Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chery-Orinoco-M11-Pin Out Ecul
Uploaded by
Manolo RodriguezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chery-Orinoco-M11-Pin Out Ecul
Uploaded by
Manolo RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL INFORMATION
Electronic Engine Controls (Page 11 of 11)
03
VISMW030039T
Chery Automobile Co., Ltd. 03–17
GENERAL INFORMATION
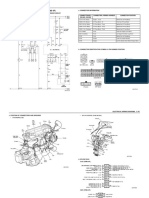
ECM Connector Pin-Out Table
ECM PIN-OUT TABLE
PIN CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION PIN CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
1 - 42 Intake Air Temperature Sensor
2 Ignition Coil 2 43 -
3 GND (Ignition) 44 Switched Supply Voltage
4 - 45 Switched Supply Voltage
5 Ignition Coil 1 46 Canister Control Valve
6 Injector 2 47 Injector 4
Upstream Oxygen Sensor Heating
7 Injector 3 48
(With EOBD)
8 - 49 -
9 - 50 Fan Relay Control
10 - 51 GND (Signal)
11 EPC Lamp 52 -
12 Continuous Supply Voltage 53 GND (Signal)
Electronic Throttle Control Actuator
13 Ignition Switch 54
(Position Sensor)
14 EMS Relay (Main Relay) 55 Downstream Oxygen Sensor
15 Crankshaft Position Sensor 56 -
16 Accelerator Position Sensor 57 A/C Stand By
17 Sensor (GND) 58 Brake Switch
18 Upstream Oxygen Sensor 59 Vehicle Speed Sensor
19 Knock Sensor 1 60 A/C Middle Pressure Switch
20 Knock Sensor 2 61 GND (Power)
21 Brake Switch 62 CAN-H
22 - 63 Switched Supply Voltage
23 - 64 Electric Throttle Control Actuator
24 - 65 Electric Throttle Control Actuator
25 - 66 Electric Throttle Control Actuator
26 - 67 Electric Throttle Control Actuator
27 Injector 1 68 Fan Relay Control 2
Downstream Oxygen Sensor
28 69 Air Compressor Relay
Heating (With EOBD)
29 - 70 Fuel Pump Relay
30 - 71 Diagnostic Link K
31 - 72 -
32 Regulated Sensor Supply 2 73 Regulated Sensor Supply 1
33 Regulated Sensor Supply 1 74 Clutch Pedal Switch
34 Crankshaft Position Sensor 75 -
03–18 Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
GENERAL INFORMATION
PIN CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION PIN CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
35 Sensor (GND) 76 Power Steering Switch
36 Sensor (GND) 77 -
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
37 (With 1.6L Engine) 78 Sensor (GND)
Air Flow Sensor (With 1.8L Engine)
Electronic Throttle Control Actuator
38 79 Camshaft Position Sensor
(Position Sensor)
39 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 80 GND (Power) 03
40 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 81 CAN-L
41 -
Chery Automobile Co., Ltd. 03–19
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
Diagnostic Help
1. The X-431 scan tool connects to the Data Link Connector (DLC) and communicates with the vehicle electronic
modules through the data network.
2. Confirm that the malfunction is current and carry-out the diagnostic tests and repair procedures.
3. If the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) cannot be deleted, it is a current fault.
4. Use only a digital multimeter to perform voltage readings on electronic systems.
5. Refer to any Technical Bulletins that may apply to the failure.
6. Visually inspect the related wiring harness.
7. Inspect and clean all Engine Control Module (ECM) grounds that are related to the most current DTC.
8. If numerous trouble codes were set, use a wiring schematic and look for any common ground circuits or voltage
supply circuits that may apply to the DTC.
Intermittent DTC Troubleshooting
Ifthe failure is intermittent perform the following:
• Check for loose connectors.
• Look for any chafed, pierced, pinched, or partially broken wires.
• Monitor the scan tool data relative to this circuit.
