Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ce8501 Design of Reinforced Cement Concrete Elements MCQ
Uploaded by
Sundar GaneshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ce8501 Design of Reinforced Cement Concrete Elements MCQ
Uploaded by
Sundar GaneshCopyright:
Available Formats
www.rejinpaul.
com
c) Fire and corrosion resistance
d) Reusable
CE8501 DESIGN OF Answer: c
REINFORCED Explanation: Steel has high strength per unit
mass, highly durable, and is reusable. But
om
CEMENT steel is poor in fire and corrosion resistance, it
needs to be protected.
CONCRETE 3. Elastic Modulus of Steel is __________
ELEMENTS a) 1.5 x 109 N/mm2
b) 2.0 x 105 N/mm2
.c
c) 2.0 x 105 N/m2
CIVIL - FIFTH d) 1.5 x 109 N/m2
SEMESTER
ul
Answer: b
Explanation: Elastic modulus = Stress/Strain.
As per IS 800-2007, elastic modulus of steel
REG. 2017 pa is 2.0 x 10⁵ N/mm².
4. Unit mass of Steel = ________
a) 785 kg/m3
b) 450 kg/m3
UNIT I INTRODUCTION c) 450 kg/cm3
jin
d) 7850 kg/m3
TOPIC 1.1 OBJECTIVE OF Answer: d
STRUCTURAL DESIGN Explanation: As per IS 800-2007, unit mass
of steel is 7850 kg/m³. A steel member with
.re
1. Steel is mainly an alloy of small section which has little self-weight is
a) Iron and Carbon able to resist heavy loads because steel
b) Sulphur and Zinc members have high strength per unit weight.
c) Zinc and tin
d) Phosphorous and Tin 5. Poisson’s ratio of steel is ________
w
a) 0.1
Answer: a b) 1.0
Explanation: Steel is alloy of iron and c) 0.3
d) 2.0
w
carbon. Apart from carbon, a small percent of
manganese, sulphur, phosphorous, chrome,
nickel, and copper are added to give special Answer: c
properties to steel. Explanation: Poisson’s ratio = transverse
w
strain/axial strain. As per IS 800-2007,
2. Which of the following is a disadvantage Poisson’s ratio of steel is 0.3 in elastic range
of Steel? and it is 0.5 in plastic range.
a) High strength per unit mass
b) High durability
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
6. Structural Steel normally has carbon Phosphorous in Steel ?
content less than _______ a) yields high strength
a) 1.0% b) affects weldability
b) 0.6% c) increases resistance to corrosion
c) 3.0% d) improves resistance to high temperature
d) 5.0%
om
Answer: b
Answer: b Explanation: When sulphur and phosphorous
Explanation: Structural Steel normally have is used beyond 0.06%, it imparts brittleness
a carbon content less than 0.6%. Carbon and affects weldability and fatigue strength.
content increases hardness, yield and tensile
strength of steel but it decreases ductility and 10. Which of the following is added to steel
toughness. to increase resistance to corrosion?
.c
a) Carbon
7. What is the permissible percentage of b) Manganese
Sulphur and Phosphorous content in steel? c) Sulphur
a) 0.1%, 0.12% d) Copper
ul
b) 1.0%, 3.0%
c) 3.0%, 1.0% Answer: d
d) 1.0%, 1.0% Explanation: Addition of small quantity of
copper increases resistance to corrosion. Even
Answer: a
pa
Explanation: Sulphur content is generally
Chrome and Nickel are added to impart
corrosion resistance property to steel.
between 0.02 – 0.1%. If more than 0.1%, it
decreases strength and ductility of steel. If 11. Which of the following properties are
Phosphorous is more than 0.12%, it reduces affected due to addition of carbon and
jin
shock resistance, ductility and strength of manganese to steel?
steel. (i) tensile strength and yield property (ii)
Ductility (iii) Welding (iv) Corrosion
8. What happens when Manganese is added to resistance
steel? a) i and ii only
.re
a) decreases strength and hardness of steel b) i and iii only
b) improves corrosion resistance c) i, ii, iii
c) decreases ductility d) i and iv only
d) improves strength and hardness of steel
Answer: c
w
Answer: d Explanation: Increased quantity of carbon
Explanation: Manganese is added to improve and manganese imparts higher tensile
strength and hardness of steel . Based on strength and yield properties but lowers
Manganese content, steel are classified as ductility which is more difficult to weld.
w
Carbon Manganese steel (Mn >1%) and
Carbon Steel (Mn <1%). If its content 12. Chrome and Nickel are added to Steel to
exceeds 1.5%, it increases the formation of improve _________
w
martensite and hence decreases ductility and a) corrosion resistance and high temperature
toughness. resistance
b) strength
9. Which of the following is the effect of c) ductility
increased content of Sulphur and d) weldablity
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
Answer: a Answer: d
Explanation: Steel is weak in fire and Explanation: Due to buckling we don’t use
corrosion resistance. So, to improve corrosion diameter of longitudinal bars of a column less
resistance and high temperature resistance, than 12 mm diameter.
chromium and nickel are added to steel.
4. Thickened part of a flat slab over its
om
supporting column, is technically known as
TOPIC 1.2 STEPS IN RCC _____________
STRUCTURAL DESIGN a) drop panel
PROCESS b) capital
c) column head
1. What does R.C.C. stand for? d) cannot be determined
.c
a) Reinforced Cement Concrete
Answer: a
b) Reinforced Concrete Cement
Explanation: Drop panel is used for resisting
c) Reinforced Combined Cement
high shear at the column, drop panels have
d) Reinforced Constituent Cement
thickness more than the slab thickness and
ul
Answer: a they are mostly used when the span is large or
Explanation: When we say concrete in the shear load is high.
building trade, we actually mean reinforced
pa While column capital is the upper head of the
concrete. Its full name is reinforced cement column which is thickened to reduce the
concrete, or RCC. RCC is concrete that punching shear on the column, column capital
contains steel bars, called reinforcement bars, also reduces the clear span.
or rebars.
5. The minimum cube strength of concrete
used for a prestressed member, is ________
jin
2. The maximum area of tension
reinforcement in beams shall not exceed a) 50 kg/cm2
_________ b) 150 kg/cm2
a) 2% c) 350 kg/cm2
b) 4%
d) 100 kg/cm2
.re
c) 0.15%
d) 1.5% Answer: c
Explanation: M35 is minimum required
Answer: b
concrete for prestressed concrete.
Explanation: According to the clause
26.5.1.1 maximum reinforcement-the Here 35 is in N/mm2. So convert it into
w
maximum area of tension reinforcement shall kg/cm2.
not exceeds 0.04 bD. So, 0.04 bD/bD*100 = N/mm2 = 10 kg/cm2.
4%. So 35 N/mm2 = 350 Kg/cm2.
w
3. The diameter of longitudinal bars of a 6. The number of treads in a flight is equal to
column should never be less than _________ __________
a) 6 mm
w
a) risers in the flight
b) 8 mm b) risers plus one
c) 10 mm c) risers minus one
d) 12 mm d) risers plus three
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
Answer: c COMBINATIONS- CODE OF
Explanation: The part of the stairway that is PRACTICES AND
stepped on. It is constructed to the same
specifications (thickness) as any other SPECIFICATIONS - CONCEPT
flooring. The tread “depth” is measured from OF WORKING STRESS
the outer edge of the step to the vertical METHOD
om
“riser” between steps. The “width” is
measured from one side to the other. 1. Which of the following is correct criteria to
be considered while designing?
7. For initial estimate for a beam design, the
a) Structure should be aesthetically pleasing
width is assumed _____________
a) 1/15th of span but structurally unsafe
b) 1/10th of span b) Structure should be cheap in cost even
.c
c) 1/20th of span though it may be structurally unsafe
d) 1/30th of span c) Structure should be structurally safe but
less durable
Answer: d d) Structure should be adequately safe, should
ul
Explanation: Beams are traditionally have adequate serviceability
descriptions of building or civil engineering
Answer: d
structural elements, but any structures such as
Explanation: Structure should be designed
pa
automotive automobile frames, aircraft
components, machine frames, and other
mechanical or structural systems contain
such that it fulfils it intended purpose during
its lifetime and be adequately safe in terms of
strength, stability and structural integrity and
beam structures that are designed to carry
have adequate serviceability. Structure should
lateral loads are analyzed in a similar.
also be economically viable, aesthetically
jin
8. A foundation rests on _____________ pleasing and environment friendly.
a) base of the foundation
2. What is serviceability?
b) subgrade
a) It refers to condition when structure is not
c) foundation soil
usable
d) base of the foundation, subgrade and
.re
foundation soil b) It refers to services offered in the structure
c) It means that the structure should perform
Answer: d satisfactorily under different loads, without
Explanation: A foundation (or, more discomfort to user
commonly, base) is the element of an d) It means that structure should be
economically viable
w
architectural structure which connects it to the
ground, and transfers loads from the structure
to the ground. Foundations are generally Answer: c
Explanation: Serviceability is related to
considered either shallow or deep. Foundation
w
utility of structure. The structure should
engineering is the application of soil
perform satisfactorily under service loads,
mechanics and rock mechanics (Geotechnical
without discomfort to user due to excessive
engineering) in the design of foundation
deflection, cracking, vibration, etc. Other
w
elements of structures.
considerations of serviceability are durability,
impermeability, acoustic and thermal
TOPIC 1.3 TYPE OF LOADS ON insulation etc.
