Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name:-Sachin Sharma Course: - Mca 4 Semester Subject: - Blockchain and Technology
Uploaded by
Sachin SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:-Sachin Sharma Course: - Mca 4 Semester Subject: - Blockchain and Technology
Uploaded by
Sachin SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Name :- Sachin Sharma
Course :- MCA 4th Semester
Subject :- BlockChain and Technology
Q1 :- What are centralized services?
Centralized services is a service which we provide to more than one customer (usually all of them) to
ensure a fast, efficient, and secure IT experience. These services are managed behind the scenes, and are
centralized in that we can administer them across our entire customer base with a few clicks of the mouse.
Take antivirus as an example. Smart Dolphins deploys one antivirus product, whenever possible, to all of
our clients. It is included in every single Smart Dolphins agreement as part of the monthly fee. Our
antivirus product (on your machines) receives all of its configuration settings from a computer at Smart
Dolphins, and it also reports directly to a dashboard of ours whenever it finds a virus.
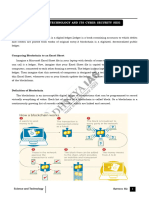
Q2. What do you mean by trusted third party?
Trusted third parties (TTPs) are often employed to facilitate trust in commercial transactions. Banks,
lawyers and brokers are typical examples in everyday use.
On moving to the electronic world, the environment for establishing trust is significantly changed and,
consequently, TTPs are required to play new roles. Important TTP services for electronic commerce
include certification, time-stamping and notarisation. This paper describes these new TTP services and the
vital roles they play in electronic commerce.
3. Why do we need blockchain?
Blockchain started in 1991 as a way to store and secure digital data. Blockchain is an open ledger that
several parties can access at once. One of its primary benefits is that the recorded information is hard to
change without an agreement from all parties involved. IBM explained that each new record becomes a
block with a unique, identifying hash. Linking the blocks into a chain of records forms a blockchain. Bitcoin
cryptocurrency uses blockchain technology.
Blockchain helps in the verification and traceability of multistep transactions needing verification and
traceability. It can provide secure transactions, reduce compliance costs, and speed up data transfer
processing. Blockchain technology can help contract management and audit the origin of a product. It also
can be used in voting platforms and managing titles and deeds.
4. What is the problem area of bitcoin?
Bitcoin has come a long way in the eight or so years it's been in existence, but there's still a long way to
go before the digital currency becomes a widely used method of paying for goods and services.
1. Volatility
Bitcoin has been incredibly volatile since its inception. I wrote in September that $10 worth of
bitcoin in 2010 would be worth millions of dollars today
2. Ease of use
To be fair, it has gotten much easier to buy, sell, and use bitcoin over the past several years, but
it still isn't user-friendly enough to encourage mainstream adoption.
3. Potential for theft
Security measures exist that make bitcoin virtually impossible to steal, but taking advantage of
them involves a somewhat complex knowledge of how bitcoin works and can often require
significantly more effort on the part of the user.
Q5 :- do you mean by internet of value?
The Internet of Value, described in simple terms, is an online space where people can instantly transfer value
between each other, eliminating the need for the middlemen and most costs. Theoretically, anything of
monetary or social value can be transferred between parties, including currency, assets, stocks, securities,
intellectual property rights, scientific discoveries, and even a vote in an election.
Transferring value is already supported by legacy financial rails like SWIFT, blockchain like Bitcoin or Ethereum and
new and emerging technologies or solutions like Interledger (ILP), PayID and many, many apps that make
transferring value easier with existing infrastructure. All of these need to be connected somehow to achieve the
vision and there are likely still a lot of unknowns.
