Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcohol Phenol Ethers
Alcohol Phenol Ethers
Uploaded by
Ganesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document contains notes from a Grade 12 Chemistry class on November 11th, 2021. It discusses aspirin uses such as reducing fever and relieving mild to moderate pain. It also discusses reactions involving the cleavage of a carbon-oxygen bond, including reactions of alcohols with hydrogen halides to form alkyl halides, and the dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes. The mechanism of alcohol dehydration is outlined in three steps: formation of a protonated alcohol, formation of a carbocation, and elimination of a proton to form an alkene.
Original Description:
Original Title
Alcohol phenol ethers (10)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains notes from a Grade 12 Chemistry class on November 11th, 2021. It discusses aspirin uses such as reducing fever and relieving mild to moderate pain. It also discusses reactions involving the cleavage of a carbon-oxygen bond, including reactions of alcohols with hydrogen halides to form alkyl halides, and the dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes. The mechanism of alcohol dehydration is outlined in three steps: formation of a protonated alcohol, formation of a carbocation, and elimination of a proton to form an alkene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesAlcohol Phenol Ethers
Alcohol Phenol Ethers
Uploaded by
GaneshThis document contains notes from a Grade 12 Chemistry class on November 11th, 2021. It discusses aspirin uses such as reducing fever and relieving mild to moderate pain. It also discusses reactions involving the cleavage of a carbon-oxygen bond, including reactions of alcohols with hydrogen halides to form alkyl halides, and the dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes. The mechanism of alcohol dehydration is outlined in three steps: formation of a protonated alcohol, formation of a carbocation, and elimination of a proton to form an alkene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Grade 12
Chemistry cw on 11/11/21
ASPIRIN USES
Aspirin is used to reduce fever (antipyretic) and relieve mild to moderate pain from conditions
such as muscle aches, toothaches, common cold, and headache (analgesic). It may also be
used to reduce pain and swelling in conditions such as arthritis. Aspirin is known as a
salicylate and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
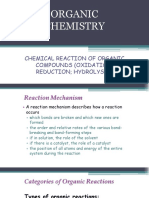
REACTIONS INVOLVING CLEAVAGE OF C–O BOND
• The reactions involving cleavage of C–O bond take place only in alcohols.
• Phenols show this type of reaction only with zinc.
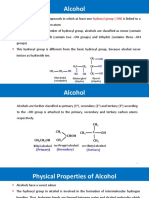
1. Reaction with hydrogen halides:
• Alcohols react with hydrogen halides to form alkyl halides.
ROH + HX → R–X + H2O
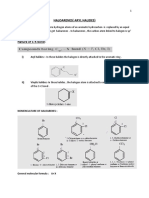
(Lucas test):
• Alcohols are soluble in Lucas reagent (conc. HCl and ZnCl2) while their halides
are immiscible and produce turbidity in solution.
• In case of tertiary alcohols, turbidity is produced immediately as they form the halides
easily.
• Primary alcohols do not produce turbidity at room temperature
•
2. Dehydration:
• Alcohols undergo dehydration (removal of a molecule of water) to form alkenes on
treating with a protic acid
e.g., Concentrated H2SO4 or H3PO4, or catalysts such as anhydrous zinc chloride or
alumina .
• Ethanol undergoes dehydration by heating it with concentrated H2SO4 at 443 K.
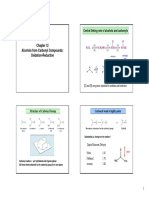
MECHANISM
Step 1:Formation of protonated alcohol.
Step 2:Formation of carbocation: It is the slowest step and hence, the rate determining step of
the reaction.
Step 3:Formation of ethene by elimination of a proton
You might also like
- 11acyl Halideisrael Jude P.Document16 pages11acyl Halideisrael Jude P.Angelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Alcoholes 2Document31 pagesAlcoholes 2Moisés ChucNo ratings yet
- Alcoholes 2Document31 pagesAlcoholes 2Moisés ChucNo ratings yet
- Alcoholes 2Document31 pagesAlcoholes 2Alfredo TlapaleNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundDocument37 pagesHydroxy CompoundZuhailimuna MudaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document42 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Gloria NumpaqueNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument11 pagesAlcoholsJeneava ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Dehydration: Alcohols, Ethers, and ThiolsDocument3 pagesDehydration: Alcohols, Ethers, and ThiolsPaul Alfred SoNo ratings yet
- Study of Mechanism & Application of Name Reaction: Ozonolysis Michael Addition ReactionDocument19 pagesStudy of Mechanism & Application of Name Reaction: Ozonolysis Michael Addition ReactionSanket koreNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument42 pagesAlcoholSubhankar basakNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document53 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry,: Chapter 9 and 12 Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides Oxidation - ReductionDocument26 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Chapter 9 and 12 Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides Oxidation - Reductionsyaripatul haniNo ratings yet
- Distinguish TestDocument1 pageDistinguish TestAnsia MeenazNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 3Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3GundanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols LabDocument7 pagesAlcohols Lab7sky7harveyNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument11 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersSandeepNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Ethers CHM457Document51 pagesAlcohols and Ethers CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- The Alchemy of Alcohols:: A Beginner's Guide in Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesThe Alchemy of Alcohols:: A Beginner's Guide in Organic ChemistrypentojochaunceyNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument25 pagesAlcoholKING RAFINo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Reactions of Alcohol (Compatibility Mode)Document13 pagesChapter 11 - Reactions of Alcohol (Compatibility Mode)Billy HoNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument81 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethersjjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocument5 pagesAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document6 pagesChap 4Doris KimNo ratings yet
