Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Chapter 7
Uploaded by
NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Chapter 7
Uploaded by
NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)Copyright:
Available Formats
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
7 Balance
of Payments
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
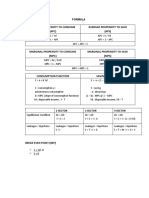
BALANCE OF PAYMENT
ITEMS NOTE
Trade export
- Trade import
Balance On Trade/Goods/Merchandise Account A
Transportation
+ Travel
+ Government Transaction
+ Other services
Balance On Services Account B
Balance On Goods And Services C A+B
Compensation Of Employees
+ Investment Income
Balance On Income Account D
+ Current Transfer E
BALANCE ON CURRENT ACCOUNT F C+D+E
+ Capital transfer
+ Acquisition/disposal of non-produced, non-financial assets
Balance On Capital Account G
+ Direct investment
+ Portfolio investment
+ Other investment
Official sector
Private sector
Balance On Financial Account H
BALANCE ON CAPITAL AND FINANCIAL ACCOUNT I G+H
+ Error and omissions J
OVERALL BALANCE F+I+J
Net Changes In Central Bank International Reserves
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
a. Merchandise / Goods trade Balance
The difference between export and import of physical goods
Trade Surplus = export > import
Trade deficit = export < import
b. Service Balance
The difference of receipts and payments from services
c. Income Account
The difference between investment income flows into and out of a country
d. Current Transfer
Records all transfer payments received and paid abroad by public and private sectors
e. Capital Account
Records all international capital transfer
Eg. The acquisition or disposal of a non-financial asset and non-produced assets (eg.
Land)
f. Financial Account
i. Direct Investment
Long-term Investment
Foreign investors establish new firms and industries in Malaysia
Transfer of existing assets from local firms to foreign firms
(merger & acquisition)
When an industry abroad provides inputs for a firm’s domestic
production process
ii. Portfolio Investment
Short-term Investment
Purchase of shares, stocks in a foreign company
Purchase of bonds issued by a foreign government
iii. Other Investment
Includes all transactions in currency and bank deposits by a foreigner in a
local bank to earn a high-interest rate
g. Errors and Omissions
Also known as a statistical discrepancy
A balancing item in which the credits and debits must be equal
It occurs in short term capital flow to record adjustments for unrecorded transactions
h. Official Reserve Account
Consists of :
1. Government Gold & Foreign Currency Reserve
2. Government Reserves with the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
3. Special Drawing Right (SDR) – in the form of bookkeeping entries that can
be used by countries to settle their international accounts.
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. The balance of payment is
A. a record of the payments made by one company in one country to another company in another
country.
B. the identity that illustrates the balance between exports and imports.
C. a periodic statement of the monetary value of all transactions between residents in one country
and residents of all other countries.
