Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid Fast Staining
Uploaded by
Micah Joy MacalaladCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Fast Staining
Uploaded by
Micah Joy MacalaladCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Fast Staining
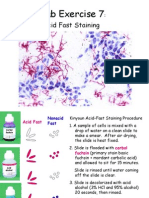
Objective:
The main aim of this staining is to differentiate bacteria into acid fast group and non-acid fast groups.
Reagent
Carbolfuchsin
Acid-alcohol
Methylene blue
Materials
paper towel
wire loop
gloves
rack
Procedure
Add one loopful of sterile water to a microscope slide.
Make a heavy smear of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Mix thoroughly with your loop. Then
transfer a small amount of Staphylococcus epidermidis to the same drop of water. You will now
have a mixture of M. smegmatis and S. epidermidis.
Air dry and heat fix well.
Cover the smear with carbolfuchsin dye. Place a piece of paper towel on top of the dye. Be sure
the paper towel is saturated with the dye. Carbolfuchsin is a potential carcinogen. Please wear
gloves when working with this dye
Place the slide on the rack over dry heat for 2 minutes.
Cool and rinse with water.
Decolorize by placing a drop of acid alcohol on the slide and allowing it to sit for 15 seconds.
Wash the top and bottom of slide with water and clean the slide bottom well.
Counterstain with Methylene Blue for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
Wash and blot the slide with bibulous paper. 11. Focus 10X - then use oil immersion.
Observation: Tabulate the data and results
Reagent Acid-fast Bacteria Nonacid-fast Bacteria
Carbolfuchsin RED RED
Acid-alcohol RED COLORLESS
Methylene blue RED BLUE
Mycobacterium and many Nocardia species are called acid-fast because during an acid-fast staining
procedure they retain the primary dye carbol fuchsin despite decolorization with the powerful solvent
acid-alcohol (95% ethanol with 3% HCl). Nearly all other genera of bacteria are nonacid-fast. The acid
fast genera have the waxy hydroxy-lipid called mycolic acid in their cell walls. It is assumed that mycolic
acid prevents acid-alcohol from decolorizing protoplasm. The acid-fast stain is a differential stain.
Conclusion
The acid-fast Mycobacterium retains carbolfuchsin and stains hot pink. The Staphylococcus epidermidis
is decolorized and the counterstain colors them blue. This method is used for those microorganisms
which are not staining by simple or Gram staining method, particularly the member of genus
Mycobacterium, are resistant and can only be visualized by acid-fast staining. The acid-fast stain is a
laboratory test that determines if a sample of tissue, blood, or other body substance is infected with the
bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB) and other illnesses.
You might also like
- Acidfaststaining 140111210509 Phpapp02Document16 pagesAcidfaststaining 140111210509 Phpapp02AnjuNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesDocument130 pagesThe Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesTricia Mae CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Menstruation and FertilizationDocument54 pagesMenstruation and FertilizationJanaica JuanNo ratings yet
- Eysenck Personality TheoryDocument11 pagesEysenck Personality TheoryKarthika RsNo ratings yet
- Is Childhood A Universal Experience?Document8 pagesIs Childhood A Universal Experience?camilo jamesNo ratings yet
- StainingDocument60 pagesStainingved.g007No ratings yet
- (Brawer) Prostate Specific AntigenDocument342 pages(Brawer) Prostate Specific Antigenseeranga_raghuNo ratings yet
- Staining Techniques in Microbiology.Document9 pagesStaining Techniques in Microbiology.rajendraprasadreddyNo ratings yet
- Applying A CastDocument13 pagesApplying A CastHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- The Smoking Scare De-Bunked William T WithbyDocument61 pagesThe Smoking Scare De-Bunked William T WithbyPietje PukNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From CyclohexeneDocument6 pagesExperiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From Cyclohexenesaransh1994No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- Steps of Acid-Fast Staining and Their Expected ResultDocument2 pagesSteps of Acid-Fast Staining and Their Expected ResultJirou BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Endospore Stain-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesEndospore Stain-WPS Officejoven delos santosNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast StainingDocument2 pagesAcid Fast StainingAhmed RazaNo ratings yet
- Gram StainDocument26 pagesGram StainFahad FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast StainingDocument13 pagesAcid Fast StainingDhanushika Sakthi VBNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms StainingDocument21 pagesMicroorganisms StainingNelson michaelNo ratings yet
