Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Control Statements
Uploaded by
Gurudas Swain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesOriginal Title
30-July-2021
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesUnderstanding Control Statements
Uploaded by
Gurudas SwainCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Understanding Control Statements
Control flow statements, change or break the flow of
execution by implementing decision making, looping, and
branching your program to execute particular blocks of code
based on the conditions.
Java Provides ‘3’ types of control statements.
Selection Statements
Java selection statements allow to control the flow of
program’s execution based upon conditions known
only during run-time.
Java provides four selection statements:
1) if
2) if-else
3) if-else-if
4) switch
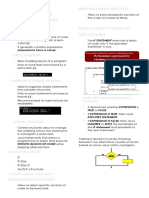
Understanding ‘if’ statement
The argument passing to the ‘if’ statement should be boolean
Syntax:
if(condition)
{
//executes this block if the result is ‘true’
}
else
{
//executes this block if the result is ‘false’
}
Both ‘else’ and braces are optional in if.
If we don’t write braces after if, we can write only one statement
which is dependent on ‘if’.
We should not declare any statement in that sentence.
You might also like
- BE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertFrom EverandBE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertNo ratings yet
- Chap4-Control Flow in JavaDocument5 pagesChap4-Control Flow in JavaVarsha KalagiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5Document8 pagesUnit - 5abhishekthummar6No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Selection StatementsDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Selection StatementsWAN FAZLINI IDAYU BINTI WAN FAKARI - PKTNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Control Structures Decision Making Structures:: Zero or Null, Then It Is Assumed AsDocument24 pagesUnit-Iii Control Structures Decision Making Structures:: Zero or Null, Then It Is Assumed Asshahabuddin khanNo ratings yet
- Java Control Statements - Control Flow in JavaDocument16 pagesJava Control Statements - Control Flow in JavaAnshita VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Cap281 Ca2Document5 pagesCap281 Ca2Nainpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Progamming 1 - Lesson 3Document13 pagesProgamming 1 - Lesson 3Joenell CabungcalNo ratings yet
- If StatementDocument11 pagesIf StatementEdeson John CabanesNo ratings yet
- Control StatementsDocument23 pagesControl StatementsNavya ParashirNo ratings yet
- Assignment Answer KeyDocument18 pagesAssignment Answer Keysubhathira prabakaranNo ratings yet
- A674940238 - 21789 - 9 - 2019 - 05. Control StructuresDocument48 pagesA674940238 - 21789 - 9 - 2019 - 05. Control StructuresSai TejaNo ratings yet
- Control StatementDocument11 pagesControl StatementworkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The If - Else (If) Statement and Nested StatementsDocument6 pagesChapter 4 - The If - Else (If) Statement and Nested Statementsanon_9685930No ratings yet
- IF - ELSE StatementDocument6 pagesIF - ELSE Statementayan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Java Slem Module WhatDocument10 pagesJava Slem Module WhatrajNo ratings yet
- Control StatmentsDocument14 pagesControl StatmentsEdeson John CabanesNo ratings yet
- C Programming-Control StatementsDocument13 pagesC Programming-Control StatementsSaurabh WaghNo ratings yet
- Conditional Branching StatementsDocument5 pagesConditional Branching Statementsjashanpreetsingh2111No ratings yet
- Session 16 IF ELSEDocument12 pagesSession 16 IF ELSESANIDHYSINGH RAGHUWANSHINo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Question and AnsweresDocument23 pagesUnit-2 Question and Answeresmallajasmitha7No ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument10 pagesChapter ThreeDesyilalNo ratings yet
- FORTRAN Programming - L07Document13 pagesFORTRAN Programming - L07asadujjaman studentNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument2 pagesDecision MakingAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- Week5 Java Flow Control and LoopDocument65 pagesWeek5 Java Flow Control and Loopjiwonhyung0234No ratings yet
- Com Eng Module13Document13 pagesCom Eng Module13April Jane ManaloNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument16 pagesDecision MakingAnshika DubeyNo ratings yet
- Java NotesDocument329 pagesJava Notesshoeb ahmadNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Concepts Using JavaDocument125 pagesObject Oriented Programming Concepts Using Javaamancha SANJANANo ratings yet
- BIT 2104 Lecture 5 & 6Document23 pagesBIT 2104 Lecture 5 & 6naaaj2638No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Decision and Loop Control Statements: StructureDocument70 pagesUnit 5 Decision and Loop Control Statements: StructureSafnamol PmNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Decision and Loop Control Statements: StructureDocument21 pagesUnit 5 Decision and Loop Control Statements: Structurert1220011No ratings yet
- C++ Decision Making Statements: Lecture ThreeDocument19 pagesC++ Decision Making Statements: Lecture ThreeCarabNo ratings yet
- Control StatementsDocument7 pagesControl StatementsVASUDEVAN N (RC2113003011006)No ratings yet
- C Programming 5Document17 pagesC Programming 5CarabNo ratings yet
- Oopr MidtermsDocument9 pagesOopr MidtermsChristine Marie CasasNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document19 pagesModule 2goursheteatharvaNo ratings yet
