Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Best First Search?: G (N) Path Distance H (N) Estimate To Goal
What Is Best First Search?: G (N) Path Distance H (N) Estimate To Goal
Uploaded by
Saranya NarayanasettiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Best First Search?: G (N) Path Distance H (N) Estimate To Goal
What Is Best First Search?: G (N) Path Distance H (N) Estimate To Goal
Uploaded by
Saranya NarayanasettiCopyright:
Available Formats
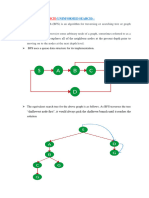
What is Best First Search?
If we consider searching as a form of traversal in a graph, an uninformed search algorithm would blindly
traverse to the next node in a given manner without considering the cost associated with that step. An informed
search, like Best first search, on the other hand would use an evaluation function to decide which among the
various available nodes is the most promising (or ‘BEST’) before traversing to that node.
The Best first search uses the concept of a Priority queue and heuristic search. To search the graph space, the
BFS method uses two lists for tracking the traversal. An ‘Open’ list which keeps track of the current
‘immediate’ nodes available for traversal and ‘CLOSED’ list that keeps track of the nodes already traversed.
Best First Search Algorithm
1. Create 2 empty lists: OPEN and CLOSED
2. Start from the initial node (say N) and put it in the ‘ordered’ OPEN list
3. Repeat the next steps until GOAL node is reached
1. If OPEN list is empty, then EXIT the loop returning ‘False’
2. Select the first/top node (say N) in the OPEN list and move it to the CLOSED list. Also capture
the information of the parent node
3. If N is a GOAL node, then move the node to the Closed list and exit the loop returning ‘True’.
The solution can be found by backtracking the path
4. If N is not the GOAL node, expand node N to generate the ‘immediate’ next nodes linked to
node N and add all those to the OPEN list
5. Reorder the nodes in the OPEN list in ascending order according to an evaluation function f(n)
This algorithm will traverse the shortest path first in the queue. The time complexity of the algorithm is given
by O(n*logn) .
Variants of Best First Search
The two variants of Best First Search are Greedy Best First Search and A* Best First Search. The Greedy
BFS algorithm selects the path which appears to be the best, it can be known as the combination of depth-first
search and breadth-first search. Greedy BFS makes use of Heuristic function and search and allows us to take
advantages of both algorithms.
The only difference between Greedy BFS and A* BFS is in the evaluation function. For Greedy BFS the
evaluation function is f(n) = h(n) while for A* the evaluation function is f(n) = g(n) + h(n).
Essentially, since A* is more optimal of the two approaches as it also takes into consideration the total distance
travelled so far i.e. g(n).
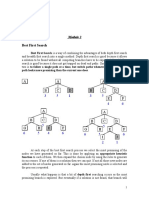
Best First Search Example
Let’s have a look at the graph below and try to implement both Greedy BFS and A* algorithms step by step
using the two list, OPEN and CLOSED.
g(n) Path Distance
h(n) Estimate to Goal
f(n) Combined Hueristics i.e. g(n) + h(n)
Even though you would find that both Greedy BFS and A* algorithms find the path equally efficiently, number
of steps, you may notice that the A* algorithm is able to come up with is a more optimal path than Greedy BFS.
So in summary, both Greedy BFS and A* are Best first searches but Greedy BFS is neither complete, nor
optimal whereas A* is both complete and optimal. However, A* uses more memory than Greedy BFS, but it
guarantees that the path found is optimal.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Best First Search
Advantages:
1. Can switch between BFS and DFS, thus gaining the advantages of both.
2. More efficient when compared to DFS.
Disadvantages:
