Professional Documents
Culture Documents
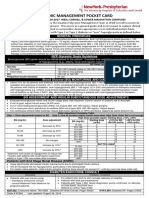
ICU One Pager Blood Products
ICU One Pager Blood Products
Uploaded by
EvertCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ICU One Pager Blood Products
ICU One Pager Blood Products
Uploaded by
EvertCopyright:
Available Formats
BLOOD PRODUCT TRANSFUSIONS by Nick Mark MD ONE onepagericu.
com Link to the
most current
@nickmmark version →
DEFINITIONS: Whole blood TRANSFUSION REACTIONS:
The goal of transfusion is to provide minimum O2 carrying AB+ (stored at 4°C up to 35 days)
capacity (RBCs) & sufficient platelets and clotting factors to
Rh positive
EXP 2021-01-01 23:30 ~450 ml + 60 ml citrate REACTION EXPLANATION MANAGEMENT
permit hemostasis. The goal is not correcting to “normal.” A9999 20 123456 K
Good at achieving hemostasis
12
Most common immune reaction to transfusion. Prevention: APAP + H2 blockers,
Although RBC transfusions increase CaO2 they might not (contains all factors) but limited Febrile Non-
Occurs within 4 hours of transfusion due to accumulated consider leukoreduced units
normalize DO2 due to less efficient unloading of O2 in availability (autologous, military) Hemolytic
inflammatory cytokines in the banked donor blood. May Treatment: stop infusion, APAP,
transfused blood (2,3-BPG is degraded in storage). Transfusion recur; 25% of patients who had FNHTR once had another meperidine. R/o other causes.
Reaction (FNHTR) reaction subsequently. Notify blood bank.
Type and screen – determines blood type and detects
antibodies in recipient (e.g., indirect Coombs test) AB+ AB+ AB+ Occurs during or shortly after transfusion. A true emergency
Treatment with anti-CD38 antibodies (daratumumab, Rh positive Rh positive Rh positive Occurs due to mismatch of donor antigens (often ABO/Rh) & Prevention: carefully check units
EXP 2021-01-01 23:30 Acute Hemolytic
isatuximab) can cause a false positive on screen for minor
EXP 2021-01-01 23:30 EXP 2021-01-01 23:30
recipient antibodies leading to hemolysis & agglutination. Treatment: Stop transfusion,
A9999 20 123456 K
Transfusion
12
A9999 20 123456 K A9999 20 123456 K
12
12
antigens for up to six months (notify blood bank). S/sx: Fever, flank pain, dark urine, DIC, hypoTN, renal failure. notify blood bank, test for
Reaction (AHTR) Hemolysis on labs (↓haptoglobin, ↑LDH, etc) hemolysis & DIC, aggressive IV
Crossmatch – involves testing patient blood and specific
hydration (goal UOP > 100/hr).
donor units for compatibility. Crossmatch takes ~45 min.
RBCs Pooled Platelet FFP Occurs 24 hours to 30 days after transfusion due to mismatch Treatment: Notify blood bank,
In emergencies crossmatch can be skipped. (stored at 4°C (stored at RT up (frozen -25 °C Delayed Hemolytic
of minor antigens (often false negative crossmatch). 2nd repeat testing (DAT, type &
In extreme emergencies non-type specific blood can be up to 42 days) to 5 days) up to 3 yrs) Transfusion
IMMUNE MEDIATED
exposure can be faster, more severe. May have drop in Hct, screen, etc)
used (e.g., O- RBCs in women, O- or O+ RBCs in men). ~350 ml ~300 ml ~225 ml Reaction (DHTR) fever, minor hemolysis.
↑ Hb ~1 gm/dl* ↑ Plt by ~5-7k* (*in 70 kg pt)
Usually anaphylactoid (not IgE mediated). Prevention: washed (or IgA
EVIDENCE BASED TRANSFUSION THRESHOLDS:
v1.0 (2021-07-10) CC BY-SA 3.0
S/sx urticaria, maculopapular rash, pruritis, fv & hypoTN deficient) RBCs.Check for IgA
•Restrictive transfusion strategies (Hb > 7) are comparable/superior to Allergic reaction Occurs minutes to hours after transfusion, due to antibodies deficiency if recurrent anaphylaxis
liberal strategies in most settings including GI bleed, septic shock, against proteins on plts, leukocytes, or in plasma, including Tx: epi, H2 blockers, steroids
AB+
Rh positive cardiac surgery, TBI, and in most ICU patients. IgA (in recipients w/ IgA deficiency)
0.9% Sodium
EXP 2021-01-01 23:30
Chloride • Massive transfusion protocols (MTP) (e.g., trauma pts or massive GI
A9999 20 123456 K Injection USP Occurs 7-10 days after transfusion, due to anti-platelet Treatment: IVIG, plasmapheresis
bleed) target hemodynamic stability not a specific Hb. Among patients
12
1000mL
L o re m ip s u m d o lo r s it a m e t,
Post Transfusion antibodies in donor blood. Causes purpura & severe
receiving MTP, balanced ratio (e.g., 1 RBC : 1 FFP : 1 Plt unit) is superior
c o n s e c te tu r a d ip is c in g e lit, s e d d o
e iu s m o d te m p o r in c id id u n t u t la b o re
Purpura (PTP)
e t d o lo re m a g n a a liq u a . U t e n im a d
thrombocytopenia, may be life-threatening.
m in im ve n ia m , q u is n o s tru d
e x e rc ita tio n u lla m c o la b o ris n is i u t
• Platelet transfusion thresholds are disease dependent: For most
a liq u ip e x e a c o m m o d o c o n s e q u a t.
D u is a u te iru re d o lo r in re p re h e n d e rit
More common in women (85%) & Caucasians.
in vo lu p ta te ve lit e s s e c illu m d o lo re e u
f u g ia t n u lla p a ria tu r. E x c e p te u r s in t
o c c a e c a t c u p id a ta t n o n p ro id e n t, s u n t
diseases 10k is adequate, if bleeding or needing surgery 50k may be
in c u lp a q u i o f f ic ia d e s e ru n t m o llit
a n im id e s t la b o ru m .
required. Limited evidence for higher targets (e.g., 100k for CNS bleed) Transfusion
Leading cause of transfusion related death (15% mortality). Treatment: ventilatory support
TRALI resembles ARDS, onset is 4-6 hours after transfusion. may be required (use LPV), use
SPECIAL BLOOD PRODUCT TYPES: Related Acute Lung
Most common following platelet transfusion from multi- platelets from male donors for
•Leukocyte reduced RBC: decreases incidence of febrile rxns & Injury (TRALI) parous female donors (due to anti-HLA or anti-HNA Ab) future transfusions.
Each unit
Y-tubing prevents allo-immunization. Also makes blood CMV-safe
contains: combines •Gamma-irradiated RBC: reduces incidence of GVHD during Occurs 8-10 days post transfusion, donor leukocytes attack Prevention: use irradiated and
Transfusion
·Blood type immunosuppressed recipient. leukocyte reduced blood in
blood & transfusions; important in very immunosuppressed patients Associated Graft
·Expiration crystalloid •Volume Reduced RBC: each unit comes in ~100 ml (instead of ~350 Versus Host Disease
Sx include: fever, cutaneous eruptions, diarrhea, liver immunosuppressed recipients
abnormalities. May progresses to pancytopenia due to Treatment: no effective treatment
·Product # ml), can reduce the incidence of febrile rxns because there are fewer (TA-GVHD)
marrow aplasia. High mortality.
·Barcodes Filter & drip plasma proteins; can also be used in volume overloaded patients
All must be chamber (though giving diuretic is probably better) Transfusion Occurs between 0-6 hrs after transfusion. Volume overload Prevention: minimum # of units,
NON-IMMUNE MEDIATED
verified! removes •Washed RBC: plasma is replaced with crystalloid; this should be done Associated Cardiac from transfusions, particularly in patients with CHF. Presents volume reduced units, diuresis
blood clots only if there was a previous allergic reaction or in IgA deficient Overload (TACO) as dyspnea potentially progressing to severe hypoxemia. Treatment: diuresis
Rate of transfusion depends patients (if no IgA deficient donors) Hypocalcemia Citrate in RBCs binds to serum calcium. Blood products Treatment: Replete calcium and
on severity of illness. In stable •Single donor (apheresis) platelets: a full unit of platelets obtained Hyperkalemia contain potassium from lysed cells. monitor for hyperkalemia.
patients, slower infusions (e.g. from a single donor via apheresis (in contrast to pooled platelets
over 2 hrs) permits earlier typically combining 5 donors). Single donor limits antigen exposure Due to low temp of transfused products. iatrogenic Prevention/Tx: Use a blood
Hypothermia hypothermia exacerbates coagulopathy & ↑bleeding warmer for massive transfusions
stopping. In unstable patients
consider using a rapid infuser.
STRATEGIES IN PEOPLE WHO DECLINE TRANSFUSION
People taking ACEi may develop hypotension due to inability Does not require intervention.
