0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views8 pagesOSPF Characteristics
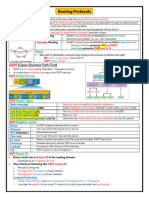
OSPF is a link state routing protocol that uses Dijkstra's algorithm to determine the best path. It supports large networks, has fast convergence, and uses multicast. The document compares OSPF to EIGRP and RIP, noting that OSPF is most commonly used and supports large networks as an open standard.
Uploaded by
Newton Dannie AbelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views8 pagesOSPF Characteristics
OSPF is a link state routing protocol that uses Dijkstra's algorithm to determine the best path. It supports large networks, has fast convergence, and uses multicast. The document compares OSPF to EIGRP and RIP, noting that OSPF is most commonly used and supports large networks as an open standard.
Uploaded by
Newton Dannie AbelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd