Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Burns Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Chiara FajardoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Burns Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Chiara FajardoCopyright:
Available Formats
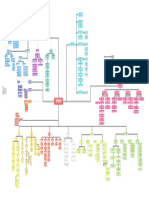
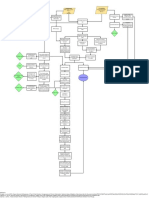
Exposure to injurious
substance (fire, hot liquid via
splash)
Endocrine
Sensory
Thermoregulatory Massive stress
Cadiovascular response,
Respiratory sympathetic nervous
Integumentary Loss of skin causes Absence of the
Rapid changes in system activation
the inability to regulate protective covering
Massive stress skeletal muscle of the epidermis
Direct exposure to body temperature
response, Release of inflammatory Increased vascular Local inflammation in Destruction of mitochondrial function Inflammatory
Loss of epithelial Singed heat or steam in an
sympathetic nervous cytokine necrosis factor permeability respose to burn damage enclosed setting (inhalation tissue (skin, connective mediators induce
integrity nasal hairs Adrenal corticoid
system activation injury) and presence of tissue, bone) peripheral insulin
Dead and denatured hormones and
neck and face burns Increased Hypothermia in the Nerve endings are resistance
epidermal and dermal layers Skeletal muscle catecholamine release
Fluid is able to Systemic release of Edema vascular early hours after injury sensitized and exposed to
remain intact over bed of mitochondria from burn
Myocardial Loss of fluid through leak out of the blood inflammatory factors permeability stimulation
Vasodilation granulation tissue victims are more
Adrenal corticoid contractility may be evaporation circulation uncoupled
hormones and suppressed Increased vascular
catecholamine Particulate matter produced permeability Hypermetabolic
Increased blood Sooty during combustion (soot) can Fluid leak results in response resets core
release Leathery, Dry top Activation of key
Distributive vessel permeability sputum mechanically obstruct and Blisters edema between dermal Source for greater temperature
and epidermal layer waxy white layer enzymes involved in hepatic epinephrine and Altered release of
shock irritate the airways heat production within Norepinephrine has the
Upper airway is appearance Pain 10/10 gluconeogenesis and inhibition adipokines from
Red skeletal muscle norepinephrine stimulate hepatic added effect of increasing the
obstructed of glucose uptake in peripheral adipose tissue cause
Leakage of fluids appearance gluconeogenesis and supply of glycerol to the liver
Burn patients become
from intravascular space Thin epidermal layer tissues such as the skeletal glycogenolysis via lipolysis insulin resistance
Peripheral hyperthermic for
into interstitium and third Wet wound forming fluid-filled vesicle muscles
vasoconstriction Reflex bronchoconstriction much of the postburn period, even
space (lungs) caused by release of histamine, breaks open in the absence of infection
Low blood serotonin, and thromboxane,
pressure a powerful vasoconstrictor, as well as
Reduced total (90/50) Massive chest constriction secondary
blood volume pulmonary edema to chest burn
clogs up alveoli Fever
(38.9 C)
Blood
glucose: 10
Increased afterload Reduced cardiac Hypovolemic mmol/L
output shock
Decreased delivery of
O2/nutrients to different organs;
decreased CO2 removal/wastes Use of
Tachypnea
from tissues accessory Stridor
(32 cpm)
muscles
Tachycardia
(126 bpm) SPO2 of 80%
kidney brain
on high oxygen
concentration, 76%
Note: Chest excursion may be greatly restricted
in room air
Decreased in chest burns, causing decreased tidal volume
GFR Anoxic
brain injury
Low
urine
output
You might also like
- Ripple Effects of The Low Touch Economy: V2 - Latest Update April 16, 2020 Strong Link Weak LinkDocument1 pageRipple Effects of The Low Touch Economy: V2 - Latest Update April 16, 2020 Strong Link Weak LinkBlink Muttaneeya UjjinNo ratings yet
- Pathos The NaziDocument2 pagesPathos The NaziMarcello Di LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExaminationDocument1 pageRespiratory ExaminationFANo ratings yet
- No NameDocument1 pageNo NamemasterNo ratings yet
- PMKP Juni-Desember 19Document256 pagesPMKP Juni-Desember 19Dini RizkyNo ratings yet
- En PDFDocument1 pageEn PDFSamir SamuelNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: MathNo ratings yet
- Eht Design Summary SampleDocument1 pageEht Design Summary SampleHolly SmithNo ratings yet