• Discuss specific reasons/concerns, understand what tx is acceptable Hypotension to break down bradykinin in transfused blood Rule out infection/hemolysis
• Correct coagulopathy (consider amicar, TXA, other products)
150 • Stop and minimize blood loss: hormonally suppress menstruation, Infection occurs due to untested organisms (rare), false negatives on testing (very rare), or bacterial contamination.
autotransfuse with cell-saver (OR) or hemothorax/chest tube (ICU)
Bacterial Platelets (stored at RT) are more likely to cause infections with skin flora (GPCs). RBCs (stored at 4C),
IINFECTION
• Minimize iatrogenic blood loss (fewer labs, less frequently, drawn in
pediatric tubes); no "routine" labs; every test should be thoughtful contamination are more likely to be contaminated with GNRs. Can lead to sepsis.
and drawn in pediatric tubes to minimize volume lost Untested Organisms NOT tested include: Malaria, Borrellia (Lyme disease), Trypanosoma (Chagas disease),
• Optimize hematopoesis (IV iron infusion, folate supplementation, organisms Babesiosis, & vCJD (varies by country)
EPO administration)
• Consider blood substitute (poly-heme) False negative Extremely rare: HIV 1 in 2,000,000,000, HBV 1 in 100,000,000, HCV 1 in 2,000,000, HTLV 1 in 650,000
You might also like
- Emergency Department Nursing Flow SheetDocument2 pagesEmergency Department Nursing Flow SheetDessi KayNo ratings yet
- Guideline Title: Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump ManagementDocument16 pagesGuideline Title: Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump ManagementJansen ChNo ratings yet
- Perfusion SystemDocument30 pagesPerfusion SystemShailendra Singh Khichi100% (1)
- 2017 05 GC Pocket CardDocument2 pages2017 05 GC Pocket Cardapi-312241089No ratings yet
- CARESCAPE R860 Modes of Ventilation FINAL Rev 3 JB72469XXDocument47 pagesCARESCAPE R860 Modes of Ventilation FINAL Rev 3 JB72469XXMichael Levit100% (1)
- TCI DiprivanDocument74 pagesTCI DiprivanVan Basten ArdiansyachNo ratings yet
- Fresenius 2008T Dialysis System - User's Troubleshooting ManualDocument20 pagesFresenius 2008T Dialysis System - User's Troubleshooting ManualCesar Alfaro100% (1)
- Troubleshooting in CXMDocument3 pagesTroubleshooting in CXMquerokeropi100% (1)
- Blood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientDocument1 pageBlood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Advanced Airway Care: Intensive Care Unit PerspectiveDocument42 pagesAdvanced Airway Care: Intensive Care Unit PerspectiveJeffery Samuel100% (1)
- Module # 5 Pharmacology NursingDocument45 pagesModule # 5 Pharmacology Nursingannyeong_123No ratings yet
- Criticalcaredrugs 2 PDFDocument2 pagesCriticalcaredrugs 2 PDFabdallah100% (1)
- Anesthesiology Pre-Op Evaluation: ExovsrtsDocument1 pageAnesthesiology Pre-Op Evaluation: Exovsrtssabbo morsNo ratings yet
- Complications of Blood TransfusionsDocument4 pagesComplications of Blood TransfusionsZain Hadi100% (1)
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E NotesDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E Notesmonica leeNo ratings yet
- CRITICAL CARE, March 2020Document47 pagesCRITICAL CARE, March 2020Jonathan Yeoh100% (1)
- Antimicrobial Guidelines 2012-13 PDFDocument84 pagesAntimicrobial Guidelines 2012-13 PDFnydushNo ratings yet
- 17 The Brigham Board Review in Critical Care Medicine 2017Document1,355 pages17 The Brigham Board Review in Critical Care Medicine 2017Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Weaning From Mechanical Ventilation Using SBT PDFDocument29 pagesWeaning From Mechanical Ventilation Using SBT PDFEdgar Bravo Santibañez100% (1)
- Normal DIE CPP Calculations:: Increased Intracranial Pressure (Cerebral Perfusion Pressure)Document79 pagesNormal DIE CPP Calculations:: Increased Intracranial Pressure (Cerebral Perfusion Pressure)Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Datascope System 98xtDocument68 pagesDatascope System 98xtTiago DiasNo ratings yet
- Review of HD Monitoring: DR Ghaleb Almekhlafi MD, SFCCM, EdicDocument105 pagesReview of HD Monitoring: DR Ghaleb Almekhlafi MD, SFCCM, EdicGHALEB A. Almekhlafi100% (1)
- Mechanical ThrombectomyDocument58 pagesMechanical Thrombectomyres.uditacharyaNo ratings yet
