Professional Documents
Culture Documents
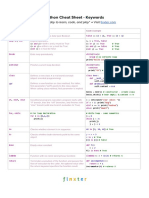
Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Strings Lists
Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Strings Lists
Uploaded by
luis vargas manchegoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Strings Lists
Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Strings Lists
Uploaded by
luis vargas manchegoCopyright:
Available Formats
> Strings > Lists Also see NumPy Arrays
Python For Data Science >>> my_string = 'thisStringIsAwesome'
>>> my_string
>>>
>>>
a = 'is'
b = 'nice'
Basics Cheat Sheet
'thisStringIsAwesome' >>> my_list = ['my', 'list', a, b]
>>> my_list2 = [[4,5,6,7], [3,4,5,6]]
String Operations
Selecting List Elements Index starts at 0
Learn Python Basics online at www.DataCamp.com >>> my_string * 2
'thisStringIsAwesomethisStringIsAwesome'
Subset
>>> my_string + 'Innit'
'thisStringIsAwesomeInnit'
>>> my_list[1]
#Select item at index 1
>>> 'm' in my_string
>>> my_list[-3] #Select 3rd last item
True Slice
> Variables and Data Types String Indexing Index starts at 0
>>>
>>>
>>>
my_list[1:3] #Select items at index 1 and 2
my_list[1:] #Select items after index 0
my_list[:3] #Select items before index 3
>>> my_list[:] #Copy my_list
Variable Assignment >>> my_string[3]
>>> my_string[4:9] Subset Lists of Lists
>>> my_list2[1][0] #my_list[list][itemOfList]
>>> x=5
>>> my_list2[1][:2]
>>> x
5
String Methods
>>> my_string.upper()
#String to uppercase
List Operations
Calculations With Variables >>>
>>>
my_string.lower()
#String to lowercase
my_string.count('w') #Count String elements
>>> my_list + my_list
>>> my_string.replace('e', 'i') #Replace String elements
['my', 'list', 'is', 'nice', 'my', 'list', 'is', 'nice']
>>> x+2 #Sum of two variables
>>> my_string.strip() #Strip whitespaces >>> my_list * 2
['my', 'list', 'is', 'nice', 'my', 'list', 'is', 'nice']
>>> x-2 #Subtraction of two variables
>>> my_list2 > 4
True
>>> x*2 #Multiplication of two variables
10
>>> x**2 #Exponentiation of a variable
25
> NumPy Arrays Also see Lists
List Methods
>>> x%2 #Remainder of a variable
>>> my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
1
>>> my_list.index(a) #Get the index of an item
>>> my_array = np.array(my_list)
>>> x/float(2) #Division of a variable
>>> my_list.count(a) #Count an item
>>> my_2darray = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
2.5 >>> my_list.append('!') #Append an item at a time
>>> my_list.remove('!') #Remove an item
Types and Type Conversion Selecting Numpy Array Elements Index starts at 0 >>>
>>>
del(my_list[0:1])
#Remove an item
my_list.reverse() #Reverse the list
>>> my_list.extend('!') #Append an item
Subset >>> my_list.pop(-1) #Remove an item
str()
>>> my_list.insert(0,'!')
