Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Traction Is A Mechanical Force Applied To The
Uploaded by
Ashley Franceska Cansanay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesOriginal Title
PT-LEC-Traction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesTraction Is A Mechanical Force Applied To The
Uploaded by
Ashley Franceska CansanayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
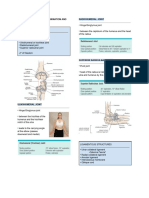
Traction is a mechanical force applied to the
body in a way that separates the joint surfaces
and elongates surrounding soft tissues. Traction
can be applied manually by the clinician,
mechanically by a machine, and by the patient
using body weight and gravity as a force.
Can be applied to peripheral joints and spine.
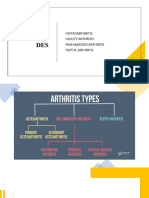
Effects of tractions Joint
• distraction (nerve root compression)
• Reduction of disc protrusion
(herniated nucleus pulposus)
Contraindications of spinal traction
• Soft tissue stretching (tendons,
ligaments, muscles) 1. Where motion is contraindicated
• Muscle relaxation (interrupts pain- (unstable fracture, cord compression,
spasm-pain cycle) post op spinal surgery)
• Joint mobilization (increased joint
mobility caused by joint related pain) • Have you been instructed not to
move your neck or back? If so, by
whom?
Clinical indications for the use of spinal • If wearing a brace or corset: Have
traction you been instructed not to remove
your brace at any time?
1. Disc bulge/herniation/herniated nucleus • How recent was your injury or
pulposus (best applied soon after injury) surgery?
2.Nerve root impingement (best applied soon
after onset of symptoms) 2. Acute injury or inflammation (trauma,
surgery, RA, OA)- injury within 72
3. Joint hypomobility (hypomobilty caused by hours.
multiple segments)
• When did your injury occur?
4.Subacute joint inflammation (reduce
pressure on inflammed joints and promote fluid • When did your pain start?
exchange) • Palpate and inspect the area to
detect signs of inflammation,
5. Paraspinal muscles spasm (interrupt pain- including heat, redness, and
spasm-pain cycle) swelling.
3. Hypermobile and unstable joints (C1- Precautions for the use of spinal traction
C2, RA, Down's syndrome, marfan
1. Structural diseases and conditions
syndrome, fracture, dislocation)
affecting the bones of the spine
• Tumor, infection, rheumatoid
• Have you dislocated a joint in this area?
arthritis, osteoporosis, prolonged
• Do you have rheumatoid arthritis or
systemic steroid use.
Marfan's syndrome?
• Do you have any disease affecting
• Are you pregnant?
your bones or joints?
• Do you have cancer, an infection in
your bones, rheumatoid arthritis, or
4. Peripheralization (worsening of
osteoporosis?
symptoms) of symptoms
• Do you take steroid medications? If
so, how long have you taken them?
• Let me know immediately if you
• Only low force traction should be
notice increased pain or other
used
symptoms farther down your arms
or legs. Stop the traction if this
occurs.
2. When pressure from the belts maybe
hazardous
5. Uncontrolled hypertension-10 minutes
• Pelvic belts- may apply
of cervical traction at 10% body weight
excessive pressure to abdomen
causes increases in blood pressure (9
to pregnant patients or those
mm Hg increase in systolic pressure,
with hiatal hernia and femoral
and 5 mm Hg increase in diastolic
artery compromise
pressure) and heart rate (7 beats per
• Thoracic belts- excessive
minute [bpm] increase)
pressure on ribs with patients
osterporosis Cervical traction-
• Do you have high blood pressure? If
patients with cerebrovascular
so, is it well controlled with
compromise as indicated by a
medications?
positive vertebral artery test
• Resting BP of 140/90: Treatment
• Are you pregnant?
should be discontinued if systolic or
• Do you have a hiatal hernia?
diastolic BP increases by more than
10 mm Hg. or if heart rate increases • Have you had any trouble with
by more than 10 bpm. blocked arteries?
• Do you have pain in your calves
when walking a short distance?
This is a sign of intermittent
claudication,
3. Displaced annular fragments (traction 6. Claustrophobia or Other Psychological
will not be effective) Aversion to Traction
7. Inability to Tolerate the Prone or Supine
• Has magnetic resonance
Position
imaging (MRI) or CT scan of
your spine been performed? • Does lying on your back with your
Please bring me the report(s) knees bent for 15 to 20 minutes cause
from that (those) test(s). any problems for you?