• Wiggle the related wiring harness and connectors while looking for an interrupted signal on the affected circuit.
• If possible, try to duplicate the conditions under which the DTC set.
• Look for the data to change or for the DTC to reset during the wiggle test.
• Look for broken, bent, pushed out or corroded terminals.
• Inspect the sensor and mounting area for any condition that would result in an incorrect signal, such as dam-
age, or foreign material.
• A data recorder, and/or oscilloscope should be used to help diagnose intermittent conditions.
• Remove the Engine Control Module (ECM) from the troubled vehicle and install in a new vehicle and test. If
the DTC cannot be deleted, the ECM is malfunctioning. If the DTC can be deleted, return the ECM to the origi-
nal vehicle.
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground connec-
tions are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can become an unwanted
resistance. This added resistance can alter the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drastically
affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can effect the circuit. Perform the following when
inspecting a ground connection:
1. Remove the ground bolt or screw.
2. Inspect all mating surface for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
3. Clean as required to assure good contact.
4. Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
5. Inspect for 9add-on9 accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
6. If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the wires
are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are crimped to one eyelet, make
sure no excess wire insulation has been crimped creating a bad ground.
Electronic Throttle Control Actuator Self-Learning Operation Introduction
Electronic Pedal Control (EPC) Lamp Control Strategy
The EPC lamp will light when the ignition switch is turned to the ON position and the engine is not running. After the
engine is started, the EPC lamp will go off if there is no EPC DTCs that exist in the ECM. If the internal EPC self-
check failed, the EPC lamp will continue to light.
Electronic Throttle Control Actuator Self-Learning Condition
• Engine stopped and the ignition switch on.
• Vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
03–20 Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
You might also like
- Chevrolet Aveo Ecm PinoutDocument2 pagesChevrolet Aveo Ecm PinoutCarlos MayerNo ratings yet
- ECM PINOUT Chevrolet-Sail-1 PDFDocument2 pagesECM PINOUT Chevrolet-Sail-1 PDFwilly_net123100% (1)
- Pines Ecu Codigos y Pruebas Control Electronico Del Motor Chery Orinoco m11 Service Manual-122-288.PDF Versión 1Document167 pagesPines Ecu Codigos y Pruebas Control Electronico Del Motor Chery Orinoco m11 Service Manual-122-288.PDF Versión 1oscar vergara100% (2)
- Epica 2.5L 2007 - 1 PDFDocument37 pagesEpica 2.5L 2007 - 1 PDFjemaliz100% (1)
- Nissan S13 SR20DET To Wolf V500 Pinouts With LinkDocument1 pageNissan S13 SR20DET To Wolf V500 Pinouts With Linkwolfems88% (8)
- Ingeautron Chevrolet Aveo 2011 1.6cc ECM Conector K Pin OutDocument3 pagesIngeautron Chevrolet Aveo 2011 1.6cc ECM Conector K Pin OutIngenieria Autotronica100% (1)
