Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kaposi-Sarcoma Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Chiara FajardoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kaposi-Sarcoma Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Chiara FajardoCopyright:
Available Formats
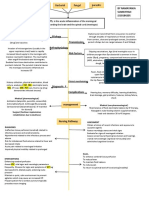
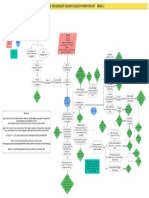
Kaposi Sarcoma
Legend
Predisposing:
Precipitating
Male (higher chance)
Immunosuppressed
Predisposing and HIV (+)
sexual activity
Precipitating Gay
HIV (+)
Factor Idiopathic
Increased ability for
malignant cells to
Persistent/Recurrent Decreased immune
evade immune
Night Sweats Infection Tissue Damage and function
defenses and thereby
inflammation persist
Pathophysiology
Viral DNA enters the
cell
Increased
inflammation and or
Increased infections
increase proliferation
Clinical of oncogenic virus
Manifestation Synthesis of proviral
DNA damage
DNA
Night Sweats
Diagnosis Insertion of proviral
DNA into host cell's
DNA
Disruption of tumor Insertion of actively
suppressor gene transcribed viral promoter
function sequence next to proto-
Introduction of
oncogene
oncogene
Decrease DNA repair,
decrease
control/inhibition of Proto-oncogene is
cellular division and transformed into an
decrease apoptosis oncogene
Cell death/disruption Virus enters epidermis,
of connections penetrates endings of
Purplish spots Increased risk of
between epidermal sensory and autonomic Excessive expression
uncontrolled cellular
cells nerves of oncogene
proliferation
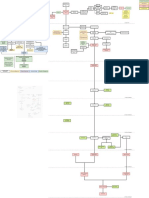
Viremia produces a virus not held back in
Fever generalized immune check by immune
response system abnormal lesion Increased cancer risk
Virus tracks along
Damage to cell abnormal vessel
nerves and establishes
Nonproductive cough
lining in the lungs ;.
latent infection in local
SOB
Lesions in the lungs
ganglia (e.g. upper
Tachypnea might block part of Kaposi Sarcoma
thoracic and cervical
an airway
ganglia) will create
inflammatory that will
infiltrate the vessels
Reduction in immune
Cell death/disruption
function leads to
of connections will create vascular
Purplish spots reactivation of latent
between epidermal mass/lesion
infection, virus tracks
cells
back out along nerves
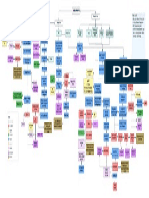
Purplish spots
severing of
inflammatory
creating flat macules
subtle proliferation of
irregular vascular
channels between
normal stromal
collagen
the extravasation of
erythrocytes and
hemosiderin into the
stroma
detection of
lymphoplasmacytic
infiltrate
worsening of
inflammatory will
made the flat macules
into plaques
proliferating spindled
cells that form interlacing
bundles closely
approximated with blood-
filled vascular spaces
intracellular hyaline
globules within lesion
cells
increased inflammatory
infiltrate consisting of
lymphocytes, plasma cells,
macrophages, and dendritic
cells
severe inflammatory will
turn it into subsequently
nodular lesions which is
the tumor stage
formation of intersecting
fascicles and sheets of
proliferating spindled
cells
Reference:
Douglas, J., et al. (2010). Kaposi Sarcoma Pathogenesis: A Triad of Viral Infection, Oncogenesis and Chronic Inflammation. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3472629/?fbclid=IwAR281Rak429AfuODZZfn9OvDw7NGy2rQtQSMap4T5VkT_zbtMOfvey9SvL8
Sigmund, E. (2015). Retroviral Infection: Mechanisms of Oncogenesis. Calgary Guide. http://calgaryguide.ucalgary.ca/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/Retroviral-Infections-Mechanisms-of-oncogenesis.jpg
Spence, S. (2012). Herpes Simplex Infection: Pathogenesis and Clinical FIndings. Calgary Guide. http://calgaryguide.ucalgary.ca/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/Herpes-Simplex-Virus-HSV.jpg
You might also like
- NIH Stroke Scale BookletDocument11 pagesNIH Stroke Scale Bookletcleber333100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)deric95% (97)
- Emergency Assistance PlanDocument4 pagesEmergency Assistance PlanTerence100% (1)
- Cna Practice ExamDocument4 pagesCna Practice ExamJennifer Venfield83% (12)
- NCP Ineffective CopingDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective CopingChiara Fajardo0% (3)
- NCP Ineffective CopingDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective CopingChiara Fajardo0% (3)
- NCP 1Document7 pagesNCP 1Mark PabalanNo ratings yet
