Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sentence With Multiple Clauses
Sentence With Multiple Clauses
Uploaded by
Bintang PermanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sentence With Multiple Clauses
Sentence With Multiple Clauses
Uploaded by
Bintang PermanaCopyright:
Available Formats
II.
SENTENCES WITH MULTIPLE CLAUSES
1. Use Coordinate Connectors Correctly
Many sentences in English have more than one clause.
Clause is a group of words containing a subject and a verb.
When we have two clauses in an English sentence, we must connect the two clauses correctly.
One way to connect two clauses is to use and, but, or, so, yet between the clauses.
Example:
Tom is singing and Paul is dancing.
Tom is tall, but Paul is short.
Tom must write the letter, or Paul will do it.
Tom told a joke, so Paul laughed.
Tom is tired, yet he is not going to sleep.
The following chart lists the coordinate connectors and the sentence pattern used with them :
Coordinate Connectors: and, but, or, so, yet
S V Coordinate connector S V
She laughed, but she wanted to cry
2. Use Adverb Time and Cause Connectors Correctly
Sentences with adverb clauses have two basic patterns in English.
Example:
I will sign the check before you leave.
Before you leave, I will sign the check.
The following chart list adverb time and cause connectors and the sentence patterns used with them :
Adverb Time and Cause Connectors
Time Cause
after as soon as once When as now that
as before since whenever because since
as long as by the time until while inasmuch as
S V adverb connector S V
Teresa went inside because it was raining
adverb connector S V S V
Because it was raining, Teresa went inside
3. Use Other Adverb Connectors Correctly
Adverb clauses not only can express the ideas of time and cause, but also can express contrast,
condition, manner, and place.
Example:
I will leave at 7:00 if I am ready.
Although I was late, I managed to catch the train.
The following chart lists the adverb contrast, condition, manner, and place connectors and the
sentence patterns used with them :
Other Adverb Connectors
Condition Contrast Manner Place
if although as where
in case even though in that wherever
provided though
providing while
unless whereas
whether
S V adverb connector S V
Bob went to school even though he felt sick.
adverb connector S V, S V
Even though Bob felt sick, he went to school.
III. MORE SENTENCES WITH MULTIPLE CLAUSES
Use Noun Clause Connectors Correctly
A noun clause is a clause that functions as a noun.
Because the noun clause is a noun, it is used in a sentence as either an object of a verb, an
object of a preposition, or the subject of the sentence.
Example:
I know when he will arrive ( Noun Clause as object of verb )
I am concerned about when he will arrive ( NC as object of prep. )
When he will arrive is not important ( Noun Clause as subject )
The following chart lists the noun connectors and the sentence patterns used with them:
Noun Clause Connectors Examples
what, when, where, why, S V Noun connector S V
how
whatever, whenever
whether, if
I know what you did
that
Noun connector S V V
What you did was wrong
Noun clause connectors were used to introduce noun subject clauses or noun object clauses
Use Noun Clause Connector / Subjects Correctly
In some cases a noun clause connector is not just a connector; a noun clause connector can also be the
subject of the clause at the same time.
Example:
I do not know what is in the box. à NC as object of verb
We are concerned about who will do the work à NC as object of preposition
Whoever is coming to the party must bring a gift à NC as subject
The following chart lists the noun clause connector / subjects and the sentence patterns used with
them :
Noun clause connector/subject : who what which
whoever whatever whichever
S V Noun connector/subject V
I know what happened
Noun connector/subject V V
What happened was great
Use Adjective Clause Connectors Correctly
An adjective clause is a clause that describes a noun.
Because the clause is an adjective, it is positioned directly after the noun that it describes.
Example:
The woman is filling the glass that she put on the table.
The glass that she put on the table contains milk.
The following chart lists the adjective clause connectors and the sentence patterns used with them :
Adjective Clause Connectors
Who/Whom which that
for people for things for people or things
S V adjective connector S V
I like the book which you recommended
S adjective connectors S V V
The book which you recommended was
interesting
Use Adjective Clause Connector / Subjects Correctly
*In some cases an adjective clause connector is not just a connector
*An adjective clause connector can also be the subject of the clause at the same time.
Example:
The woman is filling the glass that is on the table.
The glass that is on the table contains milk.