- 1995 Impreza EJ18 ECM PinoutDocument3 pages1995 Impreza EJ18 ECM Pinoutguillermo6661No ratings yet
- Ecm (Engine Control Module) : Sirius D42Document14 pagesEcm (Engine Control Module) : Sirius D42วิสูตร์ วงษ์มา100% (3)
- Pin OutDocument3 pagesPin Outjose100% (1)
- Pin ECU Captiva 2008 2Document2 pagesPin ECU Captiva 2008 2immanemm100% (1)
- 1736ABDocument1 page1736ABdaniel100% (1)
- Mazda 323F BJ ZL-DE ECU Pinout GuideDocument6 pagesMazda 323F BJ ZL-DE ECU Pinout GuideDayro Jose Geney Ortiz50% (2)
- Engine Control Module Connector End ViewsDocument3 pagesEngine Control Module Connector End ViewsEQUIPO ING COMBATE BRCONNo ratings yet
- ECU Mazda B2600i 2.2 y 2.6LDocument1 pageECU Mazda B2600i 2.2 y 2.6LMarcelo Mendoza100% (2)
- 2005 Chevrolet Spark engine sensor connector views and functionsDocument14 pages2005 Chevrolet Spark engine sensor connector views and functionsData TécnicaNo ratings yet
- L1E Ecu Pinout PDFDocument2 pagesL1E Ecu Pinout PDFMarcelo Morales Luna100% (4)
- Engine Control ME 9.7 AMGDocument11 pagesEngine Control ME 9.7 AMGReza VaraminiNo ratings yet
- Daewoo2 PDFDocument12 pagesDaewoo2 PDFMotor Csillag100% (1)
- 1996 Hyundai Accent 1996 Hyundai AccentDocument7 pages1996 Hyundai Accent 1996 Hyundai AccentLuis Merkado100% (2)
- THE.RELLAT PROPIETARIO: DAVID COBO UBICANOS EN TODAS LAS REDES SOCIALES. TIKTOK, INSTAGRAM, GOOGLEDocument4 pagesTHE.RELLAT PROPIETARIO: DAVID COBO UBICANOS EN TODAS LAS REDES SOCIALES. TIKTOK, INSTAGRAM, GOOGLEDavid CoboNo ratings yet
- Blazer 98 PINOUTDocument7 pagesBlazer 98 PINOUTmatute100% (1)
- Pinolt Ford Focus 2001Document3 pagesPinolt Ford Focus 2001sanach04120% (1)
- Ecm (Engine Control Module) - 1.6D (Sirius D4)Document20 pagesEcm (Engine Control Module) - 1.6D (Sirius D4)Men PanhaNo ratings yet
- Platinum Sprint 500 Wiring Rev F PDFDocument1 pagePlatinum Sprint 500 Wiring Rev F PDFHAYNER86No ratings yet
- 2011 G 1.4 DOHC MFI Control System Schematic DiagramsDocument1 page2011 G 1.4 DOHC MFI Control System Schematic DiagramsbryanNo ratings yet
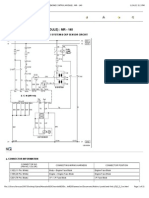
- Preview of "Electrical Wiring Diagram 2005 Nubira-Lacetti 2. ECM (ENGINE CONTROL MODULE) - MR - 140"Document21 pagesPreview of "Electrical Wiring Diagram 2005 Nubira-Lacetti 2. ECM (ENGINE CONTROL MODULE) - MR - 140"Lenin Carrillo100% (6)
- Electrical System DiagramsDocument97 pagesElectrical System DiagramsWalid SaidouneNo ratings yet
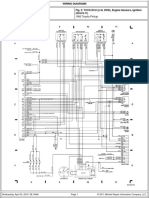
- Fig. 3 - Tccs Ecu (2.4l 2wd), enDocument1 pageFig. 3 - Tccs Ecu (2.4l 2wd), enDaniel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tacuma 2.0 2 Conectores de 32 PinesDocument41 pagesTacuma 2.0 2 Conectores de 32 PinesAnonymous 908AtSPNo ratings yet
- PCM Ford Laser 2.0LDocument9 pagesPCM Ford Laser 2.0LBenixon AvendañoNo ratings yet
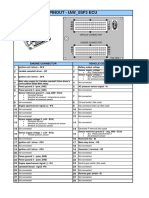
- PINOUT 5SF3 and 5sf8Document2 pagesPINOUT 5SF3 and 5sf8Pablo Nuñez80% (5)
- Engine Control Module Inspection GuideDocument1 pageEngine Control Module Inspection GuideCarlos Zelidon100% (1)
- Electronic Control System Terminal ListDocument3 pagesElectronic Control System Terminal ListDiego QuiridunbayNo ratings yet
- Aveo 2009 Ecotec ECM Connector PDFDocument4 pagesAveo 2009 Ecotec ECM Connector PDFalberto navasNo ratings yet