1. Chances of getting stuck in a loop are higher.
You might also like
- REPUBLIC ACT NO 9999. Free Legal AssistanceDocument9 pagesREPUBLIC ACT NO 9999. Free Legal AssistanceNilsaNo ratings yet
- Tecson VS Glaxo LaborDocument2 pagesTecson VS Glaxo LaborDanyNo ratings yet
- Macro Economic Policies of SwitzerlandDocument18 pagesMacro Economic Policies of SwitzerlandShashank JoganiNo ratings yet
- California Divison of Worker Compensation and Medical Billing & Payment GuideDocument176 pagesCalifornia Divison of Worker Compensation and Medical Billing & Payment Guidearunsanju78No ratings yet
- WorldSpan - 9I01 Documentation Reference ManualDocument152 pagesWorldSpan - 9I01 Documentation Reference ManualAlexandra NicNo ratings yet
- A AlgorithmDocument3 pagesA AlgorithmSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Search Techniques in AI - Best First Search, Greedy Best and ASTARdocxDocument1 pageSearch Techniques in AI - Best First Search, Greedy Best and ASTARdocxBhuvan ThakurNo ratings yet
- Informed Search AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesInformed Search AlgorithmsPriyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- AI AssgmntDocument18 pagesAI Assgmntrobel damiseNo ratings yet
- Informed Search AlgorithmsDocument12 pagesInformed Search AlgorithmsphaniNo ratings yet
- AI AssgmntDocument18 pagesAI Assgmntrobel damiseNo ratings yet
- Informed Search AI MID2 Unit 2Document8 pagesInformed Search AI MID2 Unit 2ks.umashankerNo ratings yet
- Shayantan Kabiraj Company TarDocument12 pagesShayantan Kabiraj Company Tar22Shayantan KabirajNo ratings yet
- Informed Search Algorithms in AI - JavatpointDocument10 pagesInformed Search Algorithms in AI - JavatpointNahla khanNo ratings yet
- Informed Search Algorithm Group1Document8 pagesInformed Search Algorithm Group1Yis AlNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument18 pagesArtificial IntelligenceAlima NasaNo ratings yet
- AI Search AlgorithmDocument38 pagesAI Search AlgorithmRajat KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Uninformed and Informed Searches 2Document20 pagesModule 7 Uninformed and Informed Searches 2Clash Of ClanesNo ratings yet
- SearchDocument17 pagesSearchHusayaNo ratings yet
- Uninformed Search AlgorithmsDocument63 pagesUninformed Search AlgorithmsTania CENo ratings yet
- A Star PracticeDocument31 pagesA Star PracticeShreyash VermaNo ratings yet
- BFS AlgorithmDocument14 pagesBFS AlgorithmSupriya NevewaniNo ratings yet
- Session-6 A SearchDocument10 pagesSession-6 A SearchAvinash AllaNo ratings yet
- Session-5 Uninformed Search Strategies and Informed Search StrategiesDocument6 pagesSession-5 Uninformed Search Strategies and Informed Search StrategiesAvinash AllaNo ratings yet
- Informed Search: Prepared by Dr. Megharani PatilDocument22 pagesInformed Search: Prepared by Dr. Megharani PatilPrashantNo ratings yet
- AI Imp QuestionsDocument33 pagesAI Imp Questionsumaimaaakhan0143No ratings yet
- LP-II - AI-Lab ManualDocument33 pagesLP-II - AI-Lab ManualMatin MullaNo ratings yet
- What Is HeuristicsDocument5 pagesWhat Is HeuristicsPrithiv RajNo ratings yet
- Heuristic in Ai: BY-Chiranjeev Sharma A2324717001 Suraj Kumar Ojha A2324717007 7cse3 MbaDocument14 pagesHeuristic in Ai: BY-Chiranjeev Sharma A2324717001 Suraj Kumar Ojha A2324717007 7cse3 Mbachiranjeev sharmaNo ratings yet
- Module-02 AIML NOTESDocument29 pagesModule-02 AIML NOTESbabureddybn262003No ratings yet
- AI Unit 2Document37 pagesAI Unit 2aishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Test2 PortionsDocument115 pagesTest2 PortionsAshwath GuptaNo ratings yet