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 pagesValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- 1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument7 pages1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFMAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPAnne De VeraNo ratings yet
- Ppe4 Reflection AssignmentDocument11 pagesPpe4 Reflection Assignmentapi-318846856100% (1)
- HEALTH SCIENCE JOURNAL VOLUME 7 (2013),ISSUE 3Document4 pagesHEALTH SCIENCE JOURNAL VOLUME 7 (2013),ISSUE 3Resha Pahlevi100% (1)
- ABORTION PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABORTION PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Femoral Nonunion - Risk Factors and Treatment Options PDFDocument10 pagesFemoral Nonunion - Risk Factors and Treatment Options PDFcronoss21No ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical Mobilitygianne121391No ratings yet
- Shift Transfer Roleplay in Hospital RoomDocument6 pagesShift Transfer Roleplay in Hospital RoomQonitaNo ratings yet
- Thoracentesis Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesThoracentesis Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNo ratings yet
- Post Cs Na Revised Na TohDocument31 pagesPost Cs Na Revised Na TohMinerva CortalNo ratings yet
- Soal Aggregate Community NursingDocument11 pagesSoal Aggregate Community NursingAde Ima NovikasariNo ratings yet
- Marjory GordonDocument7 pagesMarjory GordonFatih Haris Maulana100% (1)
- (Human) : Joyce Travelbee To Human RelationshipDocument3 pages(Human) : Joyce Travelbee To Human RelationshipJhanice Pejo PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Orem TheoryDocument3 pagesOrem TheoryLaverne CastroNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- Types, Causes and Treatments of ComasDocument3 pagesTypes, Causes and Treatments of ComasgcsNo ratings yet
- Becoming a NurseprenuerDocument4 pagesBecoming a NurseprenuerNova Triska Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Document20 pagesSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDocument11 pagesDrugs Acting On The Immune SystemloiselleilanoNo ratings yet
- Ipe - Neuro - Kelompok 8aDocument20 pagesIpe - Neuro - Kelompok 8aHanis NandaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Labor and DeliveryDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan for Labor and DeliveryRosemarie R. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Acute PancreatitisJamaica SaranquinNo ratings yet
- The Ebn A. Evidence Based Nursing For Level III General QuestionDocument7 pagesThe Ebn A. Evidence Based Nursing For Level III General QuestionAvyNo ratings yet
- True CertificateDocument7 pagesTrue CertificateDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous Abortion Final PaperDocument11 pagesSpontaneous Abortion Final Paperapi-241242357No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan On HyperthermiaAleah JayaganNo ratings yet
- Closed Humerus Fracture With Radial PalsyDocument35 pagesClosed Humerus Fracture With Radial PalsyEryn Farahin ZainalNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Test, Medical Management, and Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesHypertension: Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Test, Medical Management, and Nursing Care PlanMaulidyaFadilahNo ratings yet
- NCP For COPDDocument3 pagesNCP For COPDcy belNo ratings yet
- Viral, Bacterial and Fungal Meningitis Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument4 pagesViral, Bacterial and Fungal Meningitis Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentNamayanja SumayiyahNo ratings yet
- Delmar Cengage Learning Companions - Nursing Fundamentals - Caring & Clinical Decision MakingDocument3 pagesDelmar Cengage Learning Companions - Nursing Fundamentals - Caring & Clinical Decision MakingjjjNo ratings yet
- Norton Risk Assessment ToolDocument4 pagesNorton Risk Assessment ToolFadityo PrihantoroNo ratings yet
- SeizuresDocument2 pagesSeizureskaythe08No ratings yet
- NCP Hip FractureDocument5 pagesNCP Hip FractureCherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Tissue IntegrityDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Tissue IntegrityKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Stomach2Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Stomach2api-3718174100% (1)
- Deficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientDocument2 pagesDeficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientSeanmarie CabralesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetic KetoacidosisHanz AlecNo ratings yet
