Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Num 4
Uploaded by
Madhur Bain SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Num 4
Uploaded by
Madhur Bain SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
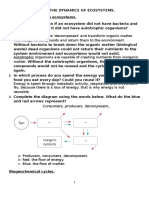
Numerical - 4
1. In a given food chain the first level carnivores on the average ingest 30% of the
production of herbivores and the second level carnivores ingest 65% of the first level
carnivores. The first level and second level carnivores assimilate 75% and 90% of the
ingested food. Estimate the assimilated energy with respected to the production of
the herbivores by the
a. First level carnivores
b. Second level carnivores
2. Plants absorb 340000 kcal/m2/yr sunlight incident on a community in the region. The
absorbed light results in a net plant production of 8833 kcal/m2/yr and
evapotranspiration of 11977 kcal/m2/yr. The herbivores consume 3368 kcal/m2/yr of
plant mass and additional intake of 536 kcal/m2/yr from other sources respiring 1760
kcal/m2/yr of it. 1478 kcal/m2/yr die of natural causes with the remaining eaten up by
the carnivores, provide a net production of 37 kcal/m2/yr for this higher tropic level
with respiration of the former level amounting to 216 kcal/m2/yr. Estimate the trophic
efficiencies for the producers, primary and secondary consumers of this food chain.
3. In a study of the energetics of a salt marsh carried out, it was found to have one
dominant plant, the grass ‘Spartina alterniflora’ apart from some algae. The trophic
organization of the marsh was a little unusual in that most of the animals there
couldn’t feed on the Spartina directly, hence had to be broken down by the bacteria.
The energy flow diagram of this eco-system is given below. Calculate the trophic
efficiency of the
a. Crabs and nematodes
b. Insects
in the diagram. All units in the figure are in kcal/m2/yr.
4. Derive the maximum efficiency for a photosynthetic process.
You might also like
- Num Sheet 4 PDFDocument1 pageNum Sheet 4 PDFbispeniydaNo ratings yet
- Num Sheet 4Document1 pageNum Sheet 4bispeniydaNo ratings yet
- Num Sheet 4 PDFDocument1 pageNum Sheet 4 PDFbispeniydaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippine1Document2 pagesRepublic of The Philippine1Clarice Barros CatedrillaNo ratings yet
- Ecology Tutorials PDFDocument4 pagesEcology Tutorials PDFSandeep Mehta100% (1)
- Ecology Tutorials PDFDocument4 pagesEcology Tutorials PDFSandeep MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ecology Tutorials PDFDocument4 pagesEcology Tutorials PDFSandeep MehtaNo ratings yet
- BIO-Chapter 19. Organisms and Their EnvironmentDocument57 pagesBIO-Chapter 19. Organisms and Their Environmentkathleen hoNo ratings yet
- S5M3L1 Energy Production16!11!2016Document63 pagesS5M3L1 Energy Production16!11!2016Nipun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2Rohit VermaNo ratings yet
- 16 Flow of EnergyDocument2 pages16 Flow of Energyramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. The Dynamics of Ecosystems.Document12 pagesUnit 7. The Dynamics of Ecosystems.nimolesaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of EcosystemDocument36 pagesDynamics of EcosystemPORAKH MONE GOHAINNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Productivity in Ecosystem Roll No 211218Document3 pagesIntroduction To Productivity in Ecosystem Roll No 211218Rajeev PratapNo ratings yet
- Exercise 14Document5 pagesExercise 14Samantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- 26 Ecological Pyramids-S RennelDocument8 pages26 Ecological Pyramids-S Rennelapi-32383118283% (18)
- Energy Flow and Ecological PyramidsDocument4 pagesEnergy Flow and Ecological Pyramidse eNo ratings yet
- Biology Slide IchiDocument23 pagesBiology Slide IchiShiro ArcadiaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems: Reading: Freeman Chapter 54Document51 pagesEcosystems: Reading: Freeman Chapter 54hhvuong5859No ratings yet