You might also like
- Ethereum: An Essential Beginner’s Guide to Ethereum Investing, Mining and Smart ContractsFrom EverandEthereum: An Essential Beginner’s Guide to Ethereum Investing, Mining and Smart ContractsNo ratings yet
- Decentralized Autonomous Organization The Book of DAO Business in the Next Generation Strategies of the Couch CEO The Healthcare and Insurance Industries Gone Blockchain 2022: Digital money, Crypto Blockchain Bitcoin Altcoins Ethereum litecoin, #1From EverandDecentralized Autonomous Organization The Book of DAO Business in the Next Generation Strategies of the Couch CEO The Healthcare and Insurance Industries Gone Blockchain 2022: Digital money, Crypto Blockchain Bitcoin Altcoins Ethereum litecoin, #1No ratings yet
- Survey On Blockchain Based Privacy Preserving Digital Ledger For Medical Data SharingDocument7 pagesSurvey On Blockchain Based Privacy Preserving Digital Ledger For Medical Data SharingRene ThomasNo ratings yet
- Digital Assets EraDocument4 pagesDigital Assets Erachauhanaakash2831No ratings yet
- Crypto Investor Network Altcoin Investing For BeginnersDocument14 pagesCrypto Investor Network Altcoin Investing For Beginnersrichyken123No ratings yet
- (E-Book) Technology Vol. 1 - Blockchain - The Unbreakable ChainDocument33 pages(E-Book) Technology Vol. 1 - Blockchain - The Unbreakable Chainchrsm.wallaceNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin Introduction Into Blockchain DevelopmentDocument2 pagesBitcoin Introduction Into Blockchain DevelopmentAiron WindsNo ratings yet
- Dex: A Dapp For The Decentralized Marketplace: Chris DaiDocument12 pagesDex: A Dapp For The Decentralized Marketplace: Chris Daigamers305No ratings yet
- Presented By: Name: Divyashree C M. Usn: 1Bi18Mca08Document16 pagesPresented By: Name: Divyashree C M. Usn: 1Bi18Mca08Smarts SNo ratings yet
- Technopreneur Development Project Proposal RandomDocument13 pagesTechnopreneur Development Project Proposal Randommuhammad hafiz khaironNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument12 pagesBlock ChainSiddhartha AnandNo ratings yet
- Fin TechDocument9 pagesFin TechShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Blockchain: Pros and Cons. and Its Application in IndustryDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Blockchain: Pros and Cons. and Its Application in IndustryKaushik RanjanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain, Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency: The Three Aspects of Modern TransactionsDocument5 pagesBlockchain, Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency: The Three Aspects of Modern TransactionsLucNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Applications: Use of Inochain in Various Applicati OnsDocument3 pagesBlockchain Applications: Use of Inochain in Various Applicati OnsIslam EisaNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin A Simple Explanation of Bitcoin and Block Chain Technology JANUARY 2015 Richard Lee TwesigeDocument7 pagesBitcoin A Simple Explanation of Bitcoin and Block Chain Technology JANUARY 2015 Richard Lee TwesigeOtilia OlteanuNo ratings yet
- Use of Blockchain Technology in Agribusiness - Transparency and Monitoring in Agricultural TradeDocument3 pagesUse of Blockchain Technology in Agribusiness - Transparency and Monitoring in Agricultural TradeNancy TomlinsonNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument13 pagesBlock Chainavaneeshy1310No ratings yet
- Block Chain TestingDocument26 pagesBlock Chain TestingpriyawrwNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report BlockDocument18 pagesSeminar Report BlockFieldartNo ratings yet
- Blockchain PresentationDocument24 pagesBlockchain PresentationAnitha TNo ratings yet
- Making IoT Safe Using BlockchainDocument12 pagesMaking IoT Safe Using BlockchainApoorv JhawarNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide For Institutional Investors: Digital Assets 101Document5 pagesA Beginner's Guide For Institutional Investors: Digital Assets 101Manan ShahNo ratings yet
- Israel A Hotspot For Blockchain InnovationDocument33 pagesIsrael A Hotspot For Blockchain InnovationSyndicated NewsNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology: An Approaching Game Changer in Financial Service IndustryDocument5 pagesBlockchain Technology: An Approaching Game Changer in Financial Service IndustryEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Asritha Mamidi (16711A0540) Dabbugunta Sukanya (16711A0514) Narayana Engineering College, NelloreDocument13 pagesPresented By: Asritha Mamidi (16711A0540) Dabbugunta Sukanya (16711A0514) Narayana Engineering College, NelloreRiddhi PaulNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin 101 2019Document11 pagesBitcoin 101 2019Vladan IvanovicNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin 101: December 2017Document11 pagesBitcoin 101: December 2017CONo ratings yet