STRUCTURES AND LOAD
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
3. Analysis is referred to _____________ elastic analysis, (ii) plastic analysis, (iii)
a) determination of cost of structure advanced analysis, (iv) dynamic analysis.
b) determination of axial forces, bending
moment, shear force etc. 6. Which method is mainly adopted for
c) determination of factor of safety design of steel structures as per IS code?
d) drafting architectural plans and drawings a) Limit State Method
om
b) Working Stress Method
Answer: b c) Ultimate Load Method
Explanation: Analysis refers to d) Earthquake Load Method
determination of axial forces, bending
moment, shear force, torsional moments etc. Answer: a
acting on different members of structure due Explanation: Steel structures and their
to applied loads and their combinations. elements are normally designed by limit state
.c
method. When limit state method cannot be
4. The structure is statically indeterminate conveniently adopted, working stress method
when________________ may be used.
a) static equilibrium equations are insufficient
ul
for determining internal forces and reactions 7. Which IS code is used for general
on that structure construction of steel?
b) static equilibrium equations are sufficient a) IS 456
b) IS 256
on that structure
c) structure is economically viable
pa
for determining internal forces and reactions
c) IS 800
d) IS 100
d) structure is environment friendly
Answer: c
Answer: a Explanation: IS 800:2007 is the code of
jin
Explanation: When the static equilibrium practice for general construction in steel. It is
equations are insufficient for determining issued by Bureau of Indian Standards.
internal forces and reactions on that structure,
the structure is said to be statically 8. Which of the following relation is correct?
indeterminate. Analysis of these structures is a) Permissible Stress = Yield Stress x Factor
.re
complex and cannot be analysed only by of Safety
using laws of statics, various analytical b) Permissible Stress = Yield Stress / Factor
methods like slope deflection method, of Safety
moment distribution method, etc. c) Yield Stress = Permissible Stress / Factor
of Safety
w
5. Which of the following is one of the d) Permissible Stress = Yield Stress – Factor
methods of analysis prescribed in the code for of Safety
steel structures?
a) Hinge Analysis Answer: b
w
b) Limit Analysis Explanation: Permissible Stress = Yield
c) Roller Analysis Stress / Factor of Safety. Permissible Stress is
d) Dynamic Analysis the amount of stress that will not cause
w
failure. It is a fraction of yield stress. It takes
Answer: d care of overload or other unknown factors.
Explanation: Code suggests the use of any of
the following methods for steel structures : (i) 9. In Working Stress Method, which of the
following relation is correct?
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
a) Working Stress ≤ Permissible Stress Answer: c
b) Working Stress ≥ Permissible Stress Explanation: For framed structure, the main
c) Working Stress = Permissible Stress elements are beam, column, beam-column, tie
d) Working Stress > Permissible Stress and lattice members.
Answer: a 13. Which of the following are subjected to
om
Explanation: In Working Stress Method, both axial loads and bending moments?
Working Stress ≤ Permissible Stress. Each a) Beam-Column
member is checked for number of different b) Column
combinations of loadings. c) Lattice member
d) Beam
10. Arrange the following in ascending order
according to their factor of safety in working Answer: a
.c
stress method : Explanation: Beams are those elements
(i) tension members, (ii) long column, (iii) which are subjected to bending moments and
short column, (iv) connections shear force only. Columns are subjected to
a) i < ii < iii < iv axial loads. Beam-Column is subjected to
ul
b) i < iv < ii < iii axial load and bending moment. In special
c) i = iii < ii < iv cases, beams are subjected to torsional
d) iv = i < iii < ii pa moments.
Answer: c 14. How much percentage increase of
Explanation: In working stress method, the permissible stress is allowed when dead load,
factor of safety for the above are as follows : live load and wind load are considered
(i) for tension members = 1.67, (ii) for long together in working stress method?
column = 1.92, (iii) for short columns = 1.67, a) 50%
jin
(iv) for connections = 2.5-3. b) 33%
c) 40%
11. What is Load Factor? d) 60%
a) ratio of working load to ultimate load
b) product of working load and ultimate load Answer: b
.re
c) product of working load and factor of Explanation: In working stress method,
safety working stress ≤ permissible stress.
d) ratio of ultimate load to working load Stress due to dead load + live load ≤
permissible stress
Answer: d Stress due to dead load + wind load ≤
w
Explanation: Load Factor = working load / permissible stress
ultimate load. In ultimate load design, Stress due to dead load + live load + wind
different types of loads and load load ≤ 1.33 permissible stress.
combinations have different load factors
w
assigned.
TOPIC 1.4 ULTIMATE LOAD
12. Which of the following is not a main DESIGN AND LIMIT STATE
w
element of framed structure? DESIGN METHODS FOR RCC -
a) Beam OF CONCRETE AND
b) Column
c) Shear connector REINFORCING STEEL,
d) Lattice member ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
SINGLY REINFORCED Answer: a
RECTANGULAR BEAMS BY Explanation: Acceptable limits for safety and
serviceability requirements before failure
WORKING STRESS METHOD, occurs is called limit state. In Limit State
LIMIT STATE PHILOSOPHY AS design, structures are designed on the basis of
DETAILED IN IS CODE - safety against failure and are checked for
om
ADVANTAGES OF LIMIT STATE serviceability requirements.
METHOD OVER OTHER 3. Which of the following format is used in
METHODS, ANALYSIS AND limit state method?
DESIGN OF SINGLY AND a) Single safety factor
DOUBLY REINFORCED b) Multiple safety factor
c) Load factor
.c
RECTANGULAR BEAMS BY d) Wind factor
LIMIT STATE METHOD
Answer: b
Explanation: Limit state method uses
ul
1. Limit State Method is based on
_____________ multiple safety factor format that helps to
a) calculations on service load conditions provide adequate safety at ultimate loads and
alone pa adequate serviceability at service loads, by
b) calculations on ultimate load conditions considering all possible limit states. Multiple
alone safety factor format is also called partial
c) calculations at working loads and ultimate safety factor format.
loads
d) calculations on earthquake loads 4. Which of the following factors is included
in the limit state of strength?
jin
Answer: c a) Fire
Explanation: Working stress method is based b) Failure by excessive deformation
on calculations on service load conditions c) Corrosion
alone. Ultimate Strength method is based on d) Repairable damage or crack due to fatigue
.re
calculations on ultimate load conditions
alone. In Limit State method, safety at Answer: b
ultimate loads and serviceability at working Explanation: Limit state of strength are
loads are considered. prescribed to avoid collapse of structure
which may endanger safety of life and
2. What is limit state? property. It includes (i) loss of equilibrium of
w
a) Acceptable limits for safety and whole or part of structure, (ii) loss of stability
serviceability requirements before failure of structure as a whole or part of structure,
occurs (iii) failure by excessive deformation, (iv)
fracture due to fatigue , (v) brittle fracture.
w
b) Acceptable limits for safety and
serviceability requirements after failure
occurs 5. Which of the following factors is included
c) Acceptable limits for safety after failure in the limit state of serviceability?
w
occurs a) Brittle facture
d) Acceptable limits for serviceability after b) Fracture due to fatigue
failure occurs c) Failure by excessive deformation
d) Deformation and deflection adversely
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
affecting appearance or effective use of Answer: d
structure Explanation: Design Load = Partial factor of
safety x Characteristic Load.
Answer: d This partial safety factor accounts for
Explanation: Limit state of serviceability possibility of unfavourable deviation of load
includes (i) deformation and deflection from characteristic value, inaccurate
om
adversely affecting appearance or effective assessment of load, uncertainty in assessment
use of structure, (ii) vibrations in structure or of effects of load and in assessment of limit
any part of its compound limiting its state being considered.
functional effectiveness, (iii) repairable repair
or crack due to fatigue, (iv) corrosion, (v) 9. Which of the following relation is correct?
fire. a) Design Strength = Ultimate strength +
Partial factor of safety
.c
6. What is permanent action according to b) Design Strength = Ultimate strength –
classification of actions by IS code? Partial factor of safety
a) due to self weight c) Design Strength = Ultimate strength
b) due to construction and service stage loads /Partial factor of safety
ul
c) due to accidents d) Design Strength = Ultimate strength x
d) due to earthquake loads Partial factor of safety
Answer: a
pa
Explanation: Permanent actions are actions
due to self weight of structural and non
Answer: c
Explanation: Design Strength = Ultimate
strength /Partial factor of safety.
structural components, fittings, ancillaries, This partial safety factor accounts for
fixed equipments etc. possibility of unfavourable deviation of
material strength from characteristic value,
jin
7. What is variable action according to variation of member sizes, reduction in
classification of actions by IS code? member strength due to fabrication and
a) due to self weight tolerances and uncertainty in calculation of
b) due to accidents strength of members.
c) due to construction and service stage loads
.re
d) due to earthquake loads 10. Which of the following criteria is to be
satisfied in selection of member in limit state
Answer: c method?
