Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAS Financial Ratios
Uploaded by
Kei Camba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOriginal Title
MAS Financial ratios
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMAS Financial Ratios
Uploaded by
Kei CambaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
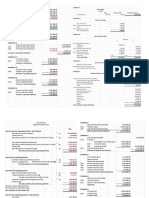
Liquidity Ratios Profitability ratios
measure a company’s ability to generate income
Liquidity ratios are financial ratios that measure a company’s ability relative to revenue, balance sheet assets, operating costs, and
to repay both short- and long-term obligations. Common liquidity equity. Common profitability financial ratios include the following:
ratios include the following: The gross margin ratio compares the gross profit of a company to its
The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off short-term net sales to show how much profit a company makes after paying its
liabilities with current assets: cost of goods sold:
Current ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities Gross margin ratio = Gross profit / Net sales
The acid-test ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off short- The operating margin ratio compares the operating income of a
term liabilities with quick assets: company to its net sales to determine operating efficiency:
Acid-test ratio = Current assets – Inventories / Current liabilities Operating margin ratio = Operating income / Net sales
The cash ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off short-term The return on assets ratio measures how efficiently a company is
liabilities with cash and cash equivalents: using its assets to generate profit:
Cash ratio = Cash and Cash equivalents / Current Liabilities Return on assets ratio = Net income / Total assets
The operating cash flow ratio is a measure of the number of times a The return on equity ratio measures how efficiently a company is
company can pay off current liabilities with the cash generated in a using its equity to generate profit:
given period: Return on equity ratio = Net income / Shareholder’s equity
Operating cash flow ratio = Operating cash flow / Current liabilities
Market Value Ratios
Leverage Financial Ratios Market value ratios are used to evaluate the share price of a
Leverage ratios measure the amount of capital that comes from company’s stock. Common market value ratios include the following:
debt. In other words, leverage financial ratios are used to evaluate a The book value per share ratio calculates the per-share value of a
company’s debt levels. Common leverage ratios include the company based on the equity available to shareholders:
following: Book value per share ratio = (Shareholder’s equity – Preferred
The debt ratio measures the relative amount of a company’s assets equity) / Total common shares outstanding
that are provided from debt:
Debt ratio = Total liabilities / Total assets The dividend yield ratio measures the amount of dividends
attributed to shareholders relative to the market value per share:
The debt to equity ratio calculates the weight of total debt and Dividend yield ratio = Dividend per share / Share price
financial liabilities against shareholders’ equity:
Debt to equity ratio = Total liabilities / Shareholder’s equity The earnings per share ratio measures the amount of net income
earned for each share outstanding:
The interest coverage ratio shows how easily a company can pay its Earnings per share ratio = Net earnings / Total shares outstanding
interest expenses:
Interest coverage ratio = Operating income / Interest expenses The price-earnings ratio compares a company’s share price to its
earnings per share:
The debt service coverage ratio reveals how easily a company can Price-earnings ratio = Share price / Earnings per share
pay its debt obligations:
Debt service coverage ratio = Operating income / Total debt service
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios, also known as activity financial ratios, are used to
measure how well a company is utilizing its assets and resources.
Common efficiency ratios include:
The asset turnover ratio measures a company’s ability to generate
sales from assets:
Asset turnover ratio = Net sales / Average total assets
The inventory turnover ratio measures how many times a company’s
inventory is sold and replaced over a given period:
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / Average inventory
The accounts receivable turnover ratio measures how many times a
company can turn receivables into cash over a given period:
Receivables turnover ratio = Net credit sales / Average accounts
receivable
The days sales in inventory ratio measures the average number of
days that a company holds on to inventory before selling it to
customers:
Days sales in inventory ratio = 365 days / Inventory turnover ratio
Profitability Ratios
You might also like
- Factors Influencingon Entrepreneurial Behaviorof Street VendorsDocument19 pagesFactors Influencingon Entrepreneurial Behaviorof Street VendorsKei CambaNo ratings yet
