Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tuckman Model
Uploaded by
Subhodeep KarmakarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tuckman Model
Uploaded by
Subhodeep KarmakarCopyright:
Available Formats
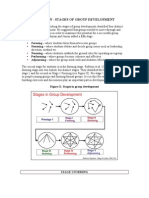
Adjourning
Exercise 1.1: The Garland, Jones, The group disbands. The feelings that members expe-
and Kolodny Model rience are similar to those in the "Separation Stage"
GOAL: This exercise is designed to help you analyze of the Garland, Jones, and Kolodny Model described
groups in terms of the Garland, Jones, and Kolodny in the previous section.
Model.
Write a description of a group that you have par Exercise 1.2: The Tuckman Model
ticipated in that has at least some of the group
development stages identified by the Garland, GOAL: This exercise is designed to help you ana-
Tuckman Model.
Jones, and Kolodny Model. Identify the stages of lyze groups in terms of the
your group that are consistent with the model. Also Write a description of a group that you have par
describe any developmental stages of your group ticipated in that has at least some of the group
that are inconsistent with this model.
development stages identified by the Tuckman
Model. Identify the stages of your group that are
consistent with the model. Also describe any devel-
Tuckman Model
opmental stages of your group that are inconsistent
Tuckman reviewed over 50 studies, primarily of with this model.
limited-duration therapy and sensitivity groups, and
concluded that these groups go through the follow- Northen and Kurland Model
ing five predictable developmental stages: forming,
33 Northen and Kurland focus on stages of group devel-
storming, norming, performing, and adjourning33
Each stage will be briefly described.
opment and point out that each stage has its own
developmental issues that must be attended to and
at least partially resolved before the group can move
Forming
into the next stage." Northen and Kurland propose a
Members become oriented toward each other, work
four-stage model with emphasis on socio-emotional
on being accepted, and learn more about the group.
themes.
This stage is marked by a period of uncertainty in u
which members try to determine their places in the Inchusion-Orientation
group and learn the group's rules and procedures.
The main socio-emotional theme of this stage, as
the title implies, is whether or not group
Storming members
will feel included. This stage is typically marked by
Conflicts begin to arise members resist the influ-
as
ence of the group and rebel against accomplishing
anxiety Anand uncertainty as group members become
their tasks. Members confront their various dif-
acquainted with the group leader and each other.
"The major task for the members is to become orl-
ferences, and the management of conflict often ented to the group and to decide to be included in the
becomes the focus of attention.
group s membership."35
Norming
The group establishes cohesiveness and commit
Uncertainty-Exploration
The major theme of this stage has to do with group
ment. In the process, the members discover new
ways to work together. Norms are also set for appro-
members' regarding issues of power and
uncertainty
control. The socio-emotional issue pertains to con-
priate behavior.
flict, especially in relationship to the group leader.
Performing
The group works as a unit to achieve group goals.
Group members at this stage explore and test their
relationship with the leader and each other in order
Members develop proficiency in achieving goals to establish roles and develop trust and acceptance.
and become more flexible in their patterns of work- The description of this model was written by
ing together. Michael Wallace, MSsW, instructor at the University of
Wisconsin-Whitewater.
