Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamics of Machines (ME22004) Tutorial 3
Dynamics of Machines (ME22004) Tutorial 3
Uploaded by
ROHITH KADIYALA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document contains 5 questions regarding dynamics of machines. Question 1 asks about determining the force developed by a hydraulic actuator tilting a beam and the force on a pin. Question 2 asks about determining the force in a link when a torque is suddenly applied to a mechanism. Question 3 asks about deriving and plotting the angular speed and variation of a cam mechanism over time. Question 4 asks about deriving the equation of motion and force required for a scissor mechanism driven by a linear actuator. Question 5 asks about determining the torque required at a crankshaft to start a mechanism with a given angular acceleration.
Original Description:
Original Title
dom-tut3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 5 questions regarding dynamics of machines. Question 1 asks about determining the force developed by a hydraulic actuator tilting a beam and the force on a pin. Question 2 asks about determining the force in a link when a torque is suddenly applied to a mechanism. Question 3 asks about deriving and plotting the angular speed and variation of a cam mechanism over time. Question 4 asks about deriving the equation of motion and force required for a scissor mechanism driven by a linear actuator. Question 5 asks about determining the torque required at a crankshaft to start a mechanism with a given angular acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesDynamics of Machines (ME22004) Tutorial 3
Dynamics of Machines (ME22004) Tutorial 3
Uploaded by
ROHITH KADIYALAThis document contains 5 questions regarding dynamics of machines. Question 1 asks about determining the force developed by a hydraulic actuator tilting a beam and the force on a pin. Question 2 asks about determining the force in a link when a torque is suddenly applied to a mechanism. Question 3 asks about deriving and plotting the angular speed and variation of a cam mechanism over time. Question 4 asks about deriving the equation of motion and force required for a scissor mechanism driven by a linear actuator. Question 5 asks about determining the torque required at a crankshaft to start a mechanism with a given angular acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Dynamics of Machines (ME22004)
Tutorial 3
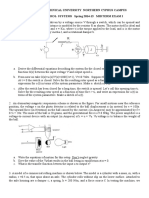
Q1 A light hydraulic actuator tilts the uniform slender 100 kg rigid
beam at a constant expansion rate ds/dt=0.2 m/s in the vertical
plane, as shown. At θ=30 deg, determine (a) the force developed
by the actuator, and (b) the force on the pin at O. Assume all
contacts to be frictionless, and take l = 1.5 m, b = 1 m, and g =
9.81 m/s2.
Q2 The mechanism shown lies in the horizontal plane and moves the slider B of
mass mB due to the motion of link OA having moment of inertia IO about
O. Determine the force in the rigid light link AB when a torque τ = 0.5 Nm
is suddenly applied as shown with the mechanism at rest at some angle θ.
Take the values of r = 0.25 m, l = 0.2 m, mB = 1.4 kg, IO = 0.3 kg m2, and θ
= 30 deg. Neglect friction at all contacts.
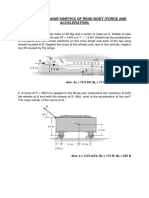
Q3 A fork is driven by a circular cam as shown in the horizontal
plane. The cam is driven by a constant torque at O.
Neglecting friction at all contacts, derive the equation of
motion of the system. Take the moment of inertia of the fork
about A as IF = 0.4 kg m2, mass of the uniform circular disc
cam mC = 0.3 kg, radius r = 0.15 m, e = 0.1 m, and OA=0.5
m. If the torque on the cam is τ = 0.1 Nm (constant), plot the
variation of angular speed of the cam with time. Also, plot
the result with θ.
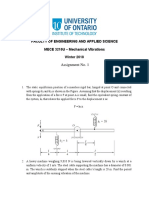
Q4 Derive the equation of motion of the scissor mechanism driven by
a linear hydraulic actuator at A (not shown) in the vertical plane.
Take the mass of the identical uniform links to be mL and the
mass of the horizontal platform to be mP. Neglect friction at all
contacts. If the pin A is to move at a constant velocity v0 as
shown, determine the force required at the actuator. Also,
calculate the net reaction force on the fixed ground pin. Take mL
= 8 kg, mP = 10 kg, L = 2 m, and g = 9.8 m/s2 to plot the results
with θ (starting from θ0 = 5 deg to θf = 30 deg) for v0=0.2 m/s.
Note carefully the definition of θ.
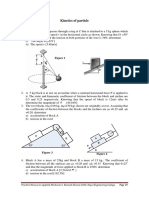
Q5 The mechanism in the horizontal plane shown is driven by the
crank OA while the slotted link experiences a counter-clockwise
constant load torque τC through the shaft at C. The moment of
inertia of the crank OA is IO about O, while that of the slotted link
is IC about C. Determine the torque required at the crankshaft O at
some given angle θ to start the crank with a clockwise angular
acceleration α from rest.