D. any transaction that supplier the domestic country’s currency.
2. The balance of payment contains information regarding
A. purchases of Malaysia’s financial assets by foreigners.
B. purchases of foreign financial assets by Malaysian.
C. levels of Malaysia’s exports and imports.
D. all of the above.
3. The situation when a country exports more than it imports is known as
A. a trade surplus.
B. a budget surplus.
C. an expansion.
D. a term of trade.
4. Which of the following is not included in the current account balance?
A. Balance of goods and services.
B. Financial account.
C. Current transfer.
D. Net income.
5. Which of the following is not a component of the current account?
A. Investment income
B. Net government transfer
C. Portfolio investment
D. Travel expenses
6. Which of the following is NOT considered as a unilateral transfer?
A. Income earned from foreign investments.
B. Personal gifts to friends or family abroad.
C. Institutional charitable donations.
D. Government transfers to foreign residents.
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
7. Deficit in the balance of payments account can be corrected by
A. lowering domestic prices.
B. raising indirect taxes.
C. increasing government expenditures.
D. lowering the interest rate.
8. A favorable balance of trade occurs when
A. export equal imports.
B. the balance of payments balances.
C. the current and capital accounts are equal.
D. the value of merchandise exports exceeds the value of merchandise imports.
9. Which of the following policies is inappropriate to correct a deficit balance of payments?
A. Encouraging import of capital.
B. Discouraging the import of goods.
C. Appreciation of the currency.
D. Imposition of foreign exchange controls.
10. Which action is not suitable for correcting a deficit in the balance of payments?
A. Discouraging import
B. Imposition of tariff
C. Appreciation of currency
D. Exchange controls
11. The balance of payment contains information regarding
A. purchases of Malaysia’s financial assets by foreigners.
B. purchases of foreign financial assets by Malaysian.
C. levels of Malaysia’s exports and imports.
D. all of the above.
12. Given the following information, calculate the value of the overall balance.
Balance of current account RM 54 000 million
Balance on capital account RM 60 000 million
Errors and omission RM 7 800 million
A. RM 106 200 million
B. RM 1800 million
C. RM 114 000 million
D. RM 121 800 million
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
13. Which of the following is not included in the current account balance?
A. Balance of goods and services.
B. Financial account.
C. Current transfer.
D. Net income
14. Which of the following is NOT considered as a unilateral transfer?
A. Income earned from foreign investments.
B. Personal gifts to friends or family abroad.
C. Institutional charitable donations.
D. Government transfers to foreign residents.
15. A deficit in the balance of payments account can be corrected by
A. lowering domestic prices.
B. raising indirect taxes.
C. increasing government expenditures.
D. lowering the interest rate.
16. A favorable balance of trade occurs when
A. export equal imports.
B. the balance of payments balances.
C. the current and capital accounts are equal.
D. the value of merchandise exports exceeds the value of merchandise imports.
17. Which action is not suitable for correcting a deficit in the balance of payments?
A. Discouraging import
B. Imposition of tariff
C. Appreciation of currency
D. Exchange controls
18. Which of the following policies is inappropriate to correct a deficit balance of payments?
A. Encouraging import of capital.
B. Discouraging the import of goods.
C. Appreciation of the currency.
D. Imposition of foreign exchange controls.
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
The following data represents the Balance of Payment of a country in 2008
ITEMS RM
Merchandise exports 4000
Merchandise imports 3500
Government transactions 1850
Giving Service to foreign ship 1800
Travel 1250
Investment income 2500
Remittance of Indonesian workers to Indonesia 2400
Portfolio investment 2600
Direct investments 2200
Other investments 1500
Errors and omissions 1000
Calculate:
a. Merchandise trade balance. (2 points)
b. Services balance. (2 points)
c. Balance on goods and services. (2 points)
d. Overall balance (2 points)
e. Net change in the country’s international reserves (2 points)
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
QUESTION 2
Table 4 shows the balance of payments for Malaysia in 2011.
Table 4
Item RM (billion)
Exports of goods 575
Imports of goods 450
Transportation 150
Net Transfer 35
Errors and Omissions 15
Foreign assets in Malaysia 299
Malaysia’s assets abroad 166
Other Services -75
Travel 50
Investment Income 13
Government Transactions -40
Calculate:
a. Merchandise account balance and the service account balance. (4 points)
b. Current account balance (2 points)
c. Balance on financial and capital account (2 points)
d. Overall balance (2 points)
10
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
11
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
QUESTION 3
The following data shows the Balance of Payment for Malaysia in 2010.
Items RM (million)
Exports 2,100
Other investment 700
Education 1,820
Imports 1,470
Income from investment 6,160
Government transaction 2,870
Insurance 1,050
Direct investment 3,500
Other services 3,220
Errors and omissions 6,300
Capital account 5,950
Current transfers 2,030
Portfolio investment 3,640
Transportation 6,580
Calculate:
a) Merchandise trade balance. (1 point)
b) Current account balance. (5 points)
c) Capital and financial account balance. (2 points)
d) Overall balance. (2 points)
12
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
13
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
QUESTION 4
The following data represents the Balance of Payment of a country in 2008
Items RM Millions
Exports 365, 223
Imports 290, 894
Freight & Insurance -12, 202
Other transportations 2, 441
Travel 8, 999
Government transactions -57
Other services -11, 309
Investment income -24, 978
Compensation of employee -15, 264
Transfer payments -7, 468
Direct investment 2, 418
Portfolio investment 4, 265
Other investment -21, 323
Errors and omissions -6, 960
a) Calculate:
i. Balance on goods and services. (2 points)
ii. Balance on current account. (2 points)
iii. Overall balance. (2 points)
iv. Net changes in the official reserve assets. (1 point)
b) Is the above country facing a surplus or deficit Balance of Payment? (1 point)
c) List two (2) effects of the above balance of payment to the position on the country. (2 points)
14
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
15
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
QUESTION 5
The following table shows the Balance of Payments for Malaysia in 1998.
Table 4
Items RM Million
Exports 319,568
Imports 233,519
Transportation -8,464
Nett transfer -6,567
Errors and omissions -4,924
Official long term capital 9,397
Direct investment -36,854
Other services -8,395
Travel 6,135
Investment income -20,275
Government transactions 23
Calculate:
a. The trade balance (2 points)
b. Service account balance (2 points)
c. Current account balance (2 points)
d. Capital and Financial account balance (2 points)
e. Overall Balance (2 points)
(Total : 10 Marks)
16
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
17
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
a
QUESTION
. 6
Table 4 shows the balance of payments for Malaysia in year 2019.
Table 4
Item RM (million)
s
Export 250,245
Import 237,500
Freight and insurance - 9,728
Net transfer 3,185
Error and omissions 4,613
Official long-term capital 11,643
Corporate investment 12,240
Net private capital - 31,798
Other transportation 1,987
Travel 5,276
Investment income 16 135
Government transaction - 84
Other services - 805
Based on the above data, calculate:
i. Balance on merchandise account (2 points)
ii. Balance on service account (2 points)
iii. Current account balance (2 points)
iv. Balance on capital and financial account (2 points)
v. Overall balance (2 points)
(Total: 10 points)
18
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
19
Compiled by: haslin hs
PEC2143 (JULY 2021) KPTM BANGI
SHORT ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Distinguish between trade deficit and trade surplus (4 points)
2. Explain disequilibrium in balance of payment. (2 points)
3. List four (4) measures to solve / correct the problem of deficit in the (4 points)
balance of payments.