Explanation: Variable actions are actions due a) Factored Load > Factored Strength
to construction and service stage loads such b) Factored Load ≤ Factored Strength
w
as imposed loads, wind loads, earthquake c) Factored Load ≥ Factored Strength
loads, etc. d) Sometimes Factored Load < Factored
Strength (or) Factored Load > Factored
8. Which of the following relation is correct? Strength
w
a) Design Load = Characteristic Load
b) Design Load = Characteristic Load + Answer: b
Partial factor of safety Explanation: Limit Sate method is also
w
c) Design Load = Characteristic Load / Partial known as load and resistance factor design.
factor of safety Load factors are applied to service loads and
d) Design Load = Characteristic Load x then theoretical strength of member is
Partial factor of safety reduced by application of resistance factor.
The criteria is to be satisfied in selection of
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
member in limit state method is factored load 1. In the case of composite sections, the
≤ factored strength. percentage of tensioned reinforcement is less
than?
11. The partial factor of safety for resistance a) Simple beams
governed by yielding is : b) Complex beams
a) 1.10 c) Tee beams
om
b) 1.5 d) Edge beams
c) 2.0
d) 1.25 Answer: a
Explanation: In case of composite sections
Answer: a the percentage of tensioned reinforcement is
Explanation: Partial factor of safety for less than that in most simple beams so that
resistance governed by yielding and the section is invariably under reinforced and
.c
resistance of member to buckling is 1.10. The the compression zone generally consists
loads are multiplied or resistances are divided entirely of insitu concrete of lower
by this factor to get design values. compressive strength, and the value of the
cube strength of concrete to be used in
ul
12. The partial factor of safety for resistance flexural strength equations will obviously be
governed by ultimate strength is : that of insitu cast concrete.
a) 1.10
b) 1.5
c) 2.0
d) 1.25
pa 2. If the compression zone contains part of
precast element, the computation is done by
considering?
a) Grades of concrete
Answer: d b) Cross section
Explanation: Partial factor of safety for c) Durability
jin
resistance governed by ultimate strength is d) Strength characteristics
1.25. Factors affecting ultimate strength are
stability, fatigue and plastic collapse. The Answer: b
loads are multiplied or resistances are divided Explanation: If the compression zone
by this factor to get design values. contains a part of precast element, the average
.re
compressive strength computed by
considering the cross sectional area of insitu
and precast concrete is used in the
computation of compressive force.
UNIT II DESIGN OF
w
BEAMS 3. The effective bonding between the two
parts of composite beams is developed by
_______________
TOPIC 2.1 ANALYSIS AND a) Smoothing
w
DESIGN OF FLANGED BEAMS b) Roughening
c) Painting
FOR - USE OF DESIGN AIDS d) Detacahing
FOR FLEXURE - BEHAVIOUR
w
OF RC MEMBERS IN SHEAR, Answer: b
BOND AND ANCHORAGE Explanation: Effective bending between the
two parts of a composite beam may be
developed by providing castellation in the
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
precast unit or by roughening the contact c) 1100mm
surface of the precast unit before placing the d) 900mm
insitu concrete or by projecting
reinforcements from the precast unit which Answer: a
serve as ahead connectors. Explanation: The ties consisting single bars,
multiple leg stirrups or vertical legs of welded
om
4. The design of shear connections depends face fabric should not have a spacing not
upon the strength of ____________ exceeding four times the least dimension of
a) Ex situ cast concrete the supported element nor 600mm whichever
b) In situ cast concrete is less the Indian standard code IS: 1343 does
c) Tampered concrete not make any specific recommendations
d) Prestressed concrete regarding the shear stresses in composite
sections.
.c
Answer: b
Explanation: In the design of shear 7. If the surface is rough tamped and without
connection it is generally assumed that the links to withstand a horizontal shear stress of
natural bond at the interface contributes a part 0.6n/mm2 and assuming the moduli of
ul
of the required shear resistance depending elasticity of precast and insitu cast concrete to
upon the strength of the insitu cast concrete be equal the centroid of the composite section
and the roughness of the precast element and
pa is located 110mm from the top of the slab,
any extra shear resistance over and above this second moment area of composite section is
should be provided by shear connectors.
2487×105mm4, calculate ultimate shearing
5. When ties are not provided the permissible resistance?
a) 14
values of the horizontal shear stress is?
b) 12
a) 0.6n/mm2
jin
c) 18
b) 4.6n/mm2 d) 21
c) 1.6n/mm2
Answer: b
d) 8.6n/mm2
Explanation: vu = ultimate shearing force, τ
.re
Answer: a = vus/ln, s= (350x30x95)mm3, b = 80mm, τ =
Explanation: The permissible values of the 0.6n/mm2, vu =
horizontal shear stress for different types of
contact surfaces is specified as: 0.6n/mm2 (0.6x2487x105x80/350x30x95) = 12000n =
when ties are not provided and the contact 12kn.
w
surface of the precast element is free of
8. Design ultimate horizontal shear stress
laitance and intentionally roughened to an
with nominal links and the contact surface are
amplitude of 5mm and 25n/mm2 when
as cast (assume τ = 1.2n/mm2)?
w
minimum vertical ties are provided and the
a) 15kn
contact surface is roughened to an amplitude
b) 23kn
of 5mm.
c) 12kn
w
6. The ties consisting of single bars and d) 24kn
multiple leg stirrups should have a spacing
Answer: d
not exceeding ____________
Explanation: The ultimate shear resistance is
a) 600mm
expressed as vu = (τlb/s) =
b) 400mm
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
(1.2x2487x105x80/350x30x95) = 24000n = modes and the design shear resistance should
24kn, τ = 1.2n/mm2. exceeded the ultimate shear due to the
transverse loads and if not, suitable transverse
reinforcements are designed to resist the
TOPIC 2.2 DESIGN balance shear force.
REQUIREMENTS AS PER
om
CURRENT CODE - BEHAVIOUR 3. Which type of shear reinforcement should
be provided for members with thin webs?
OF RECTANGULAR RC BEAMS a) Maximum shear reinforcement
IN SHEAR AND TORSION b) Minimum shear reinforcement
c) Nominal shear reinforcement
d) Tensile reinforcement
TOPIC 2.3 DESIGN OF RC
.c
MEMBERS FOR COMBINED Answer: c
BENDING, SHEAR AND Explanation: In members with thin webs
TORSION such as I and T sections nominal shear
reinforcements have to be provided to prevent
ul
cracking due to variations in temperature the
1. Which type of cables are advantages in provisions for design of shear reinforcements
reducing the effective shear? prescribed in British, American and Indian
a) Straight
b) Curved
c) Trapezoidal
pa standard have been dealt with in the case off
structural concrete members subjected to
torsion, shear stresses develop depending
d) Longitudinal upon the type of cross section and magnitude
of torque and the shear stresses in association
Answer: b
with the flexural stresses may give rise to
jin
Explanation: Curved cables are
principal tensile stress the value of which
advantageous in reducing the effective shear
when it exceeds tensile strength of the
and together with the horizontal compressive concrete results in the development of cracks
prestress, reduce the magnitude of the
on the surface of the member.
principal tension and the effect of shear is to
.re
induce tensile stresses on diagonal planes and 4. The pre and post tensioned members with
prestressing is beneficial since it reduces the bonded tendons bond stress between
magnitude of the principal tensile stress in ____________
concrete. a) Steel and concrete
b) Steel and water
2. The various codes recommend empirical
w
c) Steel and aggregates
relations to estimate ____________ d) Steel and plastic
a) Ultimate shear resistance
b) Ultimate torsional resistance Answer: a
w
c) Ultimate bending resistance Explanation: Pre tensioned or post tensioned
d) Ultimate load members with bonded tendons develop bond
stresses between steel and concrete when the
Answer: a
w
sections are subjected to transverse shear
Explanation: The various codes recommend forces due to the rate of change of moment
empirical relations to estimate the ultimate along length of the beam and in the case of
shear resistance of the section by considering type 1 and 2 members, which are uncracked
the flexure shear and web shear cracking at service loads, the flexural bond stresses
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
developed are computed by considering the (Abr/Apan) or 0.8 fci, fci = cube strength of
complete section. concrete at transfer, Abr= bearing area, Apan
= punching area.
5. In case of pre tensioned member, the
computations of transmission length are 8. The effective punching area Apun is
influenced by?
generally the contact area of ____________
om
a) Bond
b) Flexure a) Tendon device
c) Torsion b) Anchorage device
d) Tension c) Stress device
d) Strain device
Answer: a
Explanation: In the case of pre tensioned Answer: b
.c
members, the computations of the Explanation: The effective punching area is
transmission length at the ends is of practical generally the contact area of the anchoring
significance since the support positions are device and the bearing area is taken as the
influenced by bond and transmission length. maximum area of that portion of the member
ul
which is geometrically similar and concentric
6. When prestress is transferred to concrete to the effective punching area.
by means of external anchorages which
pressure is developed? 9. The end block of a beam has a rectangular
a) Bearing
b) Twisting
pa section 100mm wide by 200mm deep, the
force of cable is 200kn. Find the actual
c) Torsion bearing pressure?
d) Bent a) 30n/mm2
b) 40n/mm2
jin
Answer: a
c) 20n/mm2
Explanation: In the case of post tensioned
members where prestress is transferred to d) 10n/mm2
concrete by means of external anchorages, the
Answer: c
bearing pressures develop behind the
.re
Explanation: force of cable = 200kn, b =
anchorages have to be investigated and
100mm, d = 200mm
suitably controlled to prevent crushing failure
of the end block zone. Bearing area Abr = (100×100) = 10000mm2,
Actual bearing pressure = (200×103) / 10000
7. The bearing pressure on the concrete is
= 20n/mm2.
w
given as ____________
a) 0.4fci
10. The end block of a prestressed concrete
b) 0.8fci beam has a rectangular section; a cable
w
c) 0.12fci carrying a force of 200kn is to be anchored
d) 0.2fci against the end block at the centre if the cube
strength of concrete at transfer is 30n/mm2.