- 1cuui46 BCOct242017Document17 pages1cuui46 BCOct242017Shruti SumanNo ratings yet
- Blockchainpresentation PPT 5548313Document27 pagesBlockchainpresentation PPT 5548313Dipesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Kyc Using Blockchain: Keywords: KYC (Know Your Customer), Block-Chain, Distributed EnvironmentDocument3 pagesKyc Using Blockchain: Keywords: KYC (Know Your Customer), Block-Chain, Distributed Environmentkiranmai AmbatiNo ratings yet
- Participants BlockchainDocument10 pagesParticipants BlockchainshalyNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce Benefits of BlockchainDocument12 pagesEcommerce Benefits of BlockchainManoj JNo ratings yet
- 23 4Document5 pages23 42103010030No ratings yet
- The Role of Blockchain in The Current It Industry ScenarioDocument3 pagesThe Role of Blockchain in The Current It Industry ScenarioSᴇʀᴇɴᴅɪᴘɪᴛʏNo ratings yet
- Success Lunch of Bitcoin or BlockchainDocument2 pagesSuccess Lunch of Bitcoin or BlockchainATLASNo ratings yet
- Digital Platform and Digital Business ModelsDocument16 pagesDigital Platform and Digital Business ModelsMiya YoshimuraNo ratings yet
- Blockchain PaperDocument33 pagesBlockchain PaperAyeshas KhanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain PresentationDocument28 pagesBlockchain PresentationPaulo JunqueiraNo ratings yet
- Fint TechDocument13 pagesFint TechLaxmi SadhukhanNo ratings yet
- Types of Blockchain Technologies and Their Uses PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Blockchain Technologies and Their Uses PDFmigdonNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology PDFDocument6 pagesBlockchain Technology PDFAnirvan VinodNo ratings yet
- Current Issue Fintech-2020Document30 pagesCurrent Issue Fintech-2020Raudah YamnaNo ratings yet
- Learn How to Earn with Cryptocurrency TradingFrom EverandLearn How to Earn with Cryptocurrency TradingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Ecommerce Benefits of Blockchain: Faster, Cheaper TransactionsDocument11 pagesEcommerce Benefits of Blockchain: Faster, Cheaper TransactionsManoj JNo ratings yet
- Blockchain to Transform Financial ServicesDocument4 pagesBlockchain to Transform Financial ServicesUJJWALNo ratings yet
- Ismanto 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1179 012114Document7 pagesIsmanto 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1179 012114my songNo ratings yet
- Everything you need to know about blockchain technologyDocument7 pagesEverything you need to know about blockchain technologyRajeev Kumar JainNo ratings yet
- Blockchain PresentationDocument14 pagesBlockchain PresentationsipraNo ratings yet
- Block Chain TechnologyDocument3 pagesBlock Chain TechnologySATYANARAYANA MOTAMARRINo ratings yet
- Blockchain in Banking PDFDocument7 pagesBlockchain in Banking PDFSaurav JainNo ratings yet
- Article - 5 Blockchain Opportunities For CompaniesDocument7 pagesArticle - 5 Blockchain Opportunities For CompaniessprasadvNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology - I Told You So! - What Bitcoins, Ethereum and Other Blockchain Technologies Are and How You Can Use Them For Fun and ProfitDocument55 pagesBlockchain Technology - I Told You So! - What Bitcoins, Ethereum and Other Blockchain Technologies Are and How You Can Use Them For Fun and ProfitAnonymous sDnT9yuNo ratings yet
- INTRO TO BLOCKCHAIN BENEFITS & APPLICATIONSDocument15 pagesINTRO TO BLOCKCHAIN BENEFITS & APPLICATIONSveronicaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Crypto Currency in E-Commerce: Department of MCA Mepco Schlenk Engineering College, SivakasiDocument3 pagesInfluence of Crypto Currency in E-Commerce: Department of MCA Mepco Schlenk Engineering College, SivakasiGRD JournalsNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology PPT Project Final EditDocument17 pagesBlockchain Technology PPT Project Final EditHACKERS HOVELNo ratings yet
- How to Learn About Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies in 48 Hours or LessFrom EverandHow to Learn About Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies in 48 Hours or LessNo ratings yet
- Blockchain For Video Advertising:: A Market Snapshot of Publisher and Buyer Use CasesDocument18 pagesBlockchain For Video Advertising:: A Market Snapshot of Publisher and Buyer Use CasesKinshuk ShekharNo ratings yet
- E-Business Blockchain - PCEDocument13 pagesE-Business Blockchain - PCEaepatil74No ratings yet