- NomogramDocument2 pagesNomogramtammy_1025043737No ratings yet
- DX Alcohol Withdrawal PDFDocument3 pagesDX Alcohol Withdrawal PDFSherree Hayes100% (1)
- Stroke: AHA/ASA Guidelines For The Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (2019)Document14 pagesStroke: AHA/ASA Guidelines For The Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (2019)Natalia OrtizNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain ManagementDocument3 pagesAbdominal Pain ManagementTeenu JobyNo ratings yet
- Post Arrest CareDocument23 pagesPost Arrest CareMohamed RasoolNo ratings yet
- Adults With Suspected Epiglottitis - Supraglottitis Guidelines For The Management ofDocument2 pagesAdults With Suspected Epiglottitis - Supraglottitis Guidelines For The Management ofAlexandros MegasNo ratings yet
- 2010-2011 Antibiotic GuidelinesDocument78 pages2010-2011 Antibiotic GuidelinesMuhammad Rizki BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Bioinstrumentation II: Lecture 4: ECG MachineDocument30 pagesBioinstrumentation II: Lecture 4: ECG MachineHundessa DabaNo ratings yet
- 2018-04-09 Pediatric Emergency Nursing Assessment Record FormDocument2 pages2018-04-09 Pediatric Emergency Nursing Assessment Record FormHengkyNo ratings yet
- Critical Value ReportingDocument7 pagesCritical Value Reportingjorguey100% (1)
- Infusion Pumps, Large-Volume - 040719081048Document59 pagesInfusion Pumps, Large-Volume - 040719081048Freddy Cruz BeltranNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Document6 pagesACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraNo ratings yet
- VOCSN Clinical ManualDocument225 pagesVOCSN Clinical ManualdiegoNo ratings yet
- Post Cardiac Arrest CareDocument20 pagesPost Cardiac Arrest CareJayita Gayen Dutta100% (1)
- Cabg Vs OpcabDocument17 pagesCabg Vs OpcabVijay AnandNo ratings yet
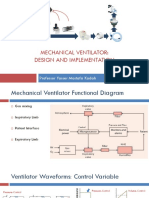
- Mechanical Ventilator: Design and Implementation: Professor Yasser Mostafa KadahDocument19 pagesMechanical Ventilator: Design and Implementation: Professor Yasser Mostafa Kadahmorton1472No ratings yet
- Liverpool Ni Modi PineDocument5 pagesLiverpool Ni Modi Pinerachmat fajar noor kNo ratings yet
- 01 Nursing Note SampleDocument1 page01 Nursing Note Sampletesttest testNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Guideline Hearth Failure PDFDocument129 pages2017 - Guideline Hearth Failure PDFMarvin M. Vargas AlayoNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Phenylephrine, Ephedrine and Mephentermine For Maintainance of Arterial Pressure During Spinal Anaesthesia in Caesarean SectionDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Phenylephrine, Ephedrine and Mephentermine For Maintainance of Arterial Pressure During Spinal Anaesthesia in Caesarean SectionInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Best Practice in ShockDocument30 pagesBest Practice in ShockFoungZanz D. LuffyzNo ratings yet
- Principles of ICU VentilatorsDocument98 pagesPrinciples of ICU VentilatorsAnanya Nanda100% (2)
- Sedation in The IcuDocument4 pagesSedation in The Icuprashsubbu100% (1)
- Drug AddictionDocument19 pagesDrug Addictiontrigui amir100% (1)
- Vitros 250, MicroSlide SummaryDocument16 pagesVitros 250, MicroSlide SummaryDiego Israel Gómez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Fresenius For The Exam PDFDocument2 pagesFresenius For The Exam PDFvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- CARDIOLABS ICU Ventilator For Adult & Pediatric Online - GeM - 950000Document10 pagesCARDIOLABS ICU Ventilator For Adult & Pediatric Online - GeM - 950000chandan kumarNo ratings yet
- ECMO and Right Ventricular FailureDocument9 pagesECMO and Right Ventricular FailureLuis Fernando Morales JuradoNo ratings yet
- Acute Stroke ProtocolDocument3 pagesAcute Stroke ProtocolKarissaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drugs 2Document23 pagesCritical Care Drugs 2Asri Ernadi100% (1)
- Neurologic Emergencies Stroke & Tia: Devin R. Harris, MD MHSC CCFP (Em)Document10 pagesNeurologic Emergencies Stroke & Tia: Devin R. Harris, MD MHSC CCFP (Em)Samantha Lui100% (2)
- Data Collection Form - Pressure InjuryDocument3 pagesData Collection Form - Pressure InjuryErwin Dela GanaNo ratings yet