- Rationale For Health AssessmentDocument8 pagesRationale For Health AssessmentRegNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching PlanSonia MambaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for FatigueDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan for FatigueChad Smith100% (1)
- Nursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Document2 pagesNursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Marianne Rose HernandezNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination KoDocument8 pagesPhysical Examination KoJm Floyd R. MedenillaNo ratings yet
- Oks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!Document10 pagesOks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!CiaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Diverticulitis PatientDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diverticulitis PatientLeny GallardoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Polite RequestDocument7 pagesUnit 2 - Polite Requestnoni puspitaNo ratings yet
- Code Green Introduction Reviewer - RedDocument4 pagesCode Green Introduction Reviewer - RedJamieNo ratings yet
- Self-Efficacy Strategies and Academic PerformanceDocument20 pagesSelf-Efficacy Strategies and Academic PerformanceDianne Mae DagaNo ratings yet
- NCP of CavDocument3 pagesNCP of CavHenry Roque TagalagNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 MiDocument16 pagesNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesActivity 4 Critical ThinkingDenisse Angelie CastroNo ratings yet
- Test Result Normal Range Interpreta Tion Implicatio NDocument11 pagesTest Result Normal Range Interpreta Tion Implicatio NSitty Aizah MangotaraNo ratings yet
- CPC Group-3Document1 pageCPC Group-3Jhayber AndradeNo ratings yet
- Courtney Chinn - Skin InfectionsDocument1 pageCourtney Chinn - Skin InfectionsMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocument1 pageOsteoarthritis Concept MapJanselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia InfographicsDocument1 pageAcute Limb Ischemia InfographicsChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Pneumocystis Jiruveci Pneumoniae PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePneumocystis Jiruveci Pneumoniae PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- SBARXDocument1 pageSBARXChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Burns PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBurns PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Grading - ICU SKILLS SimulationDocument1 pageRubric For Grading - ICU SKILLS SimulationChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Wound Care InfographicsDocument5 pagesWound Care InfographicsChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Drops Per Minute Reference ChartDocument1 pageDrops Per Minute Reference ChartChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- JOURNALDocument4 pagesJOURNALChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Nurse Leaders' Strategies To Foster Nurse ResilienceDocument4 pagesNurse Leaders' Strategies To Foster Nurse ResilienceChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance: Kozier & Erb's Fundamentals of Nursing, 8eDocument64 pagesFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance: Kozier & Erb's Fundamentals of Nursing, 8eChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Post Mortem Care DiscussionDocument18 pagesPost Mortem Care DiscussionChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Amebiasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAmebiasis PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument4 pagesJournalChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Addison'S Disease Pathophysiology Group I-1Document1 pagePrimary and Secondary Addison'S Disease Pathophysiology Group I-1Chiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Signs and TagsDocument12 pagesElectrical Safety Signs and TagsChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExamDocument3 pagesMental Status ExamCHIARA FAJARDONo ratings yet