- The EcosystemDocument5 pagesThe EcosystemPrincess Lourdes CarinNo ratings yet
- 16 - Ecosystem EnergeticsDocument39 pages16 - Ecosystem EnergeticsSyarif Kawandinasbangkitlah HidayatNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument7 pagesEcosystempcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Usable Energy Decreases With Each Link in A Food Chain or WebDocument9 pagesUsable Energy Decreases With Each Link in A Food Chain or WebPaul Jeremy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document18 pagesGroup 3Elfla OrenzaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Energy FlowDocument4 pagesEcosystem and Energy FlowRohini SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Flow of EnergyDocument3 pagesLesson 3: Flow of EnergyCanapi AmerahNo ratings yet
- What Is Ecology PDFDocument113 pagesWhat Is Ecology PDFDarshan MarjadiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1 2 3Document7 pagesJurnal 1 2 3Achmadana Nurul FalaaqNo ratings yet
- Energy and ProductivityDocument9 pagesEnergy and ProductivityApple Mae Balunan AndujarNo ratings yet
- 26 Ecological Pyramids Manuel TzulDocument6 pages26 Ecological Pyramids Manuel Tzulapi-32383118267% (9)
- Bioresource Technology: D. Hernández, B. Riaño, M. Coca, M.C. García-GonzálezDocument6 pagesBioresource Technology: D. Hernández, B. Riaño, M. Coca, M.C. García-GonzálezAndres MilquezNo ratings yet
- 01 Food Energy Through EcosystemsDocument46 pages01 Food Energy Through Ecosystemsapi-275516003No ratings yet
- Ecosystems CambDocument20 pagesEcosystems CambarmvelNo ratings yet
- APES Food For Thought Modified 2014Document5 pagesAPES Food For Thought Modified 2014Alvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Ecological Pyramids: 470 KcalDocument6 pagesEcological Pyramids: 470 KcalOlivia RaiaNo ratings yet
- Richard Cartagena - PT 7Document4 pagesRichard Cartagena - PT 7api-651631551No ratings yet
- Utilization of Different Plant Species Available in Coconut Plantation To Produce Nutrient Rich VermicompostDocument10 pagesUtilization of Different Plant Species Available in Coconut Plantation To Produce Nutrient Rich VermicompostiplascakNo ratings yet
- Percamon: Renewable EnergyDocument6 pagesPercamon: Renewable EnergyyemresimsekNo ratings yet
- Energy FlowDocument21 pagesEnergy Flowapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Kami Export - Emily Moran - 26 Ecological Pyramids-SDocument6 pagesKami Export - Emily Moran - 26 Ecological Pyramids-SEmily MoranNo ratings yet
- Topic 5. ENERGY Flow Through EcosystemsDocument11 pagesTopic 5. ENERGY Flow Through Ecosystemsallen mae aballeNo ratings yet
- BLY 111 - Ecology by AKWASH-1Document10 pagesBLY 111 - Ecology by AKWASH-1stephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Ecological PyramidsDocument12 pagesLecture 3 Ecological PyramidsParva PatelNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument8 pagesEcosystembn65dgcqdfNo ratings yet
- The Major Components of An EcosystemDocument6 pagesThe Major Components of An EcosystemCrisha Joy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Energy Generation From Paddy Straw: An Analysis of Bioenergy ModelsDocument6 pagesEnergy Generation From Paddy Straw: An Analysis of Bioenergy ModelsRNNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ecosysten and BiodiversityDocument21 pagesUnit Ii Ecosysten and BiodiversityRajinithanuNo ratings yet
- Focus On Essay - Ecology PDFDocument7 pagesFocus On Essay - Ecology PDFLim Yu En100% (1)
- EcosystemDocument43 pagesEcosystemPhantom DeluxNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Different IPM Modules Against Pest Complex of Chilli (Cv. Byadgi Dabbi)Document6 pagesEvaluation of Different IPM Modules Against Pest Complex of Chilli (Cv. Byadgi Dabbi)akshata kurbettNo ratings yet
- Aquaponic Production of Tilapia and Basi - Comparing A Batch and Staggered Cropping System. Rakocy, James.Document8 pagesAquaponic Production of Tilapia and Basi - Comparing A Batch and Staggered Cropping System. Rakocy, James.Selbor951No ratings yet