#Insert an item
'5', '3.45', 'True' #Variables to strings >>> my_array[1] #Select item at index 1
>>> my_list.sort() #Sort the list
2
int()
Slice
5, 3, 1 #Variables to integers
>>> my_array[0:2]
#Select items at index 0 and 1
float()
5.0, 1.0 #Variables to floats
array([1, 2])
Subset 2D Numpy arrays
> Python IDEs (Integrated Development Environment)
bool() >>> my_2darray[:,0] #my_2darray[rows, columns]
array([1, 4])
True, True, True #Variables to booleans
Leading open data science
Free IDE that is included
Create and share
Numpy Array Operations platform powered by Python with Anaconda documents with live code
> Libraries >>> my_array > 3
> Asking For Help
array([False, False, False, True], dtype=bool)
>>> my_array * 2
array([2, 4, 6, 8])
>>> my_array + np.array([5, 6, 7, 8])
Data analysis Scientific computing 2D plotting Machine learning array([6, 8, 10, 12]) >>> help(str)
Import Libraries Numpy Array Functions
>>> import numpy
>>> my_array.shape #Get the dimensions of the array
>>> import numpy as np >>> np.append(other_array) #Append items to an array
>>> np.insert(my_array, 1, 5) #Insert items in an array
>>> np.delete(my_array,[1]) #Delete items in an array
Selective import >>>
>>>
np.mean(my_array) #Mean of the array
np.median(my_array) #Median of the array
>>> my_array.corrcoef() #Correlation coefficient
>>> from math import pi >>> np.std(my_array) #Standard deviation
Learn Data Skills Online at
www.DataCamp.com
You might also like
- Python Cheat Sheet 2.0Document10 pagesPython Cheat Sheet 2.0Dario Camargo100% (1)
- 12 Comp Sci 1 Revision Notes Pythan Advanced ProgDocument5 pages12 Comp Sci 1 Revision Notes Pythan Advanced ProgAtanuBhandaryNo ratings yet
- Numpy Pandas Cheatsheet PDFDocument1 pageNumpy Pandas Cheatsheet PDFShailesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Python - Module 3Document86 pagesPython - Module 3Syed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Python DataScience Cheat-SheetDocument7 pagesPython DataScience Cheat-SheetZain UL ABIDIN100% (1)
- Final Cheat Sheet TemplateDocument3 pagesFinal Cheat Sheet TemplateCloudnLoud TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- List and DictionariesDocument36 pagesList and DictionariesEgi LikardoNo ratings yet
- Python Cheatsheets 1635792640Document9 pagesPython Cheatsheets 1635792640Mokhtar Alerte100% (1)
- PythonForDataScience Cheatsheet PDFDocument21 pagesPythonForDataScience Cheatsheet PDFGreet Labs100% (2)
- Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet: Subset SliceDocument1 pagePython For Data Science Cheat Sheet: Subset SliceHayath Masthan50% (2)
- Python Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesPython Cheat Sheet: by ViaDavid BumphisNo ratings yet
- Data Structures - Python 3.7.0Document13 pagesData Structures - Python 3.7.0JustinNo ratings yet
- 8 Best Python Cheat Sheets For Beginners and Intermediate LearnersDocument17 pages8 Best Python Cheat Sheets For Beginners and Intermediate LearnersMOHAN S100% (1)
- Python Cheat Sheet: TopicsDocument16 pagesPython Cheat Sheet: TopicsDexie Cabañelez ManahanNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesPython Cheat SheetSebas CorvalánNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet: Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pageCheat Sheet: Python For Data ScienceShishir Ray100% (1)
- CheatSheet Python 10 Machine Learning SVMDocument1 pageCheatSheet Python 10 Machine Learning SVMSATYAJEET SARFARE (Alumni)No ratings yet
- What Is Python 3?Document2 pagesWhat Is Python 3?Prashant GauravNo ratings yet
- Scipy (Python Library) : Prepared By: Jenish Patel Jesal Zala Kirtan Shah Sanyukta GautamDocument17 pagesScipy (Python Library) : Prepared By: Jenish Patel Jesal Zala Kirtan Shah Sanyukta GautamKirtanNo ratings yet
- Working With Dates in Pandas: Prepared by Asif BhatDocument13 pagesWorking With Dates in Pandas: Prepared by Asif BhatdawodyimerNo ratings yet
- Python Basic and Advanced-Day 8Document20 pagesPython Basic and Advanced-Day 8Ashok Kumar100% (1)
- Python - ProgrammingDocument9 pagesPython - ProgrammingDong Hai NguyenNo ratings yet
- BanditsDocument2 pagesBanditsIgnée FleurNo ratings yet
- Scikit - Notes MLDocument12 pagesScikit - Notes MLVulli Leela Venkata Phanindra100% (1)
- Data Structures in PythonDocument17 pagesData Structures in Pythonshreepad S HNo ratings yet
- Python Date TimeDocument6 pagesPython Date TimeNataliaNo ratings yet
- Python LabDocument27 pagesPython LabPrajwal P GNo ratings yet
- OOP Using Python Hands-On AssessmentDocument10 pagesOOP Using Python Hands-On AssessmentSonakshi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- K-Nearest Neighbor On Python Ken OcumaDocument9 pagesK-Nearest Neighbor On Python Ken OcumaAliyha Dionio100% (2)
- Numpy Notes CsaiDocument8 pagesNumpy Notes CsaiNishiNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Basics: An Illustrated Guide For Non-Technical ReadersDocument16 pagesMachine Learning Basics: An Illustrated Guide For Non-Technical ReadersGuoqi DingNo ratings yet
- Python AdvanceDocument35 pagesPython AdvanceNaveen NaikNo ratings yet
- API Reference - Scikit-Learn 0.19.2 DocumentationDocument21 pagesAPI Reference - Scikit-Learn 0.19.2 Documentation08mpe026No ratings yet
- Real Python ?? ?Document214 pagesReal Python ?? ?Anoop A S100% (1)
- Python Built in Functions TutorialDocument26 pagesPython Built in Functions TutorialdorokshaNo ratings yet
- Learn Python Programming LanguageDocument178 pagesLearn Python Programming LanguageanastasiosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Image Processing in Engineering Using PythonDocument8 pagesTeaching Image Processing in Engineering Using PythonSelva RajNo ratings yet
- Python For Reverse Engineering and Malware AnalysisDocument3 pagesPython For Reverse Engineering and Malware AnalysisRotem SalinasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine LearningDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Machine LearningKylleNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet Machine Learning Tips and Tricks PDFDocument2 pagesCheatsheet Machine Learning Tips and Tricks PDFAshwini NatesanNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Machine Learning Algorithms (With Python and R Codes) PDFDocument20 pagesEssentials of Machine Learning Algorithms (With Python and R Codes) PDFTeodor von Burg100% (1)
- Python CheatsheetDocument28 pagesPython CheatsheetMunguntuya AltangerelNo ratings yet
- Class XII (As Per CBSE Board) : Informatics PracticesDocument43 pagesClass XII (As Per CBSE Board) : Informatics PracticesAnushya RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Using Python PDFDocument2 pagesMachine Learning Using Python PDFVivian Nickson ViegasNo ratings yet
- Practical File of Machine Learning 1905388Document42 pagesPractical File of Machine Learning 1905388DevanshNo ratings yet
- PythonGuide V1.2.9Document2 pagesPythonGuide V1.2.9Samir Al-Bayati100% (1)
- Time Series Anomaly Detection With DLDocument18 pagesTime Series Anomaly Detection With DLAnonymous 9tJYscsNo ratings yet
- PythonScientific SimpleDocument356 pagesPythonScientific SimpleNag PasupulaNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning - Part 1Document80 pagesMachine Learning - Part 1cjon100% (1)
- Python GuideDocument82 pagesPython GuideTfy CocoNo ratings yet
- Built-In Functions - Python 3.9.0 DocumentationDocument29 pagesBuilt-In Functions - Python 3.9.0 DocumentationjandraqNo ratings yet
- Python CheetsheetDocument1 pagePython CheetsheetKunal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Complexity AnalysisDocument15 pagesLecture 02 Complexity AnalysisMuhammad AmmarNo ratings yet
- Numpy Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceDocument5 pagesNumpy Cheat Sheet & Quick Referencedad dunnoNo ratings yet
- DSA Cheat SheetDocument24 pagesDSA Cheat SheetDebasish SenapatyNo ratings yet
- Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet: Numpy BasicsDocument3 pagesPython For Data Science Cheat Sheet: Numpy BasicsAkshay YawaleNo ratings yet
