Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Plan
Types of Plan
Uploaded by
Rohit Ramesh Kale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views22 pagesOriginal Title
types of plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views22 pagesTypes of Plan
Types of Plan
Uploaded by
Rohit Ramesh KaleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Thank you
{>
Aglaia
connecting you
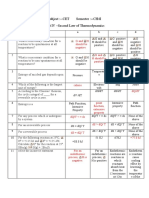
Short term plans
* Short-term plans generally allocate resources for a
year or less.
* They may also be referred to as operational plans
because they are concemed with daily activities and
standard business operations.
* It must be monitored and updated, and this is the
role of middle- and first-level management.
* Different managerial levels have responsibility for
implementing different types of short-term plans.
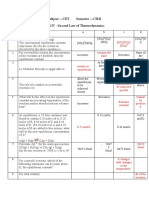
Long term plan (based on the
time)
« Along-term plan is crucial to the ullimate success
of the organization.
* Along-term plan extends four to five years into the
future.
* For some industries it may took two or three years.
« After that, it becomes too difficult to predict the
future with any degree of certainty.
* Top management is responsible for the development
of the long-term plan.
* The larger and more complex the organization, the
larger and more complex the long-term plan will be
to include all of the individual departments and
functions.
Single plan (Based on use)
* Single-use plans refer to plans that address a
one-time project or event.
¢ The length of the plans varies, but the most
common types are budgets and project
schedules.
* The obvious advantage of a single-use plan is
that it can be very specific in how it addresses the
needs of a particular situation.
Standing plans
* Standing plans are plans designed to be used
again and again.
* Examples include policies, procedures, and
regulations.
* The advantage of standing plans is that they foster
unity and fairness within an organization and help
to support stated organizational values.
* Standing plans save time because managers know
in advance how to address common situations.
* It aids in the delegation of work, because
employees are already familiar with the procedures
and regulations followed by the organization.
Operational Plans
« They are the plans that are made by frontline, or
low-level, managers.
* All operational plans are facused on the specific
procedures and processes that occur within the
lowest levels of the organization.
* Managers must plan the routine tasks of the
department using a high level of detail.
Tactical Plans
* Tactical plans support strategic plans by
translating them into specific plans relevant to a
distinct area of the organization.
* Tactical plans are concemed with the
responsibility and functionality of lower-level
departments to fulfill their parts of the strategic
plan.
Strategic Plans(based on nature)
* They are designed with the entire organization in mind
and begin with an organization's mission.
¢ Top-level managers, such as CEOs or presidents, will
design and execute strategic plans to paint a picture of
the desired future and long-term goals of the
organization.
* Essentially, strategic plans look ahead to where the
organization wants to be in three, five, even ten years.
* Strategic plans, provided by top-
¢
as the framework for lower-level g: .
Types of plans
* On the basis of nature:- Strategic plans ,Tactical
plans ,Operational plans .
* One the basis of use:-Single plan, Standing plan.
* One the basis of time:-long term plan, Short term
plan.
Numbering Plans by Budgeting
«When decisions are made and plans are set, the final
step to give meaning to them is to quantify them with
numbers converting them into budgets.
Formulating Derivative Plans
®Managers often still need to develop one or more
supportive plans to bolster their basic plan and to
explain the many details involved in reaching a broad
major plan.
*derivative plans are essentially required to support the
basic or general plan.
Selecting a Course
® After identifying the alternatives and considering the
merits of each carefully, managers now shall have to
adopt a plan and select one course of action.
*Managers may decide to follow several courses
instead of one best course.
Evaluating Alternative Courses
*Once alternative courses of action have been
identilied after seeking out alternative courses and
examining their strong and weak points, they must be
evaluated in light of how well each would help the
organization reach its goals. \
Evaluation
OUTSTANONS
determining the costs and expected PES
*Evaluating alternatives also includes
ory on
effects of each. }
peor
Determining Alternative Courses
* The fourth step is to search for and find out alternative
courses of action, especially those nol immediately
apparent.
Finding alternative is not the problem normally.
«Reducing the number of alternatives in order to analyze
i: eee
and find out the best one is the
problem,
Developing Premises
«The third step in the logical sequence of planning is
the establishment of the premises or assumptions on
which action statements are buill.
*The equality and success of any plan depend on the
equality of the assumptions on which it is based.
*Even one wrong assumption can
produce a poor or unrealistic
decision.
Establishing Objectives
eThis involves determining goals or objectives for
enterprise as a whole and then for each subordinate
tier and unit.
Establishment of objectives involves determining
the same for the enterprise as a whole and for each
subordinate level or unit.
@< @bjectives
Being Aware of Opportunities
+ Awareness of opportunities in the environment
both external to and internal in the organization is
the real beginning point for planning.
*At this stage, managers tend to create a foundation
from which they will develop their plans for the next
planning period.
* It is the basic management function which
includes formulation of one or more detailed
plans to achieve optimum balance of needs or
demands with the available resources.
* According to Urwick, “Planning is a mental
predisposition to do things in orderly way, to think
before acting and to act in the light of facts rather
than guesses".
* Planning is deciding best alternative among
others to perform different managerial functions in
order to achieve predetermined goals.
Steps of Effective Planning
Process
a
2
i
Introduction
* Planning means looking ahead and chalking out
future courses of action to be followed.
* lt is a preparatory step.
* It is a systematic activity which determines when,
how and who is going to perform a specific job.
« Planning is a detailed programme regarding future
courses of action.
« Itis rightly said “Well plan Is half done”. Therefore
planning takes into consideration available &
prospective human and physical resources of the
organization so as to get effective co-ordination,
contribulion & perfect adjustment.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 3 Cre MCQDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Cre MCQRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Pad. Dr. Vitthalrao Vikhe Patil Polytechnic, Loni: Micro-Hydro Power PlantDocument30 pagesPad. Dr. Vitthalrao Vikhe Patil Polytechnic, Loni: Micro-Hydro Power PlantRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- HTO MCQ Conduction-1Document3 pagesHTO MCQ Conduction-1Rohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- EErcDocument108 pagesEErcRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Processing of Oil SeedsDocument20 pagesProcessing of Oil SeedsRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Program CH-1: "Food Processing"Document42 pagesE-Learning Program CH-1: "Food Processing"Rohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Topic-2 Fruits and Vegetable Processing", Marks - 14Document35 pagesTopic-2 Fruits and Vegetable Processing", Marks - 14Rohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- ASS - HTO Lectures Topic-2Document39 pagesASS - HTO Lectures Topic-2Rohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- "Brewing Beverages" (Marks - 20) : Unit Outcomes (Uos)Document15 pages"Brewing Beverages" (Marks - 20) : Unit Outcomes (Uos)Rohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Bioenergy: Biomass, Which Can Be Used To ProduceDocument15 pagesBioenergy: Biomass, Which Can Be Used To ProduceRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- CH 3. Accident and Incident Investigation-1Document10 pagesCH 3. Accident and Incident Investigation-1Rohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Safety PlanningDocument10 pagesCH - 1 Safety PlanningRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Cet-Iv - MCQDocument6 pagesCet-Iv - MCQRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Cet-V - MCQDocument5 pagesCet-V - MCQRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- CET-III MCQsDocument8 pagesCET-III MCQsRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- CET-II MCQsDocument8 pagesCET-II MCQsRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet