Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic Outline: Nasal Cannula Tent
Uploaded by
Mariah Jane TaladuaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic Outline: Nasal Cannula Tent
Uploaded by
Mariah Jane TaladuaCopyright:
Available Formats
Oxygen Inhalation
Week 2 / January 24, 2022
Topic Outline
1 Definition
2 Purposes
3 Principles
4 Equipment
5 Procedure and rationale
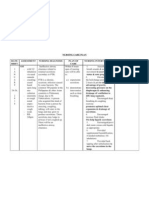
Definition
- Involves breathing O2 in pressurized chamber / tube Prescribed face mask of Padding for elastic band
- Allows lungs to gather up to 3x more O2 than by appropriate size
breathing O2 at normal air pressure
- Extra O2 moves through blood and to organs and body
tissues
- Can be administered by cannula, face mask, face tent
Purposes
Nasal cannula
- Deliver relatively low conc. Of O2 when only minimal
O2 support is required
- Allow uninterrupted delivery of O2 while client ingest Tent
food / fluids Oxygen supply w/ flow meter Humidifier w/ distilled water
Face mask & adapter or tap water
- Provide moderate O2 support and higher conc. Of O2
and/or humidity than provided by cannula
Tent
- Provide high humidity
- Provide O2 when mask is poorly tolerated
- Provide high flow of O2 when attached to venturi sys
Principles
- Secure and maintain airway patency
- Enhance circulation
- Avoid reverse respiratory depressants
Equipment Face tent of appropriate size
Nasal cannula
Oxygen supply w/ flow meter Humidifier w/ distilled water /
and adapter tap water acc to agency
protocol
Procedure and rationale
1) Bring necessary equipment to bedside stand / overbed table
a. Save time and energy
2) Explain procedure to pt and review safety precautions
necessary when oxygen is in use. Place “no smoking”
signs in appropriate areas
a. Gain pt’s cooperation and avoid combustion
b. O2 support combustion
Nasal cannula and tubing Tape 3) Perform hand hygiene and put on PPE if indicated
a. Deter spread of microorganisms
4) Identify pt
a. Be sure to have right pt
5) Close curtains around bed and close door to room if
possible
a. Maintain privacy
Nasal cannula
6) Connect nasal cannula to O2 setup w/ humidification if
Padding for elastic band one is use. Adjust flow rate as ordered by physician.
Check O2 is flowing out of prongs
a. O2 forced through water reservoir is
humidified before it is delivered to pt,
preventing dehydration of mucous membranes
b. Low-flow O2 does not require humidification
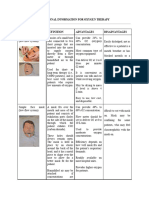
7) Place prongs in pt’s nostrils. Place tubing over and
behind each air w/ adjuster comfortably under chin.
Face mask Tubing may be placed around pt’s head w/ adjuster at
Oxygen w/ flow meter and Humidifier w/ distilled water back / base of head. Place gauze at ear beneath tubing as
adapter or tap water acc to agency necessary
protocol a. Correct placement of prongs and fastener
facilitates O2 administration and pt comfort
8) Place gauze pads at ear beneath tubing and adjust fit of
cannula as necessary. Tubing should be snug but not
tight against skin
1
a. Pads reduce irritation and pressure and protect a. Documentation ensures continuity of care and
skin ongoing assessment record
9) Encourage pt to breathe through nose, w/ mouth close
a. Nose breathing provides optimal delivery of
O2 to pt
10) Remove and clean cannula and assess nares at least
every 8 hrs or acc to agency recommendations. Check
nares for evidence of irritation / bleeding
a. Continued presence of cannula causes irritation
and dryness of mucous membranes
b. Water-soluble lubricants counteract drying
effects of O2
Face mask
11) Attach face mask to O2 source (w/ humidification for
specific mask). Start flow of O2 at specified rate. For
mask w/ reservoir, be sure to allow O2 to fill bag before
proceeding to next step
a. O2 forced through water reservoir is
humidified before it is delivered to pt, thus
preventing dehydration of mucous membranes
b. Reservoir bag must be inflated w/ O2 bc bag is
source of O2 supply for pt
12) Position face mask over pt’s nose and mouth. Adjust
elastic strap so that mask fits snugly but comfortably on
face. Adjust flow rate to prescribed rate
a. Loose / poorly fitting mask result in O2 loss
and decreased therapeutic value
b. Masks cause feeling of suffocation and pt
needs frequent attention & reassurance
13) Use gauze pad under elastic strap at pressure points to
reduce irritation to ears and scalp
a. Pads reduce irritation and pressure and protect
skin
14) Remove mask and dry skin every 2-3 hrs if O2 is
running continuously. Do not use powder around mask
a. Tight-fitting mask and moisture from
condensation can irritate skin on face
b. There is danger of inhaling powder if it is
placed on mask
Tent
15) Place tent over crib / bed. Connect humidifier to O2
source in wall and connect tent tubing to humidifier.