- The Incorporation of Soft Skills Into Accounting CDocument23 pagesThe Incorporation of Soft Skills Into Accounting CKei CambaNo ratings yet
- Ais Reviewer 2Document12 pagesAis Reviewer 2Kei CambaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Intention To Start A New Business Comparing Business and Non-Business OwnersDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting Intention To Start A New Business Comparing Business and Non-Business OwnersKei CambaNo ratings yet
- Ais Reviewer 1Document15 pagesAis Reviewer 1Kei CambaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Practice Subsidiaries Affiliates: What Is Transfer Pricing?Document14 pagesAccounting Practice Subsidiaries Affiliates: What Is Transfer Pricing?Kei CambaNo ratings yet
- Cash BudgetDocument8 pagesCash BudgetKei CambaNo ratings yet
- Acctg 108 Pre Qua Answer Key PDF FreeDocument23 pagesAcctg 108 Pre Qua Answer Key PDF FreeKei CambaNo ratings yet
- Short Term Budgeting PDF FreeDocument15 pagesShort Term Budgeting PDF FreeKei CambaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Fall of Barings Bank: Rakesh Kumar YadavDocument11 pagesThe Fall of Barings Bank: Rakesh Kumar YadavRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Salesmanship CHAPTER 2Document45 pagesSalesmanship CHAPTER 2Israel Ad FernandoNo ratings yet
- Family Security Is Considering The Introduction of A Child SecurityDocument1 pageFamily Security Is Considering The Introduction of A Child SecurityFreelance WorkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4divaNo ratings yet
- China: Vaccination Rollout Is Relatively SlowDocument4 pagesChina: Vaccination Rollout Is Relatively Slowahmad.subhan1411No ratings yet
- Statement 115377 Oct-2022Document8 pagesStatement 115377 Oct-2022Mary MacLellanNo ratings yet
- Form 26QB Property Tax Payment Form13Document3 pagesForm 26QB Property Tax Payment Form13JayCharleysNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management in T.K. MaxxDocument42 pagesCustomer Relationship Management in T.K. Maxxtendertayo4163100% (2)
- An Empirical Study On The Impact of Exchange Rate and Inflation Rate On NSE IndexDocument7 pagesAn Empirical Study On The Impact of Exchange Rate and Inflation Rate On NSE IndexchitkarashellyNo ratings yet
- SAPM Module 1 HandoutDocument10 pagesSAPM Module 1 HandoutmmuneebsdaNo ratings yet
- FIN358 Chapter1 Introduction To Investment StudentDocument7 pagesFIN358 Chapter1 Introduction To Investment StudentMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Cost ConceptsDocument19 pagesCost ConceptsPrabha Karan100% (1)
- Sample Research Proposal On The Influence and Impact of Advertising To Consumer Purchase MotiveDocument19 pagesSample Research Proposal On The Influence and Impact of Advertising To Consumer Purchase MotiveallanNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: World Bond Market Vs Bangladesh Bond MarketDocument14 pagesAssignment On: World Bond Market Vs Bangladesh Bond Marketswapnil swadhinataNo ratings yet
- Role of Consumer in National Economy & Consumer MovementDocument46 pagesRole of Consumer in National Economy & Consumer MovementSANJAYSINGHMEENA33% (3)
- Tele ShoppingDocument7 pagesTele ShoppingAswathy SathyanNo ratings yet
- Jarratt Davis Book PDFDocument47 pagesJarratt Davis Book PDFclarkpd6100% (1)
- Glob Finc - Practice Set For Exam 1 - SolutionsDocument7 pagesGlob Finc - Practice Set For Exam 1 - SolutionsInesNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE) Is The Only Stock Exchange in The Philippines. It Is One of The OldestDocument7 pagesThe Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE) Is The Only Stock Exchange in The Philippines. It Is One of The OldestDaren TolentinoNo ratings yet
- KLP 5 PaymentDocument14 pagesKLP 5 PaymentkartikadmyNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Perfect CompetetionDocument101 pagesUnit 9 - Perfect CompetetionRavi GargNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan - SampleDocument35 pagesMarketing Plan - SampleTUMMALAPENTA BHUVAN SAI KARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Klaus Uhlenbruck - Hochland CaseDocument15 pagesKlaus Uhlenbruck - Hochland CaseAvogadro's ConstantNo ratings yet
- Cristina Laroa MedinaDocument2 pagesCristina Laroa Medinaapi-620979504No ratings yet
- FM II Assignment 17 19Document1 pageFM II Assignment 17 19RaaziaNo ratings yet
- Ashok LeylandDocument16 pagesAshok LeylandSHIVAM AHUJANo ratings yet
- Copy Trading Secrets GuideDocument22 pagesCopy Trading Secrets Guidearies_teaNo ratings yet
- MBA Weekend Handbook 2019Document73 pagesMBA Weekend Handbook 2019KD TricksNo ratings yet
- Fat Finger' Trade On NSE May Have Cost Broker 250 Crore Loss TimesDocument2 pagesFat Finger' Trade On NSE May Have Cost Broker 250 Crore Loss TimesPrashantPatilNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management. Lecture 1.Document13 pagesSupply Chain Management. Lecture 1.Hisham ShihabNo ratings yet