yet
- Sieve AnalysisDocument51 pagesSieve AnalysisBadar Hayat100% (1)
- Decide On The Individual Components First, and Then Determine How They Will Fit Together Best To Form The Complete PlanDocument9 pagesDecide On The Individual Components First, and Then Determine How They Will Fit Together Best To Form The Complete PlanseemasainiNo ratings yet
- Test-01 2Document6 pagesTest-01 2Tech SeeNo ratings yet
- Cost and Return Estimate For Rice ProductionDocument37 pagesCost and Return Estimate For Rice ProductionJose Noel S. VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Wheat Flour Determination of Damaged Starch From Whole WheatDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Wheat Flour Determination of Damaged Starch From Whole WheatSiddhant UndeNo ratings yet
- Grain Size of SoilDocument4 pagesGrain Size of SoilAhmadjakwarNo ratings yet
- Grain Size Analysis by Wet and Dry Sieve Analysis: 1. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesGrain Size Analysis by Wet and Dry Sieve Analysis: 1. ObjectiveMuhammad AfrasiyabNo ratings yet
- Dry and Wet AnalysisDocument4 pagesDry and Wet AnalysisManish SolankiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 8 Grain-Size Analysis - Mechanical MethodDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 8 Grain-Size Analysis - Mechanical MethodJL TubilNo ratings yet
- Wet Sieve: University of Maine Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CIE 366 Soil Mechanics LaboratoryDocument4 pagesWet Sieve: University of Maine Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CIE 366 Soil Mechanics LaboratorypvsvprasadcivilNo ratings yet
- Article Nov 2017 Sheep HousingDocument8 pagesArticle Nov 2017 Sheep Housingrafimuttaqin19No ratings yet
- Index Properties of SoilsDocument16 pagesIndex Properties of SoilsTarpan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Objective: Grain Size Analysis by Wet and Dry Sieve AnalysisDocument7 pagesObjective: Grain Size Analysis by Wet and Dry Sieve Analysisdeepak singhNo ratings yet
- Calculating Harvest Yields PDFDocument3 pagesCalculating Harvest Yields PDFFeteneNo ratings yet
- Blow Room Production Calculations Formula With ExampleDocument23 pagesBlow Room Production Calculations Formula With ExampleAbel TayeNo ratings yet
- Maize Growers Guide: Zambia Agribusiness SocietyDocument21 pagesMaize Growers Guide: Zambia Agribusiness SocietyIretioluwa OlawuyiNo ratings yet
- 350L Soil Lab ManualDocument125 pages350L Soil Lab ManualrahaaafalsalemmNo ratings yet
- Granulometria Malte - IngDocument4 pagesGranulometria Malte - IngPhilip WalkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Rice MillingDocument85 pagesChapter 16 Rice MillingRyza MartizanoNo ratings yet
- UK Sub6 The Livestock Waste Control Scheme - Soakaway-SystemDocument5 pagesUK Sub6 The Livestock Waste Control Scheme - Soakaway-SystemLuiz AlvesNo ratings yet
- Engineering 3A: Seive AnalysisDocument11 pagesEngineering 3A: Seive AnalysisCarl MigaelNo ratings yet
- USP-NF Absorbent Gauze 2022Document3 pagesUSP-NF Absorbent Gauze 2022dtecnicaprovigasaNo ratings yet
- Zirbus General CatalogDocument16 pagesZirbus General Catalogentesharat.tarasht3No ratings yet
- Specification and Capacities For DAVIS Super Duty Mixers: H. C. Davis Sons Manufacturing Co., IncDocument1 pageSpecification and Capacities For DAVIS Super Duty Mixers: H. C. Davis Sons Manufacturing Co., IncSambasiva PasumarthyNo ratings yet
- COMBINED SOIL MECH PRAC REPORT Final (GRADING AND ATTERBERG LIMITS)Document20 pagesCOMBINED SOIL MECH PRAC REPORT Final (GRADING AND ATTERBERG LIMITS)Scott MuthuriNo ratings yet
- Name: Mcdonald Kudakwashe Juma Student Number: N0163337C Course Code: EMR 3205 Course Name: Practical Metallurgy Lab Report 1 Sieve AnalysisDocument9 pagesName: Mcdonald Kudakwashe Juma Student Number: N0163337C Course Code: EMR 3205 Course Name: Practical Metallurgy Lab Report 1 Sieve Analysismcdonald jumaNo ratings yet
- 10.manure HandlingDocument21 pages10.manure HandlingGAMUCHIRAI MUGADZANo ratings yet
- ATT-26/96, SIEVE ANALYSIS, 20 000 FM Minus: Aggregate Top Size (FM) Minimum Dry Sample Weight (G)Document12 pagesATT-26/96, SIEVE ANALYSIS, 20 000 FM Minus: Aggregate Top Size (FM) Minimum Dry Sample Weight (G)wayco50No ratings yet
- Busness Plan Cocoa Group 5Document11 pagesBusness Plan Cocoa Group 5rita tamohNo ratings yet
- Can Robots Milk Cows?: Questions and Answers About Farm MachinesFrom EverandCan Robots Milk Cows?: Questions and Answers About Farm MachinesNo ratings yet
- Farmatan PlusDocument1 pageFarmatan PlusMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Table O1. Summary: Type: Growing/Finishing Solution: 1: EmpiricalDocument2 pagesTable O1. Summary: Type: Growing/Finishing Solution: 1: EmpiricalMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Quid PDFDocument1 pageQuid PDFMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Summary Report: Animal InputsDocument6 pagesSummary Report: Animal InputsMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- MG PopularScreenResolutions Graph-2Document1 pageMG PopularScreenResolutions Graph-2Mihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Summary Report: Animal InputsDocument11 pagesSummary Report: Animal InputsMihailo Radivojevic100% (1)
- 1hiruska PDFDocument1 page1hiruska PDFMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- 1 HiruskaDocument1 page1 HiruskaMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Print Online CalendarDocument1 pagePrint Online CalendarMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Print Online Calendar2Document1 pagePrint Online Calendar2Mihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- ŠtampaDocument1 pageŠtampaMihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Vol 19 3-4Document226 pagesVol 19 3-4Mihailo RadivojevicNo ratings yet
- Strategi Meningkatkan Kapasitas Penangkar Benih Padi Sawah (Oriza Sativa L) Dengan Optimalisasi Peran Kelompok TaniDocument24 pagesStrategi Meningkatkan Kapasitas Penangkar Benih Padi Sawah (Oriza Sativa L) Dengan Optimalisasi Peran Kelompok TaniHilmyTafantoNo ratings yet
- Quality Test of FlourDocument7 pagesQuality Test of FlourNur Fadhilah100% (1)
- The Little Red Hen: Leveled Book - GDocument6 pagesThe Little Red Hen: Leveled Book - GAndrei RusuNo ratings yet
- Agbeniga ProjectDocument11 pagesAgbeniga ProjectademosumuhammadNo ratings yet
- CH Image EnglDocument6 pagesCH Image Englkaniappan sakthivel100% (1)
- Uttar Pradesh Millet Value Added Products CatalogueDocument32 pagesUttar Pradesh Millet Value Added Products CataloguePankaj YadavNo ratings yet
- CeralsDocument3 pagesCeralssanjeev100% (1)
- Vishnu Documents Abou T APDocument4 pagesVishnu Documents Abou T APVishnu Reddy Vardhan PulimiNo ratings yet
- Mahyco GrowDocument4 pagesMahyco Growbonat07No ratings yet
- Cereal Products AssignmentsDocument9 pagesCereal Products AssignmentsSaima100% (1)
- Corporation PK For Purchase of Wheat From PasscoDocument6 pagesCorporation PK For Purchase of Wheat From PasscoTalha ChaudryNo ratings yet
- As Grains of WheatDocument1 pageAs Grains of WheatAnthony SysantosNo ratings yet
- Millet Leaf Product CatalogueDocument6 pagesMillet Leaf Product CatalogueAmudha priyaNo ratings yet
- FOOD ReportDocument6 pagesFOOD ReportPam LylahNo ratings yet
- Leche Gloria Azul GrandeDocument3 pagesLeche Gloria Azul GrandeConklin Valdivia Tarazona ConklinNo ratings yet
- Variety Codes of Palay and Milled RiceDocument7 pagesVariety Codes of Palay and Milled RiceMary - Ann AndalNo ratings yet
- Tamilnadu Millet Value Added Products CatalogueDocument43 pagesTamilnadu Millet Value Added Products CataloguePunit BhatiaNo ratings yet
- FAO Cereal Supply and Demand BriefDocument6 pagesFAO Cereal Supply and Demand BriefSadig GuseinovNo ratings yet
- Specification of The Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese Production StandardsDocument17 pagesSpecification of The Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese Production StandardsidiazmNo ratings yet
- Why Is Nutrition: Important in Dancing?Document1 pageWhy Is Nutrition: Important in Dancing?Stephen BritosNo ratings yet
- Gorenje Recipes++Document24 pagesGorenje Recipes++ima gemNo ratings yet
- List of Maize Varieties in Nepal (1966-2010)Document2 pagesList of Maize Varieties in Nepal (1966-2010)anon_565564664100% (1)
- BikoDocument5 pagesBikonathanmaprettyNo ratings yet
- Rice Corn and Other CerealsDocument9 pagesRice Corn and Other CerealskassycarandangNo ratings yet
- Agri CheckDocument4 pagesAgri CheckPancho GuerraNo ratings yet
- Kelloggs HistoryDocument2 pagesKelloggs HistorytashNo ratings yet
- Lablab Bean: Lablab Purpureus (Syn Dolichos Lablab, Lablab Niger)Document1 pageLablab Bean: Lablab Purpureus (Syn Dolichos Lablab, Lablab Niger)Akash RambhiaNo ratings yet