Design the maximum permissible bearing
w
Answer: b
Explanation: According to the Indian pressure?(Abr = 10000mm2)
standard code IS: 1343-1980, the permissible
unit bearing pressure on the concrete after a) 24n/mm2
allowing for all losses is limited to: 0.48fci b) 48n/mm2
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
c) 54n/mm2 order and the uninterrupted floor space is
d) 12n/mm22 desirable for which reason longer span
between the supporting elements are required.
Answer: a
Explanation: Assuming an anchor plate of 2. The precast prestressed hollow core slabs,
size 50mm by 50mm, punching area Apun = with or without topping is an important
om
structural element in __________
(50×50) = 2500mm2, Abr = 10000mm2, a) Structures
maximum permissible bearing pressure = b) Industries
0.48fci(Abr/Apun) or 0.8fci whichever is c) Aquariums
smaller, fb = 0.48x30x(10000/2500)1/2 = d) Nurseries
28.8n/mm2 or (0.8×30) = 24n/mm22. Answer: b
.c
Explanation: Precast prestressed hollow core
slabs, with or without topping are important
structural elements in industrialized and large
panel building construction and the slabs,
ul
UNIT III DESIGN OF produced on long casting beds using the
SLABS AND STAIRCASE pretensioning systems and cut to shorter
specified span lengths, are mainly used in one
TOPIC 3.1 ANALYSIS AND
DESIGN OF CANTILEVER, ONE
pa way floors which are freely supported by
transverse walls or base.
3. Prestressed pretensioned cored slabs with
WAY SIMPLY SUPPORTED AND differ types of cavities are widely used as
CONTINUOUS SLABS AND __________
jin
SUPPORTING BEAMS a) Floor panels
b) Tendons
c) Wall coatings
TOPIC 3.2 TWO WAY SLAB - d) Reinforcements
DESINGN OF SIMPLY
.re
SUPPORTED AND Answer: a
Explanation: Prestressed pretensioned cored
CONTINUOUS SLABS USING IS slabs with differ types of cavities are widely
CODE COEFFICIENTS used as Floor panels of civil and industrial
buildings in erstwhile U.S.S.R Graduck
w
1. The prestressed concrete slab systems are reports that these panels are produced in
ideally suited for __________ multiples of 200mm nominal width and
a) Roofs lengths from 3.6 to 6.4m and hollow panels of
b) Slabs oval cavity type are most economical for
w
c) Beam larger spans since they contain the least
d) Column volume of concrete as compared to round
cavity panels and prestressed concrete
w
Answer: b ribbons have been used as reinforcement for
Explanation: Prestressed concrete slabs hollow-cored slabs and these consist of
systems are ideally suited for floor and roof tensioned wires or strands embedded in high
construction of industrial buildings where the grade concrete of star of rectangular cross
live loads to base supported are of a higher section.
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
4. One way slabs may be supported across the principal directions of the slab and the slab
entire width of the slab by means of may be supported on masonry walls or beams
__________ and mayor may not be continuous over the
a) Columns supports and transverse loads are resisted by
b) Piers the development of two way slab action,
c) Ridges resulting in moments in longer and shorter
om
d) Footings span directions.
Answer: b 7. The moment coefficients derived from the
Explanation: One way slabs may be ultimate load method are generally lower in
supported across the entire width of the slab __________
by beams, piers or abutments or bearing a) Span
walls, which are positioned perpendicular to b) Eccentricity
.c
the longitudinal axis of the span or the c) Strength
supports may be at an angle of the span d) Magnitude
directions and one way slabs may be
continuous over one or several support. Answer: d
ul
Explanation: The moment coefficients
5. The simple or continuous slabs are derived from the ultimate load method are
analyzed for __________ pa generally lower in magnitude than those
a) Design foundation evaluated from elastic theories thus naturally
b) Design reinforcement resulting in savings in reinforcement and
c) Design moments however slabs designed by the ultimate load
d) Design slab method should be checked service loads
according to the principle of limit state
Answer: c design.
jin
Explanation: The simple or continuous slabs
are analyzed for design moments by 8. A simple prestressed flat slab is generally
considering a unit width of the slab and the supported by a network of __________
prestressing force and the eccentricity of the a) Beams
cable required at prominent sections to resist b) Columns
.re
the dead and live load moments are c) Spans
determined and the spacing of the cables or d) Deflections
wires fixed based on the availability of type
of tendon. Answer: b
Explanation: A simple prestressed flat slab is
w
6. The design of a two-way-slab supported on generally supported by a network of columns
all four sides involves the computation of without beams and prestressed in two
__________ perpendicular directions and the design of
a) Moments typical simple flat slab involves the analysis
w
b) Cross sections of moments in the two principal directions so
c) Bending moment that cables may be arranged to resist these
d) Deformations moments and the slab is analyzed as one way
w
slab and the total number of cables required
Answer: c to resist the moments in each of two principal
Explanation: The design of a two way slab directions are determined.
supported on all four sides involves the
computation of bending moment in the
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
9. The proportioning of tendons in design of step on. It is the horizontal portion. The
prestressed concrete simple flat slab between vertical distance between consecutive treads
the column and middle strips may be based is called the riser. It may or may not be
on __________ present (open stair effect).
a) Moments
b) Codes 2. The figure below represents a:
om
c) Deflections
d) Loads
Answer: b
Explanation: The column strips being stiffer
than the middle strips, a greater percentage of
the tendons are housed in the column strips
.c
and the proportioning of the tendons between a) Dog-legged stairs
the column and middle strips may be based b) Turning stairs
on the provisions of codes such as IS:456 and c) Straight stairs
BS:8110, where column strips share a higher d) Well stairs
ul
proportion of total moment.
Answer: a
10. The design principles of continuous flat Explanation: It is the most common stairs in
schools, houses, other buildings. The flights
a) One way slab
b) Two way slab
pa
slab floors are similar to __________
are at right angles.
c) Continuous 3. Baluster in a stair is the _________
d) Deformed member supporting _________
a) Horizontal, handrail
jin
Answer: b b) Vertical, landing
Explanation: The design of continuous flat c) Vertical, handrail
slab floors are similar to those of two way d) Horizontal, landing
reinforced concrete slabs and a strip of slab of
unit width continuous over supports is Answer: c
.re
analyzed as continuous beam and its Explanation: The baluster is usually wooden
prestressing results in secondary moments. or metallic. It is a vertical member provided
at specific intervals and is used to support the
handrail.
TOPIC 3.3 TYPES OF
STAIRCASES €“ DESIGN OF 4. How many types of stairs are there based
w
on the material?
DOG-LEGGED STAIRCASE
a) 4
b) 5
w
1. The vertical portion between each tread on c) 8
the stair is called: d) 6
a) Going
b) Nosing Answer: b
w
c) Winder Explanation: The five materials used in stairs
d) Riser are stone, metal, wood, R.C.C. and brick.
Answer: d 5. Speed of an escalator is usually:
Explanation: Tread is the place where we a) 10-20m/min
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
b) 30-45m/min 9. The decorative cap to the top of a newel
c) 40-50m/min post is called:
d) 25-30m/min a) Finial
b) Fillet
Answer: d c) Easing
Explanation: Escalators are electronically d) Apron
om
moving stairs. They can carry heavy traffic of
people. The speed is kept at a minimal of 25- Answer: a
30m/min so that people of all age groups can Explanation: Newel post is a large baluster
access it. used to anchor the handrail. It is usually given
a decorative cap to hold on to and is called a
6. The space housing the stairs is called: Finial.
a) Staircase
.c
b) Stair room 10. How many types of stone stairs are used?
c) Stair head a) 2
d) Stair space b) 5
c) 4
ul
Answer: a d) 3
Explanation: Staircase is also used to refer to
the stairs, handrail, balusters, other structures Answer: b
as a whole. The space housing and all these Explanation: These stairs are used in places
are also called staircase.
pa where durable and hard stones are available
locally. The five types are rectangular,
7. Which IS code gives details about wooden spandril, tread and riser, cantilevered tread
stairs? and built up steps.
a) IS 2634
jin
b) IS 2643 11. After how many stairs is a landing
c) IS 1634 provided in public, residential places?
d) IS 1643 a) 18
b) 20
Answer: c c) 12
.re
Explanation: IS 1634 gives the code of d) 16
practice for the design and construction of
wooden stairs for houses. Answer: c
Explanation: Generally, after 10 to 12 steps a
8. __________ stairs are a variation of L landing is to be provided. A person can
w
shaped stairs. comfortably walk 10-12 steps without getting
a) Winder exhausted. A landing can be given after a
b) Spiral maximum of 16 steps and not more than that.
c) Half turn A floor requires 2 flights.
w
d) Switch back
Answer: a
w
Explanation: L shaped stairs have a bend, at
90o usually. The bend is achieved by adding a UNIT IV DESIGN OF
flat landing at the bend transition point. In
winder stairs, instead of a flat landing, COLUMNS
triangle steps are provided.
