Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PE & Health
Uploaded by
shoti lahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PE & Health
Uploaded by
shoti lahCopyright:
Available Formats
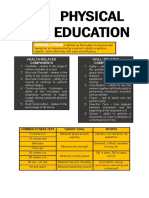
Injuries Q – Angle of the Knee
- are damaged tissues or organs which occur - the angle formed by a line drawn from the
when it encounters trauma or physical force Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) to the
that is greater than what it can resist or center of the patella and to the tibial tubercle
absorb
Acute Types of Injury
Factors Influencing the Ability of Tissues or Organs to
Effectively Resist or Absorb force 1. Sprain
- caused by twisting or pulling force
1. Inherent Abnormality - overstretched ligaments
2. Age - can be classified as mild, moderate, and
3. Technique severe depending on the loss of function and
4. Fitness Level the number of torn fibers
5. Equipment - a commonly sprained ligament is the
6. Environmental Aspects Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) which is a
connective tissue that helps stabilize the knee
Tissues and Organs that react to Impact and Direction every time the muscles contract
of the Force: 2. Strain
1. Tensile Forces - caused by pulling force during rapid
- are those that act away from the center of acceleration and excessive stretching that
the structure, causing a pull or stretch causes tears in the muscle tendon unit
2. Compressive Forces 3. Fracture
- impact the center causing it to bend or fold - caused by falling or breaking a fall
3. Shear Forces - breaks in the continuity of the bone
- are opposing forces toward the different - usually occurs as a result of high impact
ends of the structure causing it to twist forces that cause the bone to bend or twist
4. Dislocation
Classification of Sports Injuries - caused by falling or breaking a fall
- are bones that are pushed out from their
1. Acute Injuries
joint capsule
- have signs and symptoms that manifest
5. Contusions or Concussion or Bruise
immediately after force application
- caused when blood vessels are damaged or
2. Chronic or Overuse Injuries
broken as the result of a blow to the skin
- have signs and symptoms that occur after a
long period of exposure to the force Overuse or Chronic Types of Injury
Structure Function Acute Injury 1. Stress Fracture
ligaments stabilized joints sprain - caused by repetitive high impact stress and
tendons attach muscle to bones sprain application of force
muscles create movements strain
- tiny cracks in a bone
bones anchor for muscles fracture
joints fulcrum for movement dislocation 2. Tendinopathy or Tenditis
- caused by repetitive movement using poor
technique
Fibers - most common overuse injury in sports
Category Loss of Function
Damaged usually due to muscle imbalance between
mild minimal pain when
muscle pairs
(first degree) tear moved
3. Osteoarthritis
moderate partial pain at rest when
(second degree) tear moved - caused by repetitive high impact stress
severe complete complete loss of - is the wear and tear of a joint that results to
(third degree) tear function its deterioration
4. Bursitis - this injury is common to contact and combat
- caused by repetitive movement using poor sports like boxing and is caused by a strong
technique blow to the head that temporarily impairs
- when Bursa (a small balloon like sac found brain function
around joints and other moving parts of the - aside from being unconscious, the injured
body) is inflamed and filled with fluid athlete might show other signs of amnesia,
loss of balance, poor motor coordination, and
Strategies to Minimize Sports Injuries slurred speech
1. adopt a Comprehensive Training Program - the signs may manifest right after the trauma
2. use a protective equipment and practice or it could be delayed for a few hours
correct technique - can be life-threatening if blood vessels in the
3. incorporate recovery strategies in the training brain are ruptured
program Types of Concussion
4. follow rules and decorum during competition
Category Description Characteristics
Strategies to Minimize Training Injuries no loss of consciousness,
grade I mild condition normalizes in
1. proper attire less than 15 minutes
2. proper technique no loss of consciousness,
3. gym etiquette grade II moderate condition normalized
4. proper environmental conditions beyond 15 minutes
5. adequate recovery grade III severe loss of consciousness
How to Choose the Right Kind of Shoes?
