Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Year Chapter 2 TS
Uploaded by
Kamran Khursheed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 page2nd Year Chapter 2 TS
Uploaded by
Kamran KhursheedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
THE PISCES EDUCATION SYSTEM
Ghauri Town Phase 4-B, 0320-8585974, 051-2159122
2nd Year Physics – Chapter 2 – Total Marks: 8 + 15 + 12 = 35
SECTION - A
1. A charged conductor has charge on its.
(A) Inner-surface (B) outer-surface (C) middle-surface (D) surrounding space
2. Drift velocity of electrons is:
3. Heat generated by a 50 watt bulb in one hour is:
(A) 36000 J (B) 48000 J (C) 18000 J (D) 180000 J
4. For ohmic device the graph between V and I is:
(A) A straight line (B) Curve (C) Hyperbola (D) Parabola
5. When a wire of length" ” and resistance R is cut into two equal parts then resistivity of each part.
(A) Becomes half (B) Remains unchanged (C) Becomes two times (D) Becomes four times
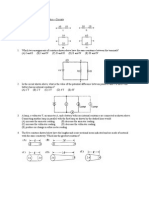
6. The current through a resistance of when connecting across a source of is:
(A) 22000 A (B) 22 A (C) 2.2 A (D) 0.45 A
7. The potential difference between the head and tail of an electric eel to:
(A) 600 volt (B) 700 volt (C) 800 volt (D) 900 volt
8. The substance having negative temperature co-efficient is:
(A) Carbon (B) Iron (C) tungsten (D) Gold
SECTION – B
1. Find out equivalent resistance when resistances are connected in series and in parallel.
2. Describe a circuit which will give a continuously varying potential
3. Distinguish between electromotive force (emf) and potential difference
4. Which charges actually flow in case of conventional current?
5. What are the difficulties in testing whether the filament of a lighted bulb obeys Ohm’s Law?
Section - C
1. A typical 12 V automobile battery has a resistance of 0.012 Ω. What is the terminal voltage of this
battery when the starter draws a current of 100 A. Also calculate R, P, PR and Pr.
2. Find the terminal potential difference of each cell in the circuit.
You might also like
- Circuits MC Practice ProblemsDocument29 pagesCircuits MC Practice ProblemsMark CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocument20 pagesCurrent Electricity Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGRavi YadavNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument10 pagesAlternating Currentnikhils.ind18No ratings yet
- 12 PhysicsDocument6 pages12 PhysicsMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity ExerciseDocument36 pagesCurrent Electricity ExerciseBeena JayNo ratings yet
- Electronics PaperDocument2 pagesElectronics PaperVikash ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Current and Circuits Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesCurrent and Circuits Practice ProblemsAnthony HuiNo ratings yet
- Marks Each, Section D Contains One Case Study Based Question of Four Marks and Section E Contains Two Long Answer Questions of Five Marks EachDocument6 pagesMarks Each, Section D Contains One Case Study Based Question of Four Marks and Section E Contains Two Long Answer Questions of Five Marks EachSri SriNo ratings yet
- Physics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Document6 pagesPhysics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Rayan SinghNo ratings yet
- VIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyDocument3 pagesVIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyRani PandeyNo ratings yet
- 11a-Circuits MC Practice ProblemsDocument37 pages11a-Circuits MC Practice Problemsminviking25No ratings yet
- B. Decrease: Egypt Exam 2020Document6 pagesB. Decrease: Egypt Exam 2020Lobna QassemNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Unit TestDocument4 pagesXii Physics Unit TestNeelima VobugariNo ratings yet
- Scan Dec 14, 2023Document5 pagesScan Dec 14, 2023ask99ayush.studyNo ratings yet
- 12 - Physics Question Paper (Pre-Board Ii)Document7 pages12 - Physics Question Paper (Pre-Board Ii)VaniceWhilderNo ratings yet
- Cbse Paper Set-1Document10 pagesCbse Paper Set-1maheshsoni10051982No ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesPre Board 1 PhysicsMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document5 pagesPaper 1Nitin JadhavNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics 2Document6 pages12 Physics 2Nihar Ranjan NikuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engg-IDocument6 pagesElectrical Engg-IXYZNo ratings yet
- Major Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1Document13 pagesMajor Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1DeaDShoT 618No ratings yet
- Ut 2 2023-24Document4 pagesUt 2 2023-24yashrao425299No ratings yet