You might also like
- Group Development Theory PDFDocument2 pagesGroup Development Theory PDFMark Diyammi100% (1)
- Group Dynamics - GWDocument18 pagesGroup Dynamics - GWsolomonNo ratings yet
- Group Development Stages and The Role of SocialDocument17 pagesGroup Development Stages and The Role of Socialasad khan0% (1)
- INFO - NOTE - How Groups Develop - Work Effectively (4 Stages)Document4 pagesINFO - NOTE - How Groups Develop - Work Effectively (4 Stages)Sylvia HendersonNo ratings yet
- Bruce Tuckman Secuencia de Desarrollo de Grupos PequeñosDocument18 pagesBruce Tuckman Secuencia de Desarrollo de Grupos PequeñosBernardoomNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Group 10 1Document16 pagesModule 5 Group 10 1jacky mollejonNo ratings yet
- FC 431 e 7Document37 pagesFC 431 e 7bhatippNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamics: By-Dr. Aprajita UpadhyayDocument36 pagesGroup Dynamics: By-Dr. Aprajita UpadhyaybhatippNo ratings yet
- Written Output in Module 4Document4 pagesWritten Output in Module 4Apple SangreNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour - 9 - Managing Group and TeamsDocument42 pagesOrganizational Behaviour - 9 - Managing Group and TeamsJaatooNo ratings yet
- Tuckman S Stages of Group Development PDFDocument2 pagesTuckman S Stages of Group Development PDFMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Definition of A Small GroupDocument12 pagesDefinition of A Small GroupPhilip FelicitasNo ratings yet
- 4 GroupdynamicsDocument37 pages4 Groupdynamicsdapurna860% (1)
- 4b Group FormationDocument8 pages4b Group FormationLarneyNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamics PDFDocument14 pagesGroup Dynamics PDFlanka naveenNo ratings yet
- Group BehaviorDocument13 pagesGroup BehaviorManisha VarsaniNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Ob-Notes-FinalDocument10 pagesUnit Iv Ob-Notes-FinaljoycyNo ratings yet
- Bcu-G88-Magc-206-Lesson 3-MidtermDocument27 pagesBcu-G88-Magc-206-Lesson 3-MidtermJoan BayanganNo ratings yet
- Bcu-G88-Magc-206-Lesson 3-MidtermDocument27 pagesBcu-G88-Magc-206-Lesson 3-MidtermJoan BayanganNo ratings yet
- Major Interventions To Facilitate Work Group: 1. Provide The Necessary Orientation, Structure andDocument32 pagesMajor Interventions To Facilitate Work Group: 1. Provide The Necessary Orientation, Structure andRuffa Mae F. MODESTONo ratings yet
- Unit 3: 1.1. Groups in OrganisationsDocument15 pagesUnit 3: 1.1. Groups in OrganisationsEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Report in Elec 5Document3 pagesReport in Elec 5Apple SangreNo ratings yet
- HBO Module No. 9Document5 pagesHBO Module No. 9Ruby A BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Formation of Group PDFDocument10 pagesFormation of Group PDFabid hussainNo ratings yet
- CHN-Finals (1) - 1Document18 pagesCHN-Finals (1) - 1M.I Dia Izibelle F. AMENAMENNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Group Behaviors in ConsumDocument5 pagesFoundations of Group Behaviors in Consumlarry.napata.blueleafenergyNo ratings yet
- A Model of Stages of Group Development: Stage 1. Forming (Orientation and Initiation)Document2 pagesA Model of Stages of Group Development: Stage 1. Forming (Orientation and Initiation)Praneeth ReddyNo ratings yet
- The Group Development Behavioral Models: Kurt Lewin's Individual Change ProcessDocument3 pagesThe Group Development Behavioral Models: Kurt Lewin's Individual Change ProcessBishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Organizacija I Poslovna KulturaDocument10 pagesOrganizacija I Poslovna KulturaJana PekovicNo ratings yet
- Group and Work Group Behavior. Ppp..Document36 pagesGroup and Work Group Behavior. Ppp..Dharz Daryl100% (2)
