Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MS Must Study Questions 2020
Uploaded by
Logesh Govind0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views3 pagesOriginal Title
MS Must study Questions 2020
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views3 pagesMS Must Study Questions 2020
Uploaded by
Logesh GovindCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
SRI MANAKULA VINAYAGAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE
I-B.TECH / SEMESTER – II / MATERIAL SCIENCE
UNIT-I
2 Marks Questions
1. Define Primitive cell and unit cell.
2. Define bravais Lattice and space Lattice.
3. Define Atomic radius and coordination number.
4. What is meant by Atomic packing factor?
5. What are Miller indices?
6. Why X-rays are used for crystal diffraction studies?
7. What is the relation between lattice parameter and inter planar distance?
8. Name the various defects occurs in crystalline solids.
9. What are Frenkal and Schottky defects?
10. What is Burger vector.
5 Marks Questions
1. Prove that the atomic packing factor for FCC and HCP are equal.
2. What are miller indices? Explain how they are determined.
3. Explain point defects with appropriate diagrams.
4. Show that HCP structure demands an axial (c/a) ratio of 1.633.
5. Determine atomic radius and packing factor for FCC structure.
6. Explain screw and edge dislocation of crystal imperfection.
11 Marks Questions
1. Explain with a Neat sketch the unit cell structure, coordination number, atomic radius and APF
for FCC and HCP crystal systems.
2. What are Bravais Lattice? Draw the Unit cell and specify the lattice parameters for them.
3. Explain the Powder diffraction method for crystal structure determination. Mention their
advantages and disadvantages.
4. Explain briefly about a) Point defect b) Line defect c) Surface defect and d) Volume defect.
UNIT-II
2 Marks Questions
1. Define dielectric polarization.
2. What is dielectric strength?
3. What is polarization vector?
4. Define dielectric Susceptibility.
5. Define orientational polarization.
6. What is Ionic polarization?
7. Explain the temperature dependence of dielectric polarization.
8. Explain dielectric loss and loss tangent.
9. What is meant by internal field or local field in a dielectric material?
10. What are active and passive dielectrics?
11. Define Ferro electric materials. List down their importance.
12. What are pyroelectric and Piezo electric materials? Give examples.
5 Marks Questions
1. Derive an expression for electronic and ionic polarizabilities.
2. Explain the effect of frequency and temperature on polarization of dielectrics.
3. Derive an expression for local field or internal field in the dielectric for a cubic structure.
4. Deduce Clausius-Mosotti relation from local field or internal field.
11 Marks Questions
1. Explain different types of polarization mechanism in dielectric materials and hence deduce
Langevin Debye equation.
2. Derive an expression to find the internal field in a Dielectric material hence deduces Clausius-
Mosotti relation.
3. Explain Schering bridge method to measure dielectric constant.
4. Explain in details piezoelectric, ferroelectric and pyroelectric materials with their applications.
UNIT-III
2 Marks Questions
1. Define Magnetic susceptibility.
2. What is Bohr magneton?
3. What are diamagnetic materials? Give example.
4. Define Curie Weiss law.
5. Define Hysteresis loss or eddy current loss.
6. What are Retentivity and Coercivity?
7. Define energy product.
8. Distinguish hard and soft magnetic materials.
9. What are reversible and irreversible domains?
10. What are ferrites? Give Examples.
5 Marks Questions
1. Briefly explain the different types of energy involved in domain growth.
2. Discuss the Hysteresis in ferromagnetic materials.
3. Briefly explain the structure of ferrites.
4. Explain magnetic recording and readout of data in floppy disc.
11 Marks Questions
1. Write an essay about different types of magnetic materials.
2. Derive the expression for Curie Weiss law based on quantum theory of Ferro magnetic
materials.
