Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Keys N4Api Ing Topics
Keys N4Api Ing Topics
Uploaded by
zakirahyaakobOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Keys N4Api Ing Topics
Keys N4Api Ing Topics
Uploaded by
zakirahyaakobCopyright:
Available Formats
KEYS To
32 CIJRRTCTJLI]N,{
N4API>ING
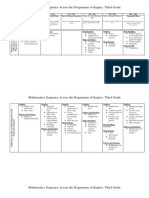
Figure 3.2 Math Topics and Content
Topic Content
[Mathematical Process Problem solving
Number order
Number Operations and Flelationships Number computing
Ordinal numbers
Even and odd numbers
Geometry Shapes
Area
N/easurement Time
Calendar
Statistics and Probability Graphing
Fractions and Decimals Fractional parts
Algebraic Relationships Patterns
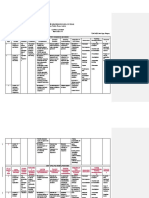
Figure 3.3 Language ArtsTopics and Content
Month Topic Content
September Reading The Tales of Olga da Polga
Writing Sentences
Grammar Subjects and predicates
Spelling Short vowel words
Double consonant words
By subcategorizing the multifaceted nature of the language arts curricu-
Ium, these primary teachers were better able to look at the specific units and
lessons taught each month and organize them according to the content topics.
This format helped every teacher document where the specific content area and
skills vr,ere taught, and greatly assisted the curriculum analysis within and
across grade levels that occurs later in the curriculum mapping process.
Recordtng Skills
Skills are the precise expectations or outcomes students are expected to
know, and should reflect the content and academic standards. Traditionally, cur-
riculum skills have been documented as behavioral objectives that usually begin
with the words "The students will . , , " They are often wordy and, in many cases,
do not address the specific student expectations. As a result, there is the tendency
You might also like
- 5 Healing SalvesDocument5 pages5 Healing SalvesAmber McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Aircrack NG Linux Tutorial PDFDocument4 pagesAircrack NG Linux Tutorial PDFYumi Vhelena KoenNo ratings yet
- The Telephone The Life Story of A TechnologyDocument177 pagesThe Telephone The Life Story of A Technologyvfan100% (1)
- Entire Maths ProgramDocument51 pagesEntire Maths ProgramLeah Daley100% (4)
- Nikon 17-55mm f2.8d Repair ManualDocument85 pagesNikon 17-55mm f2.8d Repair ManualAnonymous XuOGlMi0% (1)
- Diagramas Electricos Dodge NeonDocument256 pagesDiagramas Electricos Dodge Neongtran100% (2)
- Poems of The Decade Key PointsDocument6 pagesPoems of The Decade Key PointsOscar MasindeNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Fractions and PercentagesDocument20 pagesYear 8 Fractions and PercentagessanduedNo ratings yet
- UP B1plus Test 1BDocument7 pagesUP B1plus Test 1BEni RanxhaNo ratings yet
- KnowledgeAdvisors Metrics That Matter® BrochureDocument6 pagesKnowledgeAdvisors Metrics That Matter® BrochureHatta HalimNo ratings yet
- Legal Technique and LogicDocument9 pagesLegal Technique and LogicAb CastilNo ratings yet
- Rainbow BhajanDocument36 pagesRainbow BhajanBodhi VimalNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance Aa Revison Notes 2019Document85 pagesAudit and Assurance Aa Revison Notes 2019Jeshna JoomuckNo ratings yet
- Starch Booklet 2013Document42 pagesStarch Booklet 2013Amelya Nurlaelaa ShariiNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan G-8Document7 pagesAnnual Plan G-8Siraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Simplify Rational ExpressionsDocument4 pagesSimplify Rational ExpressionsJonalyn AngelesNo ratings yet
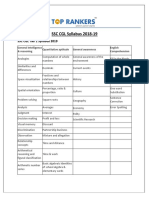
- Three Month Strategy For SSC CGL - Quantitative AptitudeDocument3 pagesThree Month Strategy For SSC CGL - Quantitative AptitudeAnonymous 1FBBMmStsNo ratings yet