- Introductory Notes: Matplotlib: PreliminariesDocument11 pagesIntroductory Notes: Matplotlib: PreliminariesJohnyMacaroniNo ratings yet
- Itom Cheat Sheet Python 3: ZerodivisionerrorDocument2 pagesItom Cheat Sheet Python 3: Zerodivisionerrorvikas_250% (2)
- Tensor FlowDocument12 pagesTensor Flowlevin696No ratings yet
- Chuletas DataCamp-2Document1 pageChuletas DataCamp-2Francisca SilvaNo ratings yet
- Python Civil Structural EngineersDocument299 pagesPython Civil Structural EngineersSiddhant Pandey100% (1)
- Mark Gowen - Python Programming For Beginners - The Simplified Beginner's Guide To Mastering Python Programming in One Week-Independently Published (2023)Document96 pagesMark Gowen - Python Programming For Beginners - The Simplified Beginner's Guide To Mastering Python Programming in One Week-Independently Published (2023)Nazarullah Nazarullah100% (1)
- Titanic PDFDocument101 pagesTitanic PDFAnindya MaitiNo ratings yet
- Advance Mathematics: Dosen Pengampu: Indrazno Siradjuddin, ST., MT., PH.DDocument6 pagesAdvance Mathematics: Dosen Pengampu: Indrazno Siradjuddin, ST., MT., PH.DPuspa AyuNo ratings yet
- Python ControlDocument99 pagesPython ControlJesus Alonso DiazNo ratings yet
- NumPy & PandasDocument27 pagesNumPy & PandasPavan DevaNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework-Xii-2024Document34 pagesHoliday Homework-Xii-2024Rudraa SinghNo ratings yet
- Quantiacs Python Toolbox Documentation PDFDocument35 pagesQuantiacs Python Toolbox Documentation PDFdarwin_huaNo ratings yet
- Electric Machine Design ANSYS Maxwell ToolkitTuToDocument310 pagesElectric Machine Design ANSYS Maxwell ToolkitTuToYsid Bello C67% (3)
- Food CalorieDocument28 pagesFood CaloriePremaNo ratings yet
- Sixte TutorialDocument11 pagesSixte TutorialSudip ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Python Lab Manual - 25.02.2022Document62 pagesPython Lab Manual - 25.02.2022vengai67% (3)
- Python Lab Manual BietDocument16 pagesPython Lab Manual BietKoolknight M05No ratings yet
- About Python For AI and MLDocument3 pagesAbout Python For AI and MLHitesh Son SonNo ratings yet
- Numba - A Dynamic Python Compiler For ScienceDocument39 pagesNumba - A Dynamic Python Compiler For ScienceYamabushi0% (1)
- Top 50+ Python Interview Questions (2022) - JavatpointDocument40 pagesTop 50+ Python Interview Questions (2022) - JavatpointIuvenis WorldNo ratings yet
- Dbms db03 2020 Assessment (Solved) : Find Study ResourcesDocument12 pagesDbms db03 2020 Assessment (Solved) : Find Study ResourcesGupta Anacoolz50% (2)
- Industrial Visit ReportDocument23 pagesIndustrial Visit ReportyousufNo ratings yet
- Personalized Food Recommendation System by Using Machine Learning ModelsDocument5 pagesPersonalized Food Recommendation System by Using Machine Learning ModelsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Python Essentials CE 215 Python Notes 0.0.1 DocumentationDocument11 pagesPython Essentials CE 215 Python Notes 0.0.1 DocumentationMlkhr lgndbNo ratings yet
- The Tip of The Iceberg: 1 Before You StartDocument18 pagesThe Tip of The Iceberg: 1 Before You Startregupathi6413No ratings yet
- ML Lab RecordDocument15 pagesML Lab Recordrr3870044No ratings yet
- Question Bank Python For Data ScienceDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank Python For Data Sciencesandeep kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Practical File Artificial Intelligence Class 10 For 2022-23Document24 pagesPractical File Artificial Intelligence Class 10 For 2022-23amitgaurav992100% (1)
- UNIT 1 Exploratory Data AnalysisDocument21 pagesUNIT 1 Exploratory Data Analysisdivyar674No ratings yet
- Data Science Lab: Numpy: Numerical PythonDocument71 pagesData Science Lab: Numpy: Numerical PythonPhamThi ThietNo ratings yet
- DSBDA Lab Manual 2022-23Document148 pagesDSBDA Lab Manual 2022-23Mishra Ji100% (2)
- Ch-2 Panda: #Import The Pandas Library and Aliasing As PDDocument5 pagesCh-2 Panda: #Import The Pandas Library and Aliasing As PDRC SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final Project ReportDocument76 pagesFinal Project ReportMr. KarkiNo ratings yet