Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is A Block Chain ?
Uploaded by
Anshul TembhareOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is A Block Chain ?
Uploaded by
Anshul TembhareCopyright:
Available Formats
Block Chain
What is a Block Chain ?
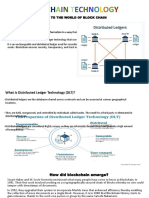
Blockchain is a distributed ledger, which simply means that a ledger is spread across
the network among all peers in the network, and each peer holds a copy of the
complete ledger.
It works with Blocks, where as spreadsheet works with “rows” and “columns”.
A block in a blockchain is a collection of data. The data is added to the block in
blockchain, by connecting it with other blocks in chronological order creating a chain
of blocks linked together. The first block in the Blockchain is called Genesis Block.
Some key attributes of Blockchain are which proves that blockchain is better than
traditional systems of ledger information keeping:
1. Peer-To-Peer: No central authority to control or manipulate it. All participant
talks to each other directly. This allows for data exchange to be made directly with
third-parties involvement.
2. Distributed: The ledger is spread across the whole network which makes
tampering not so easy.
3. Cryptographically Secured: Cryptography is used for the security services to
make the ledger tamper-proof .
4. Add-Only: Data can only be added in the blockchain with time-sequential order.
This property implies that once data is added to the blockchain, it is almost
impossible to change that data and can be considered practically immutable. We
can say it has:
“The right to be forgotten or right to erasure” defined here.
5. Consensus: This is the most critical attribute of all. This gives blockchain the
ability to update the ledger via consensus. This is what gives it the power of
decentralization. No central authority is in control of updating the ledger.
Instead, any update made to the blockchain is validated against strict criteria
defined by the blockchain protocol and added to the blockchain only after a
consensus has been reached among all participating peers/nodes on the network.
How does a Block Chain work ?
1. A node starts a transaction by first creating and then digitally signing it with its
private key (created via cryptography) . A transaction can represent various
actions in a blockchain. Most commonly this is a data structure that represents
transfer of value between users on the blockchain network. Transaction data
structure usually consists of some logic of transfer of value, relevant rules, source
and destination addresses, and other validation information.
2. A transaction is propagated (flooded) by using a flooding protocol, called Gossip
protocol, to peers that validate the transaction based on preset criteria. Usually,
more than one node is required to verify the transaction.
3. Once the transaction is validated, it is included in a block, which is then
propagated onto the network. At this point, the transaction is considered
confirmed.
4. The newly-created block now becomes part of the ledger, and the next block links
itself cryptographically back to this block. This link is a hash pointer. At this
stage, the transaction gets its second confirmation and the block gets its first
confirmation.
5. Transactions are then reconfirmed every time a new block is created. Usually, six
confirmations in a network are required to consider the transaction final.
Transactions are then reconfirmed every time a new block is created. Usually, six
confirmations in the Bitcoin network are required to consider the transaction final.
You might also like
- BlockchainDocument11 pagesBlockchainJeffer MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument7 pagesBlockchain Technologymahmoodtareq0000No ratings yet
- Mahnoor Qaisar - #1056 - Computer Application in Education Assignment-2Document7 pagesMahnoor Qaisar - #1056 - Computer Application in Education Assignment-2HaseeB MalikNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument9 pagesBlock ChainNurul Rofifah MNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument9 pagesBlock Chainkopi fompyNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument4 pagesBlockchainMichele VaselliNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: The Distributed LedgerDocument5 pagesBlockchain: The Distributed LedgerKSHITIJ PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Blockchain AnswerDocument35 pagesBlockchain AnswerGaurav ShankarNo ratings yet
- Banking and Insurance II Unit NewDocument31 pagesBanking and Insurance II Unit NewKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 STDocument40 pagesChapter 4 STAschalew AyeleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document11 pagesUnit 1Prashant AtmakuriNo ratings yet