- Bcu-G88-Magc-206-Lesson 2-MidtermDocument13 pagesBcu-G88-Magc-206-Lesson 2-MidtermJoan BayanganNo ratings yet
- Ahe 607-2Document18 pagesAhe 607-2PRASHANT REVANKARNo ratings yet
- Group DynamicsDocument12 pagesGroup Dynamicsblast2111100% (1)
- Working in Groups and Teams: WWW - Ianr.unl - Edu/pubs/misc/cc352.htm#eytdDocument8 pagesWorking in Groups and Teams: WWW - Ianr.unl - Edu/pubs/misc/cc352.htm#eytdsabania_222646563No ratings yet
- CSC 171 Sprint 2018 Four Stages of Team Development: in Small GroupsDocument6 pagesCSC 171 Sprint 2018 Four Stages of Team Development: in Small Groupsfariez79No ratings yet
- Week 9 HborDocument5 pagesWeek 9 HborEll VNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Group DaynamicDocument5 pagesAssignment of Group DaynamicSACHIN GAURNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.1Document25 pagesChapter 4.1Nur Aisyah AuniNo ratings yet
- Group Behaviour NotesDocument9 pagesGroup Behaviour NotesSwapnil DasNo ratings yet
- Work Group BehaviourDocument21 pagesWork Group BehaviourAlie GabianaNo ratings yet
- Tuckman's ModelDocument17 pagesTuckman's ModelAshutosh TripathiNo ratings yet
- in Module 4Document24 pagesin Module 4Apple SangreNo ratings yet
- 94 02 PDFDocument2 pages94 02 PDFRaquel Cabaliza JervosoNo ratings yet
- Group Develoment - TuckmanDocument4 pagesGroup Develoment - TuckmanMuhammad ZaIdNo ratings yet
- Ob - Unit 4Document14 pagesOb - Unit 4SAMNo ratings yet
- Group: Two or More Individuals, Interacting and Interdependent, Who Come Together To Achieve Particular ObjectivesDocument68 pagesGroup: Two or More Individuals, Interacting and Interdependent, Who Come Together To Achieve Particular ObjectivesRahul RastogiNo ratings yet
- Group DynamicsDocument5 pagesGroup DynamicsMat GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phases of Group DevelopmentDocument6 pagesPhases of Group DevelopmentRuhiel Ty ManuelNo ratings yet
- Groupdynamics-130810000303-Phpapp01 1Document43 pagesGroupdynamics-130810000303-Phpapp01 1rasneetNo ratings yet
- OB - Groups and TeamsDocument102 pagesOB - Groups and TeamsShraddha RawatNo ratings yet
- Kasturba Gandhi Nursing College Class Teaching ON Group DynamicsDocument14 pagesKasturba Gandhi Nursing College Class Teaching ON Group DynamicsFriends ThamizhaNo ratings yet
- 10 Understanding Groups and Managing Work TeamsDocument32 pages10 Understanding Groups and Managing Work TeamsJesse NoelNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour MG-482: Faiza Jehangir (Khan - Faiza1993@cloud - Neduet.edu - PK)Document20 pagesOrganizational Behaviour MG-482: Faiza Jehangir (Khan - Faiza1993@cloud - Neduet.edu - PK)HAMMAD ALI100% (1)
- Tuckman's ModelDocument17 pagesTuckman's Modelpratikshyaghimire89No ratings yet
- Group ProcessDocument32 pagesGroup ProcessAswathiNo ratings yet
- A Study On Group Group DynamicsDocument46 pagesA Study On Group Group DynamicsAkansha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mhbor 9 12Document12 pagesMhbor 9 12Christa LenzNo ratings yet
- Group DynamicsDocument19 pagesGroup DynamicskomalpreetNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamic TopicDocument12 pagesGroup Dynamic Topicsuman guptaNo ratings yet
- Creating an Effective and Efficient Work Team: Managing the Group Dynamics towards Team PerformanceFrom EverandCreating an Effective and Efficient Work Team: Managing the Group Dynamics towards Team PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Social Work Concepts and Primary MethodsDocument3 pagesSocial Work Concepts and Primary MethodsSubhodeep KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Theories of Group WorkDocument33 pagesTheories of Group WorkSubhodeep KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Social WorkersDocument52 pagesStatistics For Social WorkersSubhodeep KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Social Work Research: Meaning, Importance and ScopeDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Social Work Research: Meaning, Importance and ScopeSubhodeep KarmakarNo ratings yet