- Assigment: Types of Control Statements in CDocument32 pagesAssigment: Types of Control Statements in CAmisha VermaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7:control FlowDocument17 pagesLesson 7:control FlowhoaNo ratings yet
- Control StatementsDocument24 pagesControl StatementsREESHU RANJANNo ratings yet
- Java01 Seq288 Day 3Document11 pagesJava01 Seq288 Day 3Nelson MusiliNo ratings yet
- 2 Computer Programming Module 4Document6 pages2 Computer Programming Module 4joel lacayNo ratings yet
- Practical 05Document4 pagesPractical 05Danish TahirNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5-C Control StatementDocument26 pagesLecture-5-C Control StatementSadman WasifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Control StructuresDocument8 pagesLecture 5 - Control StructuresDervpolo VansNo ratings yet
- Java Control StatementsDocument20 pagesJava Control StatementsProjects 2022No ratings yet
- Conditional StatementDocument7 pagesConditional Statementjmpale505No ratings yet
- Comprog - Java Chap 4Document23 pagesComprog - Java Chap 4Kristel Joy Eledia NietesNo ratings yet
- Control StructuresDocument14 pagesControl StructuresVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dsa Notes of Class 03 by Manoj KumarDocument5 pagesDsa Notes of Class 03 by Manoj Kumardevilkapoor133No ratings yet
- The ?: Operator: Statement DescriptionDocument2 pagesThe ?: Operator: Statement DescriptionOlga MillerNo ratings yet
- Java Decision MakingDocument2 pagesJava Decision MakingRaj Kumar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Explain All About If Statements?: Decision Making and BranchingDocument11 pagesExplain All About If Statements?: Decision Making and BranchingSaiveera lykNo ratings yet
- Java Fundamentals For Android DevelopmentDocument17 pagesJava Fundamentals For Android DevelopmentRajatKumarNo ratings yet
- OOP Unit 3 NotesDocument18 pagesOOP Unit 3 Notesharshlaptop001No ratings yet
- Python 4Document13 pagesPython 4HemangNo ratings yet
- Apex - Decision - Making PDFDocument1 pageApex - Decision - Making PDFkiranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document41 pagesLecture 5asif sadekNo ratings yet
- Making Decision TololDocument2 pagesMaking Decision TololIssam BalaNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering DR B. C. Roy Engineering College, Durgapur Continuous Assessment #2Document5 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering DR B. C. Roy Engineering College, Durgapur Continuous Assessment #2Dibyam DeyNo ratings yet
- Instantaneous Values - ORU34234 - 02-Jul-2022 06-28-51-000 PMDocument2 pagesInstantaneous Values - ORU34234 - 02-Jul-2022 06-28-51-000 PMGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- 630 Kva Emmvee GTPDocument3 pages630 Kva Emmvee GTPGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Events - RCSU2132 - 19-Jul-2022 08-47-45-767 AMDocument2 pagesEvents - RCSU2132 - 19-Jul-2022 08-47-45-767 AMGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Interrupt Method: The Interrupted Thread Must Be in Either Sleep State or Wait StateDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Interrupt Method: The Interrupted Thread Must Be in Either Sleep State or Wait StateGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Character Streams:: 2 BytesDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Character Streams:: 2 BytesGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- InceptionDocument1 pageInceptionGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- 33Kv O/G Feeder Meter Readings of 132/33Kv Grid, Balugaon For The Month of Mar-2015Document1 page33Kv O/G Feeder Meter Readings of 132/33Kv Grid, Balugaon For The Month of Mar-2015Gurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- 13 Aug 2021Document5 pages13 Aug 2021Gurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Exception Handling: Compile Time Errors: Errors Which Occur Due To Syntax orDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Exception Handling: Compile Time Errors: Errors Which Occur Due To Syntax orGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- The Java Buzzwords: The Key Considerations Were Summed Up by The Java Team in The Following List of BuzzwordsDocument4 pagesThe Java Buzzwords: The Key Considerations Were Summed Up by The Java Team in The Following List of BuzzwordsGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitati On (CPR) : 2.1 HistoryDocument34 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitati On (CPR) : 2.1 HistoryGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- 07 PipelineDocument62 pages07 PipelineGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Internal Architecture of JVMDocument6 pagesInternal Architecture of JVMGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Understanding String Handling: ImmutableDocument8 pagesUnderstanding String Handling: ImmutableGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Tmegm 20132Document10 pagesTmegm 20132Gurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Training Programme 2022Document2 pagesTraining Programme 2022Gurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Programme Project Report (PPR) Masters of Arts in Sanskrit (Mask)Document10 pagesProgramme Project Report (PPR) Masters of Arts in Sanskrit (Mask)Gurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Types of ApplicationsDocument5 pagesTypes of ApplicationsGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Data Exchange Standards and ProtocolsDocument175 pagesProposal For Data Exchange Standards and ProtocolsGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- 40-SDMS-02B REV.08 WC OBIS Code Specifications Rev.8 - Sep-2019Document140 pages40-SDMS-02B REV.08 WC OBIS Code Specifications Rev.8 - Sep-2019Gurudas SwainNo ratings yet