1. choose shoes specific to the sports or activity
2. determine appropriate shoe size
3. evaluate foot movement pattern
Brannock Device
- classifies the size of the foot by measuring the
length and width of the foot
Diagnostic Process
- done by the doctor only in the doctor’s clinic
- accounts all the information needed to see a
holistic picture of the cause and severity of
the injury such as patient’s history
comprehensive physical exam
Injury Evaluation Process
- happens in the field
- to rule out the presence of a severe injury or a
2 signs of life threatening conditions:
life-threatening condition
✓Unconsciousness and ✓Not breathing
Primary Survey
- a quick evaluation if there are life-threatening
injuries present
Concussion
You might also like
- Muscle InjuryDocument33 pagesMuscle InjuryYuNa YoshinoyaNo ratings yet
- Procreate User GuideDocument75 pagesProcreate User GuideOmar Páez0% (1)
- Document GDocument30 pagesDocument GWLLM100% (2)
- 1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFDocument44 pages1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFMark Anthony Nazareth100% (2)
- Amc Offer 500 Kva & 380 Kva DGDocument8 pagesAmc Offer 500 Kva & 380 Kva DGabhibawa100% (3)
- Orthopedic NursingDocument23 pagesOrthopedic Nursinggabrielle magdaraog100% (1)
- Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument19 pagesSafety Practices in Sports and ExerciseRiza Indelible Sibullas80% (5)
- NU632 Unit 4 Discussion CaseDocument2 pagesNU632 Unit 4 Discussion CaseMaria Ines OrtizNo ratings yet
- Muscle Strain Injury - Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument8 pagesMuscle Strain Injury - Diagnosis and TreatmentAiri FirdausiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseMr. CRAFTNo ratings yet
- Okuma GENOS M560R-V TECHNICAL SHEET (4th Edition)Document79 pagesOkuma GENOS M560R-V TECHNICAL SHEET (4th Edition)Ferenc Ungvári100% (1)
- The Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit PlantDocument7 pagesThe Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit Plantttk_maniNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument21 pagesSafety Practices in Sports and ExerciseJinaan Mahmud0% (1)
- How To Use A MicroscopeDocument12 pagesHow To Use A MicroscopeTommy LeungNo ratings yet
- Methodology and Specifications Guide: Crude OilDocument34 pagesMethodology and Specifications Guide: Crude Oil066709No ratings yet
- Lisa-Operation Manual: Installation and Operation Instructions (Part B)Document41 pagesLisa-Operation Manual: Installation and Operation Instructions (Part B)majdNo ratings yet
- 2001: A Space Odyssey - Film AnalysisDocument4 pages2001: A Space Odyssey - Film AnalysisSummerNo ratings yet
- Technology and The Transformation of Performance - Chris Salter PDFDocument49 pagesTechnology and The Transformation of Performance - Chris Salter PDFFelipe Merker Castellani100% (1)
- Write A Short Note On Carbon FiberDocument4 pagesWrite A Short Note On Carbon FiberMOJAHID HASAN Fall 19No ratings yet
- PEH REVIEWER (Final Exam)Document3 pagesPEH REVIEWER (Final Exam)Ally OcbianNo ratings yet
- Ligaments Stabilize Joints Sprain Tendons Attaches Muscles To Bones StrainDocument5 pagesLigaments Stabilize Joints Sprain Tendons Attaches Muscles To Bones StrainKyla Patricia ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Pe Ni Ms NicaDocument2 pagesPe Ni Ms NicaLouise GermaineNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 5 SPORTS INJURIESDocument6 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 5 SPORTS INJURIESRowan Yñigo TamayoNo ratings yet
- PE and HealthDocument3 pagesPE and HealthRia Ellaine Cornelio LachicaNo ratings yet
- H o P e - 2-Mid-ReviewerDocument2 pagesH o P e - 2-Mid-ReviewerClaire RamosNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument3 pagesPhysical EducationEuan Marlee F. SampeloNo ratings yet
- Pe MT ReviewerDocument2 pagesPe MT ReviewerPhiloNo ratings yet