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
ends
TOPIC 4.1 TYPES OF COLUMNS
Effectively held in position at
- AXIALLY LOADED COLUMNS
both ends but not restrained 1.00 × l
- DESIGN OF SHORT against rotation
RECTANGULA SQUARE AND
CIRCULAR COLUMNS 3. What is the minimum value of eccentricity
om
provided in columns?
a) 50 mm
TOPIC 4.2 DESIGN OF b) 20 mm
SLENDER COLUMNS - DESIGN c) 30 mm
FOR UNIAXIAL AND BIAXIAL d) 45 mm
BENDING USING COLUMN Answer: c
.c
CURVES Explanation: No column can have a perfectly
axial load. There may be some moments
1. Eccentrically loaded columns have to be acting due to imperfection of construction or
ul
designed for combined axial and ________ due to actual conditions of loading. Hence IS
a) Shear force 456 -2000, recommend eccentricity of 20
b) Bending moments mm.
c) Torsion
d) Creep
pa 4. The strength of the column with helical
reinforcement shall be ____ times the
strength of similar column with lateral ties.
Answer: b
Explanation: When the line of action of the a) 2.0
resultant force doesn’t coincide with the axis b) 1.05
jin
of centre of gravity then it is called c) 3
eccentrically loaded column. An eccentrically d) 1.5
loaded column has to be designed for
combined axial force and bending moments. Answer: b
Explanation: The strength of column with
.re
2. What is the recommended value of helical reinforcement Shall be 1.05 times the
effective length if the column is effectively strength of similar column with lateral ties,
held in position and fixed against rotation in provided the ratio of the volume of helical
both ends? reinforcement to the volume of the core shall
a) 0.8 l not be less than 0.36(Ag/Ak – 1) fck/fy.
b) 0.5 l
w
c) 0.65 l 5. The minimum diameter provided for the
d) 0.9 l longitudinal bars is ________
a) 15 mm
w
Answer: c b) 20 mm
Explanation: Effectively held in position and c) 12 mm
fixed against rotation in both ends is 0.65 l. d) 18 mm
w
Value of
Answer: c
End Positions Of a Column effective
Explanation: The minimum diameter of the
length
longitudinal bars provided in the column is 12
Effectively held in position and 0.65 × l mm and the spacing of longitudinal bars
fixed against rotation in both
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
measured along the periphery of the column 9. Which of the following reservoirs is also
shall not exceed 300 mm. known as ___________
a) Ground service reservoirs
6. What is the minimum number of b) Elevated reservoirs
longitudinal bars provided in the rectangular c) Over head reservoirs
column? d) Storey reservoirs
om
a) 4
b) 5 Answer: a
c) 6 Explanation: Ground service reservoirs are
d) 8 constructed at ground level and mainly used
to store water. They are generally constructed
Answer: a with masonry (or) RCC slab. These are also
Explanation: According to IS 456-2000, known as surface reservoirs or not elevated
.c
clause 26.5.3, the minimum number of reservoirs.
longitudinal bars to be provided is 4 for
rectangular columns and the minimum 10. A system in which water is supplied only
number of longitudinal bars to be provided for fixed few hours, such system is called
ul
for circular columns is 6. ____
a) Closed
7. The ends of ________ shall be properly b) Intermittent
anchored.
a) Longitudinal reinforcement
b) Transverse reinforcement
pa c) Combined
d) Lift
c) Torsional reinforcement Answer: b
d) Shear reinforcement Explanation: In the intermittent system, the
water is supplied only for a few hours the
jin
Answer: b system is adopted when adequate water from
Explanation: The effective lateral support is the source is not available. The system is
given by transverse reinforcement either in widely adopted by much local water authority
the form of circular rings or by lateral ties. it is functioned through phases.
The ends of transverse reinforcement shall be
.re
properly anchored. 11. In ___________ system, air relief valves
are not required.
8. For longitudinal reinforcing bar, the a) Gravity
nominal cover should not be less than b) Intermittent
___________ c) Continuous
w
a) 30 mm d) Grid
b) 20 mm
c) 40 mm Answer: c
d) 50 mm Explanation: In the continuous system, the
w
supply of water is 24 hours a day. This is the
Answer: c most ideal system and is adopted when plenty
Explanation: According to IS 456-2000, of water is available. As the water doesn’t get
w
clause 26.4.2.1, the nominal cover for contaminated and circulating at uniform
longitudinal reinforcing bars in any case shall pressure, air relief valves are not required
not be less than 40 mm or less than the essentially.
diameter of such bar.
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
12. Which of the following is one of the b) Principle of moments
layouts of distribution systems? c) Principle of points
a) Dual system d) Theory of couple
b) Gravity system
c) Grid Iron system Answer: b
d) Pressure system Explanation: Varignon’s theorem states that
om
“the moment of a force about any point is
Answer: c equal to the sum of moments of the
Explanation: In grid iron systems, there are components about the same point”. This
no dead ends hence stagnation of water and principle is also known as the principle of
its consequences are eliminated. The water is moments.
kept in good circulation due to the absence of R.r = P.p + Q.c
dead ends. The system is suitable for well Where P, Q are forces and R is resultant.
.c
planned towns. “c” is the perpendicular distance of Q.
13. Which of the following system is also
known as an interlaced system?
ul
a) Tree system
b) Grid iron system UNIT V DESIGN OF
c) Circle system
d) Radial system
pa FOOTINGS
Answer: b TOPIC 5.1 CONCEPTS OF
Explanation: Grid iron system is an
improvement over the tree system. In the
PROPORTIONING FOOTINGS
system, the mains, sub lines and branches are AND FOUNDATIONS BASED ON
jin
interconnected with each other. This system is SOIL PROPERTIES
also known as interlaced or reticulation
system. 1. Foundations can be broadly classified
under __________
14. Which of the following is also known as a
.re
a) Shallow foundation and Deep foundation
ring system?
b) Pile foundation
a) Circle
c) None of the mentioned
b) Reticulation
d) All of the mentioned
c) Radial
d) Interlaced Answer: a
w
Explanation: Foundations may be broadly
Answer: a
classified under two heads: shallow
Explanation: In a circle system, the entire
foundations and deep foundations.
locality is divided into either rectangular (or)
w
circular blocks. The water mains are laid 2. A foundation is said to be shallow if its
along the peripheral roads with sub mains depth is ________ than its width.
branching out from mains. This system is also a) Equal to and Less than
w
known as ring system. b) Greater than
c) None of the mentioned
15. Varignon’s theorem is called as
d) All of the mentioned
_________
a) Principle of Forces
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
Answer: a 6. Once the pressure distribution is known
Explanation: According to Terzaghi, a ___________ in the reinforced concrete
foundation is shallow if its depth is equal to footing can be calculated.
or less than its width. In the case of deep a) Bending moment and Shear force
foundations, the depth is equal to or greater b) Bearing pressure
than the width. c) None of the mentioned
om
d) All of the mentioned
3. which of the following, is a type of shallow
footing? Answer: a
a) Spread footing Explanation: Knowing the pressure
b) Pile foundation distribution is known, the bending moment
c) Pier foundation and shear force can be calculated, and the
d) Well foundation thickness of the structural member of the
.c
member can be calculated using properties of
Answer: a reinforced concrete.
Explanation: The shallow foundations are of
the following types: spread footing (or simple 7. In conventional design, allowable bearing
ul
footing), strap footing, combined footing, and capacity should be taken smaller than which
mat footing or raft footing. of the following value?
a) Safe bearing capacity and Allowable
4. Which of the below is the most commonly
used shallow foundation?
a) Strap footing
pa bearing pressure
b) The pressure intensities beneath the footing
c) None of the mentioned
b) Spread footing d) All of the mentioned
c) Combined footing
d) Raft footing Answer: a
jin
Explanation: In conventional design, the
Answer: b allowable bearing capacity should be taken as
Explanation: In spread footing, load is the smaller of the following two values: i) the
transmitted through an isolated column or safe bearing capacity based on ultimate
wall to the subsoil; hence this is most capacity, and ii) the allowable bearing
.re
common type of foundation. pressure on tolerable settlement.
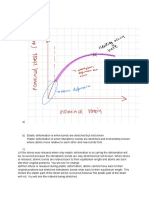
5. The pressure intensity beneath the footing 8. In cohesive soil, the pressure distribution
depends upon ___________ beneath the footing is ___________
a) Rigidity of the footing a) Linear
w
b) Soil type b) Non linear
c) Condition of soil c) Zero
d) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned
w
Answer: d Answer: a
Explanation: Both from observations as well Explanation: When a footing rests on
as the analytical studies from elasticity, it is cohesive soil, the edge stresses may be very
w
known that the pressure distribution beneath large, but the pressure distribution may be
footing is not uniform and it depends on the considered to be linear.
rigidity of footing, the soil type, and the
condition of the soil. 9. When do strap footings are used in
foundation?
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
a) To transfer load of an isolated column centimetres, m = safe modulus of rupture of
b) Distance between the columns are long concrete mix, q = net soil bearing pressure.
c) Two column loads are unequal
d) All of the mentioned 2. If the wall or column under construction is
near some other property, it will not be
Answer: b possible to spread the footing to both the
om
Explanation: A strap footing may be used sides of War or column. In search case which
where the distance between the columns is so footing is used?
great that the combined trapezoidal footing a) Simple pad footing
becomes quite narrow, with a high bending b) Eccentric footing
moment. c) Isolated footing
d) Reinforced footing
10. When two column loads are unequal,
.c
which of the possible footing can be Answer: b
provided? Explanation: Normally, the footing are so
a) Strap footing designed and proportion that the centre of
b) Raft footing gravity of the superimposed load coincides
ul
c) Trapezoidal combined footing with the CG of the base area, so that the
d) Mat footing footing is subjected to concentric loading,
resulting in uniform bearing pressure.
Answer: c
pa
Explanation: When the two columns load are
unequal, with the outer column carrying a
However, it may not be possible to do so and
hence eccentric loading footings are applied.
heavier load, and when there is space 3. Identify the given footing below.
limitation beyond the outer column, a
trapezoidal footing is provided.
jin
TOPIC 5.2 DESIGN OF WALL
FOOTING
.re
1. The formula d=a×√(3q)/m is used to
calculate _________
a) Depth of soil
b) Height of column a) Strip footing
c) Depth of concrete bed block b) Combine footing
w
d) Height of footing c) Reinforced footing
d) Isolated footing
Answer: c
Explanation: The depth of concrete bed Answer: a
w
block depends upon the type of concrete, the Explanation: A strip footing is the one that
projection of block and the soil bearing provides a continuous longitudinal bearing.
pressure. It is found on the basis of the Thus, a spread footing for a continuous wall
w
bending moment imposed on it, and on the is called a strip footing. The above given
basis of safe modulus of rupture. Here, d = diagram shows two types of strip footings for
depth of concrete block in metre, a = a wall- i) Simple strip footing without
projection beyond the masonry face in masonry offset and
ii) Strip footing with masonry offset.
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
4. Identify the given footing below. 6. Identify the given footing below.
om
a) Continuous footing
b) Cantilever footing
c) Strip footing
d) Combine footing
.c
Answer: b
a) Simple pad footing
Explanation: A cantilever footing consist in
b) Steeped footing
an eccentric footing for the exterior column,
ul
c) Strip footing
the concentric footing for the interior column
d) Stepped pad footing
and a strap or a cantilever beam joining these
two footing as shown in the given figure
pa Answer: d
above.
Explanation: If the column load is more, or if
the safe bearing pressure of soil is less, the
5. Identify the given footing below.
base area found by equation b+2a and hence
there is a use of stepped pad footing instead
of simple pad footing.
jin
7. Identify the type of foundation below.
a) Cantilever footing
.re
b) Continuous footing
c) Strip footing
d) Pad footing
Answer: b
w
Explanation: In this type of construction, the a) Wall footing
footings of two or three adjacent columns are b) Combine footing
made continuous by providing beans between c) Grillage footing
the successive footings as shown in the above d) Strap footing
w
given figure. This type of construction is
cheaper than raft foundations and it is Answer: c
adopted to avoid differential or uneven Explanation: The grillage Foundation is a
w
settlement of the structure. special type of isolated footing, generally
provided for heavily loaded steel, specially in
those location where bearing capacity of soil
is poor.
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
8. Which type of footing is applicable when LOADED SQUARE,
the wall carries light loads or when the safe RECTANGULAR PAD AND
bearing pressure is very high?
a) Simple strip footing SLOPED FOOTINGS
b) Stepped footing
c) Simple pad footing 1. Eccentrically loaded columns have to be
om
d) Eccentric footing designed for combined axial and ________
a) Shear force
Answer: a b) Bending moments
Explanation: In this case, the width of the c) Torsion
footing would be very low. In this type of d) Creep
footing, the wall directly rests on the concrete
base and no masonry offset are provided Answer: b
.c
since spread is not required. Explanation: When the line of action of the
resultant force doesn’t coincide with the axis
9. The shape of combined footing is mostly of centre of gravity then it is called
___________ eccentrically loaded column. An eccentrically
ul
a) Rectangular loaded column has to be designed for
b) Square combined axial force and bending moments.
c) Circular pa
d) Trapezoidal 2. What is the recommended value of
effective length if the column is effectively
Answer: d held in position and fixed against rotation in
Explanation: The shape of the combined both ends?
footing should be so selected that the centres a) 0.8 l
of gravity of the column loads of soil reaction b) 0.5 l
jin
remains in the same vertical line. Usually a c) 0.65 l
rectangular or a trapezoidal shape is selected. d) 0.9 l
10. A spread footing for a single column is Answer: c
known as the __________ Explanation: Effectively held in position and
.re
a) Isolated footing fixed against rotation in both ends is 0.65 l.
b) Combine footing Value of
c) Strip footing End Positions Of a Column effective
d) Eccentric footing length
Effectively held in position and
w
Answer: a
Explanation: A spread footing for a single fixed against rotation in both 0.65 × l
column is either known as the isolated footing ends
or pad footing. The base area of such a Effectively held in position at
w
footing is given by A = P/q where P is the both ends but not restrained 1.00 × l
total load transmitted by the column, against rotation
including that of the footing and q is the safe
w
bearing pressure for the soil. 3. What is the minimum value of eccentricity
provided in columns?
a) 50 mm
TOPIC 5.3 DESIGN OF AXIALLY b) 20 mm
AND ECCENTRICALLY
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
c) 30 mm Answer: a
d) 45 mm Explanation: According to IS 456-2000,
clause 26.5.3, the minimum number of
Answer: c longitudinal bars to be provided is 4 for
Explanation: No column can have a perfectly rectangular columns and the minimum
axial load. There may be some moments number of longitudinal bars to be provided
om
acting due to imperfection of construction or for circular columns is 6.
due to actual conditions of loading. Hence IS
456 -2000, recommend eccentricity of 20 7. The ends of ________ shall be properly
mm. anchored.
a) Longitudinal reinforcement
4. The strength of the column with helical b) Transverse reinforcement
reinforcement shall be ____ times the c) Torsional reinforcement
.c
strength of similar column with lateral ties. d) Shear reinforcement
a) 2.0
b) 1.05 Answer: b
c) 3 Explanation: The effective lateral support is
ul
d) 1.5 given by transverse reinforcement either in
the form of circular rings or by lateral ties.
Answer: b The ends of transverse reinforcement shall be
Explanation: The strength of column with
pa
helical reinforcement Shall be 1.05 times the
strength of similar column with lateral ties,
properly anchored.
8. For longitudinal reinforcing bar, the
provided the ratio of the volume of helical nominal cover should not be less than
reinforcement to the volume of the core shall ___________
not be less than 0.36(Ag/Ak – 1) fck/fy. a) 30 mm
jin
b) 20 mm
5. The minimum diameter provided for the c) 40 mm
longitudinal bars is ________ d) 50 mm
a) 15 mm
b) 20 mm Answer: c
.re
c) 12 mm Explanation: According to IS 456-2000,
d) 18 mm clause 26.4.2.1, the nominal cover for
longitudinal reinforcing bars in any case shall
Answer: c not be less than 40 mm or less than the
Explanation: The minimum diameter of the diameter of such bar.
w
longitudinal bars provided in the column is 12
mm and the spacing of longitudinal bars 9. Which of the following reservoirs is also
measured along the periphery of the column known as ___________
shall not exceed 300 mm. a) Ground service reservoirs
w
b) Elevated reservoirs
6. What is the minimum number of c) Over head reservoirs
longitudinal bars provided in the rectangular d) Storey reservoirs
w
column?
a) 4 Answer: a
b) 5 Explanation: Ground service reservoirs are
c) 6 constructed at ground level and mainly used
d) 8 to store water. They are generally constructed
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
with masonry (or) RCC slab. These are also dead ends. The system is suitable for well
known as surface reservoirs or not elevated planned towns.
reservoirs.
13. Which of the following system is also
10. A system in which water is supplied only known as an interlaced system?
for fixed few hours, such system is called a) Tree system
om
____ b) Grid iron system
a) Closed c) Circle system
b) Intermittent d) Radial system
c) Combined
d) Lift Answer: b
Explanation: Grid iron system is an
Answer: b improvement over the tree system. In the
.c
Explanation: In the intermittent system, the system, the mains, sub lines and branches are
water is supplied only for a few hours the interconnected with each other. This system is
system is adopted when adequate water from also known as interlaced or reticulation
the source is not available. The system is system.
ul
widely adopted by much local water authority
it is functioned through phases. 14. Which of the following is also known as a
ring system?