- Aldehid Dan KetonDocument31 pagesAldehid Dan KetonchobbhNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 1Document13 pagesAlcohols 1Suresh VedpathakNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- 8 Alcohols-2 and EthersDocument24 pages8 Alcohols-2 and EthersNova sounds - No copyright musicNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions PPT AlcoholsDocument43 pagesOrganic Reactions PPT Alcoholssmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Unit 11 Alcohols Ethers Thiols UST Template 1Document31 pagesUnit 11 Alcohols Ethers Thiols UST Template 1Daniel BalubalNo ratings yet
- Alcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsDocument12 pagesAlcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsAmihanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsDocument102 pagesChapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsCute ni LeynesNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Phenols FinalDocument45 pagesAlcohols and Phenols Finalmalikchandkhokhar2211No ratings yet
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDocument41 pagesHasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDEEBANNo ratings yet
- Actinide SeparationDocument35 pagesActinide SeparationZain MSDNo ratings yet
- A - Topic 07 - Acids Bases and SaltsDocument48 pagesA - Topic 07 - Acids Bases and SaltsMuhammad Dzul Akrom Nasaruddin (Manjusriss)No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes & Haloarenes ISC 23-24Document71 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenes ISC 23-24jjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- Lecture. 13,14,15 PDFDocument45 pagesLecture. 13,14,15 PDFsarah100% (1)
- KD 2 (Pertemuan 5-6) PDFDocument93 pagesKD 2 (Pertemuan 5-6) PDFMaulana SaktiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 1630993189Document56 pagesAlcohols 1630993189Sahisa MahatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04mauDocument24 pagesChapter 04maunoor awshanNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of AlcoholDocument4 pagesPhysical Properties of AlcoholrhiNo ratings yet
- Name - Shivpoojan Singh Course-B.Sc (Hon.) Maths ROLL NO - 202110203110008Document17 pagesName - Shivpoojan Singh Course-B.Sc (Hon.) Maths ROLL NO - 202110203110008Siddhant PatelNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersDocument57 pagesCh-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersBhavishya VermaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1Document93 pagesAldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1jjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Document16 pages3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Vergil HashimotoNo ratings yet
- Haloarenes (Aryl Halides)Document11 pagesHaloarenes (Aryl Halides)A BeheraNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument9 pagesHydroxy Compoundschong56No ratings yet
- Reduction Reactions: N-Oxides Sulphoxides S-S C-CDocument41 pagesReduction Reactions: N-Oxides Sulphoxides S-S C-CEmad MustafaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 11. Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - NotesDocument17 pagesUNIT - 11. Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - NotesAngelina DaisyNo ratings yet
- Updated Grade 12 Organic Name Reactions-Units 10,11,12,13Document10 pagesUpdated Grade 12 Organic Name Reactions-Units 10,11,12,13Tanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aldehidi I KetoniDocument24 pagesAldehidi I KetoniunknownNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument5 pagesAldehydes and KetonesFlorence Lynn BaisacNo ratings yet
- Concepts & Connections: Fifth Edition by Charles H. CorwinDocument45 pagesConcepts & Connections: Fifth Edition by Charles H. CorwinMarcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument55 pagesChapter OneJihad OmarNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument17 pagesOxidation Reductionmehwish.wajidi82No ratings yet
- Assignment DPS CHEM Notes-2 Class-X 0110Document3 pagesAssignment DPS CHEM Notes-2 Class-X 0110bunny reedNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRDocument19 pagesUnit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRThilanka LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Study SlidesDocument31 pagesChapter 17 Study SlidesMakenzie DownsNo ratings yet
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidFrom EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNo ratings yet
- KRM Public School: Periodic Assessment (April - 2021)Document4 pagesKRM Public School: Periodic Assessment (April - 2021)GaneshNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol EthersDocument2 pagesAlcohol Phenol EthersGaneshNo ratings yet
- KRM Public School 2Document3 pagesKRM Public School 2GaneshNo ratings yet
- Child LabourDocument8 pagesChild LabourGaneshNo ratings yet
- KRM Public School 1Document3 pagesKRM Public School 1GaneshNo ratings yet
- ZOOM ONLINE CLASS-TIMETABLE - GRADE 6 To 10Document3 pagesZOOM ONLINE CLASS-TIMETABLE - GRADE 6 To 10GaneshNo ratings yet
- KRM Public School Biology - Exam Class Xii Date: 27.11.21 Duration: 90 MinutesDocument21 pagesKRM Public School Biology - Exam Class Xii Date: 27.11.21 Duration: 90 MinutesGaneshNo ratings yet
- English Core Code No. 301 Class XI (2021-22) Term Wise SyllabusDocument2 pagesEnglish Core Code No. 301 Class XI (2021-22) Term Wise SyllabusGaneshNo ratings yet
- SQP Physics 12 CH 01Document2 pagesSQP Physics 12 CH 01GaneshNo ratings yet