- SSC Mts Syllabus 2019.pdf 62 PDFDocument5 pagesSSC Mts Syllabus 2019.pdf 62 PDFAbhi NandhanNo ratings yet
- Article Careers360 20240129080611Document7 pagesArticle Careers360 20240129080611Devara MithilaNo ratings yet
- GATE General Aptitude (GA) Syllabus 2022 - Check Topic-Wise SyllabusDocument3 pagesGATE General Aptitude (GA) Syllabus 2022 - Check Topic-Wise SyllabusSri GowthamNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Algebra: 1. Catfunda Content CoverageDocument5 pagesArithmetic Algebra: 1. Catfunda Content CoveragesivasimplexNo ratings yet
- TCS Quantitative Aptitude Syllabus: Percentages Work and Time Ratios and ProportionDocument2 pagesTCS Quantitative Aptitude Syllabus: Percentages Work and Time Ratios and ProportionAmmu AmmuluNo ratings yet
- RRB Alp SyllabusDocument4 pagesRRB Alp Syllabusshubham.upadhyaydse21No ratings yet
- Curriculum Map 7Document65 pagesCurriculum Map 7elay gervacioNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Syllabus 2019Document10 pagesSSC CGL Syllabus 2019Anonymous fntE0WolNo ratings yet
- Given Below Is The CAT Syllabus and The Topics You Need To Cover For The VA RC Section (Verbal Ability and Reading Comprehension)Document4 pagesGiven Below Is The CAT Syllabus and The Topics You Need To Cover For The VA RC Section (Verbal Ability and Reading Comprehension)Mandakini PudipeddiNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier 1 Syllabus 2016:: Subjects Topics UnderDocument3 pagesSSC CGL Tier 1 Syllabus 2016:: Subjects Topics UnderGanesh EshwarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 CM 3Document6 pagesGrade 10 CM 3Ryan XDNo ratings yet
- MTH220ADocument7 pagesMTH220AMarian Odencio BillonesNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL SyllabusDocument2 pagesSSC CGL SyllabusAbhishek SwamiNo ratings yet
- Volume For Cylinders, Pyramids, Cones, and SpheresDocument11 pagesVolume For Cylinders, Pyramids, Cones, and SpheresChristian nebreNo ratings yet
- Year 10 TrigonometryDocument25 pagesYear 10 TrigonometrySuzie DingNo ratings yet
- K-12 Mathematics CG (Glossary and Code Book Legend)Document4 pagesK-12 Mathematics CG (Glossary and Code Book Legend)Dublin DjoyzNo ratings yet
- MyBook 13768 826084084Document24 pagesMyBook 13768 826084084VijayaChandran UvarajanNo ratings yet
- GATE CS Topic Wise Preparation Notes GeeksforGee+ - 1663310584807Document48 pagesGATE CS Topic Wise Preparation Notes GeeksforGee+ - 1663310584807Big BossNo ratings yet
- JHE114Document2 pagesJHE114paulyeboah168No ratings yet
- Gr. 9Document8 pagesGr. 9Joyce Anne Tuala YabutNo ratings yet
- G3 at A Glance Desktop CurricDocument7 pagesG3 at A Glance Desktop CurricIulia RosuNo ratings yet
- AA Syllabus Outline 2019Document87 pagesAA Syllabus Outline 2019derrickzptofficialNo ratings yet
- IBPS RRB PoDocument2 pagesIBPS RRB PoAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Pgnum 632462254c4b6 Margin 632461e936e4a 632461dcccff5Document48 pagesPgnum 632462254c4b6 Margin 632461e936e4a 632461dcccff5Big BossNo ratings yet
- Royal Colleges of Science and Management Inc.: College Algebra (MATH 1) First Semester AY: 2022-2023Document6 pagesRoyal Colleges of Science and Management Inc.: College Algebra (MATH 1) First Semester AY: 2022-2023Reynold BaborNo ratings yet
- Star Math FlyerDocument2 pagesStar Math Flyerapi-377871508No ratings yet
- Course Handbook BMDocument9 pagesCourse Handbook BMSarah AndersonNo ratings yet
- Iift Mba Syllabus and Exam Pattern PDF Bf308a87Document9 pagesIift Mba Syllabus and Exam Pattern PDF Bf308a87siddharth muruganNo ratings yet
- VocabularyDocument9 pagesVocabularydeyp5095No ratings yet