3. Explain domain theory of Ferro magnetic materials on the basis of Hysteresis.
4. What are Ferrites? Explain their structure, properties and applications.
5. Explain the construction and working of CD ROM and MO recording systems.
UNIT-IV
2 Marks Questions
1. List down the properties of Semiconductors.
2. What is meant by operating temperature of a semiconductor?
3. Define Hall Effect and Hall voltage.
4. Write down the importance of Hall coefficient.
5. Define Super conductivity.
6. What is meant by transition temperature or critical temperature?
7. Define critical field (Hc) and critical current(Ic).
8. What is meant by Meissner effect?
9. Define persistence current.
10. What are High temperature superconductors? Give example.
11. What are elemental and compound semiconductors?
5 Marks Questions
1. Explain the properties of superconductors.
2. What are high Tc superconductors? Briefly explain 123 superconductors.
3. Describe Type I and Type II superconductors.
4. Explain the applications of hall effect.
11 Marks Questions
1. Derive an expression to find the intrinsic charge carrier concentration.
2. Derive the expression for Hall coefficient and also explain the determination of Hall voltage
experimentally.
3. What are Type-I and Type-II Superconductors Give Example also explain how their
magnetization varies with applied field.
4. What are High temperatures Superconductors? Explain the structure, Synthesis, properties and
applications of 123 superconductors.
UNIT-V
2 Marks Questions
1. What are the Characteristics of LCD?
2. What are liquid crystals?
3. What are Metallic Glasses? List their Properties.
4. How do nano materials differ from macro materials?
5. What is meant by nano phase materials?
6. What are one, two and three dimensional nano materials? Give Examples.
7. What are the different structures found in carbon nano tubes?
8. What are Shape memory alloys? Name their two different phases.
9. Define pseudo elastic and super elastic behavior of SMA.
10. Write any four applications of SMA.
5 Marks Questions
1. What are metallic glasses and how are they prepared?
2. Describe the properties of metallic glasses.
3. What are liquid crystals? Explain in detail the working of dynamic scattering and twisted nematic
liquid crystal display
4. Explain the synthesis of nanomaterials by nanolithography.
5. Explain Ball milling, PVD and CVD for synthesis of nanomaterials.
11 Marks Questions
1. Explain the two different display methods of LCD.
2. What are the different types of metallic glasses? Explain the Melt spinning technique for metallic
glasses also list down their properties and applications.
3. What are Carbon Nano tubes? Explain the Synthesis, properties and applications of CNT.
4. Explain the two different phase transformations in SMA. Also menthion the properties and
applications of SMA.
You might also like
- Crystal Structure and Defects GuideDocument14 pagesCrystal Structure and Defects GuideLogesh GovindNo ratings yet
- M-II Correction Version 1 and 3Document1 pageM-II Correction Version 1 and 3Logesh GovindNo ratings yet
- 1 CorrectedDocument9 pages1 CorrectedLogesh GovindNo ratings yet
- 2 - Biodiversity CorrectedDocument5 pages2 - Biodiversity CorrectedLogesh GovindNo ratings yet
- 2 - Ecosystem CorrectedDocument4 pages2 - Ecosystem CorrectedLogesh GovindNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Catalogo Secadores Spray - GEA (Niro)Document9 pagesCatalogo Secadores Spray - GEA (Niro)San ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Physics Particle Model DensityDocument23 pagesPhysics Particle Model DensityFloNo ratings yet
- PP, PE, PVC, POM, PET, PA6G material characteristicsDocument1 pagePP, PE, PVC, POM, PET, PA6G material characteristicsandytuorNo ratings yet
- Structural data for wet well designDocument328 pagesStructural data for wet well designHarsh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- OrcaManual 2 8 0.finalDocument489 pagesOrcaManual 2 8 0.finalLei LiuNo ratings yet