- PEH2 Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesPEH2 Finals ReviewerPedro HampaslupaNo ratings yet
- Green and Brown UI Frame Style Types of Bullying Poster - 20240414 - 141003 - 0000Document4 pagesGreen and Brown UI Frame Style Types of Bullying Poster - 20240414 - 141003 - 0000alcuirezjane2No ratings yet
- 7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument25 pages7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseFirst GhostNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders (For Students)Document5 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders (For Students)Chaina MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Handouts Topic 1 CS15 2 4TH QuarterDocument3 pagesHandouts Topic 1 CS15 2 4TH Quarternicole balgumaNo ratings yet
- Hope MidtermsDocument2 pagesHope MidtermsLian Rose San CarlosNo ratings yet
- Pe Reviewer: Acute InjuryDocument3 pagesPe Reviewer: Acute InjuryAizell NobleNo ratings yet
- What's More: Let's Try . Sport Injury. Injury Type Causes of Injury Sprain WDocument7 pagesWhat's More: Let's Try . Sport Injury. Injury Type Causes of Injury Sprain Wjaypee sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementDocument4 pagesSafety Practices and Sports Injury Managementchristine mae picocNo ratings yet
- Sports - Injury - Classification 3Document36 pagesSports - Injury - Classification 3zaydawwadNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-in-P EDocument24 pagesReviewer-in-P E1900248No ratings yet
- Health 11 3rdqDocument7 pagesHealth 11 3rdqflbshyneNo ratings yet
- Causes of Sports InjuriesDocument15 pagesCauses of Sports InjuriesMarmie Babaran GallibuNo ratings yet
- Pe ReviewerDocument10 pagesPe ReviewerLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- PEH Causes of Sports InjuriesDocument7 pagesPEH Causes of Sports InjuriesFaye TiuNo ratings yet
- Dance Related InjuriesDocument24 pagesDance Related InjuriessigmanityscorpioNo ratings yet
- Bone FractureDocument16 pagesBone FractureMurad KurdiNo ratings yet
- SHS Lesson 10 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument10 pagesSHS Lesson 10 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseKylie CadenasNo ratings yet
- VoyagerDocument13 pagesVoyagerrhyshryroch royerasNo ratings yet
- 316 Lecture Finals NotesDocument23 pages316 Lecture Finals NotesBaylon AngelicaNo ratings yet
- SLM PE 4th QuarterDocument12 pagesSLM PE 4th QuarterRichmond LeeNo ratings yet
- 12 Physical Education Imp ch9 5 PDFDocument7 pages12 Physical Education Imp ch9 5 PDFkaranveerNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - THXDocument21 pagesMODULE 2 - THXZgama AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Injury and Immobilization On MuscleDocument19 pagesEffect of Injury and Immobilization On Musclesonali tushamerNo ratings yet
- Spe2: Introduction To Outdoor RecreationDocument10 pagesSpe2: Introduction To Outdoor RecreationMs. ArceñoNo ratings yet
- BEDMAKINGDocument4 pagesBEDMAKINGAndrea PeriguaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders in ChildrenDocument8 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders in ChildrenshainakyllebarbonNo ratings yet
- Causes Signs & Symptoms Diagnostic Test Nutrition Therapy Pharmacotherapy Surgical Management Nursing ManagementDocument2 pagesCauses Signs & Symptoms Diagnostic Test Nutrition Therapy Pharmacotherapy Surgical Management Nursing ManagementSheila SaclotNo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument3 pagesSports InjuriesMario MurilloNo ratings yet
- StretchingDocument10 pagesStretchingCyenel DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Tracy M. de Guzman: Strategic Intervention Material in - P. E. and HEALTHDocument7 pagesMrs. Tracy M. de Guzman: Strategic Intervention Material in - P. E. and HEALTHTrace de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ankle Sprain Medical BackgroundDocument13 pagesAnkle Sprain Medical BackgroundWilyam SerilNo ratings yet