• Does lying on your stomach for 15 to 20
minutes cause any problems for you?
4. Medial disc protrusion (traction may
aggravate symptoms) 8.Disorientation
• Has an MRI or CT scan of your
spine been performed? Please Precautions For The Use Of Cervical
bring me the report(s) from that Traction
(those) test(s) 1. TMJ problems- Do you have problems with
your jaw?
5. When Severe Pain Resolves Fully With
Traction 2. Dentures- Do you wear dentures? Do you
have them in now?
• If severe pain resolves fully
with traction, this may indicate
that the fraction has increased
rather than decreased
compression on a nerve root,
causing a complete nerve block.
• After a few minutes of traction:
Have your symptoms changed?
• If the patient had severe pain
and reports that the pain has
decreased: Has the pain
completely gone away, or is it
just less severe?
• Test sensation, reflexes, and
strength before treatment.
• Also, if the patient reports
complete resolution of severe
pain during treatment, check
these again, and assess for any
changes.
You might also like
- Plantar Heel Pain, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPlantar Heel Pain, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- DHP W. TableDocument21 pagesDHP W. Tablejenika studiesNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Injuries and Pain: Indranil Neel' Kushare, MDDocument55 pagesFoot and Ankle Injuries and Pain: Indranil Neel' Kushare, MDrizwan.mughal1997No ratings yet
- Low Back and SacrumDocument27 pagesLow Back and SacrumdwNo ratings yet
- Common Sports Injuries: Ukris Gunadham, MD, FRCOST Department of Orthopaedics Trang HospitalDocument71 pagesCommon Sports Injuries: Ukris Gunadham, MD, FRCOST Department of Orthopaedics Trang HospitalMohammed SaqoorNo ratings yet
- Cad wk9-10 QsDocument10 pagesCad wk9-10 Qsapi-468597987No ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Emergencies AndreDocument49 pagesOrthopaedic Emergencies AndreLusi MunawarohNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Category 2Document4 pagesWeek 8 Category 2api-468093714No ratings yet
- CARE of ADOLESCENTSDocument15 pagesCARE of ADOLESCENTSaprilkate banagodosNo ratings yet
- Daftar Tilik APNDocument17 pagesDaftar Tilik APNmarindadaNo ratings yet
- High Velocity Manipulation TechniquesDocument2 pagesHigh Velocity Manipulation TechniquesBhargavaNo ratings yet
- MSK Lec #3.1.2 HipDocument11 pagesMSK Lec #3.1.2 HipCUTE ONENo ratings yet
- Lesson - Elbow Region Examination and EvaluationDocument8 pagesLesson - Elbow Region Examination and EvaluationJULIANE MAE BALANGNo ratings yet
- Warning: You May Want To Look Away at Times!: Youtube VideoDocument47 pagesWarning: You May Want To Look Away at Times!: Youtube VideoRaffy B. MabilingNo ratings yet
- Differential DiagnosisDocument14 pagesDifferential DiagnosisnurulNo ratings yet
- Medical Rehabilitation in Musculoskeletal Trauma - Prof. Dr. Dr. Angela BM Tulaar SPKFR (K)Document41 pagesMedical Rehabilitation in Musculoskeletal Trauma - Prof. Dr. Dr. Angela BM Tulaar SPKFR (K)YanuarNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics PDFDocument14 pagesOrthopedics PDFSam christenNo ratings yet
- McKenzie LumbarDocument51 pagesMcKenzie LumbarRouqia HamedNo ratings yet
- McKenzie LumbarDocument91 pagesMcKenzie LumbarPraneetha100% (1)
- AnD FT Elbow-1Document26 pagesAnD FT Elbow-1Nazwa KamilatunnisaNo ratings yet
- Ankel Heel PainDocument51 pagesAnkel Heel PainMeno Ali100% (1)
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Orthopedi eDocument61 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Orthopedi eSurya AbigamikaNo ratings yet
- Hip (Word)Document32 pagesHip (Word)dwNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Diagnosis For Canine Hip Dysplasia: 18 August 2021Document85 pagesRadiographic Diagnosis For Canine Hip Dysplasia: 18 August 2021Thirada sosawangNo ratings yet
- 3D Regional Rheumatic PainDocument50 pages3D Regional Rheumatic PainIkhsan Amadea9969No ratings yet
