Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sol 45
Uploaded by
Harshul SingalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sol 45
Uploaded by
Harshul SingalCopyright:
Available Formats
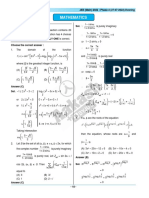
Solution
Week 45 (7/21/03)
Sliding along a plane
The normal force from the plane is N = mg cos θ. Therefore, the friction force on
the block is µN = (tan θ)N = mg sin θ. This force acts in the direction opposite to
the motion. The block also feels the gravitational force of mg sin θ pointing down
the plane.
Because the magnitudes of the friction force and the gravitational force along the
plane are equal, the acceleration along the direction of motion equals the negative
of the acceleration in the direction down the plane. Therefore, in a small increment
of time, the speed that the block loses along its direction of motion exactly equals
the speed that it gains in the direction down the plane. Letting v be the speed of
the block, and letting vy be the component of the velocity in the direction down the
plane, we therefore have
v + vy = C, (1)
where C is a constant. C is given by its initial value, which is V + 0 = V . The final
value of C is Vf + Vf = 2Vf (where Vf is the final speed of the block), because the
block is essentially moving straight down the plane after a very long time. Therefore,
V
2Vf = V =⇒ Vf = . (2)
2
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- 18 March Shift II PhysicsDocument5 pages18 March Shift II PhysicsHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Rit 5 - 19 12 22Document19 pagesRit 5 - 19 12 22Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Ans Sol JEEMain 2022 Phase 2-27-07 2022 E MathsDocument11 pagesAns Sol JEEMain 2022 Phase 2-27-07 2022 E MathsHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- DCC SR Xii 21dec 23dec22Document1 pageDCC SR Xii 21dec 23dec22Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Ans Sol JEEMain 2022 Phase 2-27-07 2022 M MathsDocument10 pagesAns Sol JEEMain 2022 Phase 2-27-07 2022 M MathsHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Camp23 QeeDocument67 pagesCamp23 QeeHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- CellDocument9 pagesCellHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Pan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2017Document17 pagesPan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2017Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Pan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2016Document8 pagesPan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2016Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Pan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2017Document5 pagesPan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2017Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Elasticity of CantileverDocument8 pagesExperiment: Elasticity of CantileverHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- However, This Construction Will Not Work If ' Is Too Large or Too Small. We Will Determine These Bounds BelowDocument3 pagesHowever, This Construction Will Not Work If ' Is Too Large or Too Small. We Will Determine These Bounds BelowHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Elasticity of Cantilever (10 Points)Document4 pagesExperiment: Elasticity of Cantilever (10 Points)Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Theory Q1 EnglishDocument4 pagesTheory Q1 EnglishHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Theory Question 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesTheory Question 1 SolutionHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Elasticity of Cantilever (10 Points)Document4 pagesExperiment: Elasticity of Cantilever (10 Points)Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Theory Problem3 SolutionDocument7 pagesTheory Problem3 SolutionHarshul SingalNo ratings yet
- The 51St23Rd Internationalrudolf Ortvay Problem Solving Contest in Physics 22 October2 November 2020Document11 pagesThe 51St23Rd Internationalrudolf Ortvay Problem Solving Contest in Physics 22 October2 November 2020Harshul SingalNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)