Adjust flow rate as ordered by physician. Check that O2
is flowing into tent
a. O2 forced through water reservoir humidified
before it is delivered to pt thus preventing
dehydration of mucous membranes
16) Turn analyzer on. Place O2 analyzer probe in tent, out of
pt’s reach
a. Analyzer give accurate reading of conc of O2
in crib / bed
17) Adjust O2 as necessary, based on sensor readings. Once
O2 levels reach prescribed amount, place pt in tent
a. Pt receive O2 once placed in tent
18) Roll small blanket like jelly roll and tuck tent edges
under blanked rolls as necessary
a. Blanket helps keep edges of tent flap from
coming up and letting O2 out
19) Encourage pt and family members to keep tent flap
closed
a. Every time tent flap opened, O2 is released
20) Frequently check bedding and pt’s pajamas for moisture
a. Large amount of humidification delivered in
O2 tent quickly makes cloth moist which
would be uncomfortable for pt
For any method
21) Reassess pt’s respiratory status including respiratory
rate, effort, lung sounds. Note any signs of respiratory
distress such as tachypnea, nasal flaring, use of accessory
muscles, dyspnea
a. Pt’s respiratory rate and pattern, color, chest
movements, so forth indicate effectiveness of
O2 therapy
22) Remove PPE if used. Perform hand hygiene
a. Deter spread of microorganisms
23) Document amount of O2 applied, respiratory rate, O2
saturation and lung sounds
2
You might also like
- Wim Hof Method PDFDocument4 pagesWim Hof Method PDFAnonymous HsAAhXFnGp100% (12)
- Preparation For ChildbirthDocument3 pagesPreparation For ChildbirthMariah Jane Taladua100% (1)
- Chapter 30 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 30 NotesMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia EquipmentDocument16 pagesAnesthesia EquipmentnggulanberNo ratings yet
- Administering OxygenDocument26 pagesAdministering Oxygenjhuzt4_facebook_343onlyNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 Lec RespiDocument26 pagesNCM 102 Lec RespiLindsay NateNo ratings yet
- Dust Control and Air Cleaning: International Series of Monographs in Heating, Ventilation and RefrigerationFrom EverandDust Control and Air Cleaning: International Series of Monographs in Heating, Ventilation and RefrigerationNo ratings yet
- Administering Oxygen by Nasal Catheter, CannulaDocument28 pagesAdministering Oxygen by Nasal Catheter, CannulaAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- TrematodesDocument30 pagesTrematodesJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Administering O2 TherapyDocument22 pagesAdministering O2 TherapyWilbert Andrew FlojemonNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument46 pagesOxygen Therapyoxidalaj100% (4)
- Demo TracheostomyDocument12 pagesDemo TracheostomyTopeshwar TpkNo ratings yet
- PFT - 253 LEAF GREEN BaruDocument4 pagesPFT - 253 LEAF GREEN Barueva andriana putriNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation ChecklistDocument22 pagesOxygenation ChecklistKen Morales Alcantara100% (1)
- NCM 118 Skills Lab Week 11Document5 pagesNCM 118 Skills Lab Week 11kNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On NebulizationDocument8 pagesLesson Plan On Nebulizationsuchitra80% (5)
- FUNDA Lab 11 Oxygen Therapy Suctioning Procedures23Document38 pagesFUNDA Lab 11 Oxygen Therapy Suctioning Procedures23loijhonmuchillasNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Administration ProcedureDocument4 pagesOxygen Administration ProcedureJay Harold Cordero PanlilioNo ratings yet
- OXYGEN INHALATION (Demo)Document16 pagesOXYGEN INHALATION (Demo)Rinchin ChhotenNo ratings yet
- Funda MidtermsDocument13 pagesFunda MidtermsMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Administration ChecklistDocument3 pagesOxygen Administration ChecklistNoronisa D. CabugatanNo ratings yet
- Supplying Oxygen InhalationDocument4 pagesSupplying Oxygen Inhalationjanna mae patriarcaNo ratings yet
- N118 0XYGEN Checklist FinalDocument7 pagesN118 0XYGEN Checklist FinalAmandaNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation - Administering Oxygen by Nasal Cannula and MaskDocument3 pagesOxygenation - Administering Oxygen by Nasal Cannula and MaskJoarlin BianesNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument3 pagesOxygen Therapymarie100% (3)
- NCM 109 Rle Procedure - Oxygen InhalationDocument8 pagesNCM 109 Rle Procedure - Oxygen InhalationRAZELLE JOY CATIAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Equipment: Administering Oxygen by Way of Endotracheal and Tracheostomy Tubes With A T-Piece (Briggs) AdapterDocument2 pagesEquipment: Administering Oxygen by Way of Endotracheal and Tracheostomy Tubes With A T-Piece (Briggs) AdapterIan TuNo ratings yet