You might also like
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- FINAL EXAMINATION in Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument1 pageFINAL EXAMINATION in Dynamics of Rigid BodiesRochelle TugadeNo ratings yet
- Server Eaton Specificaton General PDFDocument78 pagesServer Eaton Specificaton General PDFJames Scott Valderrama RiscoNo ratings yet
- Embodied IntelligenceDocument31 pagesEmbodied IntelligenceNagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- JLG Codes PDFDocument180 pagesJLG Codes PDFfrank kamuhanda33% (3)
- Kinetics of Rigid BodyDocument32 pagesKinetics of Rigid BodyMuhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- HW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationDocument8 pagesHW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- For A System of Particles:: Week 13 Lecture Notes Impulse-Momentum Principle For A Rigid BodyDocument7 pagesFor A System of Particles:: Week 13 Lecture Notes Impulse-Momentum Principle For A Rigid Bodysuraj raiNo ratings yet
- The Secret To: Japanese SuccessDocument44 pagesThe Secret To: Japanese Successmaria neneng bulakNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-Equilibrium 1Document2 pagesTutorial 2-Equilibrium 1Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Tems Discovery 3.1 - User Manual PDFDocument371 pagesTems Discovery 3.1 - User Manual PDFChu Quang TuanNo ratings yet
- Micro OBSDocument10 pagesMicro OBSMelchor Felipe SalvosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- Landscape Visual Impact AssessmentDocument22 pagesLandscape Visual Impact AssessmentIzzrul Lee ZaharudinNo ratings yet
- GIA Ruby Montepuez Mozambique PDFDocument84 pagesGIA Ruby Montepuez Mozambique PDFVaishali JhaveriNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2010 Mcg3130Document12 pagesFinal Exam 2010 Mcg3130Brian Pham Vu100% (1)
- Assignment (4) Forced Vibration of SDOF Systems PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment (4) Forced Vibration of SDOF Systems PDFKarim FangaryNo ratings yet
- Examples Force AccelDocument105 pagesExamples Force AccelMuhammad DaffaNo ratings yet
- Q3-BPP-Module 2Document13 pagesQ3-BPP-Module 2Jeffrey C. Serrano100% (1)
- Dynamics of Machines (ME22004) Tutorial 3Document2 pagesDynamics of Machines (ME22004) Tutorial 3ROHITH KADIYALANo ratings yet
- Test1Review 1Document2 pagesTest1Review 1Cathy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Desarrollado ONDASDocument5 pagesEjercicios Desarrollado ONDASMariangelica Preciado NunezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document19 pagesTutorial 3Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- CH-10 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies 2Document13 pagesCH-10 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies 2Anshuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4Document13 pagesUnit 3 & 4Ram Chandra0% (1)
- Mech304 MT1Document3 pagesMech304 MT1Muhammed AliNo ratings yet
- Vibrations ExDocument1 pageVibrations ExMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Planar Kinetics of Rigid Body (Force and Acceleration)Document5 pagesTutorial - Planar Kinetics of Rigid Body (Force and Acceleration)Chin Tiong LeeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2AkhilNo ratings yet
- Phys124s10 hw02Document5 pagesPhys124s10 hw02snyderbl2100% (1)
- Solved Problems in VibrationDocument57 pagesSolved Problems in VibrationRasikaPereraNo ratings yet
- Machines Tutorial Sheet #2 (2024)Document4 pagesMachines Tutorial Sheet #2 (2024)Riya KoretiNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science MECE 3210U - Mechanical VibrationsDocument4 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Applied Science MECE 3210U - Mechanical VibrationsBilly JhunNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 6 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 6 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 7Document4 pagesProblem Set 7azzaguidaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment2ed PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment2ed PDFIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- WS31Document3 pagesWS31Minte MuluNo ratings yet
- Problemas de Vibraciones PDFDocument6 pagesProblemas de Vibraciones PDFKhristian VinicioNo ratings yet
- Rigid BodiesDocument8 pagesRigid BodiesQuim SimonNo ratings yet
- 149 Impulse MomentumDocument21 pages149 Impulse Momentumsaurabhtyagi245No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Amir Chip100% (1)
- Qns For End TermDocument8 pagesQns For End TermNilesh Tanna TannaNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Practical 1: Static and Dynamic Balancing of Rotating MassesDocument21 pagesSr. No. Practical 1: Static and Dynamic Balancing of Rotating MassesFa CaNo ratings yet