The following chart lists the adjective clause connector / subjects and the sentence patterns used with
them :
Adjective Clause Connector / Subjects
who Which that
(for people) (for things) (for people or things)
S V adjective connector/subject V
She needs a secretary who types fast
S adjective connector/subject V V
A secretary who types fast is invaluable
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Showboat - History and SignificanceDocument6 pagesShowboat - History and SignificanceJohnny Watt100% (3)
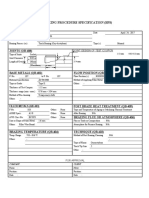
- Brazing Procedure Specification (BPS) : JOINTS (QB-408)Document1 pageBrazing Procedure Specification (BPS) : JOINTS (QB-408)Bernard PenuliarNo ratings yet
- Tests AudioscriptsDocument6 pagesTests AudioscriptsVANo ratings yet
- Stage2412 DMX Manual-EnDocument36 pagesStage2412 DMX Manual-Enisasro1458No ratings yet
- Ant Grassapher FO-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesAnt Grassapher FO-WPS OfficeRey DesolocNo ratings yet
- EU PresentationDocument34 pagesEU PresentationJulieBDavis100% (2)
- English ActivitiesDocument3 pagesEnglish ActivitiesPAOLA BOLIVARNo ratings yet
- RIGHT TO BAIL Case DoctrinesDocument37 pagesRIGHT TO BAIL Case DoctrinesEileen MañiboNo ratings yet
- Xin Yi Liu He Quan and Strengthening The BodyDocument53 pagesXin Yi Liu He Quan and Strengthening The BodyMiguelin666100% (2)
- CRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument4 pagesCRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 1 - IntroductionMoke Fetane AmboNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pie RecipeDocument2 pagesChicken Pie RecipeMichelleNo ratings yet
- Kim Seol Hee, 2019, The Effects of Orofacial Myofunctional Training On The PDFDocument9 pagesKim Seol Hee, 2019, The Effects of Orofacial Myofunctional Training On The PDFSerina Cahya NabilahNo ratings yet
- EM 1110-1-3500 31 Jan 95: B. Chemical Grouting. Chemical Grouting Is TheDocument3 pagesEM 1110-1-3500 31 Jan 95: B. Chemical Grouting. Chemical Grouting Is TheChetan SabadraNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature On Investment Behaviour of InvestorsDocument7 pagesReview of Literature On Investment Behaviour of Investorsc5jxjm5mNo ratings yet
- LG LAVADORA FH496TDAD - MFL68585950-Spain PDFDocument45 pagesLG LAVADORA FH496TDAD - MFL68585950-Spain PDFA Eugenio RiosNo ratings yet
- X33J Plus enDocument2 pagesX33J Plus enMornstar MornstarNo ratings yet
- SvobodaCartwright MummyPortraitsDocument197 pagesSvobodaCartwright MummyPortraitsAgustín DiezNo ratings yet
- XII Computer Science MCQDocument352 pagesXII Computer Science MCQshivansh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Report - Smart Irrigation SystemDocument32 pagesReport - Smart Irrigation SystemKani mozhiNo ratings yet
- Acer Aspire 1700 Quanta Dt1 - WWW - Cursodeportatil.esDocument35 pagesAcer Aspire 1700 Quanta Dt1 - WWW - Cursodeportatil.esWilgen GarciaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods Lectures Universi-53-60Document8 pagesFinite Element Methods Lectures Universi-53-60Muhammad WahyuNo ratings yet
- 9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2007 Question PaperDocument8 pages9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2007 Question PapercheekybuoiNo ratings yet
- IJICRDocument6 pagesIJICRrkkoiriNo ratings yet
- LDCUREB FORM 2C Study Protocol Assessment FormDocument6 pagesLDCUREB FORM 2C Study Protocol Assessment FormHareen “areshapesgay-” AdlaonNo ratings yet
- Shaping The Panama Canal by Blasting - Pacific Complex's WorksDocument10 pagesShaping The Panama Canal by Blasting - Pacific Complex's WorksMulti Nitrotama KimiaNo ratings yet
- DMM GW Istek GDM-8261A-manual PDFDocument230 pagesDMM GW Istek GDM-8261A-manual PDFDycki RizqiNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Cultural Existence Practically Disappears in Its Own HomeDocument1 pageIndonesian Cultural Existence Practically Disappears in Its Own HomeArman SalamNo ratings yet
- Tau Planters CatalogDocument25 pagesTau Planters CatalogSantosh BastolaNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 2Document38 pages07 Chapter 2arunsethuramNo ratings yet
- Audio-Lingual Method (Assignment)Document13 pagesAudio-Lingual Method (Assignment)Lisa Kwan100% (12)