- Module-02 AIML 21CS54Document27 pagesModule-02 AIML 21CS54Deepali Konety67% (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Questions SolvedDocument17 pagesArtificial Intelligence Questions SolvedAlima NasaNo ratings yet
- A Star AlgoDocument78 pagesA Star Algojiminisinbts02No ratings yet
- Astar TutorialDocument5 pagesAstar Tutorialayesha_khan963No ratings yet
- 2-1 CAI Unit II Q & ADocument6 pages2-1 CAI Unit II Q & Aluciferk0405No ratings yet
- BFS and DFS-4Document27 pagesBFS and DFS-4Anushka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document94 pagesModule 31rn21cd008.chandanmNo ratings yet
- An Implementation of Path Planning Algorithms For Mobile Robots On A Grid Based MapDocument6 pagesAn Implementation of Path Planning Algorithms For Mobile Robots On A Grid Based MapSergio LobatoNo ratings yet
- Search Algorithms in AI6Document17 pagesSearch Algorithms in AI6jhn75070No ratings yet
- AI Mod2Document17 pagesAI Mod2Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Searching AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesSearching Algorithmsinpiresherlock07No ratings yet
- Path Finding AlgorithmDocument13 pagesPath Finding Algorithmksenthil77No ratings yet
- Session 12 Informed Search Strategies (Heuristic Search Techniques) A Search (Minimizing The Total Estimated Solution Cost)Document33 pagesSession 12 Informed Search Strategies (Heuristic Search Techniques) A Search (Minimizing The Total Estimated Solution Cost)Markapuri Santhoash kumarNo ratings yet
- AI Chapter 4Document13 pagesAI Chapter 4Antonio Peji JrNo ratings yet
- The Admissibility of GivenDocument4 pagesThe Admissibility of GivenRajdeep DasNo ratings yet
- Ai LP-II Lab ManualDocument42 pagesAi LP-II Lab ManualAbubaker QureshiNo ratings yet
- AI Algo and DifferenceDocument3 pagesAI Algo and DifferenceajitbitNo ratings yet
- BFS Greedybfs Astar Search Techniques in AI Difference and DetailsDocument2 pagesBFS Greedybfs Astar Search Techniques in AI Difference and DetailsBhuvan ThakurNo ratings yet
- Best First Search & A-Star AlgorithmDocument16 pagesBest First Search & A-Star AlgorithmHarishKumar RNo ratings yet
- Algorithms and Complexity 2003 Graph Searching AlgorithmsDocument2 pagesAlgorithms and Complexity 2003 Graph Searching AlgorithmsPhanindra Babu PabbaNo ratings yet
- A Star MaterialDocument7 pagesA Star MaterialAditya IyerNo ratings yet
- A Star AlgorithmDocument24 pagesA Star AlgorithmPreeTi KalWarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document15 pagesLecture 7MemoryNo ratings yet
- Optimized AO Algorithm For And-Or Graph Search: Aby Abahai TDocument4 pagesOptimized AO Algorithm For And-Or Graph Search: Aby Abahai TIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Aimodule 2Document21 pagesAimodule 2Joona JohnNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence/Search/Heuristic Search/astar SearchDocument6 pagesArtificial Intelligence/Search/Heuristic Search/astar SearchAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- Anytime A-Star AlgorithmDocument4 pagesAnytime A-Star AlgorithmDisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Chapter-1 NotesDocument17 pagesModule-2 Chapter-1 NotesKavya VNo ratings yet
- 5, Informed Searching Algorithms-IDocument54 pages5, Informed Searching Algorithms-ITania CENo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Heuristic Functions, Best First SearchDocument23 pagesUnit - 2 Heuristic Functions, Best First Searchthummalavasanth5No ratings yet
- Ignou Mcs 031 Solved PaperDocument7 pagesIgnou Mcs 031 Solved PaperGaurav Sood0% (2)
