Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand Out For Plane Mirrors
Uploaded by
api-6093474540 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views1 pageOriginal Title
hand out for plane mirrors
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views1 pageHand Out For Plane Mirrors
Uploaded by
api-609347454Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
REFLECTION OF LIGHT IN PLANE MIRRORS
REFLECTION IMAGE FORMATION IN MIRRORS cannot be projected on a screen. Virtual
*Reflection is the bouncing back of light into the *A mirror is an object or device that reflects images are always upright.
original medium where it has been traveling light. It may be classified as a plane mirror, a *Real images are formed when light rays
after hitting a surface. concave mirror, or a convex mirror. actually converge. Real images are inverted
and can be projected on a screen. They are
Two Types of Reflection *Images produced by mirrors depend on the always inverted.
1. Regular or Specular Reflection – In type of mirror and the location of the object.
specular reflection, the reflected rays IMAGES FORMED BY A PLANE MIRROR
are parallel to each other. This type of *The characteristics of an image may be *The image formed by a plane mirror is of the
reflection is done by smooth surfaces. described in terms of its location, orientation, same size as the object, as far behind the mirror
2. Irregular or Diffuse Reflection – In size (magnification), and type. as the object is in front; virtual and upright but
diffuse reflection, the reflected rays are 1. Location – an image may be formed in front laterally reversed.
in different angles and directions. or at the back of a mirror
Rough surfaces have irregular 2. Orientation – an image may either be SOME USES OF PLANE MIRRORS
reflections. upright or inverted *Plane mirrors have variety of uses which
3. Size (magnification) – the image formed can include being used in kaleidoscopes, reflecting
THE LAWS OF REFLECTION either be reduced or enlarged telescopes, compound microscopes, and
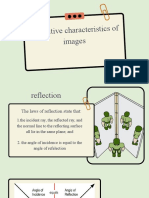
*The laws of reflection are: 4. Type – an image can be real or virtual periscopes. They are also used as a looking
• The incident ray, the normal, and the *Virtual images are formed when light rays glass, as a reflector, and for other practical
reflected ray lie in one plane. only appear to converge but do not actually purposes.
• The angle of incidence is equal to the do so. Virtual images are right side up and
angle of reflection. LEGENDS:
Reflected ray
Incident ray
Normal line
Virtual lines
mirror
Fig 2. Image Formation in Plane Mirrors
Fig 1. Laws of Reflection
You might also like
- Aramco-GI Instruciton Manual PDFDocument12 pagesAramco-GI Instruciton Manual PDFRiaz ahmed100% (2)
- 01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedDocument73 pages01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedKyra Lim100% (1)
- 5.1 Reflection of LightDocument16 pages5.1 Reflection of LightJunaidah Mohamad RamliNo ratings yet
- Reflection and MirrorsDocument51 pagesReflection and MirrorsLieh Arvey MabilingNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - NotesDocument17 pagesDelhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - Notesbaby doodlesNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Guide English Medium 215874 PDFDocument26 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Guide English Medium 215874 PDFvasanthagokilam rajendranNo ratings yet
- NDT PresentationDocument120 pagesNDT PresentationTapan Kumar Nayak100% (3)
- Radiation Exposure and Image Quality in X-Ray Diagnostic Radiology Physical Principles and Clinical Applications (PDFDrive)Document208 pagesRadiation Exposure and Image Quality in X-Ray Diagnostic Radiology Physical Principles and Clinical Applications (PDFDrive)Eskadmas BelayNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties of Solids 2nd Ed by Mark FoxDocument118 pagesOptical Properties of Solids 2nd Ed by Mark FoxAnshuman Banerjee75% (24)
- TWI Radiographic Interpretation Part 1 Course Reference WIS 20 2004Document66 pagesTWI Radiographic Interpretation Part 1 Course Reference WIS 20 2004ehsan hatamiNo ratings yet
- Arihant CBSE Physics Term 2 Class 12 - RemovedDocument176 pagesArihant CBSE Physics Term 2 Class 12 - RemovedPayal KhabaleNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 5Document8 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 5Jess Anthony Efondo100% (1)