- 5 - Knee DisordersDocument85 pages5 - Knee Disordersraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument46 pagesAssessment of The Musculo-Skeletal SystemRaquel M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Joint Pain in Primary CareDocument34 pagesJoint Pain in Primary CarelilydariniNo ratings yet
- Week 10 PCP Workbook QuestionsDocument6 pagesWeek 10 PCP Workbook Questionsapi-479717740No ratings yet
- Mastering Your Musculoskeletal Exam: Laurel Short, MSN, FNP-CDocument46 pagesMastering Your Musculoskeletal Exam: Laurel Short, MSN, FNP-CPrathap Kumar0% (1)
- Handout Lat Elbow Pain PDFDocument47 pagesHandout Lat Elbow Pain PDFgemichan26No ratings yet
- Case 2: Ask The Questions About What Pain Activity Causes The Pain?Document8 pagesCase 2: Ask The Questions About What Pain Activity Causes The Pain?api-479717740No ratings yet
- Spinal Surgery in The DogDocument38 pagesSpinal Surgery in The Doglovefriends_845661No ratings yet
- Knee Pes Anserine Bursitis BWHDocument7 pagesKnee Pes Anserine Bursitis BWHlionita sugandiNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain - 1-07Document39 pagesLow Back Pain - 1-07Nur Sabriany LihawaNo ratings yet
- 10 Lumbosacral SpineDocument10 pages10 Lumbosacral Spine楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Pediatric Fractures QT PDFDocument42 pagesPediatric Fractures QT PDFyanNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain:: Approach To The Patient in The E.DDocument39 pagesLow Back Pain:: Approach To The Patient in The E.DLidiaAMonroyRNo ratings yet
- Stress Fractures: Dave Haight, MD Sports Medicine Fellow April 2009Document45 pagesStress Fractures: Dave Haight, MD Sports Medicine Fellow April 2009Gunjan PatilNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Physical ExaminationDocument94 pagesOrthopaedic Physical ExaminationPriza RazunipNo ratings yet
- SPONDYLOLISTHESISDocument27 pagesSPONDYLOLISTHESISJulioYoko100% (1)
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument4 pagesRheumatoid Arthritisapi-3822433No ratings yet
- Pengayaan Koass Ortho - Update 5 VersionDocument122 pagesPengayaan Koass Ortho - Update 5 Versionanon_967171484No ratings yet
- Spasticity Management by Susan Kim DODocument69 pagesSpasticity Management by Susan Kim DONicoleta StoicaNo ratings yet
- Scfe PDFDocument39 pagesScfe PDFMuhammad Tabish SaleemNo ratings yet
- 2 2-ArthritidesDocument76 pages2 2-ArthritidesAvinash KaushikNo ratings yet
- Lower Back Pain: DR Robert Ramcharan MBBS, Frcsed, DM (Neurosurgery) NeurosurgeonDocument69 pagesLower Back Pain: DR Robert Ramcharan MBBS, Frcsed, DM (Neurosurgery) NeurosurgeonShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Common Upper Extremity AilmentsDocument47 pagesCommon Upper Extremity AilmentsStephensemailNo ratings yet
- Lee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Document25 pagesLee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Star CruiseNo ratings yet
- Hamstring Injury - Diagnosis and Injury Management DiagnosisDocument5 pagesHamstring Injury - Diagnosis and Injury Management Diagnosisgemichan26No ratings yet
- Low Back Pain Therapy GuideDocument38 pagesLow Back Pain Therapy GuideArunima SharmaNo ratings yet
- High Ankle SprainDocument10 pagesHigh Ankle Sprainferd dinanNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy: DR - DharmavatiDocument78 pagesManual Therapy: DR - DharmavatiHitesh RohitNo ratings yet
- MusculoskeletalDocument77 pagesMusculoskeletalMiden AlbanoNo ratings yet
- Amputee RehabDocument89 pagesAmputee RehabAli FahesNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment MSK Level 3 2019Document93 pagesPhysical Assessment MSK Level 3 2019Daniela OrtalNo ratings yet
- Running Injury: Hui-Ting Lin, PT, PHDDocument36 pagesRunning Injury: Hui-Ting Lin, PT, PHDMandy NgNo ratings yet
- Knee Pain Knee Pain: Focused History Focused Physical ExamDocument1 pageKnee Pain Knee Pain: Focused History Focused Physical ExamKristine Joyce Quilang AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pseudo-Claudication Central Spinal Stenosis Foraminal Spinal StenosisDocument4 pagesPseudo-Claudication Central Spinal Stenosis Foraminal Spinal StenosissentimentalflareNo ratings yet
