Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STRUCTURE:-Largest Organ of The Body. Non-Uniform Thickness (Avg Thickness 1 To 2mm) Thick in Palm, Sole
Uploaded by
Rushikesh KarandeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STRUCTURE:-Largest Organ of The Body. Non-Uniform Thickness (Avg Thickness 1 To 2mm) Thick in Palm, Sole
Uploaded by
Rushikesh KarandeCopyright:
Available Formats
SKIN
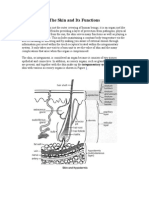
STRUCTURE:- Largest organ of the body. Non-uniform thickness(avg thickness=1 to 2mm); thick in palm ,sole
and interscapular region(about 5mm); thin in eyelids and penis (0.5mm only). It has two layers outer
epidermis and Inner epidermis
EPIDERMIS
Outer layer of skin formed by stratified epithelium.
Blood vessels are absent. Capillaries of dermis provide nutrition.
Layers: 1] Stratum corneum 2] Stratum lucidum 3] Stratum granulosum 4] Stratum spinosum 5] Stratum
germinativum
1] STRATUM CORNEUM :
• It is also known as horny layer
• Outermost layer; consists of dead cells called corneocytes.
• The cytoplasm is flattened with fibrous protein known as keratin
2] STRATUM LUCIDUM :
• Flattened epithelial cells. Many cells have degenerated nucleus and some have no nucleus.
• Has Shiny character, thus, appear as homologous translucent zone
3] STRATUM GRANULOSUM :
• Thin layer with two to five rows of flattened rhomboid cells.
• Cytoplasm contains granules of a protein called keratohyalin. (Keratohyalin is the precursor of keratin)
4] STRATUM SPINOSUM :
• Cells of this layer possess some spine like protoplasmic projections by which the cells are connected to
one another.
5] STRATUM GERMINATIVUM
• Thick layer made up of polygonal cells, superficially and columnar or cuboidal epithelial cells in the deeper
parts.
• New cells are constantly formed by mitotic division. The newly formed cells move continuously towards the
stratum corneum.
• The stem cells, which give rise to new cells, are known as keratinocytes
• Melanocytes produce the pigment called melanin. The color of the skin depends upon melanin.
• Projections called rete ridges extend down up to dermis. These projections provide anchoring and
nutritional function.
DERMIS
Inner layer of the skin; C.T layer, made up of collagen fibers, fibroblasts and histiocytes.
Collagen fibers exhibit elastic property and are capable of storing or holding water; contains the enzyme
collagenase . Layers of Dermis : 1. Superficial papillary layer 2. Deeper reticular layer.
1] SUPERFICIAL PAPILLARY LAYER
• Projects into the epidermis. It contains blood vessels, lymphatic and nerve fibers.
• This layer also has some pigment containing cells known as chromatophores.
• Dermal papillae are fingerlike projections, arising from the superficial papillary dermis. The papillae are
surrounded by rete ridges.
2] RETICULAR LAYER
• Made up of reticular and elastic fibers (found around the hair bulbs, sweat glands and sebaceous
glands).
• Immediately below the dermis, subcutaneous tissue is present.
• Lot of smooth muscles called arrector pili are also found in skin around the hair follicles
APPENDAGES OF SKIN : Hair follicles with hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands and mammary glands.
1] PIGMENTATION OF SKIN
• Skin cells contain a brown pigment called melanin, synthesized by melanocytes. After synthesis, melanin
spreads to other layers cells.
• Skin becomes dark when melanin content increases.
• It is protein in nature and it is synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine via dihydroxyphenylalanine
(DOPA).
• Deficiency of melanin leads to albinism .