- Module 9 Mechanical Ventilation PDFDocument46 pagesModule 9 Mechanical Ventilation PDFChabboo SutabrataNo ratings yet
- 15Document21 pages15Tyson Easo JonesNo ratings yet
- Early Warning Scoring System (Unit 9) - 1Document6 pagesEarly Warning Scoring System (Unit 9) - 1Zharlene PadillaNo ratings yet
- ASIA International Standards For Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument2 pagesASIA International Standards For Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord InjuryMicah Tagle100% (1)
- Vascular Responses to PathogensFrom EverandVascular Responses to PathogensFelicity N.E. GavinsNo ratings yet
- Hpia Version 6.0 PDFDocument48 pagesHpia Version 6.0 PDFAl- ImanuddinNo ratings yet
- Serolab MidDocument92 pagesSerolab MidEman JandaliNo ratings yet
- Special, Emergency, Electronic Cross MatchingDocument4 pagesSpecial, Emergency, Electronic Cross MatchingAkash SarkarNo ratings yet
- TAT For Issuing Blood Products in EmergencyDocument4 pagesTAT For Issuing Blood Products in Emergencyirdinamarchsya100% (1)
- ProposedSupplemental Checklist On Blood Transfusion 1Document4 pagesProposedSupplemental Checklist On Blood Transfusion 1Charisse de RoxasNo ratings yet
- MLS 201 Lecture Note - Introduction To BGSDocument7 pagesMLS 201 Lecture Note - Introduction To BGSBarry AllenNo ratings yet
- Ahg NotesDocument5 pagesAhg NotesRonron GarciaNo ratings yet
- Isbb FC Part 3Document13 pagesIsbb FC Part 3Lynther Myle Arizo100% (1)
- B Blab 6 Crossmatch SP 05Document14 pagesB Blab 6 Crossmatch SP 05Rutchelle Joyce PugoyNo ratings yet
- Terminologi LOINC Laboratorium v1.1Document138 pagesTerminologi LOINC Laboratorium v1.1rufus dianNo ratings yet
- Venesection: Phlebotomy orDocument21 pagesVenesection: Phlebotomy orLesly Marie LaxamanaNo ratings yet
- Blood Banking and Serology and Immunology Refresher Exam With AnswersDocument8 pagesBlood Banking and Serology and Immunology Refresher Exam With AnswersJohn Rhel DenqueNo ratings yet
- Difficult Crossmatch1Document13 pagesDifficult Crossmatch1Devie MaraNo ratings yet
- 4 - WADiana BroþürDocument13 pages4 - WADiana BroþürAlex Eduardo Bilbao BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Management & Blood Component TherapyDocument48 pagesFluid Management & Blood Component TherapySinta AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank PracticalDocument24 pagesBlood Bank Practicalmoonfire2009No ratings yet
- Antibody Screening and Identification ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAntibody Screening and Identification ObjectivesApril SudarioNo ratings yet
- 2014 Acute Hemorrhage and Blood Transfusions in Horses PDFDocument10 pages2014 Acute Hemorrhage and Blood Transfusions in Horses PDFCamila CalleNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank ManualDocument29 pagesBlood Bank ManualMarice Ferrufino SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Management System Project Submition-1Document16 pagesBlood Bank Management System Project Submition-1Uttam KumarNo ratings yet
- 2nu03-Group1 Case-Presentation ArmmcpediapmDocument39 pages2nu03-Group1 Case-Presentation ArmmcpediapmCyrus GarciaNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Procedure Checklist 2Document3 pagesBlood Transfusion Procedure Checklist 2Rainier CervantesNo ratings yet
- Pathology Quality ManualDocument82 pagesPathology Quality ManualAdriana Gabriela Ugarte MacíasNo ratings yet
- Blood Group Systems: Agaton T. Panopio, JR., MD, MhpedDocument48 pagesBlood Group Systems: Agaton T. Panopio, JR., MD, MhpedAz JaingaNo ratings yet
- Crossmatching Procedure PDFDocument2 pagesCrossmatching Procedure PDFgreatgeniusNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology NotesDocument1 pageImmunohematology NotesAlyanna BaldoquinNo ratings yet
- Hazards of Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesHazards of Blood TransfusionSakshi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Anti-A1 - ? Clinical Significance: Jo Cameron ACT Pathology The Canberra HospitalDocument14 pagesAnti-A1 - ? Clinical Significance: Jo Cameron ACT Pathology The Canberra HospitalYunita RapaNo ratings yet
- A Compendium of Tranfusion Prectice Guidelines ARC Edition 4.0 Jan 2021Document75 pagesA Compendium of Tranfusion Prectice Guidelines ARC Edition 4.0 Jan 2021H Stuard B CocNo ratings yet