Explain TWO (2) effects of deficit in the Balance of Payments of a
4. (4 points)
country.
20
Compiled by: haslin hs
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Arahan SeminarDocument1 pageArahan SeminarNURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Rb-Forum PBS3214Document1 pageRb-Forum PBS3214NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Rb-Seminar PBS3214Document2 pagesRb-Seminar PBS3214NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Ground Work Document - Notice of Meeting - Memo - Agenda - AttendanceDocument9 pagesGround Work Document - Notice of Meeting - Memo - Agenda - AttendanceNURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Tutorial Chapter 6Document13 pagesTutorial Chapter 6NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Chapter 3 Determination of National Income Equilibrium - 2Document68 pagesChapter 3 Determination of National Income Equilibrium - 2NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Chapter 3 - FormulaDocument1 pageChapter 3 - FormulaNURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Chapter 7 Balance of PaymentsDocument14 pagesChapter 7 Balance of PaymentsNURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Assignment Rubric Financial Management PFN1223Document2 pagesAssignment Rubric Financial Management PFN1223NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Tutorial Chapter 1, 2, 3Document57 pagesTutorial Chapter 1, 2, 3NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- Midterm Test April2021Document5 pagesMidterm Test April2021NURUL FATIN NABILA BINTI MOHD FADZIL (BG)No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Transaction Report: Zahid AbuDocument4 pagesTransaction Report: Zahid AbuSãbbìŕ Ràhmâñ0% (1)
- IF Hericourt Lecture1Document10 pagesIF Hericourt Lecture1Jerónimo BedoyaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- How The U.S. Dollar Became The World's Reserve CurrencyDocument9 pagesHow The U.S. Dollar Became The World's Reserve CurrencyParvez ShakilNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 2022 WTO Moot Court ProblemDocument5 pages2022 WTO Moot Court ProblemPrince KatheweraNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- D.A.V.V., Indore Institute of Management Studies: International FinanceDocument10 pagesD.A.V.V., Indore Institute of Management Studies: International FinanceSNo ratings yet
- PDF MiradonizDocument1 pagePDF MiradonizEva MafteiNo ratings yet
- Code Country Country, CurrencyDocument16 pagesCode Country Country, Currencyarihant_jainNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Free Trade Agreement Mercosur - IsraelDocument21 pagesFree Trade Agreement Mercosur - Israelapi-25992509No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Kelas 2 - Latihan Soal PTS 2 MathDocument7 pagesKelas 2 - Latihan Soal PTS 2 MathShakti Mikayla Tsamara Karima100% (1)
- Export Import Bank of Bangladesh LimitedDocument2 pagesExport Import Bank of Bangladesh LimitedRichard GateNo ratings yet
- Inventory ReceiptDocument1 pageInventory ReceiptJuvz BezzNo ratings yet
- M2 eDocument67 pagesM2 eDavid DinhNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- FAIR CYS Long Report ENG Nov EDITIONDocument49 pagesFAIR CYS Long Report ENG Nov EDITIONALLANo ratings yet
- Co Form VKDocument1 pageCo Form VKphuong88146No ratings yet
- KashifRasool - 2333 - 16644 - 6 - Lecture 3 - International Trade Theory, Hill - 300116Document31 pagesKashifRasool - 2333 - 16644 - 6 - Lecture 3 - International Trade Theory, Hill - 300116AhmadNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument38 pagesInternational Businessshubham abhangeNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Forward Rates - January 12 2022Document2 pagesForward Rates - January 12 2022Lisle Daverin BlythNo ratings yet
- International Finance 3Document24 pagesInternational Finance 3Rahul BambhaNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS International Trade Practice QuestionsDocument18 pagesSOLUTIONS International Trade Practice QuestionsJaime SánchezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Nine:: Nontariff Trade Barriers and The New ProtectionismDocument26 pagesChapter Nine:: Nontariff Trade Barriers and The New ProtectionismAhmad RonyNo ratings yet
- CetaDocument36 pagesCetaTudor SimionovNo ratings yet
- Terms of TradeDocument40 pagesTerms of TradeRuchitha PrakashNo ratings yet
- Fixed Exchange Rates - Implications For Global Trade - Anni - KarichashviliDocument4 pagesFixed Exchange Rates - Implications For Global Trade - Anni - KarichashvilianaNo ratings yet
- KGupta-Study Guidelines-International Econ-5th SemDocument9 pagesKGupta-Study Guidelines-International Econ-5th SemPanvel PatilNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Forex PDFDocument9 pagesBeginners Guide To Forex PDFMonde CeleNo ratings yet
- The World Trade OrganizationDocument7 pagesThe World Trade Organizationketanrana2No ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CP 18Document59 pagesCP 18Celpan ElenaNo ratings yet
- Section B Csec Social Studies NotesDocument4 pagesSection B Csec Social Studies NotestaliyaforresterNo ratings yet
- Foreiagn Chapter ThreeDocument45 pagesForeiagn Chapter ThreeLidya AberaNo ratings yet