2] HEMOGLOBIN IN THE BLOOD
Skin becomes:
▪ Pale, when hemoglobin content decreases
▪ Pink, when blood rushes to skin due to cutaneous vasodilatation (blushing)
▪ Bluish during cyanosis, which is caused by excess amount of reduced hemoglobin
FUNCTIONS OF SKIN
1] Protective – a)Bacteria and toxic substances ii. Mechanical blow iii. Ultraviolet rays.
2] Sensory 3] storage 4] Synthetic 5] regulation of body temperature 6] regulation of water and electrolyte
balance 7]excretory 8]absorptive 8]Secretory
GLANDS OF SKIN -1]Sebaceous glands 2]Sweat glands
1]SEBACEOUS GLAND
Simple or branched alveolar glands, situated in the dermis of skin.
Structure: ovoid / spherical in shape
Location: At the side of the hair follicle. These glands develop from hair follicles.So, the sebaceous glands are
absent over the thick skin, which is devoid of hair follicles.
Secretion: Secrete an oily substance called sebum.
Composition of Sebum:1. Free fatty acid 2. Triglycerides 3. Squalene 4. Sterols 5. Waxes 6. Paraffin
Functions of Sebum : 1. Antibacterial & antifungal actions 2. Keeps the skin smooth & oily 3.Prevent heat loss.
Activation of Sebaceous Glands at Puberty:
At the time of puberty, these glands are activated by sex hormones in both males and females. At the time of
puberty, particularly in males, due to the increased secretion of sex hormones, especially
dehydroepiandrosterone, the sebaceous glands are stimulated suddenly. It leads to the development of acne
on the face.
Acne : Localized inflammatory condition of the skin. It occurs because of overactivity of sebaceous glands.
Acne vulgaris is the common type of acne that is developed during adolescence. Acne disappears within few
years, when the sebaceous glands become adapted to the sex hormones.
2] SWEAT GLANDS
Two types: 1. Eccrine glands 2. Apocrine glands.
You might also like
- Skin PhysiologyDocument7 pagesSkin PhysiologyYash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Policy For B.ed HonsDocument67 pagesPolicy For B.ed HonsJameelaNo ratings yet
- SKINDocument30 pagesSKINShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document32 pagesPresentation 2bhava4dharaniNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Skin: Dr. Mohamed HassanDocument45 pagesPhysiology of The Skin: Dr. Mohamed HassanSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy - 4Document22 pagesGeneral Anatomy - 4Divya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Integumentary SystemDocument64 pagesLecture 9 Integumentary Systemhafiz patahNo ratings yet
- LG2 Histology of The SkinDocument26 pagesLG2 Histology of The SkinRawa AyubNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument15 pagesReviewerYza Grace S. PayangdoNo ratings yet
- Skin Anatomy: Prof: Shekhar TeliDocument21 pagesSkin Anatomy: Prof: Shekhar TeliShekhar TeliNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Document25 pagesIntegumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Islam SamirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SkinDocument40 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SkinRicko Ciady100% (1)
- Integumentray System by Hasnairah M. LimbotonganDocument47 pagesIntegumentray System by Hasnairah M. LimbotonganHasnairah LimbotonganNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Integumentary System: For Year 1 Medicine Students By: Zelalem. ADocument54 pagesOverview of The Integumentary System: For Year 1 Medicine Students By: Zelalem. AAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Histology Skin & AppendagesDocument44 pagesHistology Skin & AppendagesMathew JosephNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2020Document91 pagesIntegumentary System 2020Danielle AvelynNo ratings yet
- 1 LG) Histology of The SkinDocument25 pages1 LG) Histology of The SkinJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Integumentary SystemDocument32 pagesTopic 5 - Integumentary SystemAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Histology by - Dr.abdirahman Gagajir 1Document40 pagesHistology by - Dr.abdirahman Gagajir 1HusseinNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument32 pagesIntegumentary SystemSurvivors DreamsNo ratings yet