11. In ___________ system, air relief valves a) Circle
are not required.
a) Gravity
pa b) Reticulation
c) Radial
b) Intermittent d) Interlaced
c) Continuous
d) Grid Answer: a
jin
Explanation: In a circle system, the entire
Answer: c locality is divided into either rectangular (or)
Explanation: In the continuous system, the circular blocks. The water mains are laid
supply of water is 24 hours a day. This is the along the peripheral roads with sub mains
most ideal system and is adopted when plenty branching out from mains. This system is also
.re
of water is available. As the water doesn’t get known as ring system.
contaminated and circulating at uniform
pressure, air relief valves are not required 15. Varignon’s theorem is called as
essentially. _________
a) Principle of Forces
w
12. Which of the following is one of the b) Principle of moments
layouts of distribution systems? c) Principle of points
a) Dual system d) Theory of couple
b) Gravity system
w
c) Grid Iron system Answer: b
d) Pressure system Explanation: Varignon’s theorem states that
“the moment of a force about any point is
w
Answer: c equal to the sum of moments of the
Explanation: In grid iron systems, there are components about the same point”. This
no dead ends hence stagnation of water and principle is also known as the principle of
its consequences are eliminated. The water is moments.
kept in good circulation due to the absence of R.r = P.p + Q.c
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
Where P, Q are forces and R is resultant. in contact with soil, and thus does not transfer
“c” is the perpendicular distance of Q. any pressure to the soil.
4. When the allowable soil is low or the
TOPIC 5.4 DESIGN OF building loads are heavy, the footing used is
COMBINED RECTANGULAR ___________
om
FOOTING FOR TWO COLUMNS a) Raft footing
ONLY b) Strap footing
c) Trapezoidal combined footing
d) Rectangular combined footing
1. The design of rigid rectangular combined
footing consist in determining the Answer: a
____________ Explanation: When the allowable soil
.c
a) Pressure distribution pressure is low, or the building loads are
b) Location of center of gravity of column heavy, the use of spread footings would cover
c) Shear force more than one-half of the area and it may
d) Safe bearing pressure prove more economical to use mat or raft
ul
foundation.
Answer: b
Explanation: The design of rigid rectangular 5. If the resultant of the soil pressure
footing consists in determining the location of coincides with the resultant of the loads, the
pa
center of gravity of the column loads and
using length and width dimension such that
soil is pressure is assumed to be
____________
centroid of footing and the center of gravity a) Non-uniformly
of columns loads coincide. b) Uniformly distributed
c) Zero
jin
2. If the independent spread footing of two d) None of the mentioned
columns are connected by a beam, it is called
___________ Answer: b
a) Combined footing Explanation: If the resultant of the soil
b) Trapezoidal combined footing pressure coincides with the resultant of the
.re
c) Strap footing loads and the center of gravity of the footing,
d) Raft footing the soil pressure is assumed to be uniformly
distributed.
Answer: c
Explanation: In strap footing, two 6. In designing rectangular combined footing
independent columns are supported by as trap
w
_________ should be adopted as the design
or beam at the bottom. value.
a) Stress distribution
3. Which of the following condition is true b) Compression index
w
regarding the transfer of load from strap to c) Maximum bending moment
soil, used in strap footing? d) Safe bearing pressure
a) Transfer load to soil
b) Does not transfer load to soil
w
Answer: c
c) Partially transfer to load Explanation: The maximum bending
d) None of the mentioned moment should be adopted as the design
value for the reinforced concrete rectangular
Answer: b
Explanation: The strap used does not remain
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
www.rejinpaul.com
footing, which should also be checked for 9. The design procedure of strap footing is
maximum shear and bond etc. essentially that of _____________
a) Direct method
7. For a rectangular combined footing, x̅ is b) Trial and error method
given as ___________ c) Graphical method
a) x̅ = L/2 d) None of the mentioned
om
b) L/3 < x̅ < L/2
c) x̅ = L/3 Answer: b
d) None of the mentioned Explanation: The designing of strap or
cantilever footing is based on trial and error
Answer: a method, it begins with a trial value of e so
Explanation: For a rectangular combined that the length L1 is known. The calculations
footing, x̅ = L/2 and for a trapezoidal are repeated with another value of e till values
.c
combined footing solutions lies between the of the reactions R1 and R2 calculated by both
limits L/3 < x̅ < L/2. the procedure, coincide.
8. Generally combined footing is assumed to 10. What will be the shape of footing if a=0,
ul
rest on ___________ is substituted in the pressure intensity
a) Cohesive soil equation “q2 = a. qs”?
b) Homogeneous soil a) Rectangular
c) Cohesion-less soil
d) Non homogeneous soil
pa b) Triangular
c) Trapezoidal
d) Circular
Answer: b
Explanation: It is assumed that the combined Answer: b
footings are rigid and rests on a homogeneous Explanation: In the pressure intensity
jin
soil, so as to give rise to a linear stress equation q2 = a. qs, if a= 0 we have a triangle
distribution on the bottom of the footing. with x̅ = L/3.
.re
w
w
w
Downloaded updated materials from Rejinpaul Network App
You might also like
- Machine Design TermsDocument301 pagesMachine Design Termsitsmechelle100% (1)
- Elementary Design of Structures Notes PDFDocument53 pagesElementary Design of Structures Notes PDFAsiimwe Moses Kasirika100% (7)
- MCQ DosDocument17 pagesMCQ DosMuqeetNo ratings yet
- Ch-27.7 Alloying Element of Steel and Alloy SteelDocument51 pagesCh-27.7 Alloying Element of Steel and Alloy SteelSmruti Ranjan PattanayakNo ratings yet
- CE3050 Tutorial01 2023Document2 pagesCE3050 Tutorial01 2023rockbottom 123No ratings yet
- CV1013 - Tutorial On SteelDocument22 pagesCV1013 - Tutorial On SteelAsh KongNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structures: Concert Hall in Downtown LosDocument15 pagesDesign of Steel Structures: Concert Hall in Downtown LosKEN ADAMSNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection, Steels Multi - Choice Question Paper (MFY-007)Document7 pagesWelding Inspection, Steels Multi - Choice Question Paper (MFY-007)Moses_JakkalaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Materials and Processes Interview Questions and Answers For Experienced - SanfoundryDocument6 pagesAerospace Materials and Processes Interview Questions and Answers For Experienced - SanfoundrySample UseNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Materials and Processes Interview Questions and Answers For Experienced - SanfoundryDocument6 pagesAerospace Materials and Processes Interview Questions and Answers For Experienced - SanfoundrySample UseNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy For Non Metallurgist Work Shop - Module 3 QuestionsDocument2 pagesMetallurgy For Non Metallurgist Work Shop - Module 3 QuestionsCheeragNo ratings yet
- 1p2 2013 14 Materials Examples Paper 6Document5 pages1p2 2013 14 Materials Examples Paper 6davidsmith24026No ratings yet
- 12-0-2016 Cpi, Equip - Plant Design-QuestionaireDocument3 pages12-0-2016 Cpi, Equip - Plant Design-QuestionaireShania Caroline CanaoNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions122Document75 pagesInterview Questions122Sai GnanadeepNo ratings yet
- ME 461 FirstExam-Fall 2015Document7 pagesME 461 FirstExam-Fall 2015JaneNo ratings yet
- Ces 2Document6 pagesCes 2LegendaryNNo ratings yet
- Mats 1192Document3 pagesMats 1192Valentine CherryNo ratings yet
- Behavior of High-Nickel Type Weathering Steel Bars in Simulated Pore Solution and Mortar Under Chloride-Containing EnvironmentDocument12 pagesBehavior of High-Nickel Type Weathering Steel Bars in Simulated Pore Solution and Mortar Under Chloride-Containing EnvironmentagungbasNo ratings yet
- Course Objective... : 111101: Introduction To Engineering Materials (Fall-2020) Instructor: Dr. Ibrahim Qazi, Prof & HodDocument10 pagesCourse Objective... : 111101: Introduction To Engineering Materials (Fall-2020) Instructor: Dr. Ibrahim Qazi, Prof & HodAaila AkhterNo ratings yet
- Material Properties: (ESE - 1992) (ESE - 1992)Document121 pagesMaterial Properties: (ESE - 1992) (ESE - 1992)Sanket ManeNo ratings yet
- Oml 751-Tom MCQDocument21 pagesOml 751-Tom MCQVijay KanthNo ratings yet
- Cast Irons - Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument6 pagesCast Irons - Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Questions and Answers - SanfoundrySample UseNo ratings yet
- Ces 1Document5 pagesCes 1p2703936No ratings yet
- 9-Metals, Strengthening and Corrosion Practice Problems SolutionsDocument7 pages9-Metals, Strengthening and Corrosion Practice Problems Solutionsandrescasas850No ratings yet
- Chapter01Mat SienceDocument28 pagesChapter01Mat Sienceahmed abdel8nyNo ratings yet
- Course Material: Required TextDocument11 pagesCourse Material: Required TextmakhsanulfikriNo ratings yet
- Edigcse Aap sc15.15wDocument2 pagesEdigcse Aap sc15.15wHassan EL ACHEKNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Material SelectionDocument6 pagesTest 2 Material Selectionsilent spritsNo ratings yet
