Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blockchain
Uploaded by
Michele VaselliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blockchain
Uploaded by
Michele VaselliCopyright:
Available Formats
Blockchain
Blockchain is a system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult or
impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system.
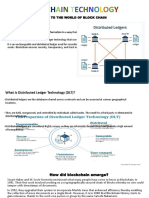
A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed
across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain. Each block in the chain
contains a number of transactions, and every time a new transaction occurs on the
blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger. The
decentralised database managed by multiple participants is known as Distributed Ledger
Technology (DLT).
Blockchain is a type of DLT in which transactions are recorded with an immutable
cryptographic signature called a hash.
How blockchain works
As each transaction occurs, it is recorded as a “block” of data
Those transactions show the movement of an asset that can be tangible (a product) or
intangible (intellectual). The data block can record the information of your choice.
Each block is connected to the ones before and after it
These blocks form a chain of data as an asset moves from place to place or ownership changes hands. The
blocks confirm the exact time and sequence of transactions, and the blocks link securely together to prevent any
block from being altered or a block being inserted between two existing blocks.
Transactions are blocked together in an irreversible chain: a blockchain
Each additional block strengthens the verification of the previous block and hence the
entire blockchain. This renders the blockchain tamper-evident, delivering the key strength
of immutability. This removes the possibility of tampering by a malicious actor — and
builds a ledger of transactions you and other network members can trust.
What Is a Block?
Every chain consists of multiple blocks and each block has three basic elements:
The data in the block.
The nonce: “number used only once.” A nonce in blockchain is a whole number
that’s randomly generated when a block is created, which then generates a
block header hash.
The hash: a hash in blockchain is a number permanently attached to the nonce.
What Is Decentralization in Blockchain?
One of the most important concepts in blockchain technology is decentralization. No
one computer or organization can own the chain. Instead, it is a distributed ledger via
the nodes connected to the chain. Blockchain nodes can be any kind of electronic
device that maintains copies of the chain and keeps the network functioning.
Every node has its own copy of the blockchain and the network must algorithmically
approve any newly mined block for the chain to be updated, trusted and verified.
Since blockchains are transparent, every action in the ledger can be easily checked
and viewed, creating inherent blockchain security. Each participant is given a unique
alphanumeric identification number that shows their transactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Higher Accuracy of Limit on Transactions per
Transactions Second
No Need for Intermediaries High Energy Costs
Extra Security Risk of Asset Loss
More Efficient Transfers Potential for Illegal Activity
Public Blockchain: These blockchains are completely open to following the idea of decentralization. They
don’t have any restrictions, anyone having a computer and internet can participate in the network.
As the name is public this blockchain is open to the public, which means it is not owned by anyone.
Anyone having internet and a computer with good hardware can participate in this public blockchain.
All the computer in the network hold the copy of other nodes or block present in the network
In this public blockchain, we can also perform verification of transactions or records
Private Blockchain: These blockchains are not as decentralized as the public blockchain only selected
nodes can participate in the process, making it more secure than the others.
These are not as open as a public blockchain.
They are open to some authorized users only.
These blockchains are operated in a closed network.
In this few people are allowed to participate in a network within a company/organization.
Hybrid Blockchain: It is the mixed content of the private and public blockchain, where some part is
controlled by some organization and other makes are made visible as a public blockchain.
It is a combination of both public and private blockchain.
Permission-based and permissionless systems are used.
User access information via smart contracts
Even a primary entity owns a hybrid blockchain it cannot alter the transaction
Consortium Blockchain: It is a creative approach that solves the needs of the organization. This blockchain
validates the transaction and also initiates or receives transactions.
Also known as Federated Blockchain.
This is an innovative method to solve the organization’s needs.
Some part is public and some part is private.
In this type, more than one organization manages the blockchain.