- Integumentary: Skin, Hair, Nails, GlandsDocument67 pagesIntegumentary: Skin, Hair, Nails, GlandsJosephNo ratings yet
- Skin - HistologyDocument30 pagesSkin - Histologydaw022100% (11)
- Skin Layers and Skin Appendages (L2) : Dr. Afrah HameedDocument25 pagesSkin Layers and Skin Appendages (L2) : Dr. Afrah HameedJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: For Year 1 Generic Nursing Students By: Zelalem. ADocument48 pagesThe Integumentary System: For Year 1 Generic Nursing Students By: Zelalem. AAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument90 pagesIntegumentary SystemJennyreen LenonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Functions of SkinDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System: Functions of SkinSoniyaJI84No ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM AnaphysioDocument62 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM AnaphysioNAMERAH GOTENo ratings yet
- ANAPHY ReviewerDocument10 pagesANAPHY ReviewerChristyl AmadorNo ratings yet
- Histo IntDocument3 pagesHisto IntNooredin JomaaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of Integumentary SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy Physiology of Integumentary SystemRaquel M. Mendoza100% (1)
- Integumentary System ReportDocument46 pagesIntegumentary System ReportMarilou Dacles IINo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument21 pagesIntegumentary SystemMythily manivannanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of Skinaimi Batrisyia100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument51 pagesIntegumentary SystemAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFDocument14 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFKeiNo ratings yet
- SKINDocument45 pagesSKINLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- Chap 3-Integumentary SystemDocument28 pagesChap 3-Integumentary Systemedward dimacaliNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument135 pagesIntegumentary SystemTrishaNo ratings yet
- MidwiferyDocument84 pagesMidwiferyAya LumumbaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pDocument4 pagesThe Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pdbelmerNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 4 - IntegumentaryDocument45 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 4 - Integumentaryprincesinclair77No ratings yet
- Kulit: Produk Kosmetik Lidya AmelianaDocument32 pagesKulit: Produk Kosmetik Lidya AmelianakarinaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Dr. Ammarah NaseerDocument67 pagesIntegumentary System: Dr. Ammarah NaseerAaqib RiazNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates'Integumentary System 2021 UpdatedDocument62 pagesVertebrates'Integumentary System 2021 UpdatedLumanlan ArcadioNo ratings yet
- Structure of Skin - MBBS PresentationDocument10 pagesStructure of Skin - MBBS PresentationPratikNo ratings yet
- Integumentary PDFDocument35 pagesIntegumentary PDFloey skiiesNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Anatomy of The SkinDocument23 pagesPart 3 - Anatomy of The SkinAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Structure SkincolorDocument32 pagesStructure SkincolorHelping Five (H5)No ratings yet
- AnaPhy Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesAnaPhy Integumentary SystemLeah Valerie EstolasNo ratings yet
- Skin AnatomyDocument21 pagesSkin Anatomyayesha khanNo ratings yet
- The Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDocument72 pagesThe Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDeborahMcCloudNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIntegumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument34 pagesIntegumentary SystemALAN MAGPANTAYNo ratings yet
- And Its Appendages: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowDocument44 pagesAnd Its Appendages: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowCesar Ivan Ruiz DiazNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Castroverde, Bacsa, TababaDocument98 pagesIntegumentary System Castroverde, Bacsa, TababaLemuel Lagasca Razalan IVNo ratings yet