- Anti-Malware With Blockchain - CSE105Document2 pagesAnti-Malware With Blockchain - CSE105Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Unlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanDocument14 pagesUnlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanMihai TiberiuNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Note by HasanDocument6 pagesBlockchain Note by HasanMd.HasanNo ratings yet
- Use of Blockchain Technology: By-Kunal Khandelwal Vikas Saini Arshdeep Rajnish KumarDocument8 pagesUse of Blockchain Technology: By-Kunal Khandelwal Vikas Saini Arshdeep Rajnish KumarRaj NishNo ratings yet
- BCT - Unit-1 (Notes)Document28 pagesBCT - Unit-1 (Notes)Keshav RaoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Security from the Bottom Up: Securing and Preventing Attacks on Cryptocurrencies, Decentralized Applications, NFTs, and Smart ContractsFrom EverandBlockchain Security from the Bottom Up: Securing and Preventing Attacks on Cryptocurrencies, Decentralized Applications, NFTs, and Smart ContractsNo ratings yet
- Blockchain For BusinessDocument13 pagesBlockchain For BusinessDivyanshu ChopraNo ratings yet
- Module 5 CsitDocument12 pagesModule 5 CsitPulkit JainNo ratings yet
- BCT Notes For Unit-1Document47 pagesBCT Notes For Unit-1MayankNo ratings yet
- Blockchain What is Blockchain Technology, Cryptocurrency Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Smart Contracts? Blockchain for dummies.From EverandBlockchain What is Blockchain Technology, Cryptocurrency Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Smart Contracts? Blockchain for dummies.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Blockchain AssignmentDocument13 pagesBlockchain AssignmentMer'at LoulNo ratings yet
- Blockchain for Beginners: Understand the Blockchain Basics and the Foundation of Bitcoin and CryptocurrenciesFrom EverandBlockchain for Beginners: Understand the Blockchain Basics and the Foundation of Bitcoin and CryptocurrenciesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Blockchain Facts What Is It, How It Works, and How It Can Be UsedDocument14 pagesBlockchain Facts What Is It, How It Works, and How It Can Be UsedJeffreyNo ratings yet
- LMS 13Document11 pagesLMS 13prabakar1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BlockchainDocument7 pagesChapter 2 BlockchainFarheen AkramNo ratings yet
- Rahman's Technical ReportDocument14 pagesRahman's Technical ReportMohammed Abdur RahamanNo ratings yet
- About Blockchain TechnologyDocument8 pagesAbout Blockchain TechnologyMadalina AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument9 pagesBlockchain TechnologySakshi GaulNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin: What Is A Blockchain?Document10 pagesBitcoin: What Is A Blockchain?Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Document6 pagesBlockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Amen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- Overview of Blockchain TechnologyDocument1 pageOverview of Blockchain TechnologyJagannatha NNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technologyriley zeroNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument12 pagesBlock ChainISHA AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Sarfirey GamersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BlockchainDocument9 pagesChapter 3 BlockchainArebu MarufNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Unit 2Document19 pagesBlock Chain Unit 2pilli maheshchandraNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: Step By Step Guide To Understanding The Blockchain Revolution And The Technology Behind ItFrom EverandBlockchain: Step By Step Guide To Understanding The Blockchain Revolution And The Technology Behind ItRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 4.2-Blockchain ArchitectureDocument8 pages4.2-Blockchain ArchitectureRahul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Set 1:-Blockchain Is Defined AsDocument2 pagesSet 1:-Blockchain Is Defined AsTryst DestineNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument2 pagesBlockchainSeun OgunlaNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument11 pagesBlock ChainPratibhaNo ratings yet
- MinorprojectDocument58 pagesMinorprojectAnshul DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Blockchain QBDocument12 pagesBlockchain QBKarishma AvhadNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Blockchain NotesDocument19 pagesUNIT I Blockchain Notesmanoj tilakchandNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Technology InformationDocument24 pagesBlock Chain Technology InformationDeepa ChuriNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: What Is A Blockchain?Document6 pagesBlockchain: What Is A Blockchain?Anurag BairagiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain - Curs 2Document36 pagesBlockchain - Curs 2Farmacie Baia de AramaNo ratings yet