- University of The Cumberlands Final Paper ITS 832 - Info Tech in A Global EconomyDocument10 pagesUniversity of The Cumberlands Final Paper ITS 832 - Info Tech in A Global EconomySrinivas AdityaNo ratings yet
- Deshpal ScholorshipDocument1 pageDeshpal ScholorshipSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ejazul ScholarshipDocument1 pageEjazul ScholarshipSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chatbot AIDocument20 pagesChatbot AIAmandeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Chatbot AIDocument20 pagesChatbot AIAmandeep kaurNo ratings yet
- EndsemDocument738 pagesEndsemVratikaNo ratings yet
- Considering The Impact of Ai in InsuranceDocument25 pagesConsidering The Impact of Ai in Insuranceagasthiya parshithNo ratings yet
- Array List in JavaDocument22 pagesArray List in JavaAira AlanNo ratings yet
- How to change Excel separator comma from millions to lakhsDocument6 pagesHow to change Excel separator comma from millions to lakhsSaphal LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Jaya Pandey: Customer Support, Service Quality & Vendor Management - South AsiaDocument3 pagesJaya Pandey: Customer Support, Service Quality & Vendor Management - South AsiaJaya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu M10-4/SPARC M10-4: Installation GuideDocument154 pagesFujitsu M10-4/SPARC M10-4: Installation GuideMD.JOBAED ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Tic Tac ToeDocument22 pagesTic Tac ToeLipikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Compiled With Reference From: Software Testing Techniques: Boris Beizer Craft of Software Testing: Brain MarrickDocument68 pagesUnit 1: Compiled With Reference From: Software Testing Techniques: Boris Beizer Craft of Software Testing: Brain MarrickAjay100% (1)
- Tableau Sparkline Chart 61Document11 pagesTableau Sparkline Chart 61Giri RajNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis TemplateDocument1 pageGap Analysis TemplateMarcelo Partes de Oliveira100% (1)
- Cross Docking ProcedureDocument2 pagesCross Docking ProcedureKumar Rajadhyaksh67% (3)
- Starting and Stopping The SAP System Using CommandsDocument5 pagesStarting and Stopping The SAP System Using Commandsshivajishiva689_3969No ratings yet
- Datamining Lab ManualDocument62 pagesDatamining Lab ManualAditya srivastavaNo ratings yet
- URL Rewrite and Responder With Citrix NetScalerDocument36 pagesURL Rewrite and Responder With Citrix NetScalerbienth89No ratings yet
- InView AOI Sample Code User InstructionsDocument55 pagesInView AOI Sample Code User InstructionsRrhh EstNo ratings yet
- Exam 350-401 - Pg10Document5 pagesExam 350-401 - Pg10Info4 DetailNo ratings yet
- Proiect LIME 963UW 2063UW Training Manual ENG 0128Document73 pagesProiect LIME 963UW 2063UW Training Manual ENG 0128Nicu LiviuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing Disk Storage DevicesDocument10 pagesChapter 17 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing Disk Storage DevicesSumati BaralNo ratings yet
- Weighing in On Photonic-Based Machine Learning For Automotive MobilityDocument2 pagesWeighing in On Photonic-Based Machine Learning For Automotive MobilitymtkliemaNo ratings yet
- India's #1 Practical Training Institute for Data ScienceDocument18 pagesIndia's #1 Practical Training Institute for Data Scienceswayam vijayNo ratings yet
- CA LISA Virtualization - PresentationDocument15 pagesCA LISA Virtualization - Presentationsharmila boseNo ratings yet
- J1.L.P0029-Tour Management-500Document3 pagesJ1.L.P0029-Tour Management-500shinkiriloveforeverNo ratings yet
- Jianhang Chen Activity Recognition On Kinect-3d Videos Using Transfer LearningDocument3 pagesJianhang Chen Activity Recognition On Kinect-3d Videos Using Transfer Learningapi-339792990No ratings yet
- Devops Roadmap Template: For Use With The Implement DevopsDocument35 pagesDevops Roadmap Template: For Use With The Implement DevopsErendira PerezNo ratings yet
- 16.1.2 Lab - Implement a GRE Tunnel - ITExamAnswersDocument20 pages16.1.2 Lab - Implement a GRE Tunnel - ITExamAnswershayltonmonteiroNo ratings yet
- JETIR2211472 Reseach Paper PDFDocument4 pagesJETIR2211472 Reseach Paper PDFpriyaNo ratings yet
- Connecting SONY Bluetooth EarbudsDocument2 pagesConnecting SONY Bluetooth EarbudsAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Personal Financial Planning Online TrainingDocument2 pagesPersonal Financial Planning Online TrainingMansi PanwarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument17 pagesIntroductionmalak hbiyelNo ratings yet
- Rubrik CDM Version 6.0 CLI Reference Guide (Rev. B3)Document86 pagesRubrik CDM Version 6.0 CLI Reference Guide (Rev. B3)Chill BeatzNo ratings yet