- 蝴蝶夫人Document5 pages蝴蝶夫人jellymysiyk526No ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- BURNS Concept MapDocument1 pageBURNS Concept MapJunam DisimbanNo ratings yet
- OUTPUT - MS - Poster MikroDocument1 pageOUTPUT - MS - Poster MikroHeriNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionvictor.garcia4080No ratings yet
- Member List For Indonesia Mold & Die AssociationDocument14 pagesMember List For Indonesia Mold & Die AssociationDaniel Pandapotan MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Sample Cause & EffectDocument1 pageSample Cause & EffectNishant AroraNo ratings yet
- See, See, The Word Is IncarnateDocument20 pagesSee, See, The Word Is IncarnateLopezNo ratings yet
- Attendance Register of BENGAL INDUSTRIES PRIVATE LIMITED Day or Night For The Month of AUGUST-2020Document8 pagesAttendance Register of BENGAL INDUSTRIES PRIVATE LIMITED Day or Night For The Month of AUGUST-2020Sharad RastogiNo ratings yet
- Plano Eléctrico 797B PDFDocument6 pagesPlano Eléctrico 797B PDFFrancisco Alejandro TelloNo ratings yet
- Page 1Document10 pagesPage 1sanjeeda fatimaNo ratings yet
- The Colourful Biography of Chinese Characters, Volume 1: The Complete Book of Chinese Characters with Their Stories in Colour, Volume 1From EverandThe Colourful Biography of Chinese Characters, Volume 1: The Complete Book of Chinese Characters with Their Stories in Colour, Volume 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- What Squirt Teaches Me about Jesus: Kids Learning about Jesus while Playing with FidoFrom EverandWhat Squirt Teaches Me about Jesus: Kids Learning about Jesus while Playing with FidoNo ratings yet
- Strangers' Voices In My Head: A Journey Through What Made Me Who I Am from My MindFrom EverandStrangers' Voices In My Head: A Journey Through What Made Me Who I Am from My MindNo ratings yet
- The First Extraterrestrial Signal: The Global Reaction to the Signal from the Outer Space AliensFrom EverandThe First Extraterrestrial Signal: The Global Reaction to the Signal from the Outer Space AliensNo ratings yet
- Rookie Rescuer: Learning about God and 'First Responder' Work through Real Calls!From EverandRookie Rescuer: Learning about God and 'First Responder' Work through Real Calls!No ratings yet
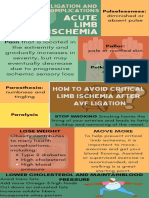
- Acute Limb Ischemia InfographicsDocument1 pageAcute Limb Ischemia InfographicsChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Drops Per Minute Reference ChartDocument1 pageDrops Per Minute Reference ChartChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Kaposi-Sarcoma PathophysiologyDocument1 pageKaposi-Sarcoma PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Signs and TagsDocument12 pagesElectrical Safety Signs and TagsChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- ABORTION PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABORTION PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- JOURNALDocument4 pagesJOURNALChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Post Mortem Care DiscussionDocument18 pagesPost Mortem Care DiscussionChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Focus Data Action Responce: Risk For Injury Related To Vision or As Evidence byDocument2 pagesFocus Data Action Responce: Risk For Injury Related To Vision or As Evidence byChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Lyceum-Northwestern University Tapuac District, Dagupan City College of Tourism Management PRELIMS (Part 1)Document4 pagesLyceum-Northwestern University Tapuac District, Dagupan City College of Tourism Management PRELIMS (Part 1)Chiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Delegation in Nursing LeadershipDocument25 pagesDelegation in Nursing LeadershipChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective CopingDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective CopingChiara Fajardo0% (3)