You might also like
- Blockchain: Step By Step Guide To Understanding The Blockchain Revolution And The Technology Behind ItFrom EverandBlockchain: Step By Step Guide To Understanding The Blockchain Revolution And The Technology Behind ItRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Mahnoor Qaisar - #1056 - Computer Application in Education Assignment-2Document7 pagesMahnoor Qaisar - #1056 - Computer Application in Education Assignment-2HaseeB MalikNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Note by HasanDocument6 pagesBlockchain Note by HasanMd.HasanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument7 pagesBlockchain Technologymahmoodtareq0000No ratings yet
- Blockchain Security from the Bottom Up: Securing and Preventing Attacks on Cryptocurrencies, Decentralized Applications, NFTs, and Smart ContractsFrom EverandBlockchain Security from the Bottom Up: Securing and Preventing Attacks on Cryptocurrencies, Decentralized Applications, NFTs, and Smart ContractsNo ratings yet
- BCT Notes For Unit-1Document47 pagesBCT Notes For Unit-1MayankNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BlockchainDocument9 pagesChapter 3 BlockchainArebu MarufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BlockchainDocument7 pagesChapter 2 BlockchainFarheen AkramNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument9 pagesBlock ChainNurul Rofifah MNo ratings yet
- chapter 4 STDocument40 pageschapter 4 STAschalew AyeleNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ArchitectureDocument2 pagesBlockchain Architecturenagham abuwarda0% (1)
- Unraveling the Enigma of Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Powering the FutureFrom EverandUnraveling the Enigma of Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Powering the FutureNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Document6 pagesBlockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Amen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- Use of Blockchain Technology: By-Kunal Khandelwal Vikas Saini Arshdeep Rajnish KumarDocument8 pagesUse of Blockchain Technology: By-Kunal Khandelwal Vikas Saini Arshdeep Rajnish KumarRaj NishNo ratings yet
- Blockchain for Beginners: Understand the Blockchain Basics and the Foundation of Bitcoin and CryptocurrenciesFrom EverandBlockchain for Beginners: Understand the Blockchain Basics and the Foundation of Bitcoin and CryptocurrenciesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Understanding Blockchain: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandUnderstanding Blockchain: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: The Distributed LedgerDocument5 pagesBlockchain: The Distributed LedgerKSHITIJ PANDEYNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument5 pagesBlockchainGood for NothingNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Technology InformationDocument24 pagesBlock Chain Technology InformationDeepa ChuriNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technologyriley zeroNo ratings yet
- The First Comprehensive Guide To Blockchain: Bitcoin, Cryptocurrencies, Smart Contracts, and the Future of BlockchainFrom EverandThe First Comprehensive Guide To Blockchain: Bitcoin, Cryptocurrencies, Smart Contracts, and the Future of BlockchainNo ratings yet
- Blockchain AssignmentDocument13 pagesBlockchain AssignmentMer'at LoulNo ratings yet
- Blockchain What is Blockchain Technology, Cryptocurrency Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Smart Contracts? Blockchain for dummies.From EverandBlockchain What is Blockchain Technology, Cryptocurrency Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Smart Contracts? Blockchain for dummies.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Banking and Insurance II Unit NewDocument31 pagesBanking and Insurance II Unit NewKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Revolutionizing IndustriesDocument6 pagesBlockchain Revolutionizing IndustriesAnurag BairagiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain For BusinessDocument13 pagesBlockchain For BusinessDivyanshu ChopraNo ratings yet
- What Is A Block Chain ?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Block Chain ?Anshul TembhareNo ratings yet
- Blockchain AnswerDocument35 pagesBlockchain AnswerGaurav ShankarNo ratings yet
- Blockchain RAPORDocument4 pagesBlockchain RAPORAylin ErdoğanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document11 pagesUnit 1Prashant AtmakuriNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Blockchain NotesDocument19 pagesUNIT I Blockchain Notesmanoj tilakchandNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1From EverandBlockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1No ratings yet
- Blockchain: Real-World Applications And UnderstandingFrom EverandBlockchain: Real-World Applications And UnderstandingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Blockchain Technology Overview (B19CS7072Document28 pagesBlockchain Technology Overview (B19CS7072Keshav RaoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Facts; What is It, How It Works, And How It Can Be UsedDocument14 pagesBlockchain Facts; What is It, How It Works, And How It Can Be UsedJeffreyNo ratings yet
- On Block ChainDocument16 pagesOn Block Chainshaik ashraffNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument12 pagesBlock ChainISHA AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: The Building Blocks of Trust and Transparency in the Digital AgeFrom EverandBlockchain: The Building Blocks of Trust and Transparency in the Digital AgeNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument8 pagesBlockchain Technology20CM052-Shravani Shinganwadikar. CMNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument20 pagesBlockchain Technologyabreham ashebirNo ratings yet