- Peh Module 5Document2 pagesPeh Module 5Hannah VillocenoNo ratings yet
- Elm Grade 11 (Peh)Document28 pagesElm Grade 11 (Peh)Kimberly GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pe Mod 5Document6 pagesPe Mod 5ALLIA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Sprains and Strains: The Medical Disability Advisor: Workplace Guidelines For Disability DurationDocument5 pagesSprains and Strains: The Medical Disability Advisor: Workplace Guidelines For Disability DurationKevin AnindytaNo ratings yet
- Sport InjuriesDocument9 pagesSport InjurieswriterseinnaaaoNo ratings yet
- PE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2Document15 pagesPE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2nhoj eiram Rodavlas50% (2)
- Eapp StrainDocument6 pagesEapp StrainHanes ArthurNo ratings yet
- In Practice 2012 Moores 22 6Document6 pagesIn Practice 2012 Moores 22 6ransinghNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics - Brodno: TraumatologyDocument29 pagesOrthopedics - Brodno: TraumatologyKamila Anna JakubowiczNo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument17 pagesSports InjuriesAmeera Yazmin DiegoNo ratings yet
- Handouts Hope 2Document4 pagesHandouts Hope 2Elmera AmoraNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices and Sports Injury Management.Document8 pagesSafety Practices and Sports Injury Management.cejaygecainNo ratings yet
- Are You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsFrom EverandAre You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsNo ratings yet
- Commercial Galvanic Cells: BatteriesDocument9 pagesCommercial Galvanic Cells: BatteriesKamalpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Differential Release of Mast Cell Mediators and The Pathogenesis of InflammationDocument14 pagesDifferential Release of Mast Cell Mediators and The Pathogenesis of InflammationklaumrdNo ratings yet
- Aiwa CX jn5 ETDocument78 pagesAiwa CX jn5 ETluzmarospiNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength Prediction of Crushed Stone Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams Without StirrupsDocument2 pagesShear Strength Prediction of Crushed Stone Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams Without StirrupsSulaiman Mohsin AbdulAziz100% (1)
- 06 Story StiffnessDocument2 pages06 Story StiffnessDigvijay GiraseNo ratings yet
- trivia questions 学生版Document9 pagestrivia questions 学生版YING YUNo ratings yet
- 10th PET POW EM 2023 24Document6 pages10th PET POW EM 2023 24rpradeepa160No ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Pt6a27Document7 pagesTroubleshooting Pt6a27Okky Pangestoe WibowoNo ratings yet
- DIO 20. ZAŠTITA PRI RADU I SMJEŠTAJ POSADE Jan 2015Document44 pagesDIO 20. ZAŠTITA PRI RADU I SMJEŠTAJ POSADE Jan 2015Samo SpontanostNo ratings yet
- Vo 1263 AaDocument8 pagesVo 1263 Aa801400No ratings yet
- MCM (ENGLISH) Product SheetDocument4 pagesMCM (ENGLISH) Product SheetArdi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Virtual Work and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Virtual Work and Its Applicationprem adhikari100% (1)
- A 204Document1 pageA 204AnuranjanNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Language Development and Nutritional Status of The Child in The Region South of The City of Kediri Region Public HealthDocument12 pagesThe Relationship of Language Development and Nutritional Status of The Child in The Region South of The City of Kediri Region Public Healthdoddyk kurniawanNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument110 pagesPDFBikash NayakNo ratings yet
- Solving Poisson's Equation Using The FFTDocument9 pagesSolving Poisson's Equation Using The FFTJhon CerónNo ratings yet
- Каталог Remeza - 2015 Ганновер 2015 PDFDocument32 pagesКаталог Remeza - 2015 Ганновер 2015 PDFbinhleduc36No ratings yet
- Aqa CHM4 W QP Jun09Document20 pagesAqa CHM4 W QP Jun09dharmik47No ratings yet