- Puharich Apparatus For Shielding A Person From ELF WavesDocument10 pagesPuharich Apparatus For Shielding A Person From ELF Wavesoscarnine100% (1)
- Science10 Q2 Mod3 QualitativeCharacteristicsOfImagesDocument12 pagesScience10 Q2 Mod3 QualitativeCharacteristicsOfImagesKOBE BRYANT TIDOYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document185 pagesChapter 13farhanasikder123No ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedDocument6 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics NotesDocument23 pagesGrade 12 Physics NotesAlphonso TulayNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 - Module 3: Qualitative Characteristics of Images (REVIEWER)Document4 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 - Module 3: Qualitative Characteristics of Images (REVIEWER)Ella AuriaNo ratings yet
- 05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 pages05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Nikki NinjaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of ImagesDocument23 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Imagesmantilejoshua05No ratings yet
- 25 Activity MirrorsDocument4 pages25 Activity MirrorsJenny BayengNo ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument72 pagesLight WavesJeffrey MaNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument40 pagesOPTICSJanelle Ann BacoNo ratings yet
- Types of ReflectionDocument3 pagesTypes of ReflectionArjix HandyManNo ratings yet
- LightDocument16 pagesLightlomash.vijay.18No ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of Images Formed by MirrorsDocument6 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Images Formed by MirrorsGenina TejadaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument63 pagesReflection and Refraction of Lightzarish ziaNo ratings yet
- Science 3 4 ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience 3 4 ReviewerAngelica VersolaNo ratings yet
- Q2C3L2 Introduction and Plane MirrorsDocument25 pagesQ2C3L2 Introduction and Plane Mirrorsashleeyishin30No ratings yet
- Answer Key OpticsDocument14 pagesAnswer Key OpticsLeah ClovisNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 1Document20 pagesLight Lesson 1rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 1Document20 pagesLight Lesson 1rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Light PDFDocument1 pageLight PDFsatish dongardiyeNo ratings yet
- ZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecDocument8 pagesZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecJaymarie ZabateNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionDocument12 pagesChapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- Reflection Mirrors 2022 2023Document92 pagesReflection Mirrors 2022 2023Jeon ManobanNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument40 pagesLight Mirrors and LensescrizaannmonguezNo ratings yet
- Grade-10-Module-4-Mirrors-and-Lenses-Second-EditionDocument17 pagesGrade-10-Module-4-Mirrors-and-Lenses-Second-EditionroseNo ratings yet
- Eve Ross - 10.2 - Reflection of LightDocument6 pagesEve Ross - 10.2 - Reflection of LightEve RossNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - W5Document13 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - W5rawisadaniNo ratings yet
- 10 Reflection of LightDocument8 pages10 Reflection of LightMugdhaNo ratings yet
- Light - Strand 2Document10 pagesLight - Strand 2aaravNo ratings yet
- Laws of ReflectionDocument24 pagesLaws of ReflectionEdAnNo ratings yet
- LightDocument5 pagesLightpranav .gNo ratings yet
- Light Printed NotesDocument6 pagesLight Printed Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- LightDocument18 pagesLightAyush BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Physics 18 - Reflection and RefractionDocument53 pagesPhysics 18 - Reflection and Refractionsalmasoma100% (1)
- Wave and Optics DLPDocument8 pagesWave and Optics DLPlopezchinshin28No ratings yet
- 12th Physics Vol 2 Guide EMDocument85 pages12th Physics Vol 2 Guide EMRaghulNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Quarter 2 Module 3 - Qualitative CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesGrade 10 Quarter 2 Module 3 - Qualitative CharacteristicsAlljhon Dave Joshua MagnoNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 3Document34 pagesQ2 Module 3Ryza AcunaNo ratings yet