- Ecm (Engine Control Module) - 2.0D (Itms-6F)Document12 pagesEcm (Engine Control Module) - 2.0D (Itms-6F)Men PanhaNo ratings yet
- 1997 Hyundai Accent Wiring System DiagramsDocument37 pages1997 Hyundai Accent Wiring System Diagramsexte rianNo ratings yet
- Aveo 2006 ECM Connector PDFDocument3 pagesAveo 2006 ECM Connector PDFYesith Narvaez100% (3)
- Pin Out Ford Ranger 92-94Document6 pagesPin Out Ford Ranger 92-94Dannnyyo TorresNo ratings yet
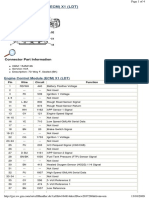
- Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC) : Connector Part Information Circuit No. FunctionDocument3 pagesInstrument Panel Cluster (IPC) : Connector Part Information Circuit No. Functiongerardo fazio0% (1)
- Diagramas AveoDocument21 pagesDiagramas AveoNestor Torra100% (1)
- Mazda Protege ES 1.8l FP-DE ECU Pin Out Diagram 1999-2000Document4 pagesMazda Protege ES 1.8l FP-DE ECU Pin Out Diagram 1999-2000GabrielNo ratings yet
- C - ECU Pinout - Toyota - Land Crusier 5vz-Fe (6 Cylinder - 1 Coil Control 2 Ignition Point) - 5vz-3rz-Right Manual For Lahore Landcruiser 5vz-1998Document4 pagesC - ECU Pinout - Toyota - Land Crusier 5vz-Fe (6 Cylinder - 1 Coil Control 2 Ignition Point) - 5vz-3rz-Right Manual For Lahore Landcruiser 5vz-1998Boomer Boomer100% (1)
- ECM Gran Vitara V6 H27Document6 pagesECM Gran Vitara V6 H27Alexa SaltosNo ratings yet
- Manual Inyeccion Chery S11 SiemensDocument20 pagesManual Inyeccion Chery S11 SiemensJose RengelNo ratings yet
- H-MOD1 J121 Igniter Wiring Revision 1Document1 pageH-MOD1 J121 Igniter Wiring Revision 1Claudio Rene Silva HernandezNo ratings yet
- Engine Control Module (ECM) : Pin No. Description Connected ToDocument14 pagesEngine Control Module (ECM) : Pin No. Description Connected ToNathan Gálvez CantinetNo ratings yet
- Demio (DW) : Mazda 1.5 16V B5Document2 pagesDemio (DW) : Mazda 1.5 16V B5Richard Wilson Mera JaimeNo ratings yet
- 2010 Chevrolet Captiva Sport X1Document3 pages2010 Chevrolet Captiva Sport X1PANHA MEN100% (1)
- Demio (DW) : Mazda 1.3 16V B3Document2 pagesDemio (DW) : Mazda 1.3 16V B3Richard Wilson Mera JaimeNo ratings yet
- AE6108 ECU System Wiring Diagram - 01V180119Document1 pageAE6108 ECU System Wiring Diagram - 01V180119Store-BlackberryJhonnymarNo ratings yet
- Captiva 2.4 CajaDocument3 pagesCaptiva 2.4 CajaHERNAN DARIO ZAPATA BUSTAMANTE100% (1)
- Vehicle: Electrical Diagrams Engine Control ModuleDocument7 pagesVehicle: Electrical Diagrams Engine Control ModuleAlexis Jose Campos100% (1)
- Yaris ECMDocument1 pageYaris ECMImran MuhammadNo ratings yet
- E6X WIRING DIAGRAM GUIDEDocument1 pageE6X WIRING DIAGRAM GUIDEAbdulrahman Marina50% (2)
- The Specifications of M59556FP: Details PDFDocument1 pageThe Specifications of M59556FP: Details PDFjulio montenegroNo ratings yet
- Omega B X20XEVDocument3 pagesOmega B X20XEVZloy Tatarin100% (1)
- Implement ECM: Electronic Control (Brake System) (M0111643) 2020/12/09Document23 pagesImplement ECM: Electronic Control (Brake System) (M0111643) 2020/12/09Rio AkbrNo ratings yet
- Pinout VECUDocument3 pagesPinout VECUcentraltechgvNo ratings yet
- Engine Kontrol 1Document35 pagesEngine Kontrol 1imat ruhimatNo ratings yet
- Still r70 PDFDocument86 pagesStill r70 PDFMyhaiKatalina100% (4)