- Ecosystem, GPP, NPP: Energy Flow Through EcosystemsDocument3 pagesEcosystem, GPP, NPP: Energy Flow Through EcosystemsalwfanNo ratings yet
- Eco Midterm ReviewerDocument18 pagesEco Midterm ReviewerbfhdsjNo ratings yet
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetDocument5 pagesEcological Pyramids Worksheetace0% (1)
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 8Document37 pagesBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 8Shephard Png100% (8)
- Topic 4Document8 pagesTopic 4Alianna GonzálezNo ratings yet
- New Strategies Enhancing Feasibility of Microalgal CultivationsDocument30 pagesNew Strategies Enhancing Feasibility of Microalgal CultivationsFabianNo ratings yet
- Transcript-Energy Flow in An Ecosystem.Document6 pagesTranscript-Energy Flow in An Ecosystem.Suraj O V 1820368No ratings yet
- Demystifying Climate Science: Accelerating Food & Clean Energy SecurityFrom EverandDemystifying Climate Science: Accelerating Food & Clean Energy SecurityNo ratings yet
- Aquaponics systems, fish. Volume 3: Sistemas de acuaponíaFrom EverandAquaponics systems, fish. Volume 3: Sistemas de acuaponíaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Based Assignment of ESL742 (2021-2022 First Semester)Document1 pageResearch Paper Based Assignment of ESL742 (2021-2022 First Semester)Madhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Num 3Document1 pageNum 3Madhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Self Study Component - 2 of ESL742 (2021-2022 Batch)Document1 pageSelf Study Component - 2 of ESL742 (2021-2022 Batch)Madhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- List of Research Papers Using SAM (For Self Study and Assignment Component of ESL 742, 2021-2022 Batch)Document5 pagesList of Research Papers Using SAM (For Self Study and Assignment Component of ESL 742, 2021-2022 Batch)Madhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Resource-E Cient Technologies: Deepak Bishoyi, K. SudhakarDocument13 pagesResource-E Cient Technologies: Deepak Bishoyi, K. SudhakarMadhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Mel725 14Document25 pagesMel725 14Akshat MehrotraNo ratings yet
- ESL 711 (Fuel Technology) : S. NO. Name of Student Entry NoDocument4 pagesESL 711 (Fuel Technology) : S. NO. Name of Student Entry NoMadhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Issues Associated With Wind Energy - A ReviewDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Issues Associated With Wind Energy - A ReviewMadhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Life Cycle Assessment of Sugar Industry: A ReviewDocument9 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Life Cycle Assessment of Sugar Industry: A ReviewNikhil MohiteNo ratings yet
- All India Installed Capacity (In MW) of Power Stations: (As On 31.08.2021) (Utilities)Document7 pagesAll India Installed Capacity (In MW) of Power Stations: (As On 31.08.2021) (Utilities)Madhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- H W Energy and EnvirnDocument1 pageH W Energy and EnvirnMadhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Crude Refining: Fuel Technology (ESL711) S.K TyagiDocument12 pagesCrude Refining: Fuel Technology (ESL711) S.K TyagiMadhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- AgrowKnowledge Biofuels Intro & Topic1Document23 pagesAgrowKnowledge Biofuels Intro & Topic1Madhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Green Revolution: Krishonnati YojanaDocument3 pagesGreen Revolution: Krishonnati YojanaMadhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Fresnel Re Ector (LFR) : June 2020Document11 pagesLinear Fresnel Re Ector (LFR) : June 2020Madhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet
- Effect of Emerging Water ContaminantsDocument5 pagesEffect of Emerging Water ContaminantsMadhur Bain SinghNo ratings yet