- A Group of Positions That Have Similar DutiesDocument4 pagesA Group of Positions That Have Similar DutiesPallavi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Family Centered Maternity Care PP2017Document5 pagesFamily Centered Maternity Care PP2017melaNo ratings yet
- Taylorism Too Positive About PeopleDocument25 pagesTaylorism Too Positive About PeopleAlina NawazNo ratings yet
- Political SelfDocument15 pagesPolitical SelfMichael Lalim Jr.75% (4)
- Week 5 HRMDocument28 pagesWeek 5 HRMtedi gunawanNo ratings yet
- TQM by Dale H. Besterfield Et Al (096-123)Document28 pagesTQM by Dale H. Besterfield Et Al (096-123)Zamien edanNo ratings yet
- Printable List of EmotionsDocument3 pagesPrintable List of EmotionsFarameenNo ratings yet
- Employee's Job SatisfactionDocument24 pagesEmployee's Job SatisfactionShariful Islam Shaheen0% (1)
- When Is A Man Truely Ready For MarriageDocument2 pagesWhen Is A Man Truely Ready For MarriageEmmanuel MahengeNo ratings yet
- Systems TheoryDocument5 pagesSystems Theoryferdinand manlongatNo ratings yet
- Cognitice Behavior TherapyDocument4 pagesCognitice Behavior TherapymarcelosnolNo ratings yet
- Theory of Planned BehaviorDocument3 pagesTheory of Planned BehaviorLolas TitasNo ratings yet
- BUS204Document5 pagesBUS204Luan VanNo ratings yet
- Foster Care EssayDocument3 pagesFoster Care Essayapi-242126816No ratings yet
- Taxonomy in The Affective DomainDocument10 pagesTaxonomy in The Affective DomainNaomie MacarandanNo ratings yet
- Druckenmiller August 2010 Letter To InvestorsDocument1 pageDruckenmiller August 2010 Letter To InvestorsDealBook100% (1)
- University of La Verne Induction Program Contract P 1Document5 pagesUniversity of La Verne Induction Program Contract P 1api-341729694No ratings yet
- Psychology & Health: To Cite This Article: Peter Salovey, Laura R. Stroud, Alison Woolery & Elissa S. Epel (2002)Document19 pagesPsychology & Health: To Cite This Article: Peter Salovey, Laura R. Stroud, Alison Woolery & Elissa S. Epel (2002)Khoyrunnisaa AnnabiilahNo ratings yet
- Sample Self Awareness 2Document5 pagesSample Self Awareness 2Siti SurihNo ratings yet
- 6805 Manuscript 39739 1 10 20210512Document6 pages6805 Manuscript 39739 1 10 20210512Carla Jubells GilNo ratings yet
- CV CamposRichardDocument5 pagesCV CamposRichardMhico MateoNo ratings yet
- Mapc II July 2015Document14 pagesMapc II July 2015Manisha VermaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing An IntroductionDocument46 pagesPsychiatric Nursing An Introductionsimplyrosalyn100% (1)
- Rethinking Parental Alienation and Redesigning Parent ChildDocument18 pagesRethinking Parental Alienation and Redesigning Parent ChildRicardo100% (1)
- Peer Pressure Among The Grade 12 Abm Students in The University of MindanaoDocument51 pagesPeer Pressure Among The Grade 12 Abm Students in The University of MindanaoSHAMXEL XANDRA DE CASTRO50% (2)
- Behavioral Game TheoryDocument3 pagesBehavioral Game Theoryme hahahaNo ratings yet
- 5 Dysfunctions of TeamDocument15 pages5 Dysfunctions of TeamsumitsethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Family 11Document14 pagesChapter 10-Family 11Sadia FerdowsiNo ratings yet
- When More Is LessDocument81 pagesWhen More Is LessJunelNo ratings yet
- The Recruitment, Selection and RetentionDocument28 pagesThe Recruitment, Selection and RetentionFaidin NurNo ratings yet