- Compass - Service InfoDocument1 pageCompass - Service InfoManolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Transmission With Converter - Remove&InstallDocument3 pagesTransmission With Converter - Remove&InstallManolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS 2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS: Powertrain Control Module (PCM)Document12 pages2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS 2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS: Powertrain Control Module (PCM)Manolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Compass - Service InfoDocument1 pageCompass - Service InfoManolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CAN. When Terminal 15 Is OFF, This Link Is Carried by The CAN (N10 - N10/1)Document1 pageCAN. When Terminal 15 Is OFF, This Link Is Carried by The CAN (N10 - N10/1)Manolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Trip Computer - TaskDocument1 pageTrip Computer - TaskManolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Manual Detroit Serie 60Document1,669 pagesManual Detroit Serie 60Julian Mariño Pinilla95% (60)
- Flash Availability-J2534 ApplicationDocument726 pagesFlash Availability-J2534 ApplicationAdan Pérez EchevarríaNo ratings yet
- TRANSMISSION 722.6## ## As of 2871384 As of 17.4.01, 722.7## ## As of 0153700 As of 9.7.01Document1 pageTRANSMISSION 722.6## ## As of 2871384 As of 17.4.01, 722.7## ## As of 0153700 As of 9.7.01Manolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Park Lock - Remove& Install Wire CableDocument1 pagePark Lock - Remove& Install Wire CableManolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TF Bosch VP44 Fuel Pump (Ver1)Document43 pagesTF Bosch VP44 Fuel Pump (Ver1)Carlos A Romero92% (37)
- Bosch ConversionsDocument4 pagesBosch ConversionsontheapexNo ratings yet
- Bosch m7.9.7 PDFDocument25 pagesBosch m7.9.7 PDFRuben Dario Casique83% (24)
- BMW Pinout N62 Bosch M9.2Document3 pagesBMW Pinout N62 Bosch M9.2Manuel SuarezNo ratings yet
- Bosch m7.9.7 PDFDocument25 pagesBosch m7.9.7 PDFRuben Dario Casique83% (24)
- Sensores MAP, Características y Mediciones. - Josemaco's BlogDocument2 pagesSensores MAP, Características y Mediciones. - Josemaco's BlogManuel SuarezNo ratings yet
- Códigos de Falla MID 128Document48 pagesCódigos de Falla MID 128Omar Cantón LealNo ratings yet
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument135 pagesDownloaded From Manuals Search EngineJose Andres Luis JimenezNo ratings yet
- EY - NASSCOM - M&A Trends and Outlook - Technology Services VF - 0Document35 pagesEY - NASSCOM - M&A Trends and Outlook - Technology Services VF - 0Tejas JosephNo ratings yet
- Police Report Hearing RightsDocument7 pagesPolice Report Hearing RightsYatn BangadNo ratings yet
- Balcony AnalysysDocument4 pagesBalcony AnalysysKory EstesNo ratings yet
- HACCP Plan With Flow Chart-1Document23 pagesHACCP Plan With Flow Chart-1Anonymous aZA07k8TXfNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquationsDocument22 pagesChemical EquationsSiti Norasikin MuhyaddinNo ratings yet
- Trace Log 20131229152625Document3 pagesTrace Log 20131229152625Razvan PaleaNo ratings yet