- E Learning NotesDocument260 pagesE Learning NotesGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanJimmy Andrew YoungNo ratings yet
- TRACHEOSTOMY and Wound CareDocument9 pagesTRACHEOSTOMY and Wound CareSUREEN MAY ANG REGULARNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube (INSERTION, FEEDING, & WITHDRAW)Document8 pagesNasogastric Tube (INSERTION, FEEDING, & WITHDRAW)Maricar VillelaNo ratings yet
- Skill 47 (1) ..Tracheostomy Tube Change PDFDocument2 pagesSkill 47 (1) ..Tracheostomy Tube Change PDFRadhika SethuNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal IntubationDocument11 pagesEndotracheal Intubationanon_784834955100% (1)
- Respiratory Care ModalitiesDocument12 pagesRespiratory Care ModalitiesMaria Isabel TriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Independentyanny03No ratings yet
- Midterms Retdem ChecklistDocument7 pagesMidterms Retdem ChecklistLee ShaneNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Administration ProcedureDocument5 pagesOxygen Administration Procedurej.abelis.540903No ratings yet
- Oxygen Administration: Steps RationaleDocument2 pagesOxygen Administration: Steps Rationale2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- Performing Nasotracheal SuctionDocument1 pagePerforming Nasotracheal SuctionSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALINo ratings yet
- Suctioning ChecklistDocument10 pagesSuctioning ChecklistSweet BenitezNo ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument12 pagesOxygenationCherry Lou Guanzing100% (1)
- Oxygenation Skills 112Document55 pagesOxygenation Skills 112guerrasashamearlNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniNo ratings yet
- Administering Oxygen Via Nasal Cannula (RLE)Document14 pagesAdministering Oxygen Via Nasal Cannula (RLE)Alliza LipaNo ratings yet
- MSN LEC GROUP 2 Oxygenation Ventilation Additional InfosDocument16 pagesMSN LEC GROUP 2 Oxygenation Ventilation Additional InfosJohn MalkovicNo ratings yet
- 7 - Oxygen &exchangeDocument16 pages7 - Oxygen &exchange.No ratings yet
- Oxygen InhalationDocument26 pagesOxygen InhalationdaisyNo ratings yet
- Airway Management Topic 2Document8 pagesAirway Management Topic 2Lenard SakiliNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Administration and Monitoring ProcedureDocument6 pagesOxygen Administration and Monitoring ProcedureamitNo ratings yet
- O2 Administration ReviewerDocument5 pagesO2 Administration ReviewerDustin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Asilo, Rosette Justine D. BSN3Y2-1 NCMB 312 LECDocument3 pagesAsilo, Rosette Justine D. BSN3Y2-1 NCMB 312 LECRosette AsiloNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal Tube IntubationDocument5 pagesEndotracheal Tube IntubationKim Kristine D. GuillenNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPRuth MontebonNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Midterm Lab 2022Document17 pagesNCM 112 Midterm Lab 2022JHENG MACATUGGALNo ratings yet
- Worksheet #5 Tracheostomy CareDocument3 pagesWorksheet #5 Tracheostomy CareAnonymous zVYmOxIX9SNo ratings yet
- 6.underwater Seal Chest DrainageDocument22 pages6.underwater Seal Chest DrainageEvieta CallysthaNo ratings yet
- Oro-Nasopharyngeal SuctioningDocument3 pagesOro-Nasopharyngeal SuctioningMichelle SatairapanNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Skills Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesNCM 112 Skills Midterm Reviewerljealou2002No ratings yet
- NCM 109 SkillsDocument7 pagesNCM 109 SkillsMae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Compiled Checklists For Level 3 Nursing ProceduresDocument46 pagesCompiled Checklists For Level 3 Nursing ProceduresMaria Carmela RoblesNo ratings yet
- Oxygen AdministrationDocument2 pagesOxygen AdministrationSana OlNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument3 pagesCatheterizationMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Administering Oxygen by Nasal Cannula ContinuedDocument2 pagesAdministering Oxygen by Nasal Cannula ContinuedIan TuNo ratings yet