- Physics Tes2Document4 pagesPhysics Tes2Krishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Holiday HomeworkDocument13 pagesSummer Vacation Holiday HomeworkVivek HackersNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Prepared by Babar Iqbal Awan Unit 13Document6 pagesPhysics Notes Prepared by Babar Iqbal Awan Unit 13Malik Babar Iqbal AwanNo ratings yet
- QP Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesQP Xii PhysicsSufiyan BelimNo ratings yet
- Physics 200 Question Mission 100 Class 12 THDocument48 pagesPhysics 200 Question Mission 100 Class 12 THNARENDER YadavNo ratings yet
- SNC1D Electricity Test 2Document4 pagesSNC1D Electricity Test 2venkat33% (3)
- Model Question Paper - 12th ClassDocument6 pagesModel Question Paper - 12th ClassIMRAN ANSARINo ratings yet
- Achyuta Public School Electricity-Segment-1 Electric CurrentDocument6 pagesAchyuta Public School Electricity-Segment-1 Electric Currentavp sNo ratings yet
- STD Xii Physics Bookback Objective Revised With KeyDocument33 pagesSTD Xii Physics Bookback Objective Revised With KeyOM KAILASHNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics Unit 2 Module 1 QuestionsDocument6 pagesCAPE Physics Unit 2 Module 1 QuestionstuvvacNo ratings yet
- 12th Physic One MarksDocument17 pages12th Physic One MarksKirthik Reshan.S 12'A'No ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricityatharvbaghel4444No ratings yet
- Worksheet X PhysicsDocument31 pagesWorksheet X PhysicsGuru PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Reduced Syllabus Model Question Paper EM 220586Document2 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Reduced Syllabus Model Question Paper EM 220586karthi1234No ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddRaaghav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1Document11 pages12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- 100 Most Imp Question For Jee MainsDocument23 pages100 Most Imp Question For Jee MainsgopinadhNo ratings yet
- Pre First TermDocument7 pagesPre First TermAawesh BackupsNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (QB)Document20 pagesCurrent Electricity (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- PB - I Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - I Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091No ratings yet
- 12Document4 pages12Girma chalaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 2022-2023Document18 pagesQuestion Bank 2022-2023Jamil Ahmed XI- ANo ratings yet
- XII PhysicsDocument4 pagesXII PhysicsVatsalyaNo ratings yet
- Electra Quiz: Time - Marks - +3 (Correct), - 1 (Incorrect)Document3 pagesElectra Quiz: Time - Marks - +3 (Correct), - 1 (Incorrect)RohitRajNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Document7 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023shagun sinhaNo ratings yet
- AAI ATC - Previous Year Physics QuesDocument14 pagesAAI ATC - Previous Year Physics Quesarmaan626742No ratings yet
- CH 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument7 pagesCH 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceShaurya SinghNo ratings yet
- QP&Sol 12 Term1 2022-PhyDocument13 pagesQP&Sol 12 Term1 2022-PhyDevika SinghNo ratings yet
- 2nd Internal Question BEEDocument1 page2nd Internal Question BEErakesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Practice Paper Round 1-2023-24Document4 pages12th Physics Practice Paper Round 1-2023-24adityarajsinh9990No ratings yet
- Class - Xii: (Physics)Document8 pagesClass - Xii: (Physics)kamalmeena2rkNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Physics 12thDocument2 pagesPre Board Physics 12thSyed Raza Hassan GardeziNo ratings yet
- Details: General InstructionsDocument9 pagesDetails: General InstructionsAakriti RoyNo ratings yet
- Electronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47Document134 pagesElectronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47dixitratan68No ratings yet
- HHW Class12 New PDFDocument58 pagesHHW Class12 New PDFSannidhi ShettyNo ratings yet
- Test Paper 8Document8 pagesTest Paper 8rajeshsharma4121No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- 2nd Half BookDocument2 pages2nd Half BookKamran KhursheedNo ratings yet
- The Pisces Academy, Ghauri Town Campus, Islamabad 0320-8585974, 051-2159122Document2 pagesThe Pisces Academy, Ghauri Town Campus, Islamabad 0320-8585974, 051-2159122Kamran KhursheedNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chapter 2 TSDocument1 page1st Year Chapter 2 TSKamran KhursheedNo ratings yet
- cOMPLETE BOOK PDFDocument190 pagescOMPLETE BOOK PDFJonNo ratings yet
- Ex 12 6 FSC Part1 Ver1 PDFDocument4 pagesEx 12 6 FSC Part1 Ver1 PDFKamran KhursheedNo ratings yet