Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IRAC - Eng - Moa - Structure - Poster - Update - 11-11-2021
Uploaded by
David RojasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IRAC - Eng - Moa - Structure - Poster - Update - 11-11-2021
Uploaded by
David RojasCopyright:
Available Formats
Key to Targeted Group 1: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors Group 2: GABA-gated chloride Group 21: M itochondrial com plex I electron
Group 2: GABA-gated chloride Group 21: M itochondrial com plex I electron transport inhibitors Group 22: Voltage-dependent
Physiology (Only representatives actives of the groups are shown) channel antagonists sodium channel blockers
22A
1A 2A Cyclodiene Organochlorines Indoxacarb
Nerve & Oxadiazines
Muscle Carbamates
Rotenone
O Fenazaquin Pyrimidifen
O O
Growth & Carbofuran
N S
N
Methomyl
21B
Development Pyridaben
Chlordane Endosulfan Tolfenpyrad Rotenone
Respiration Carbosulfan 22B
2B Phenylpyrazoles (Fiproles) 21A METI acaricides and
Insecticide Resistance Action Committee
O S
Semicarbazones Metaflumizone
P Fenpyroximate Tebufenpyrad insecticides
O S
Midgut S
Mode of Action Classification
Acephate Phorate
1B Group 23: Inhibitors of acetyl CoA carboxylase Group 24: M itochondrial
Unknown or Fipronil
Non-specific Organophosphates Ethiprole com plex IV electron transport
Chlorpyrifos AlP
inhibitors
Aluminium
Group 9: Chordotonal Group 10: M ite growth inhibitors phosphide PH3 CN-
Group 3: Sodium channel m odulators (Only representative actives of group 3A are shown) organ TRPV channel m odulators affecting CHS1 Spiromesifen Spirotetramat
Phosphine Cyanide
Ca3P2 Zn3P2 salts
Etoxazole Spirodiclofen Spiropidion Zinc
Calcium
Pymetrozine 24A
Diflovidazin phosphide phosphide 24B Cyanides
9B Pyridine 10B 23 Tetronic & Tetramic acid derivatives Phosphides
Bifenthrin Esfenvalerate Permethrin Afidopyropen Etoxazole
azomethine Pyrifluquinazon
10A
DDT
derivatives Clofentezine Hexythiazox
lambda-
9D Pyropenes Clofentezine,
Deltamethrin Diflovidazin,Hexythiazox Group 25: M itochondrial com plex II electron Group 28: Ryanodine 29: Chordotonal
cyhalothrin
3A transport inhibitors receptor m odulators
Methoxychlor organ
Pyrethroids N
alpha- Pyrethrins
CN N
m odulators –
cypermethrin Etofenprox Tefluthrin 3B DDT, Group 11: M icrobial disruptors of insect m idgut m em branes 25A beta-Ketonitrile Chlorantraniliprole R=Cl
derivatives undefined target
Methoxychlor O O Cyantraniliprole R=CN
Includes transgenic crops expressing Bacillus thuringiensis site
Bacillus thuringiensis and the
toxins (however, specific guidance for resistance management insecticidal proteins produced Bacillus sphaericus Cyenopyrafen O O
of transgenic crops is not based on rotation of modes of action) B.t. israelensis, B.t. aitzawai, I HN
S
Cyclaniliprole
Group 4: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) com petitive m odulators B.t. kurstaki, B.t. tenebrionis F 3C O
Flubendiamide
O O
Rotation between certain specific B.t. microbial products NC
HN
may provide resistance management benefits for some O
CF3
pests. Consult product-specific recommendations. 11A Bacillus thuringiensis 11B Bacillus sphaericus O
F
CF3 Flonicamid
O
Pyflubumide
Cyflumetofen
Dinotefuran 25B Carboxanilides 28 Diamides 29 Flonicamid
Tetraniliprole
Nicotine Sulfoxaflor
O
Group 12: Inhibitors of m itochondrial ATP synthase
N CF3
Acetamiprid 4B Nicotine 4C Sulfoximines N O
Nitenpyram S O
O O Group 30: GABA-gated chloride channel allosteric m odulators Group 31: Baculoviruses
Cl N S
N N Sn
Sn O
Sn
O O S Cl
H H
O
N
Flupyrimin N
Cl Cl Cl
N
Imidacloprid Thiamethoxam Diafenthiuron Fenbutatin Anticarsia
4F Pyridylidenes Azocyclotin oxide Tetradifon
Cydia pomonella GV gemmatalis MNPV
Propargite
12A Sn
Thaumatotibia Helicoverpa
4A Flupyradifurone Triflumezopyrim Diafenthiuron
OH
12B 12C Propargite armigera NPV
Clothianidin Thiacloprid Cyhexatin
12D Tetradifon Broflanilide Fluxametamide Isocycloseram leucotreta GV
Neonicotinoids Organotin miticides
4D Butenolides 4E Mesoionics
30 Meta-diamides & Isoxazolines 31 Granuloviruses & Nucleopolyhedroviruses
Group 13: Uncouplers of oxidative phos- Group 14: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR)
phorylation via disruption of proton gradient channel blockers Group 33: Calcium - activated Group 34: M itochondrial com plex
Group 5: Nicotinic acetylcholine Group 6: Glutam ate-gated chloride channel (GluCl) Group 32: Nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor (nAChR) allosteric m odulators Br
CN O S receptor (nAChR) allosteric potassium channel (KCa2) III electron transport inhibitors –
Spinetoram Abamectin R1 = major component R2 = Ethyl S
major component R = H, 5,6 single allosteric m odulators O
minor component R2 = Methyl
F3C
O
S
S S m odulators site II m odulators Qi site
minor component R = CH3, 5,6 double
HO N N
site I OH N
S
S
O NH2 SO 3Na
O
O O O Cl
O O S O O
O2N S
Sulfluramid
13 GS-omega/kappa
O
Spinosad
H
H
O
Lepimectin
O
Chlorfenapyr Bensultap Thiocyclam
major component R = H O R S NH 2 S F3C
Emamectin N
HXTX-Hv1a
Pyrroles,
H O N
minor component R = CH3 N N SO3Na
benzoate R1 =
N
O
H Cl peptide
Dinitrophenols,
O O
H
O
O O O O
O R
OH H
Milbemectin
NO2
14 Nereistoxin Acynonapyr Flometoquin
O
H
Cartap Thiosultap-
O O
O Sulfluramid DNOC analogues sodium
OH H
H hydrochloride
5 Spinosyns
OH
32 GS-omega/kappa HXTX-Hv1a peptide 33 Acynonapyr 34 Flometoquin
6 Avermectins & Milbemycins O
H major component R = Ethyl
OH
minor component R = Methyl
Group 15: Inhibitors of chitin Group 16: Inhibitors of chitin Group 18: Ecdysone receptor
Group 7: Juvenile horm one biosynthesis affecting CHS1 biosynthesis, type 1 agonists Unknown or uncertain mode of action
UNB UNF
Hydroprene R1 = ethyl, R2 = H m im ics (Only representative
Methoprene R1 = isopropyl, R2 – OCH3 UN Bacterial agents Fungal agents
actives of group are
7A Juvenile shown) Com pounds (non-Bt)
hormone O
analogues 7B 7C O N O
Kinoprene R1 = propargyl, R2 = H Fenoxycarb Pyriproxyfen Cl
Fenoxycarb Pyriproxyfen Diflubenzuron Chromafenozide O
Burkholderia spp,
Beauveria bassiana strains
Buprofezin Metarhizium anisopliae strain F52,
16 Buprofezin Bromopropylate
O
Wolbachia pipientis (Zap) Paecilomyces fumosoroseus
Azadirachtin Benzoximate Apopka strain 97
Flufenoxuron
Group 8: M iscellaneous non-specific (m ulti-site)
Group 17: Moulting disruptors,
inhibitors Dipteran N Cl Cl
S
Lufenuron Halofenozide O
OH Chenopodium ambrosioides
N S near ambrosioides
CCl3 extract Diatomaceous earth
Methyl
Na2B4O7·10H2O
8A Alkyl Dazomet Chinomethionat Dicofol Fatty acid monoesters with Mineral oil
bromide Cryolite Methoxyfenozide glycerol or propanediol
halides Novaluron
Borax Tartar emetic Neem oil
8E
8D Borates Cyromazine Mancozeb UNE UNM
Tartar emetic Teflubenzuron Tebufenozide
Cl
O O S
15 Benzoylureas 17 Cyromazine 18 Diacylhydrazines Cl
N Botanical essence Non-specific
CaSX
Cl O Cl CF3
8F Methyl isothiocyanate including synthetic, extracts m echanical and physical
8B Sulfuryl 8C Metam (Lime sulfur)
Chloropicrin Chloropicrin fluoride Fluorides generators Pyridalyl Sulfurs and unrefined oils disruptors
Group 19: Octopam ine Group 20: M itochondrial com plex III electron transport inhibitors – Qo site
receptor agonists O
Hydramethylnon O
Use of Groups: Use of Sub-Groups: F 3C
HN
O O
CF3 O
HN NH Poster Notes:
• Alternations, sequences or rotations of compounds between • Sub-groups represent distinct structural classes which are • Sub-group 3B: DDT is no longer used in agriculture and therefore this is only applicable for the control
O
N
N O O
N N
H O
MoA groups reduce selection for target site resistance. believed to have the same mode of action. O
O N O
of insect vectors of human disease, such as mosquitoes, because of a lack of alternatives.
