Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydroxide: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search
Uploaded by
IAN2130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Hydroen
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesHydroxide: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search
Uploaded by
IAN213Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
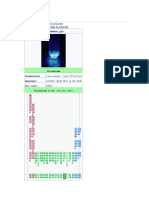
Hydroxide
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigationJump to search
Hydroxide
Names
Systematic IUPAC name
Hydroxide
Identifiers
CAS Number 14280-30-9
3D model (JSmol) Interactive image
ChEBI CHEBI:16234
ChemSpider 936
PubChem CID 961
UNII 9159UV381P
show
InChI
show
SMILES
Properties
Chemical formula OH−
−1
Molar mass 17.007 g·mol
Conjugate acid Water
Conjugate base Oxide anion
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in
their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH . It consists of
−
an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and
carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor
constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and
a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in
aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a
multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The
corresponding electrically neutral compound HO is the hydroxyl radical. The
•
corresponding covalently bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxy group.
Hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts
in organic chemistry.
Many inorganic substances which bear the word hydroxide in their names are
not ionic compounds of the hydroxide ion, but covalent compounds which
contain hydroxy groups.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EinstienniumDocument4 pagesEinstienniumIAN213No ratings yet
- Oxygen O2: 1structuresDocument3 pagesOxygen O2: 1structuresIAN213No ratings yet
- CobaltDocument4 pagesCobaltIAN213No ratings yet
- Unit 2: MeiosisDocument38 pagesUnit 2: MeiosisIAN213No ratings yet
- Different Types of MediaDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of MediaIAN213No ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Resistors in Direct Circuits ObjectivesDocument5 pagesSeries and Parallel Resistors in Direct Circuits ObjectivesIAN213No ratings yet
- Arsenal Football Club Is A Professional: ForbesDocument1 pageArsenal Football Club Is A Professional: ForbesIAN213No ratings yet
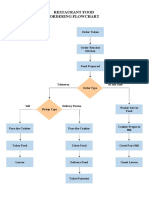
- Restaurant Food Ordering FlowchartDocument1 pageRestaurant Food Ordering FlowchartIAN213No ratings yet