- Home Gardening: Saint Louis University Baguio City School of Nursing Level IIDocument13 pagesHome Gardening: Saint Louis University Baguio City School of Nursing Level IIChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mr. Ryan Carl D. Vinluan, LPT InstructorDocument6 pagesPrepared By: Mr. Ryan Carl D. Vinluan, LPT InstructorChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Learning StrategiesDocument3 pagesLearning StrategiesChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis University School of Nursing Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory Exercise No. 14 The Digestive System I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSaint Louis University School of Nursing Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory Exercise No. 14 The Digestive System I. ObjectivesChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Ana Lab Rubric FinalDocument1 pageAna Lab Rubric FinalChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Ana Lab Rubric FinalDocument1 pageAna Lab Rubric FinalChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- My Purpose in LifeDocument1 pageMy Purpose in LifeChiara Fajardo100% (1)
- Theory 2Document2 pagesTheory 2Chiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Developing A Multimedia Courseware Using Cognitive Load TheoryDocument2 pagesDeveloping A Multimedia Courseware Using Cognitive Load TheoryChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Learnings TheoryDocument3 pagesLearnings TheoryChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Theory 1Document2 pagesTheory 1Chiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Jailev's Prices AAA - DEALER PRICES 5k 2014.05.28Document2 pagesJailev's Prices AAA - DEALER PRICES 5k 2014.05.28Margaret DimaalaNo ratings yet
- 3.histology of Skin AppendagesDocument43 pages3.histology of Skin AppendagesdenekeNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Oral Pathology 7th Edition by RegeziDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Oral Pathology 7th Edition by RegeziSteve Isola100% (24)
- 1ST Summative Test in Science 6 Q2Document4 pages1ST Summative Test in Science 6 Q2Liza Mea Guhayon Reblinca0% (1)
- Laporan Master Tarif Pelayanan Rawat Jalan: Kode Nama TindakanDocument9 pagesLaporan Master Tarif Pelayanan Rawat Jalan: Kode Nama TindakanRetna Wahyu WulandariNo ratings yet
- Hairdressing Module 2 - Stylist and ClientDocument66 pagesHairdressing Module 2 - Stylist and ClientGensai KawakamiNo ratings yet
- What Is Cosmelan and Dermamelan?: The Solution?Document1 pageWhat Is Cosmelan and Dermamelan?: The Solution?Laurynne GouwsNo ratings yet
- O Skin Med SpaDocument3 pagesO Skin Med SpaShai HabonNo ratings yet
- SkinCare Company Bangalore LeadDocument36 pagesSkinCare Company Bangalore LeadShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Mini CNA Study GuideDocument22 pagesMini CNA Study GuideDillon DiNova100% (4)
- Lilienthal SamuelDocument382 pagesLilienthal Samuelmihaipopescu0No ratings yet
- Safety QuizDocument11 pagesSafety Quiznageswara raoNo ratings yet
- HairDocument6 pagesHairlê hữu cườngNo ratings yet
- Calamansi Soap ThesisDocument4 pagesCalamansi Soap Thesisfjdxfc4v100% (2)
- Wound Documentation TipsDocument4 pagesWound Documentation TipsLaura Hernandez100% (1)
- T V NG TACN1Document18 pagesT V NG TACN1Thanh ToànNo ratings yet
- Oriflame Products Knowledge-1Document14 pagesOriflame Products Knowledge-1Aqsa100% (3)
- NAT Reviewer On AnimalsDocument7 pagesNAT Reviewer On AnimalsKent Francis Layaguin82% (38)
- Assessment of Sun-Related Behaviour, Knowledge and Attitudes Among Nursing StudentsDocument9 pagesAssessment of Sun-Related Behaviour, Knowledge and Attitudes Among Nursing StudentsAdrian Alexis Romero GuillenNo ratings yet
- Wmsu-Vpaa-Fr-33.00 Templates For The Independent Learning PacketDocument3 pagesWmsu-Vpaa-Fr-33.00 Templates For The Independent Learning PacketBeng LunaNo ratings yet
- Section 2. Skin ProblemsDocument9 pagesSection 2. Skin ProblemsAliNo ratings yet
- Moisturizers What They Are and A Practical Approach To Product SelectionDocument12 pagesMoisturizers What They Are and A Practical Approach To Product SelectionCosNo ratings yet
- MiliariasisDocument4 pagesMiliariasisperpesanan100% (1)
- Concise DermatologyDocument279 pagesConcise DermatologyVivtor Silva100% (1)
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Alone and in CombinationDocument10 pagesAlone and in CombinationJose Mauricio Suarez BecerraNo ratings yet
- Andrews - Chapter 3 - Dermatosis Resulting From Physical FactorsDocument71 pagesAndrews - Chapter 3 - Dermatosis Resulting From Physical FactorsAngeli Ramos-EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - InstructionsDocument16 pagesLab 2 - InstructionsCazzel AvilesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Sensorysystem Lesson 6.1: Sense of SightDocument6 pagesLesson 6: Sensorysystem Lesson 6.1: Sense of SightGlessy AlvaroNo ratings yet
- The Amazing Human BodyDocument77 pagesThe Amazing Human Bodycititor1111No ratings yet