• Applications are arranged into MoA spray windows defined • Sub-groups provide differentiation between compounds that may 19 Acequinocyl Fluacrypyrim Bifenazate • Sub-group10A: Hexythiazox is grouped with Clofentezine because they exhibit cross-resistance even
by crop growth stage and pest biology. Several sprays of a bind at the same target site but are structurally different enough Amitraz
CF 3
though they are structurally distinct. Diflovidazin has been added to this group because it is a close
Amitraz
compound may be possible within each spray window, but that risk of metabolic cross-resistance is lower than for close 20A Hydramethylnon 20B Acequinocyl 20C Fluacrypyrim analogue of Clofentezine and is expected to have the same mode of action.
20D Bifenazate
successive generations of a pest should not be treated with chemical analogs. • Group 20: While there is strong evidence that Bifenazate acts on the Qo site of Mitochondrial Complex
compounds from the same MoA group. Local expert advice • Cross-resistance potential between sub-groups is higher than III and some Bifenazate resistance mutations confer cross-resistance to Acequinocyl, the sites of action
on spray windows and timings should always be followed. between groups, so rotation between sub-groups should be Disclaimer: While CropLife International and IRAC make every effort to present accurate and reliable information, they do not of Fluacrypyrim and Hydramethylnon have not been determined.
• Groups in the classification whose members do not act at a considered only when there are no alternatives, and only if cross- guarantee the accuracy, completeness, efficacy, timeliness, or correct sequencing of such information. Inclusion of active ingredients • Groups 26 and 27 are unassigned.
common target site are exempt from the proscription against resistance does not exist, following consultation with local expert on the IRAC Code Lists is based on scientific evaluation of their modes of action; it does not provide any kind of testimonial for the use • In some cases, only representative actives are shown.
rotation within the group (Group 8, 13 and all UN groups: UN, advice. These exceptions are not sustainable, and alternative of a product or a judgment on efficacy. CropLife International and IRAC are not responsible for, and expressly disclaim all liability for, • Please visit www.irac-online.org for the complete IRAC classification.