- Neurological Aspect in Musculoskeletal Diseases Entrapment and CompressionDocument38 pagesNeurological Aspect in Musculoskeletal Diseases Entrapment and CompressionBakingpancakesNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 WorkbookDocument44 pagesGrade 9 WorkbookMaria Russeneth Joy NaloNo ratings yet
- IPM GuidelinesDocument6 pagesIPM GuidelinesHittesh SolankiNo ratings yet
- 2 AcknowledgementDocument8 pages2 AcknowledgementPadil KonamiNo ratings yet
- ATADU2002 DatasheetDocument3 pagesATADU2002 DatasheethindNo ratings yet
- A - PAGE 1 - MergedDocument73 pagesA - PAGE 1 - MergedGenalyn DomantayNo ratings yet
- Project Manager PMP PMO in Houston TX Resume Nicolaas JanssenDocument4 pagesProject Manager PMP PMO in Houston TX Resume Nicolaas JanssenNicolaasJanssenNo ratings yet
- Specialty Coffee Association of Indonesia Cupping Form (ARABICA)Document1 pageSpecialty Coffee Association of Indonesia Cupping Form (ARABICA)Saiffullah RaisNo ratings yet
- Use of Travelling Waves Principle in Protection Systems and Related AutomationsDocument52 pagesUse of Travelling Waves Principle in Protection Systems and Related AutomationsUtopia BogdanNo ratings yet
- Ginger Final Report FIGTF 02Document80 pagesGinger Final Report FIGTF 02Nihmathullah Kalanther Lebbe100% (2)
- Innovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschDocument28 pagesInnovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschacairalexNo ratings yet
- Oracle SOA Suite 11g:buildDocument372 pagesOracle SOA Suite 11g:buildMohsen Tavakkoli100% (1)
- Suspend and Resume Calls: Exit PlugDocument4 pagesSuspend and Resume Calls: Exit PlugrajuNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Collins RDRDocument24 pagesRockwell Collins RDRMatty Torchia100% (5)
- A Review of Stories Untold in Modular Distance Learning: A PhenomenologyDocument8 pagesA Review of Stories Untold in Modular Distance Learning: A PhenomenologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Paramount Healthcare Management Private Limited: First Reminder Letter Without PrejudiceDocument1 pageParamount Healthcare Management Private Limited: First Reminder Letter Without PrejudiceSwapnil TiwariNo ratings yet
- Participate in Safe Food Handling Practices SITXFSA002 - PowerpointDocument71 pagesParticipate in Safe Food Handling Practices SITXFSA002 - PowerpointJuan Diego Pulgarín Henao100% (2)
- Laboratorio 1Document6 pagesLaboratorio 1Marlon DiazNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledTestNo ratings yet
- BRAND AWARENESS Proposal DocumentDocument11 pagesBRAND AWARENESS Proposal DocumentBuchi MadukaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument7 pagesFrequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFNarendra AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Planning EngineerDocument1 pagePlanning EngineerChijioke ObiNo ratings yet
- Dialog+ SW9xx - SM - Chapter 7 - 2-2013 - EN - Rinsing Bridge Version 5Document1 pageDialog+ SW9xx - SM - Chapter 7 - 2-2013 - EN - Rinsing Bridge Version 5Al ImranNo ratings yet
- Obara BogbeDocument36 pagesObara BogbeOjubona Aremu Omotiayebi Ifamoriyo0% (1)
- Report On Marketing Strategy of Nestle MILKPAKDocument13 pagesReport On Marketing Strategy of Nestle MILKPAKAzeem Ahmad100% (1)
- Department of Education: Income Generating ProjectDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Income Generating ProjectMary Ann CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Pt. Trijaya Agro FoodsDocument18 pagesPt. Trijaya Agro FoodsJie MaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To M365 PresentationDocument50 pagesIntroduction To M365 Presentationlasidoh0% (1)
- Advent Wreath Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAdvent Wreath Lesson Planapi-359764398100% (1)
- Student Exploration: Digestive System: Food Inio Simple Nutrien/oDocument9 pagesStudent Exploration: Digestive System: Food Inio Simple Nutrien/oAshantiNo ratings yet
- Tree PruningDocument15 pagesTree Pruningrita44No ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (29)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (59)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)