- Chiang Kai Shek School v. CA (1989)Document2 pagesChiang Kai Shek School v. CA (1989)Amber AncaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 LEA 4 Law Enforcement Operations and Planning With Crime MappingDocument94 pagesPart 1 LEA 4 Law Enforcement Operations and Planning With Crime Mappingyomaeko CinkoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Communication by ThiruvalluvarDocument7 pagesImportance of Communication by ThiruvalluvarRamavallabhanNo ratings yet
- Equipment Sheet: Cable Laying VesselDocument2 pagesEquipment Sheet: Cable Laying Vesselsitu brestNo ratings yet
- Nurses' Documentation of Falls Prevention in A Patient Centred Care Plan in A Medical WardDocument6 pagesNurses' Documentation of Falls Prevention in A Patient Centred Care Plan in A Medical WardJAY LORRAINE PALACATNo ratings yet
- Senate Bill 365Document5 pagesSenate Bill 365samtlevinNo ratings yet
- SRX835 Spec Sheet - 11 - 11 - 19Document4 pagesSRX835 Spec Sheet - 11 - 11 - 19Eric PageNo ratings yet
- College of Industrial Technology Bachelor of Technology and Livelihood Education (TLE) CMO. No. 78, S. 2017Document5 pagesCollege of Industrial Technology Bachelor of Technology and Livelihood Education (TLE) CMO. No. 78, S. 2017Industrial TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Handout 4: Marketing Opportunity and Consumer AnalysisDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Handout 4: Marketing Opportunity and Consumer AnalysisAsset Dy100% (1)
- ERecon Software Development at Hospital Corporation of America-1553395398 PDFDocument11 pagesERecon Software Development at Hospital Corporation of America-1553395398 PDFKaren CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Began With Man's Curiosity On The Peculiar Ability of Amber and Lodestone To Attract Other Material.Document2 pagesElectricity Began With Man's Curiosity On The Peculiar Ability of Amber and Lodestone To Attract Other Material.Axle Rose CastroNo ratings yet
- Ok 1889 - PDF PDFDocument40 pagesOk 1889 - PDF PDFIngeniería Industrias Alimentarias ItsmNo ratings yet
- PRACTICA (1) (1) - Páginas-2-4Document3 pagesPRACTICA (1) (1) - Páginas-2-4EDDY POLICARPIO BRAVO HUAMANINo ratings yet
- Sap AbapDocument7 pagesSap Abapidrees aliNo ratings yet
- FEA Finite Element Analysis Tutorial ProblemsDocument16 pagesFEA Finite Element Analysis Tutorial ProblemsVinceTanNo ratings yet
- Air ConditionDocument4 pagesAir ConditionTaller Energy EnergyNo ratings yet
- Municipal Profile of Umingan, PangasinanDocument51 pagesMunicipal Profile of Umingan, PangasinanGina Lee Mingrajal Santos100% (1)
- Acute AppendicitisDocument51 pagesAcute AppendicitisPauloCostaNo ratings yet
- C. Corpo DigestDocument9 pagesC. Corpo DigestRaymarc Elizer AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Table 141: India'S Overall Balance of Payments - RupeesDocument2 pagesTable 141: India'S Overall Balance of Payments - Rupeesmahbobullah rahmaniNo ratings yet
- Atlantic Revolutions: Ogé Insurrection Inspired Haitian IndependenceDocument18 pagesAtlantic Revolutions: Ogé Insurrection Inspired Haitian IndependenceNiara ChaneyNo ratings yet
- Wa0031 PDFDocument1 pageWa0031 PDFAnaNo ratings yet
- Upliftment of Recto AveDocument6 pagesUpliftment of Recto AveFrance CortezanoNo ratings yet
- Workplace 2017Document8 pagesWorkplace 2017Vesign MediaNo ratings yet