UNB, UNE, UNF, UNM, UNP & UNV). options should be sought. damages of any kind arising out of use, reference to, or reliance on information provided. Listing of chemical classes or modes of
action must not be interpreted as approval for use of a compound in a given country. Prior to implementation, each user must
Internal
determine the current registration status in the country of use and strictly adhere to the uses and instructions approved in that country. IRAC document protected by © Copyright Poster Edition 8, November 2021. Based on the MoA Classification Version 10
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Communicative Effect Achieved Through Speech Acts of ManipulationDocument7 pagesCommunicative Effect Achieved Through Speech Acts of ManipulationlazarstosicNo ratings yet
- Control and Significant InfluenceDocument11 pagesControl and Significant InfluencePatrick ArazoNo ratings yet
- 516 Application CarDocument2 pages516 Application Carazamkhan13No ratings yet
- Integration of Islamic Education in Public SchoolsDocument7 pagesIntegration of Islamic Education in Public SchoolstimespergerakanNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Limited LiabilityDocument6 pagesDoctrine of Limited Liabilitymina villamorNo ratings yet
- Estmt - 2024 01 05Document8 pagesEstmt - 2024 01 05alejandro860510No ratings yet
- Financial Management Exam March 2019Document7 pagesFinancial Management Exam March 2019IQBAL MAHMUDNo ratings yet
- The 3 Fundamentals - MIAWDocument44 pagesThe 3 Fundamentals - MIAWfariskhosa69No ratings yet
- Set Down Servant!: . J J J. ' F R - 'Document7 pagesSet Down Servant!: . J J J. ' F R - 'Kora LapaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Global, Ethics, and Security Management: Enterprise Systems For Management, 2e (Motiwalla/Thompson)Document13 pagesChapter 10 Global, Ethics, and Security Management: Enterprise Systems For Management, 2e (Motiwalla/Thompson)Uts HughNo ratings yet
- What Is Occupational Health and Safety?Document3 pagesWhat Is Occupational Health and Safety?flex gyNo ratings yet
- Petition for issuance of second owner's duplicate titleDocument2 pagesPetition for issuance of second owner's duplicate titlebernard jonathan Gatchalian100% (1)
- Giovanna Ferrer - Language III - PW # 8 Use of EnglishDocument2 pagesGiovanna Ferrer - Language III - PW # 8 Use of EnglishGiovanna FerrerNo ratings yet
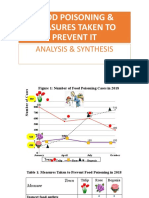
- MUET@UiTM2020 - Food Poisoning - Analysis & SynthesisDocument15 pagesMUET@UiTM2020 - Food Poisoning - Analysis & SynthesisNURUL FARRAH LIEYANA BT SHAMSUL BAHARINo ratings yet
- Adeeba Siddiqui - MEDDocument3 pagesAdeeba Siddiqui - MEDAdeeba SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- World Policy Journal: Bangladesh: A Labor ParadoxDocument11 pagesWorld Policy Journal: Bangladesh: A Labor ParadoxPranto BaraiNo ratings yet
- POL 100-Introduction To Political Science-Sameen A. Mohsin AliDocument7 pagesPOL 100-Introduction To Political Science-Sameen A. Mohsin AliOsamaNo ratings yet
- General Defences Shortest (Last Minute)Document23 pagesGeneral Defences Shortest (Last Minute)Raj DasNo ratings yet
- JBIMS Strategic MGMT Srini BMN Exam Paper Nov 2022Document4 pagesJBIMS Strategic MGMT Srini BMN Exam Paper Nov 2022nikupadhyay25No ratings yet
- Darwin Route10 Pocket Maps/TimetableDocument2 pagesDarwin Route10 Pocket Maps/TimetableLachlanNo ratings yet
- ANNEX C LGU Managed Water Utility Profile FormDocument6 pagesANNEX C LGU Managed Water Utility Profile FormZedrick Bajado TejonesNo ratings yet
- An Inscribed Nabataean Bronze Object DedDocument15 pagesAn Inscribed Nabataean Bronze Object Dedejc1717No ratings yet
- WHO Report On COVID-19 - April 22, 2020Document14 pagesWHO Report On COVID-19 - April 22, 2020CityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) in Nepal: Ministry of Population and EnvironmentDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA) in Nepal: Ministry of Population and EnvironmentAden ShahuNo ratings yet
- Reading Report G9Document50 pagesReading Report G9Grade9 2023No ratings yet
- Shanayes Budget Defense BenchmarkDocument15 pagesShanayes Budget Defense Benchmarkapi-529462240100% (1)
- Paystub 2019 05 31 PDFDocument1 pagePaystub 2019 05 31 PDFAnonymous wkIlICXmQfNo ratings yet
- Italian Renaissance Theatre DevelopmentsDocument3 pagesItalian Renaissance Theatre DevelopmentsAndrewNathanVesselNo ratings yet
- TNB Electricity System Voltages, Frequencies, Earthing Systems and Supply OptionsDocument4 pagesTNB Electricity System Voltages, Frequencies, Earthing Systems and Supply OptionsSaiful RizamNo ratings yet
- Marginal TeacherDocument19 pagesMarginal TeacherAndy AcuinNo ratings yet