Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Type of Precipitate
Type of Precipitate
Uploaded by
Ms. Wren0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views7 pagesThere are three main types of precipitates: 1) Crystalline precipitates, which form well-defined crystals that are relatively pure and easy to filter. 2) Gelatinous precipitates, which are flocculated colloids that trap impurities and water, making them very difficult to filter. 3) Curdy precipitates, which form porous particle aggregates that can be filtered when they reach a reasonable size. Examples include silver halide compounds.
Original Description:
These are the types of precipitate under Analytical Chemistry.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are three main types of precipitates: 1) Crystalline precipitates, which form well-defined crystals that are relatively pure and easy to filter. 2) Gelatinous precipitates, which are flocculated colloids that trap impurities and water, making them very difficult to filter. 3) Curdy precipitates, which form porous particle aggregates that can be filtered when they reach a reasonable size. Examples include silver halide compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views7 pagesType of Precipitate
Type of Precipitate
Uploaded by
Ms. WrenThere are three main types of precipitates: 1) Crystalline precipitates, which form well-defined crystals that are relatively pure and easy to filter. 2) Gelatinous precipitates, which are flocculated colloids that trap impurities and water, making them very difficult to filter. 3) Curdy precipitates, which form porous particle aggregates that can be filtered when they reach a reasonable size. Examples include silver halide compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
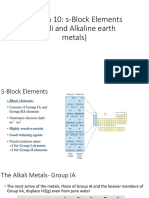
TYPES OF PRECIPITATES
1. CRYSTALLINE
• well-defined / regularly shaped
crystals whose shapes are a
function of the composition of the
salt;
• relatively pure;
• ready to filter;
• are filtered rapidly, easily and
completely;
• since these crystals are not pure
and are too small to filter
effectively, they are heated to
achieve larger and purer crystals
(digestion);
• examples are calcium oxalate and
also the alkaline earth sulfates
such as barium sulfate.
2. GELATINOUS
• flocculated colloids; jelly-like,
hydrous masses
• trap a great deal of water and
many impurities;
• very difficult to work with;
• the cation & anion react to form a
soluble colloid and then coagulate
to filterable-sized particles;
• examples are metal hydroxides
such as ferric hydroxide;
3. CURDY
AgCl AgBr AgI
• aggregates of small porous
particles;
• the cation & anion react to form a
soluble colloid and then coagulate
to filterable-sized particles;
• when reasonable in size, they are
filtered rapidly, easily and
completely;
• examples are the silver halides
compounds;
You might also like
- Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry Projectarjunv_1459% (32)
- Lecture 3 PDFDocument61 pagesLecture 3 PDFKristine CervanciaNo ratings yet
- Batuan Sedimen KimiawiDocument16 pagesBatuan Sedimen KimiawiMalik MajidNo ratings yet
- Section 10 A - S Block ElementsDocument57 pagesSection 10 A - S Block ElementsMonique AldanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument36 pagesChemistry NotesAkshay AroraNo ratings yet
- Ionic Crystals:: Why Does Sodium Chloride Have Brittle Crystals?Document1 pageIonic Crystals:: Why Does Sodium Chloride Have Brittle Crystals?KyanaNo ratings yet
- 2.4. SaltsDocument27 pages2.4. Saltsgabrielsuva6No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Land and It ResourcesDocument35 pagesChapter 6 Land and It ResourcesArif KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Rocks Minerals NotesDocument51 pagesTopic 11 Rocks Minerals Notescrammy riveraNo ratings yet
- Methods of Preparation of ColloidsDocument14 pagesMethods of Preparation of ColloidsNurhidayah Mat Sarit100% (3)
- 8 MetallurgyDocument32 pages8 MetallurgyTamiru DerejeNo ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument14 pagesMinerals and Rockskatherine corveraNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument47 pagesRocks and MineralsRoxette Rosete100% (3)
- Physics Art IntergratedDocument8 pagesPhysics Art IntergratedvishaalNo ratings yet
- Oks IdaDocument19 pagesOks IdaRanaAttiqahNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water TreatmentDocument43 pagesBoiler Water TreatmentmasoodismNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyanide Gold Mining: Orcr Usepa July 2012Document14 pagesIntroduction To Cyanide Gold Mining: Orcr Usepa July 2012Tingwe PoulNo ratings yet
- Restoration and Conservation of Artworks Made of MetalsDocument64 pagesRestoration and Conservation of Artworks Made of MetalsCrisencio M. PanerNo ratings yet