- HW05 Metu PDFDocument2 pagesHW05 Metu PDFFatih BodrumNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document5 pagesModule 6John Kennedy EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Tut1 Part29 PDFDocument1 pageTut1 Part29 PDFAnmolNo ratings yet
- Tut1 Part29Document1 pageTut1 Part29AnmolNo ratings yet
- EM Assignment 21Document2 pagesEM Assignment 21Rajat PullinNo ratings yet
- Problems On DynamicsDocument3 pagesProblems On DynamicsPablo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Kinetics of ParticlesDocument27 pagesCh3 Kinetics of Particlestik50100% (2)
- Infant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Document4 pagesInfant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Robinston Jeyasingh KNo ratings yet
- Sheet2 SolvedDocument25 pagesSheet2 Solvedirshad224No ratings yet
- CL-12 Chapter 4 Magnetism PhysicsDocument15 pagesCL-12 Chapter 4 Magnetism PhysicsSomila SchoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document44 pagesChapter 8Mohan ManickamNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)Document23 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)cbsesamplepaper0% (1)
- TD Cours Tipe PDFDocument25 pagesTD Cours Tipe PDFAnonymous hyeNVbcONo ratings yet
- Phy 1 PDFDocument15 pagesPhy 1 PDFGarlapati Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 1 (SMI Ipoh)Document10 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 1 (SMI Ipoh)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- Ex 1 Drives 12 13Document1 pageEx 1 Drives 12 13nysretNo ratings yet
- 22 Fall Spring 2004 PDFDocument164 pages22 Fall Spring 2004 PDFcombatps1No ratings yet
- Adaptive State Controller For Inverted Pendulum: Nenad Muškinja, Boris TovornikDocument6 pagesAdaptive State Controller For Inverted Pendulum: Nenad Muškinja, Boris TovornikNeagu AdrianNo ratings yet
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 3Document27 pagesJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 3Adib AzharNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7-Forced Oscillation-Pohl's PendulumDocument4 pagesExperiment 7-Forced Oscillation-Pohl's Pendulumdiyana889450% (2)
- S1 Guidelines "Lumbar Puncture and Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis"Document28 pagesS1 Guidelines "Lumbar Puncture and Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis"alejandro montesNo ratings yet
- HB 2425 Tieng Anh 9 de Minh Hoa Va HDCDocument8 pagesHB 2425 Tieng Anh 9 de Minh Hoa Va HDCYến Nhi NgôNo ratings yet
- MAHINDRADocument75 pagesMAHINDRAranjan80das80% (5)
- 1st - 4th Yr Subjects With InstructorDocument6 pages1st - 4th Yr Subjects With InstructorEddie GuiribaNo ratings yet
- Ava RichesinDodd - Module 5 NotesDocument2 pagesAva RichesinDodd - Module 5 Notesava richesin-doddNo ratings yet
- Tribhuvan University Institute of EngineeringDocument36 pagesTribhuvan University Institute of Engineeringatheb12345No ratings yet
- EE3015 Power Systems and Conversion - OBTLDocument7 pagesEE3015 Power Systems and Conversion - OBTLAaron Tan100% (1)
- Passenger Ship Safety - 18 March 2010Document15 pagesPassenger Ship Safety - 18 March 2010Bradley GoldenNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution and Its Effects On AgricultureDocument10 pagesAir Pollution and Its Effects On AgricultureIqra IjazNo ratings yet
- Rent To Own FlyerDocument2 pagesRent To Own FlyerKobe BinamiraNo ratings yet
- Eee Syllabus, HstuDocument41 pagesEee Syllabus, HstuLikhan Kumar SahaNo ratings yet
- Basic Instructions For Using AMDIS With MS SearchDocument34 pagesBasic Instructions For Using AMDIS With MS SearchМаратNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Aquifer Pumping Test Data ToDocument19 pagesAnalysis of Aquifer Pumping Test Data ToFisseha TekaNo ratings yet
- Akash Aipmt Final 2011 SolutionDocument18 pagesAkash Aipmt Final 2011 Solutionsaurav guptaNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: N - R 472C en 05.12Document42 pagesOperating Instructions: N - R 472C en 05.12Long HuynhNo ratings yet
- Technical Object First Draft & Peer Reviews - EditedDocument5 pagesTechnical Object First Draft & Peer Reviews - EditedJohn MainaNo ratings yet
- BADMINTONDocument4 pagesBADMINTONAngelica MorcozoNo ratings yet
- Imagery of Light in Abraham Valdelomar'sDocument8 pagesImagery of Light in Abraham Valdelomar'srenatoNo ratings yet
- CaseStudiesStatistics 2009Document10 pagesCaseStudiesStatistics 2009sachy24No ratings yet
- A Series PDFDocument2 pagesA Series PDFAnonymous SYadUHW50No ratings yet
- Nursery Raising of Vegetables CropsDocument7 pagesNursery Raising of Vegetables Cropsronalit malintad100% (2)