- Images: Does Light Travel in Straight Line?Document3 pagesImages: Does Light Travel in Straight Line?Narasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Mirror ImagesDocument18 pagesPlane and Spherical Mirror ImagesQueenie Faye TongolNo ratings yet
- Optics Hand OutDocument14 pagesOptics Hand OutChillyung OxytoneNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 - Lesson 2 and 3Document12 pagesGRADE 10 - Lesson 2 and 3Christian ConsignaNo ratings yet
- Quarter2 Module3Document23 pagesQuarter2 Module3Ma. Jenica CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Physics Class X For 2017 18 5 42Document38 pagesPhysics Class X For 2017 18 5 42jatinder kohliNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument77 pagesRay OpticsDiksha PublicationNo ratings yet
- Science Reflection-Of-Light MirrorsDocument3 pagesScience Reflection-Of-Light MirrorsAchilles ToringNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument19 pagesLight - Reflection and RefractionShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightsDocument39 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightsHestia SimoneNo ratings yet
- Physics 18 - Reflection and RefractionDocument53 pagesPhysics 18 - Reflection and RefractionLily PlayzNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Physics 11Document16 pagesRay Optics: Physics 11Trishla VermaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15Document46 pagesLesson 15halifa5136No ratings yet
- Antennas For VHForUHF Personal Radio A Theoretical and Experimental Study of Characteristics and PerformanceDocument10 pagesAntennas For VHForUHF Personal Radio A Theoretical and Experimental Study of Characteristics and PerformanceDiky ArtinNo ratings yet
- MindTap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test Bank DownloadDocument32 pagesMindTap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test Bank DownloadRocky Clark100% (21)
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument22 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationpriyaNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Microwave Propagation and Components: - H. D. ShuklaDocument43 pagesCh-2 Microwave Propagation and Components: - H. D. ShuklaBang Jago100% (1)
- RadiationSafetyManual PDFDocument106 pagesRadiationSafetyManual PDFphanthanhhungNo ratings yet
- Icru-58 Recommendations For Dose Reporting: BY Pratishtha Sharma Alka Kataria Saloni ChawlaDocument30 pagesIcru-58 Recommendations For Dose Reporting: BY Pratishtha Sharma Alka Kataria Saloni ChawlaSAlonii Chawla100% (2)
- 7.5 Summary: Section 7.6 Practice Set 209Document3 pages7.5 Summary: Section 7.6 Practice Set 209HUY NGUYEN QUANGNo ratings yet
- Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesReflection and Refractionanon_550444892No ratings yet
- Forensic Ass (Light)Document3 pagesForensic Ass (Light)Zacarias GarciaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Linear Attenuation Coefficient of Al, Fe and PB Applying Varying Channel MethodDocument15 pagesDetermination of Linear Attenuation Coefficient of Al, Fe and PB Applying Varying Channel MethodMyo Myint SheinNo ratings yet
- Save The Penguins Storyboard UseDocument21 pagesSave The Penguins Storyboard Useapi-306869230No ratings yet
- ENTEL - LB Minera CoronaDocument7 pagesENTEL - LB Minera CoronaEdu PomaNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity Effect of Distance and AbsorbersDocument7 pagesRadioactivity Effect of Distance and AbsorbersIstiqomah Dini PratiwiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Pulsed Dye LasersDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To Pulsed Dye Lasersgrad2013No ratings yet
- 1.2M KA BAND ANTENNA RXTX 3122 Final 0917201Document1 page1.2M KA BAND ANTENNA RXTX 3122 Final 0917201LavanyaNo ratings yet
- Iso 24444 2019Document15 pagesIso 24444 2019Jorge AfricanoNo ratings yet
- Physics 3232 Optics I: Introduction: Prof. Rick Trebino, Georgia Tech WWW - Frog.gatech - EduDocument38 pagesPhysics 3232 Optics I: Introduction: Prof. Rick Trebino, Georgia Tech WWW - Frog.gatech - EduTriaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Polarisation Maintaining FibersDocument17 pagesPresentation On: Polarisation Maintaining FibersJiren BhartiNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument39 pagesAtomic PhysicsaarNo ratings yet
- Designing of Microstrip Patch Antenna For X-Band ApplicationDocument7 pagesDesigning of Microstrip Patch Antenna For X-Band ApplicationNIET Journal of Engineering & Technology(NIETJET)No ratings yet
- TechnetiumDocument3 pagesTechnetiumDavid JonesNo ratings yet