- Bahirdar University: DistributedDocument7 pagesBahirdar University: DistributedAmen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- Module 5 CsitDocument12 pagesModule 5 CsitPulkit JainNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Basics: A Concise Guide to Distributed LedgersDocument14 pagesBlockchain Basics: A Concise Guide to Distributed LedgersparagNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Basics: A Concise Guide to Distributed LedgersDocument14 pagesBlockchain Basics: A Concise Guide to Distributed LedgersparagNo ratings yet
- Blockchain MBA9Document14 pagesBlockchain MBA9paragNo ratings yet
- Rahman's Technical ReportDocument14 pagesRahman's Technical ReportMohammed Abdur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain-Case Study (ETI)Document13 pagesBlockchain-Case Study (ETI)Omkar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument1 pageBlock Chainmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Power Blockchain: Discover How To Transform Your Business Using BlockchainFrom EverandPower Blockchain: Discover How To Transform Your Business Using BlockchainNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in Management 2Document13 pagesContemporary Issues in Management 2joseph mbuguaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Beginner To Advanced GuidesDocument1,155 pagesBlockchain Beginner To Advanced GuidesWalidNo ratings yet
- BC Unit1Document15 pagesBC Unit1prabusankarNo ratings yet
- Tài liệuDocument2 pagesTài liệuKiên LêNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 NotesDocument14 pagesUnit - 1 NotesFbz AriNo ratings yet
- 4.2-Blockchain ArchitectureDocument8 pages4.2-Blockchain ArchitectureRahul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Protein DenaturationDocument12 pagesProtein DenaturationAhmed Elhakim100% (2)
- The Cosmic Frequency of Universal ConscienceDocument23 pagesThe Cosmic Frequency of Universal ConscienceCamilo Carreño TorresNo ratings yet
- ICEA-AEIC Diameter ComparisonDocument3 pagesICEA-AEIC Diameter ComparisonsupernaenergyNo ratings yet
- Map Grid and Compass RoseDocument3 pagesMap Grid and Compass RosePatricia BelangerNo ratings yet
- Seal Pot: Seal Fluid Supply TankDocument4 pagesSeal Pot: Seal Fluid Supply Tankmadhu gawadeNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Database Systems: Fall 2008 Quiz IIDocument12 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Database Systems: Fall 2008 Quiz IIigoginNo ratings yet
- CS8603 Distributed SystemsDocument11 pagesCS8603 Distributed SystemsMohammad Bilal - Asst. Prof, Dept. of CSENo ratings yet
- JBMO ShortLists-2001Document2 pagesJBMO ShortLists-2001OklaNo ratings yet
- Python VocabulariesDocument101 pagesPython VocabulariesDennis Chen100% (1)
- 10 SQL Script Deep Dive and OIADocument6 pages10 SQL Script Deep Dive and OIArameshnaiduNo ratings yet
- Whats Map ProjectionDocument19 pagesWhats Map Projectionmahmoud abdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- GCE Examinations Mechanics Module M1 Paper K MARKING GUIDEDocument4 pagesGCE Examinations Mechanics Module M1 Paper K MARKING GUIDEAbhiKhanNo ratings yet
- Zapata MATHCADDocument22 pagesZapata MATHCADGonzalo Ale Olave A.No ratings yet
- Raynoise Manual Rn31Document377 pagesRaynoise Manual Rn31Jay JayNo ratings yet
- 330D System Operation Machine Electronic Control System PDFDocument64 pages330D System Operation Machine Electronic Control System PDFDANIEL VARGAS RODRIGUEZ60% (5)
- Shs Genmath Module 8 Core Revised DuenasDocument42 pagesShs Genmath Module 8 Core Revised DuenasAPRIL JOY ARREOLANo ratings yet
- CAM GuideDocument10 pagesCAM Guideio1_roNo ratings yet
- IN Sneddon - The Distribution of Stress in The Neighborhood of A Crack in An Elastic Solid - For Shape Factor QDocument32 pagesIN Sneddon - The Distribution of Stress in The Neighborhood of A Crack in An Elastic Solid - For Shape Factor QShaun Raphael LeeNo ratings yet
- Bolt Circle CalculatorDocument21 pagesBolt Circle CalculatorMarcos PeralesNo ratings yet
- Mac Green Button EN PDFDocument5 pagesMac Green Button EN PDFVanessa ManriqueNo ratings yet
- WIT COMP1050: Object-Oriented Programming Objects and ClassesDocument60 pagesWIT COMP1050: Object-Oriented Programming Objects and ClassesJosephNo ratings yet
- Manual Controlador InteligenDocument132 pagesManual Controlador InteligenRicardo NunesNo ratings yet
- FM DemodulationDocument4 pagesFM DemodulationRudra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- MiniProject Assignment 3Document3 pagesMiniProject Assignment 3Asadullah ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 12TH CS TERM 2 - PythonDocument8 pages12TH CS TERM 2 - PythonAnbuchelvan VKNo ratings yet
- Factor Analysis PresentationDocument158 pagesFactor Analysis PresentationAnonymous pnYfWvNo ratings yet
- MP A330 Rev 07Document1,117 pagesMP A330 Rev 07Aditya PurwansyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Advanced Modeling Techniques: Prof. Ming-Bo LinDocument42 pagesChapter 7: Advanced Modeling Techniques: Prof. Ming-Bo Linvimal_raj205No ratings yet
- Matlab R2008b-Installation InstructionDocument2 pagesMatlab R2008b-Installation InstructionDicky Chandra SuryaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Gases Through Kinetic TheoryDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Gases Through Kinetic TheoryJaimeNo ratings yet