- SSC CGL Syllabus Tier I: SSC Combined Graduate Level ExamDocument7 pagesSSC CGL Syllabus Tier I: SSC Combined Graduate Level ExamThe DivineNo ratings yet
- Lp-Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument7 pagesLp-Mathematics in The Modern WorldJowella Mae GuasisNo ratings yet
- GATE CS Topic Wise Preparation Notes GeeksforGee+ - 1663310584807-Numbered PrintDocument51 pagesGATE CS Topic Wise Preparation Notes GeeksforGee+ - 1663310584807-Numbered PrintBig BossNo ratings yet
- Applications and Interpretations GUIDEDocument95 pagesApplications and Interpretations GUIDELia ChouNo ratings yet
- 2024 Year 7 Mathematics Integers and IndicesDocument13 pages2024 Year 7 Mathematics Integers and IndicesWayiz AliNo ratings yet
- PSPCL SyllDocument1 pagePSPCL SyllSonam BaghaNo ratings yet
- Casa Del Niño Montessori School of Roxas San Rafael, Roxas, Isabela Curriculum Map Mathematics 10 GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10Document8 pagesCasa Del Niño Montessori School of Roxas San Rafael, Roxas, Isabela Curriculum Map Mathematics 10 GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10Schievvie AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics IDocument9 pagesEngineering Mathematics IIbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- EGE 7 - Comparative Study of Curriculum - JOYCE MENDEZ - III-BEED-BDocument5 pagesEGE 7 - Comparative Study of Curriculum - JOYCE MENDEZ - III-BEED-BJoyce May MendezNo ratings yet
- The Master Syllabus 2024Document11 pagesThe Master Syllabus 2024rai.devnsu8448No ratings yet
- Syllabus OutlineDocument88 pagesSyllabus OutlineKazi Ayman RAHMANNo ratings yet
- The Master SyllabusDocument10 pagesThe Master SyllabusAkshit DhoundiyalNo ratings yet
- 04 Secondary School Curriculum Form 1-3Document176 pages04 Secondary School Curriculum Form 1-3Zillah MarinNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Term 2 Test Framework 2024Document5 pagesGrade 9 Term 2 Test Framework 2024taahir.latif.786No ratings yet
- IB SL AA SyllabusDocument83 pagesIB SL AA SyllabusTariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- CAT Syllabus 2018: 1. Mathematics or Quantitative SectionDocument2 pagesCAT Syllabus 2018: 1. Mathematics or Quantitative SectionAshutosh chaturvediNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Curriculum in MalaysiaDocument38 pagesMathematics Curriculum in Malaysiaong0625No ratings yet
- Helping UniversityDocument17 pagesHelping UniversityriadNo ratings yet
- Article 82189Document7 pagesArticle 82189Keshvi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Unit of WorkDocument8 pagesMathematics Unit of Workapi-358178333No ratings yet
- Psat - Overview Format TableDocument1 pagePsat - Overview Format Tableapi-395493982No ratings yet
- ADmath For EE SyllabusDocument7 pagesADmath For EE SyllabusCarlo BensurtoNo ratings yet
- Northwestern Visayan Colleges: Subject SyllabusDocument4 pagesNorthwestern Visayan Colleges: Subject SyllabusMa. Gladys Mae PanadoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World SyllabusDocument6 pagesMathematics in The Modern World SyllabusJoseph MazoNo ratings yet