- Vibrations of Two Degree SystemsDocument28 pagesVibrations of Two Degree SystemsKautilyaChennaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On The Optimum Cold Forging PDocument72 pagesCase Study On The Optimum Cold Forging PSa RaNo ratings yet
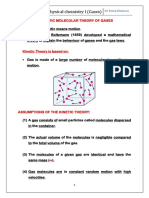
- Physical Chemistry I (Gases) : Maxwell and Boltzmann (1859) Developed A MathematicalDocument51 pagesPhysical Chemistry I (Gases) : Maxwell and Boltzmann (1859) Developed A MathematicalDina GaranNo ratings yet
- CFX Particle TransportDocument3 pagesCFX Particle Transportirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- 21 A-Classical-Perturbation-Technique-Which-Is-Valid-For-Large-Parameters PDFDocument4 pages21 A-Classical-Perturbation-Technique-Which-Is-Valid-For-Large-Parameters PDFAnonymous zXVPi2PlyNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Academic QualificationsDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Academic QualificationswongsosoegaliNo ratings yet
- RCD Assignment 5Document4 pagesRCD Assignment 5CE-Cret KuyaaDeeeNo ratings yet
- Ageing of Zinc Alloys: January 2011Document23 pagesAgeing of Zinc Alloys: January 2011Alicia Jara ChavezNo ratings yet
- Hydrotest Procedure For Pressure VesselDocument7 pagesHydrotest Procedure For Pressure Vesselvijay vickyNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation PresentationDocument110 pagesPile Foundation Presentationmujeebtalib100% (4)
- ANSYS Theory Reference For The Mechanical APDL and Mechanical Applications R13 PDFDocument0 pagesANSYS Theory Reference For The Mechanical APDL and Mechanical Applications R13 PDFfrancisco_gil_510% (1)
- Computer Lab (Example Problems For SAP2000 v9)Document9 pagesComputer Lab (Example Problems For SAP2000 v9)deepak_karna_1No ratings yet
- Manual de V6A60-BDocument38 pagesManual de V6A60-BLuis Romero100% (1)
- Tutorial 2 Solutions ECE 318Document3 pagesTutorial 2 Solutions ECE 318Tomas SmithNo ratings yet
- Guide To Whitford Industrial Products: 9th Edition - 2010Document42 pagesGuide To Whitford Industrial Products: 9th Edition - 2010cristianoluzNo ratings yet
- Van Der Lans - Parameters On Nitrogen OxideDocument29 pagesVan Der Lans - Parameters On Nitrogen OxideNelson RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 2 Transparency Worksheet .Document8 pagesPhysics Chapter 2 Transparency Worksheet .Olalekan OyekunleNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 - Adsorption Isotherm CalculationsDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 - Adsorption Isotherm CalculationsMariana Pegrucci33% (3)
- RCD NSCP 2010-2001 by Edison FloranteDocument369 pagesRCD NSCP 2010-2001 by Edison FlorantesallyNo ratings yet
- An Intuitive Guide To Physics (IoP, 2000) (324s) - PPopDocument324 pagesAn Intuitive Guide To Physics (IoP, 2000) (324s) - PPopRaden AsmoroNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Shell and Helical Coil Heat Exchanger For Hot and Cold Fluid Flowing Fe2O3 Nanofluid With Water As Its Base by Using CFDDocument5 pagesSimulation of Shell and Helical Coil Heat Exchanger For Hot and Cold Fluid Flowing Fe2O3 Nanofluid With Water As Its Base by Using CFDBhukya Naveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Determine Material Property (PSG Data Book Page No 1.9 & 1.5)Document28 pagesDetermine Material Property (PSG Data Book Page No 1.9 & 1.5)Sagarias Albus100% (1)
- Newton Laws of Motion and Friction - DPP 03 - (Arjuna NEET 3.0 2023)Document3 pagesNewton Laws of Motion and Friction - DPP 03 - (Arjuna NEET 3.0 2023)lakshyabanwani873No ratings yet
- Schroedinger EssayDocument19 pagesSchroedinger EssayMark MoodyNo ratings yet
- Transport 252525252BPhenomena 252525252B 252525252B 252525252BIntroDocument54 pagesTransport 252525252BPhenomena 252525252B 252525252B 252525252BIntrocoolkanna100% (1)