- SECTION 2 CHAPTER 4 Tracheal IntubationDocument46 pagesSECTION 2 CHAPTER 4 Tracheal IntubationRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document5 pagesChapter 20Mariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36Document7 pagesChapter 36Mariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 37Document10 pagesChapter 37Mariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline: Week 2 / January 24, 2022Document2 pagesTopic Outline: Week 2 / January 24, 2022Mariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Rectal and Vaginal Suppository InsertionDocument2 pagesRectal and Vaginal Suppository InsertionMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument3 pagesCatheterizationMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9.1-Gene Expression Protein SynthesisDocument55 pagesLecture 9.1-Gene Expression Protein SynthesisMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument2 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Imci: Assess and Classify Fever: MeaslesDocument4 pagesImci: Assess and Classify Fever: MeaslesMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 8e: Bettelheim, Brown Campbell, and FarrellDocument43 pagesGeneral, Organic, and Biochemistry, 8e: Bettelheim, Brown Campbell, and FarrellMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting HealthDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting HealthMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Public Health NursingDocument6 pagesOverview of Public Health NursingMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan: 2 Major Types of Nursing AssessmentDocument3 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan: 2 Major Types of Nursing AssessmentMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Community AssessmentDocument3 pagesCommunity AssessmentMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 32 NotesMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31: Adrenergic Antagonists: Drug ListDocument7 pagesChapter 31: Adrenergic Antagonists: Drug ListMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Administering Oxygen Via Nasal Cannula (RLE)Document14 pagesAdministering Oxygen Via Nasal Cannula (RLE)Alliza LipaNo ratings yet
- Royal Brisbane & Women's Hospital Medical Emergency / Arrest Observation and Audit FormDocument2 pagesRoyal Brisbane & Women's Hospital Medical Emergency / Arrest Observation and Audit FormYoussef MokdadNo ratings yet
- MSDS PVC001Document6 pagesMSDS PVC001medo.k016No ratings yet
- MSDS CHEMICAL Floor Stripper FreedomDocument3 pagesMSDS CHEMICAL Floor Stripper FreedomIndah Dwi SofianiNo ratings yet
- Approach To DyspneaDocument9 pagesApproach To DyspneaMuhammad LukmanNo ratings yet
- ADDS Chart With Blood Pressure Table 2012Document2 pagesADDS Chart With Blood Pressure Table 2012thayley157No ratings yet
- واقع التعليم عن بعدDocument35 pagesواقع التعليم عن بعدعبدالسلام ارفيسNo ratings yet
- 05.listado Preliminar Vuelo 13 Al 19-09-2022Document13 pages05.listado Preliminar Vuelo 13 Al 19-09-2022Mariem Rosales CarmenateNo ratings yet
- Lymph Angio Lei o Myoma to SisDocument9 pagesLymph Angio Lei o Myoma to SisEULA MARIE JOVERNo ratings yet
- MSDS 88НDocument17 pagesMSDS 88НhgfhfNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DiseaseDocument27 pagesRespiratory Diseaseعبدالسلام الأسمرNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory Changes During ExerciseDocument4 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Changes During ExerciseBrian ArigaNo ratings yet
- CAB ManagementDocument21 pagesCAB ManagementTery'sNo ratings yet
- Post Test Patho 1Document3 pagesPost Test Patho 1Kristine MangasepNo ratings yet
- Prevention Practice For Cardiopulmonary ConditionsssDocument38 pagesPrevention Practice For Cardiopulmonary ConditionsssArham ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Intergard 821 Part B MSDSDocument14 pagesIntergard 821 Part B MSDSdzul effendiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical Ventilation (SIPHW)Document68 pagesBasics of Mechanical Ventilation (SIPHW)Sudip beraNo ratings yet
- Rds NRP 2021Document33 pagesRds NRP 2021Aiwi Goddard MurilloNo ratings yet
- Admin,+7276 37909 4 PBDocument11 pagesAdmin,+7276 37909 4 PBnadyah fadlyNo ratings yet
- Contingency Plan For Covid 2020Document6 pagesContingency Plan For Covid 2020Nick Tejada100% (3)
- PSmarkup - Revisi 1 TeshalonicaDocument28 pagesPSmarkup - Revisi 1 TeshalonicaBrian TonioNo ratings yet
- Abdellah Case StudyDocument1 pageAbdellah Case StudyRey MadelosoNo ratings yet
- Asthma Action Plan For Children PDF DownloadDocument2 pagesAsthma Action Plan For Children PDF DownloadAlejandro MalagáNo ratings yet
- BA Set 10245 - 2Document14 pagesBA Set 10245 - 2Břåhimi Æmïr ĶhaledNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 Nursing Care PlansDocument15 pagesNCM 118 Nursing Care PlansElle LibalibNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia, Chemical Restraint and Pain Management in Snakes (Serpentes) - A Review Seven Mustafa, Nadya ZlatevaDocument8 pagesAnesthesia, Chemical Restraint and Pain Management in Snakes (Serpentes) - A Review Seven Mustafa, Nadya ZlatevaFirdaus BillyNo ratings yet
- BLSDocument8 pagesBLScataleya mesaNo ratings yet