- Properties of SteelDocument14 pagesProperties of SteelSIDDIQUI HasmataliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CorrosionDocument2 pagesTutorial CorrosionSana chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Super Austenitic Sainless SteelDocument20 pagesEvolution of Super Austenitic Sainless SteelMidhun K ChandraboseNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions For RevisionDocument19 pagesSample Questions For Revisionsaidinho489No ratings yet
- INS Lecture 2019 - DrMoreDocument71 pagesINS Lecture 2019 - DrMorepritamNo ratings yet
- SPH1209200605 Engineering MaterialsDocument3 pagesSPH1209200605 Engineering Materialsc1ee5686f5No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument37 pagesDocumentpriya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Full Reportholo KuloDocument60 pagesFull Reportholo KuloRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 AltDocument11 pagesChapter 01 AltIlija BozovicNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument4 pagesSample QuestionsISHITA SINGH 20BCE10971No ratings yet
- You Would Object When You See Manual Metal Arc ElectrodesDocument9 pagesYou Would Object When You See Manual Metal Arc ElectrodeshailhNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Bab 8 Pengelasan Baja Tahan Karat (Part A)Document13 pages2020 - Bab 8 Pengelasan Baja Tahan Karat (Part A)Febri AndriyudaNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Wear Behavior of Austempered Ductile Iron With Niobium AdditionsDocument8 pagesAbrasive Wear Behavior of Austempered Ductile Iron With Niobium AdditionsEverton CostaNo ratings yet
- Material Science ExamDocument1 pageMaterial Science ExamRaymond Yabut100% (1)
- CES 1 DMU Effect of Carbon Content On Properties of Plain Carbon SteelsDocument6 pagesCES 1 DMU Effect of Carbon Content On Properties of Plain Carbon SteelsShakbullahNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and Metallurgy Interview Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument4 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgy Interview Questions and Answers - SanfoundrySample UseNo ratings yet
- Metals: Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesMetals: Review QuestionsKhaled ShaabanNo ratings yet
- MISIF - SS Corrosion and How To Stop It 23 MayDocument66 pagesMISIF - SS Corrosion and How To Stop It 23 Maycelalkeskiner94No ratings yet
- RCC Conceptual Q PDFDocument11 pagesRCC Conceptual Q PDFAakash rajNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction - 1Document42 pages01 - Introduction - 1TanvirH.ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- QU MSR AWI 1 Rev7Document8 pagesQU MSR AWI 1 Rev7Benny Bustomi100% (1)
- CH 11Document55 pagesCH 11Anuj shuklaNo ratings yet
- PDF of MCQDocument26 pagesPDF of MCQSamadhan SawantNo ratings yet
- Effect of Alloying Elements Rev.03 (Ahmed Nabi)Document4 pagesEffect of Alloying Elements Rev.03 (Ahmed Nabi)Harry AnsariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 IntroductionDocument25 pagesChapter 01 IntroductionDeni Fajar FitriyanaNo ratings yet
- Ch-27.4 Plain Carbon SteelDocument11 pagesCh-27.4 Plain Carbon SteelManish Kumar MehtaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Stainlesssteel WeldingDocument90 pagesGuidelines For Stainlesssteel Weldingquiron2010No ratings yet
- MME291 TermFinalQues 09-15Document20 pagesMME291 TermFinalQues 09-15behind mirrorNo ratings yet
- Casting Steel Alloys PDFDocument6 pagesCasting Steel Alloys PDFIAmaeyNo ratings yet
- Effects of Chromium Content and Impact Load On Microstructures and Properties of High Manganese SteelDocument5 pagesEffects of Chromium Content and Impact Load On Microstructures and Properties of High Manganese SteelemadsabriNo ratings yet
- GEEN 3024 Practice Exam 2Document12 pagesGEEN 3024 Practice Exam 2ChristinaNo ratings yet
- List of Political Parties ParticipatedDocument3 pagesList of Political Parties ParticipatedSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- Kishu Inu: WhitepaperDocument11 pagesKishu Inu: WhitepaperSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- Bhartiya Janata PartyDocument2 pagesBhartiya Janata PartySundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- Instapdf - in Cosmetic Items List 639Document9 pagesInstapdf - in Cosmetic Items List 639Sundar Ganesh100% (1)
- Chennai - 25: Part - A Part - B & CDocument2 pagesChennai - 25: Part - A Part - B & CSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- Form 20 - Final Result Sheet - Part - I: No. of Valid Votes Cast in Favour ofDocument4 pagesForm 20 - Final Result Sheet - Part - I: No. of Valid Votes Cast in Favour ofSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- 01ai0604 Block Chain 1Document3 pages01ai0604 Block Chain 1Sundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument2 pagesReferenceSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- Ews Format 4Document2 pagesEws Format 4Sundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- English Record Sem 4-Pages-DeletedDocument36 pagesEnglish Record Sem 4-Pages-DeletedSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- List of Polling Stations For 226 Assembly Segment Within The 38 Parliamentary ConstituencyDocument98 pagesList of Polling Stations For 226 Assembly Segment Within The 38 Parliamentary ConstituencySundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- 8 Pillars TPM .Document2 pages8 Pillars TPM .Sundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- MA8353 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations MCQ - by LearnEngineering - inDocument11 pagesMA8353 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations MCQ - by LearnEngineering - inSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- EDC 2 Marks All Five UnitsDocument31 pagesEDC 2 Marks All Five UnitsSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- ME8451-MT-II - by WWW - LearnEngineering.inDocument102 pagesME8451-MT-II - by WWW - LearnEngineering.inSundar GaneshNo ratings yet
- Panjab University, Chandigarh-160014 (India) (Estd. Under The Panjab University Act VII of 1947-Enacted by The Govt. of India)Document175 pagesPanjab University, Chandigarh-160014 (India) (Estd. Under The Panjab University Act VII of 1947-Enacted by The Govt. of India)Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamentals of MetalworkingDocument50 pages01 - Fundamentals of MetalworkingriyamondalNo ratings yet
- TECHNOLOGY2 Solve Answer-1Document7 pagesTECHNOLOGY2 Solve Answer-1JlkKumarNo ratings yet
- Failure in MaterialsDocument28 pagesFailure in MaterialsNafisa AnikaNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics, Schreus, 2012 PDFDocument162 pagesFracture Mechanics, Schreus, 2012 PDFCarlos HernandezNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 4: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument5 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 4: Back of Chapter QuestionsMubashir RazaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties and Identification Markings For Threaded Fasteners PDFDocument96 pagesMechanical Properties and Identification Markings For Threaded Fasteners PDFRichard QuimboNo ratings yet
- 01-Pet Eng Design - PTE - 470 - IntroductionDocument30 pages01-Pet Eng Design - PTE - 470 - IntroductionHassan KhalifeNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Mechanics of Material .Document8 pagesLab 2 Mechanics of Material .Nec LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Fatigue 2010Document40 pagesFatigue 2010GazeNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior of Metals Lab ManualDocument33 pagesMechanical Behavior of Metals Lab ManualSaumya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Cswip 3.0 PDFDocument4 pagesCswip 3.0 PDFKianToro YeoNo ratings yet
- Subsize Charpy V SpecimenDocument8 pagesSubsize Charpy V SpecimennooneoveroneNo ratings yet
- Ductility by ChinnarajuDocument76 pagesDuctility by ChinnarajuRamen KishoreNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 1 Es9Document3 pagesUnit Test 1 Es9Micko AllanigueNo ratings yet
- Ijias 14 153 05 PDFDocument8 pagesIjias 14 153 05 PDFSaba SohailNo ratings yet
- Unidad N°8 MATERIALSDocument10 pagesUnidad N°8 MATERIALSFelipeNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis For Endineering MaterialsDocument18 pagesFailure Analysis For Endineering MaterialsArielle Joyce de JesusNo ratings yet
- 11mark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Correct Answer To Each of The Following QuestionsDocument6 pages11mark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Correct Answer To Each of The Following QuestionsDuong Nguyen TrieuNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 MSC Material Science SyllabusDocument51 pages1.1.1 MSC Material Science SyllabussanjeevchsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6-Metals & Non-MetalsDocument8 pagesUnit 6-Metals & Non-MetalsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Is 3024 2006 PDFDocument24 pagesIs 3024 2006 PDFAbhishek sahaNo ratings yet
- MDSP T19Document100 pagesMDSP T19Arnz BibosoNo ratings yet
- Belmont Lesson Plan Template: That Make Up MatterDocument4 pagesBelmont Lesson Plan Template: That Make Up Matterapi-251950318No ratings yet
- My Presentation..Document14 pagesMy Presentation..merlin otemakumiNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument16 pagesMetallic Bondingmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- Gearless Transmission System MD-08Document20 pagesGearless Transmission System MD-08Sameer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Brittle Fracture The Cold Hard Facts Vern Ragle FinalDocument42 pagesBrittle Fracture The Cold Hard Facts Vern Ragle FinalCharle MathewNo ratings yet
- SBVL Assignment2Document4 pagesSBVL Assignment2Nam PhuongNo ratings yet