- BLOCKCHAINDocument3 pagesBLOCKCHAINKshama PathakNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument8 pagesBlockchain Technology20CM052-Shravani Shinganwadikar. CMNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument10 pagesBlock ChainVu Trung QuanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Blockchain: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandUnderstanding Blockchain: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument23 pagesBlockchainRudra JhaNo ratings yet
- Unit - IDocument45 pagesUnit - ISivaNo ratings yet
- BC Unit1Document15 pagesBC Unit1prabusankarNo ratings yet
- New Submitted PaperDocument10 pagesNew Submitted PaperEsakki MuthuNo ratings yet
- Blockchain AbstractDocument4 pagesBlockchain AbstractGourav GhodakeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument47 pagesUnit 1 NotesKeshav RaoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ArchitectureDocument2 pagesBlockchain Architecturenagham abuwarda0% (1)
- Unit 15 - Assignment 1Document3 pagesUnit 15 - Assignment 1api-308615665No ratings yet
- Dcuci50 SG Vol2Document292 pagesDcuci50 SG Vol2kayudo80No ratings yet
- B-85314EN-1 01 (Alpha-DiA5 Custom PMC) PDFDocument242 pagesB-85314EN-1 01 (Alpha-DiA5 Custom PMC) PDFmastorres87No ratings yet
- 4 Manimagudam 01Document0 pages4 Manimagudam 01Sidran EdnihsNo ratings yet
- Security Mechanisms, Network Security Model Class-L3Document12 pagesSecurity Mechanisms, Network Security Model Class-L3Sidhant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Office Memorandum (Salary)Document2 pagesOffice Memorandum (Salary)PHED MizoramNo ratings yet
- Protect Your Source Code From Decompiling or Reverse Engineering .NET Assemblies - CodeProjectDocument19 pagesProtect Your Source Code From Decompiling or Reverse Engineering .NET Assemblies - CodeProjectYsaacx AliagaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Brigada Eskwela Teachers's Implementation PlanDocument2 pages2019 Brigada Eskwela Teachers's Implementation Plansixteen liquidoNo ratings yet
- Iec 61850 Mms Client DatasheetDocument2 pagesIec 61850 Mms Client DatasheetRishi DhimanNo ratings yet
- Starting Out With Java From Control Structures Through Data Structures 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesStarting Out With Java From Control Structures Through Data Structures 3rd Edition Ebook PDFluciano.gregory787100% (39)
- Connecting JSP Page With MS AccessDocument24 pagesConnecting JSP Page With MS AccessManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- 2-Introduction To Java Basics, Types of Java Application and Features-14-Jul-2020Material - I - 14-Jul-2020 - Lecture1-Features - of - JavaDocument11 pages2-Introduction To Java Basics, Types of Java Application and Features-14-Jul-2020Material - I - 14-Jul-2020 - Lecture1-Features - of - Javasri harsha namburiNo ratings yet
- Network TroubleshootingDocument28 pagesNetwork Troubleshootingstanley umoh100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - The Input-Process-Output (IPO)Document24 pagesLesson 2 - The Input-Process-Output (IPO)Maverik LansangNo ratings yet
- Society Law and EthicsDocument45 pagesSociety Law and Ethicssagar salalNo ratings yet
- Stephen Kasina CVDocument4 pagesStephen Kasina CVStephen KasinaNo ratings yet
- 05 Steps To Successful Adoption of Cloud Services PDFDocument17 pages05 Steps To Successful Adoption of Cloud Services PDFLuisNo ratings yet
- Telecom Interview Questions Answers Guide PDFDocument10 pagesTelecom Interview Questions Answers Guide PDFtom2626No ratings yet
- BGA Breakout Challenges: by Charles Pfeil, Mentor GraphicsDocument4 pagesBGA Breakout Challenges: by Charles Pfeil, Mentor GraphicsBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Compounding in Info Object and Analyzing The Info Object in A QueryDocument11 pagesCompounding in Info Object and Analyzing The Info Object in A QueryAli AliCanNo ratings yet
- Real-Time System AssignmentDocument4 pagesReal-Time System AssignmentTommy Kyen'de BilNo ratings yet
- MR Final PPT IntelDocument21 pagesMR Final PPT IntelRahul SttudNo ratings yet
- CPS Lab Manual - 2020Document67 pagesCPS Lab Manual - 2020Madhav100% (1)
- Magic Lantern Raw: Written and Photographed by Stephen MickDocument44 pagesMagic Lantern Raw: Written and Photographed by Stephen Mickaleksandar71No ratings yet
- ChangelogDocument2 pagesChangelogmanuelaNo ratings yet
- Schemes of Work - 2017Document2 pagesSchemes of Work - 2017Shefat Phiri100% (1)
- ADC Presentation - James Cockrell, Justin LovelessDocument14 pagesADC Presentation - James Cockrell, Justin LovelessWilliam VizzottoNo ratings yet
- Sistem MühendisliğiDocument18 pagesSistem MühendisliğiKivanç IrenNo ratings yet
- Maximo 61 UsersDocument520 pagesMaximo 61 UsersMelisaNo ratings yet
- SAP Learning System Access3Document35 pagesSAP Learning System Access3Nguyễn BảoNo ratings yet