- Ac 3Document8 pagesAc 3Saranya NarayanasettiNo ratings yet
- AI For DS - Theory Search Fundamentals and Intelligent SearchDocument15 pagesAI For DS - Theory Search Fundamentals and Intelligent SearchSaranya NarayanasettiNo ratings yet
- AI For DS - Theory CSP, Wumpus World and Probabilistic ReasoningDocument11 pagesAI For DS - Theory CSP, Wumpus World and Probabilistic ReasoningSaranya NarayanasettiNo ratings yet
- AIDS HA4 AnswersDocument8 pagesAIDS HA4 AnswersSaranya NarayanasettiNo ratings yet
- 20cs2222aa Cns Lab ManualDocument72 pages20cs2222aa Cns Lab ManualSaranya NarayanasettiNo ratings yet
- 17my GCC Mirage Catalog EngDocument10 pages17my GCC Mirage Catalog EngwreckiebNo ratings yet
- How To Post Unlimited Ads On Craigslist - pdf0Document10 pagesHow To Post Unlimited Ads On Craigslist - pdf0spinbladeNo ratings yet
- RBI PBPP Business Research Dec 2012 (F)Document78 pagesRBI PBPP Business Research Dec 2012 (F)AmbreenNo ratings yet
- Kavika TRF MFG CompanyanujDocument5 pagesKavika TRF MFG Companyanujtanwar_anuj1990No ratings yet
- User Manual: 4-Axis GPS DroneDocument24 pagesUser Manual: 4-Axis GPS DroneJaime Núññez SotomayorNo ratings yet
- 005 Khan V Simbillo MarianoDocument2 pages005 Khan V Simbillo MarianoJoshua MeracapNo ratings yet
- William Karnavas ResumeDocument1 pageWilliam Karnavas Resumeapi-340620869No ratings yet
- Via Facsimile and First Class MailDocument8 pagesVia Facsimile and First Class Mailmoveonorg100% (1)
- High Flow High Pressure Reducing RegulatorsDocument4 pagesHigh Flow High Pressure Reducing Regulatorsامیر علیNo ratings yet
- Business Math For Finals NotesDocument8 pagesBusiness Math For Finals NotesPullos, Gillian C.No ratings yet
- Isi Swro PDFDocument2 pagesIsi Swro PDFachmadinNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Dr. Fariza KhalidDocument36 pagesSampling: Dr. Fariza KhalidrameshNo ratings yet
- Fishbowl Inventory White PaperDocument6 pagesFishbowl Inventory White PaperanjocargaNo ratings yet
- FM Module With Usb FunctionDocument3 pagesFM Module With Usb FunctionShruthi BhatNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of MoneyDocument7 pagesThe Evolution of MoneyHà Nhi LêNo ratings yet
- Home Decor & Furniture Catalog by SlidesgoDocument11 pagesHome Decor & Furniture Catalog by Slidesgopejuang ITNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan AfricaDocument51 pagesMathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan AfricapeeNo ratings yet
- Rosemount 644 Head Mount Temperature Transmitter Universal Junction BoxDocument5 pagesRosemount 644 Head Mount Temperature Transmitter Universal Junction BoxjhapsinNo ratings yet
- Dedicated To Excellence: Ponsse OyjDocument8 pagesDedicated To Excellence: Ponsse OyjkeesNo ratings yet
- Field Installation Guide v4 - 5Document58 pagesField Installation Guide v4 - 5John ChouNo ratings yet
- German Pharmacies (Figures, Data, Facts) 2012Document31 pagesGerman Pharmacies (Figures, Data, Facts) 2012Vladimir ArguirovNo ratings yet
- NextGen Bus Study UpdateDocument16 pagesNextGen Bus Study UpdateMetro Los AngelesNo ratings yet
- National Day Supplement 10 Gems MarketDocument9 pagesNational Day Supplement 10 Gems Marketjanitha_dNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Eccentric Beam-Column Corner Joints Connecting Spread-Ended BeamsDocument8 pagesCyclic Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Eccentric Beam-Column Corner Joints Connecting Spread-Ended BeamsMarimuthu KaliyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- NCP6131S52MNR2G On SemiconductorDocument1 pageNCP6131S52MNR2G On SemiconductorKrista TranNo ratings yet