- MINERALS NewDocument63 pagesMINERALS NewgroyoncharlesdaviNo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixtureDocument2 pagesWays of Separating MixtureyssselNo ratings yet
- Metal Extraction 1Document16 pagesMetal Extraction 1Lusanda PayiyaNo ratings yet
- Carbonate, Sulfate and Phosphate Minerals GroupsDocument22 pagesCarbonate, Sulfate and Phosphate Minerals Groupsjaya01387No ratings yet
- MINERALSDocument28 pagesMINERALSmitsiko00000No ratings yet
- As Sing MentDocument5 pagesAs Sing MentAbdihakim Muhumed AhmedNo ratings yet
- KBTU - 2023 - Fall - С&C - Lectures 22-23 - ZeolitesDocument41 pagesKBTU - 2023 - Fall - С&C - Lectures 22-23 - ZeolitesAkerke RamazanovaNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Naturally OccurringDocument46 pagesMinerals: Naturally OccurringthazhuvaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 No VideoDocument35 pagesModule 3 No VideoApril Grace MontebanoNo ratings yet
- Scaling in BoilersDocument12 pagesScaling in BoilersVikneswaran BalakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Types of MineralsDocument26 pagesTypes of MineralsJessa NasalitaNo ratings yet
- Land and Its ResourcesDocument9 pagesLand and Its ResourcesGula MelakaNo ratings yet
- Lithosphere Final SoilDocument66 pagesLithosphere Final SoilMarcusNo ratings yet
- GoldDocument155 pagesGoldJeyson Cornejo100% (1)
- M1 L9 Zeolite Ion ExchangeDocument21 pagesM1 L9 Zeolite Ion Exchangegaurav toppoNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Large Scale Gold RefiningDocument12 pagesInstructions For Large Scale Gold RefiningearthplightNo ratings yet
- Experimental Chemistry: Methods of PurificationDocument44 pagesExperimental Chemistry: Methods of PurificationAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2.1 MineralsDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 2.1 MineralsPrincess Jaymee SuarezNo ratings yet
- Rocks & MineralsDocument14 pagesRocks & MineralsMark ChristianNo ratings yet
- Ag CLDocument1 pageAg CLMarkus MuhlthalerNo ratings yet
- Abbott's American Watchmaker: An Encyclopedia for the Horologist, Jeweler, Gold and SilversmithFrom EverandAbbott's American Watchmaker: An Encyclopedia for the Horologist, Jeweler, Gold and SilversmithNo ratings yet
- Preparation of CrystalsDocument2 pagesPreparation of Crystalsjanu kandwalNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 6 - Land and Its Resources PDFDocument5 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 6 - Land and Its Resources PDFFarah Sofea Razali87% (15)
- EXP 10 (A) Potash Alum CrystalDocument2 pagesEXP 10 (A) Potash Alum CrystalSarita BhattNo ratings yet
- Lab IntroductionDocument2 pagesLab Introductionapi-327823961No ratings yet
- Water Softening MethodsDocument34 pagesWater Softening MethodsAjitsingh Jagtap100% (1)
- Sulfur: Sulfur Is Essential To Life. It Is A Minor Constituent of Fats, Body Fluids, and Skeletal MineralsDocument48 pagesSulfur: Sulfur Is Essential To Life. It Is A Minor Constituent of Fats, Body Fluids, and Skeletal MineralsqusaiNo ratings yet
- ZeoliteDocument29 pagesZeoliteAldrienNo ratings yet
- Science F3 Chap 6 Land and It's ResourcesDocument34 pagesScience F3 Chap 6 Land and It's ResourcesRebecca Choong Xin Hui100% (1)
- Inbound 1134182110424262321Document22 pagesInbound 1134182110424262321Antonette Kim Ausejo MapiliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document33 pagesLesson 2KelvinNo ratings yet
- Petroleum System Hydrocarbon Traps: Prof. Dr. Nabeel Al-Azzawi Oct.2020Document23 pagesPetroleum System Hydrocarbon Traps: Prof. Dr. Nabeel Al-Azzawi Oct.2020demi loveNo ratings yet
- Environments EvaporitesDocument32 pagesEnvironments EvaporitesJairo PáezNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Potash AlumDocument1 pagePreparation of Potash AlumHIMANSU KUMAR PRADHANNo ratings yet
- How I Refine Gold To .999 Fine Using ARDocument11 pagesHow I Refine Gold To .999 Fine Using ARSteveLooser100% (2)
- Ec PresentationDocument35 pagesEc PresentationMuhammad Harris KhanNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Engr. Engr. Irfan Ahmad (Lecture CED UOL)Document17 pagesMinerals: Engr. Engr. Irfan Ahmad (Lecture CED UOL)Abuzar AliNo ratings yet
- Notes On Applied GeologyDocument35 pagesNotes On Applied GeologyDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Salts and Their PreparationDocument11 pagesSalts and Their PreparationWafi Bin Hassan The InevitableNo ratings yet
- SeleniteDocument6 pagesSelenitecpunxzatawneyNo ratings yet
- Petrified Embryology Volume 6: The Frozen Baby Dinosaurs – Gryposaurus monumentensisFrom EverandPetrified Embryology Volume 6: The Frozen Baby Dinosaurs – Gryposaurus monumentensisNo ratings yet