- Uasa 6im 2023 - 2024Document2 pagesUasa 6im 2023 - 2024zakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- FLOODSDocument5 pagesFLOODSzakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- N/Fapptng Process: Cycle: To To of of Thinking Will Their of ofDocument1 pageN/Fapptng Process: Cycle: To To of of Thinking Will Their of ofzakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- Evolution /: District'sDocument1 pageEvolution /: District'szakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- 2: The The Curriculum Will Within If WithinDocument1 page2: The The Curriculum Will Within If WithinzakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- With Form Findings Group's Individually Reviewing lst-5th Math 7-8Document1 pageWith Form Findings Group's Individually Reviewing lst-5th Math 7-8zakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- 46 o o o (T o O: Is Highly AnDocument1 page46 o o o (T o O: Is Highly AnzakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- Pemetaan Kurikulum (New) 1Document6 pagesPemetaan Kurikulum (New) 1zakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- Step Developing An Pian: of Initial CurriculumDocument1 pageStep Developing An Pian: of Initial CurriculumzakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- Step Revierwitrg L/'lirps Sanlple: 3rd-HowDocument1 pageStep Revierwitrg L/'lirps Sanlple: 3rd-HowzakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- Proces Mapping KurikulumDocument21 pagesProces Mapping KurikulumzakirahyaakobNo ratings yet
- Devaki Nandana - Updated CVDocument2 pagesDevaki Nandana - Updated CVNandana KalamNo ratings yet
- Data Lifeguard Diagnostic For DOS: USB Bootable Setup InstructionsDocument6 pagesData Lifeguard Diagnostic For DOS: USB Bootable Setup InstructionsalexannderthegreatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Introducing EvaluationDocument20 pagesChapter 12 - Introducing Evaluationyayee03No ratings yet
- Case Log FNP 1Document6 pagesCase Log FNP 1natalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 155 - 0710Document6 pagesChemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 155 - 0710PromagEnviro.com0% (1)
- Roll Call For The Academic Year: 2019 20 (Sem I) : Srno Grno Rollno Name of StudentDocument6 pagesRoll Call For The Academic Year: 2019 20 (Sem I) : Srno Grno Rollno Name of StudentSP WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Pub. 141 Scotland 10ed 2007Document285 pagesPub. 141 Scotland 10ed 2007joop12No ratings yet
- BPR OnLine Learning Center SeriesDocument8 pagesBPR OnLine Learning Center SeriesEdy PraveenNo ratings yet
- Triads by Second and ThirdDocument3 pagesTriads by Second and Thirdapi-302635768100% (1)
- Challanges and Ethics of ITDocument19 pagesChallanges and Ethics of ITJanu BhaktaNo ratings yet
- BBR Atlas Copco (CC125) Operation & Maintenance ManualDocument75 pagesBBR Atlas Copco (CC125) Operation & Maintenance ManualWS BANGARUPALEM GUDIPALANo ratings yet
- Agape Young Achievers' Christian Academy IncDocument6 pagesAgape Young Achievers' Christian Academy IncBrian CelineNo ratings yet
- LOE Application' Mate and Master Combined For Vessel More Than 3000GT UV' A1MCDocument2 pagesLOE Application' Mate and Master Combined For Vessel More Than 3000GT UV' A1MCraeq109No ratings yet
- Inventorwizard: Miniature Steam Engine Vertical Steam Engine With Reverse Gear (Anno 1830) Base Cast 000.001Document1 pageInventorwizard: Miniature Steam Engine Vertical Steam Engine With Reverse Gear (Anno 1830) Base Cast 000.001Lucas MaccagnanNo ratings yet
- Good Will HuntingDocument1 pageGood Will HuntingnanananNo ratings yet
- Taiwan Cinema Memory and Modernity - (Chapter 3 The Ruin Body and Time-Image in Tsai Ming-Liang's Films The ... )Document38 pagesTaiwan Cinema Memory and Modernity - (Chapter 3 The Ruin Body and Time-Image in Tsai Ming-Liang's Films The ... )Carmen LiNo ratings yet
- Mothers of A New World Maternalist Politics and The Origins of Welfare StateDocument229 pagesMothers of A New World Maternalist Politics and The Origins of Welfare StatewanNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFICATIONS OF LAW For StudentsDocument10 pagesCLASSIFICATIONS OF LAW For StudentstanzeelaataullahNo ratings yet