- Histology of SkinDocument33 pagesHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- August UntitizationDocument2 pagesAugust UntitizationRushikesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- Loota Visha ChikitsaDocument1 pageLoota Visha ChikitsaRushikesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- Asclepidaceae: DR Adavesh B HoleyacheDocument20 pagesAsclepidaceae: DR Adavesh B HoleyacheRushikesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- Vividhashitpitiya AdhyayaDocument46 pagesVividhashitpitiya AdhyayaRushikesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- VitaminesDocument3 pagesVitaminesRushikesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- RBC and WBC Pipette DifferenceDocument1 pageRBC and WBC Pipette DifferenceRushikesh KarandeNo ratings yet
- Steps For Copyright ApplicationDocument7 pagesSteps For Copyright ApplicationLeah MedenillaNo ratings yet
- Judges Kings ProphetsDocument60 pagesJudges Kings ProphetsKim John BolardeNo ratings yet
- CA39BDocument2 pagesCA39BWaheed Uddin Mohammed100% (2)
- CASE: Distributor Sales Force Performance ManagementDocument3 pagesCASE: Distributor Sales Force Performance ManagementArjun NandaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Practitioner and Student WritingDocument28 pagesA Comparison of Practitioner and Student WritingMichael Sniper WuNo ratings yet
- Reflective Learning Journal (Teacher Guide) PDFDocument21 pagesReflective Learning Journal (Teacher Guide) PDFGary ZhaiNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Words - 20.11Document2 pagesVocabulary Words - 20.11ravindra kumar AhirwarNo ratings yet
- SOLO FrameworkDocument12 pagesSOLO FrameworkMaureen Leafeiiel Salahid100% (2)
- Agrarian ReformDocument40 pagesAgrarian ReformYannel Villaber100% (2)
- Baixar Livro Draw With Jazza Creating Characters de Josiah Broo PDFDocument5 pagesBaixar Livro Draw With Jazza Creating Characters de Josiah Broo PDFCarlos Mendoza25% (4)
- Alankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONDocument84 pagesAlankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONmannuNo ratings yet
- Dry Wall, Ceiling, and Painting WorksDocument29 pagesDry Wall, Ceiling, and Painting WorksFrance Ivan Ais100% (1)
- OrderFlow Charts and Notes 19th Sept 17 - VtrenderDocument9 pagesOrderFlow Charts and Notes 19th Sept 17 - VtrenderSinghRaviNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Inglés.Document14 pagesVocabulary Inglés.Psicoguía LatacungaNo ratings yet
- Surat Textile MillsDocument3 pagesSurat Textile MillsShyam J VyasNo ratings yet
- Julian BanzonDocument10 pagesJulian BanzonEhra Madriaga100% (1)
- Economic Survey 2023 2Document510 pagesEconomic Survey 2023 2esr47No ratings yet
- COSL Brochure 2023Document18 pagesCOSL Brochure 2023DaniloNo ratings yet
- AX Series Advanced Traffic Manager: Installation Guide For The AX 1030 / AX 3030Document18 pagesAX Series Advanced Traffic Manager: Installation Guide For The AX 1030 / AX 3030stephen virmwareNo ratings yet
- ZultaniteDocument4 pagesZultaniteAcharya BalwantNo ratings yet
- Sikarep® Microcrete-4: Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesSikarep® Microcrete-4: Product Data Sheetsidharthsud28No ratings yet
- Peacekeepers: First Term ExamDocument2 pagesPeacekeepers: First Term ExamNoOry foOT DZ & iNT100% (1)
- Bon JourDocument15 pagesBon JourNikolinaJamicic0% (1)
- Group 1 Reviewer Social LegislationDocument5 pagesGroup 1 Reviewer Social Legislationxsar_xNo ratings yet
- James Ellroy PerfidiaDocument4 pagesJames Ellroy PerfidiaMichelly Cristina SilvaNo ratings yet
- Project CharterDocument10 pagesProject CharterAdnan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Project Report Devki Nandan Sharma AmulDocument79 pagesProject Report Devki Nandan Sharma AmulAvaneesh KaushikNo ratings yet
- Install GuideDocument64 pagesInstall GuideJorge Luis Yaya Cruzado67% (3)
- 03-Volume II-A The MIPS64 Instruction Set (MD00087)Document793 pages03-Volume II-A The MIPS64 Instruction Set (MD00087)miguel gonzalezNo ratings yet
- HP MSM775 ZL Controller Installation GuideDocument21 pagesHP MSM775 ZL Controller Installation GuidezarandijaNo ratings yet