- Case Study Acid-Fast BacilliDocument4 pagesCase Study Acid-Fast BacilliNur Hazirah AmaniNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter4 PDFDocument15 pagesCampylobacter4 PDFmohammednazeerNo ratings yet
- Universiti Sains Malaysia Jib 221 Microbiology Practical 2. Simple Stain and Gram Stain TechniquesDocument3 pagesUniversiti Sains Malaysia Jib 221 Microbiology Practical 2. Simple Stain and Gram Stain TechniquesBaby girlNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast Stain: PROCEDURE (Ziehl-Neelsen Method)Document3 pagesAcid Fast Stain: PROCEDURE (Ziehl-Neelsen Method)62991No ratings yet
- Acid Fast StainDocument3 pagesAcid Fast StainMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- Staining MethodsDocument8 pagesStaining MethodsMd Arshad100% (1)
- Baeyer 1Document3 pagesBaeyer 1Livaashini NadarajanNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast StainingDocument4 pagesAcid Fast Stainingchaudhary TahiraliNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise # 8 Acid-Fast BacteriaDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exercise # 8 Acid-Fast BacteriaAriana De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- COURSE MLSC 417 Staining in BacteriologyDocument38 pagesCOURSE MLSC 417 Staining in Bacteriologyالمركز الطبي الحديثNo ratings yet
- Staining NotesDocument5 pagesStaining NotesSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Staining Techniques in MicrobiologyDocument74 pagesStaining Techniques in MicrobiologyLenard MerlinNo ratings yet
- 6 TB - 2015Document20 pages6 TB - 2015Basma MohamedNo ratings yet
- AUB The MicroscopeDocument1 pageAUB The MicroscopeDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document6 pagesExercise 2Louiegi AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Review Microbiology Lab Test 2Document5 pagesReview Microbiology Lab Test 2RoyNo ratings yet
- Micro.... Staining TechniquesDocument74 pagesMicro.... Staining TechniquesArslan AzizNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast StainDocument3 pagesAcid Fast StainGUIDO ERNESTO VILLOTA CALVACHINo ratings yet
- Dyes and StainsDocument49 pagesDyes and StainsBilal Mumtaz AwanNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIDocument10 pagesLab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIErreneoNo ratings yet
- The Preparation of Culture MediaDocument7 pagesThe Preparation of Culture MediaNakyanzi AngellaNo ratings yet
- AFB Prac - MBIDDocument9 pagesAFB Prac - MBIDmem734094No ratings yet
- Aeromonas Salmonicida: User S ManualDocument4 pagesAeromonas Salmonicida: User S ManualAn-Dre BrichmanNo ratings yet
- Q1Document3 pagesQ1Jefferson RobertoNo ratings yet
- CHM 114 Exp 4 Hydrolysis of Methyl SalicylateDocument2 pagesCHM 114 Exp 4 Hydrolysis of Methyl Salicylateichigo.korosaki3110No ratings yet
- Lab Report Pathogen Microbe 7 (SPUTUM)Document5 pagesLab Report Pathogen Microbe 7 (SPUTUM)Syazmin KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Z Nstaining 210623101414Document12 pagesZ Nstaining 210623101414misdduaaNo ratings yet
- Modul - Eksperimen 10Document11 pagesModul - Eksperimen 10pangiastikaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity Revil Angelica MDocument16 pagesLaboratory Activity Revil Angelica MAngelica Malacay RevilNo ratings yet
- CHM - 114 - Exp - 3 - Nitration - of - AcetanilideDocument2 pagesCHM - 114 - Exp - 3 - Nitration - of - Acetanilideichigo.korosaki3110No ratings yet
- Acid Fast StainingDocument11 pagesAcid Fast StainingghephNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 7: Acid Fast StainingDocument6 pagesLab Exercise 7: Acid Fast StainingAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- CAT Nº: 1405: Saline Peptone Water Iso 6887Document2 pagesCAT Nº: 1405: Saline Peptone Water Iso 6887Bldjl HichemNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Microbiology I PDFDocument16 pagesTechniques in Microbiology I PDFMohd Izwan67% (3)
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Christian EduardoNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportMiami ArifNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter 2Document37 pages10 Chapter 2Hansa BorichaNo ratings yet
- ALCIAN Blue Staining IMPDocument4 pagesALCIAN Blue Staining IMPPallaval VeerabramhachariNo ratings yet
- Kinyoun Carbol Fuchsin Stain: Formulation Per 100 MLDocument3 pagesKinyoun Carbol Fuchsin Stain: Formulation Per 100 MLDELLNo ratings yet
- Exp#5 Gram StainingDocument4 pagesExp#5 Gram StainingbahadiroztenNo ratings yet
- 9353-Article Text-33256-1-10-20220826Document8 pages9353-Article Text-33256-1-10-20220826Alain Briones-VázquezNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Lab ManualDocument46 pagesFood Safety Lab ManualMarsh 42ONo ratings yet
- Acid Fast StainingDocument15 pagesAcid Fast StainingAlison 123 Parajuli 123No ratings yet
- CHEM1021 Lab09 Titration Instructions2Document7 pagesCHEM1021 Lab09 Titration Instructions2RashidNo ratings yet
- Chem 305 Lab Prelab 1Document4 pagesChem 305 Lab Prelab 1Gobe JamNo ratings yet
- MIKAL (Salmonella) 1Document13 pagesMIKAL (Salmonella) 1Kausalyaa Gajapathi RaoNo ratings yet
- Staining BacteriologyDocument54 pagesStaining BacteriologyJohn Emmanuel TayagNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExperimentsDocument9 pagesLaboratory ExperimentsSandra MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques Student Sheet: Intended Lesson OutcomesDocument19 pagesSeparation Techniques Student Sheet: Intended Lesson Outcomeslianchen251110No ratings yet
- Self Introduction, My Country, My FamilyDocument3 pagesSelf Introduction, My Country, My FamilyMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Oil and FatsDocument4 pagesQualitative Analysis of Oil and FatsMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument2 pagesScientific MethodMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Gi System: Macaraig, Janine Mae Macalalad, Maria Abegail Macatangay, Maria LourdesDocument4 pagesDrugs Affecting Gi System: Macaraig, Janine Mae Macalalad, Maria Abegail Macatangay, Maria LourdesMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing SkillDocument6 pagesReading and Writing SkillMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Cookery Terms: By: Lyka Delos Reyes & Shai Granados Grade 10 Cookery FDocument21 pagesCookery Terms: By: Lyka Delos Reyes & Shai Granados Grade 10 Cookery FMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument16 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D: Osteoporosis Vitamin A Vitamin B6 Protein Vitamin B12 Central Nervous System Vitamin C Vitamin DDocument5 pagesVitamin D: Osteoporosis Vitamin A Vitamin B6 Protein Vitamin B12 Central Nervous System Vitamin C Vitamin DMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Experiment of Vitamin: ProcedureDocument3 pagesExperiment of Vitamin: ProcedureMicah Joy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument15 pagesVital SignsSelene HmpNo ratings yet
- Ogalde Et Al. 2009Document7 pagesOgalde Et Al. 2009Juan Pablo Ogalde HerreraNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 2Document5 pagesProgress Test 2Ngát Phạm HồngNo ratings yet
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition Starr Solutions Manual DownloadDocument9 pagesBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition Starr Solutions Manual DownloadGraham Hissem100% (24)
- PDFDocument10 pagesPDFmedgadget100% (1)
- Encyclopedia ES HealthDocument9 pagesEncyclopedia ES HealthGantsooj BNo ratings yet
- Lazcano y Pereto. 2021. BioSystemsDocument6 pagesLazcano y Pereto. 2021. BioSystemsRenato AmosNo ratings yet
- Sunway University College Monash University Foundation Year (MUFY) 2010Document24 pagesSunway University College Monash University Foundation Year (MUFY) 2010Sunway UniversityNo ratings yet
- Slotwise Details July-November 2021Document138 pagesSlotwise Details July-November 2021Ch PrasadNo ratings yet
- Understanding: Bacteria:: Teacher's GuideDocument8 pagesUnderstanding: Bacteria:: Teacher's GuideKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Autonomic ReflexesDocument21 pagesAutonomic ReflexesJoe WeahNo ratings yet
- Sas 8Document12 pagesSas 8Reizel GaasNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: 7e's ApproachDocument6 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: 7e's ApproachSonny MagdadaroNo ratings yet
- US Army Survival ManualDocument277 pagesUS Army Survival ManualRadoslavNo ratings yet
- Week 4 SimDocument3 pagesWeek 4 SimJEZUE REMULTANo ratings yet
- 1,4 ButanediolDocument6 pages1,4 ButanediolVictor VikeneNo ratings yet
- An Evaluation of Fishing Activities at Kasenyi Fish Landing Site Along The Northern Shores of L.victoria (2000-2004)Document46 pagesAn Evaluation of Fishing Activities at Kasenyi Fish Landing Site Along The Northern Shores of L.victoria (2000-2004)Denis Tumusiime100% (4)
- T Cell Development Thymic Education of T CellDocument34 pagesT Cell Development Thymic Education of T Cellapi-273068056No ratings yet
- Gene InteractionDocument23 pagesGene Interactionwillayat aliNo ratings yet
- Craetagusarticle PDFDocument7 pagesCraetagusarticle PDFKatty AcostaNo ratings yet
- Growth Kinetics 2014Document33 pagesGrowth Kinetics 2014Ivan Aulia BigbandNo ratings yet
- Yearbook 2016Document308 pagesYearbook 2016achintNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document9 pagesBio 2triwicak15No ratings yet