- Risk Management Completion Activity ExaminationDocument1 pageRisk Management Completion Activity ExaminationChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Home Gardening: Saint Louis University Baguio City School of Nursing Level IIDocument13 pagesHome Gardening: Saint Louis University Baguio City School of Nursing Level IIChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mr. Ryan Carl D. Vinluan, LPT InstructorDocument6 pagesPrepared By: Mr. Ryan Carl D. Vinluan, LPT InstructorChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Lyceum-Northwestern University Tapuac District, Dagupan City College of Tourism Management PRELIMS (Part 1)Document4 pagesLyceum-Northwestern University Tapuac District, Dagupan City College of Tourism Management PRELIMS (Part 1)Chiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Focus Data Action Responce: Risk For Injury Related To Vision or As Evidence byDocument2 pagesFocus Data Action Responce: Risk For Injury Related To Vision or As Evidence byChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Internship Portfolio Guidelines (Alternative Internship)Document2 pagesInternship Portfolio Guidelines (Alternative Internship)Chiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Delegation in Nursing LeadershipDocument25 pagesDelegation in Nursing LeadershipChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Missionary ResponseDocument1 pageMissionary ResponseChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- A Teacher Is One of The Most Important People in A ChildDocument2 pagesA Teacher Is One of The Most Important People in A ChildChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- BIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFDocument2 pagesBIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFTraci GardnerNo ratings yet
- Developmental History Form 2016Document5 pagesDevelopmental History Form 2016Mariya KhanNo ratings yet
- Mount Kenya UniversityDocument3 pagesMount Kenya UniversityAnonymous DGxdAOlNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Anemia Module 2Document16 pagesTopic 1 Anemia Module 2zekoNo ratings yet
- Patho4-6 - Liver (Dr. Dy)Document13 pagesPatho4-6 - Liver (Dr. Dy)miguel cuevas100% (1)
- Introduction To VirusesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To VirusesAJAZ assadNo ratings yet
- M. Preterm and Postterm - NewDocument92 pagesM. Preterm and Postterm - NewTry Ariditya UtomoNo ratings yet
- The Utility of COMPASS 31 Questionnaire To Predict.98958Document5 pagesThe Utility of COMPASS 31 Questionnaire To Predict.98958TEOFILO PALSIMON JR.No ratings yet
- 4 2 - 181 182 PDFDocument2 pages4 2 - 181 182 PDFNam LeNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Face-Lifting: S-Lift and S-Plus Lift RhytidectomiesDocument11 pagesMinimally Invasive Face-Lifting: S-Lift and S-Plus Lift RhytidectomiesAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amsa232 PDFDocument4 pagesAmsa232 PDFSunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Dr. Indah Meyliza, M. KesDocument13 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease: Dr. Indah Meyliza, M. KesIndah MeylizaNo ratings yet
- Vázquez Justo2017 PDFDocument194 pagesVázquez Justo2017 PDFCristinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument8 pagesBasic Life SupportAdilla RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Juknis Pelayanan TB Bagi Peserta JKN PDFDocument70 pagesJuknis Pelayanan TB Bagi Peserta JKN PDFAde PurnaNo ratings yet
- Lilly's Donanemab Significantly Slowed Cognitive and Functional Decline in Phase 3 Study of Early Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument3 pagesLilly's Donanemab Significantly Slowed Cognitive and Functional Decline in Phase 3 Study of Early Alzheimer's DiseaseAna Cecília RizzuttiNo ratings yet
- India's National Diabetes ProgrammeDocument9 pagesIndia's National Diabetes ProgrammeNaveenNo ratings yet
- Kuk 260Document28 pagesKuk 260Kuk-Punjabi SamacharNo ratings yet
- Board Notes and QuestionsDocument481 pagesBoard Notes and QuestionsAnil S. BhavsarNo ratings yet
- GTN Ointment Relieves Chronic Anal FissuresDocument8 pagesGTN Ointment Relieves Chronic Anal FissuresAndrew SuryaNo ratings yet
- Vital Sign RubricDocument2 pagesVital Sign RubricFrank CuvinNo ratings yet
- VBMDocument24 pagesVBMSupervisor HCVNo ratings yet
- Role of Drug Repurposing in Current TreaDocument6 pagesRole of Drug Repurposing in Current TreagygyNo ratings yet
- TMDDocument170 pagesTMDVinaya Srinivasan100% (2)
- Orthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Janisthaaivfcenter Wordpress Com 2023-11-08 How To Increase The Efficiency of Ivf by Lifestyle ChangesDocument2 pagesJanisthaaivfcenter Wordpress Com 2023-11-08 How To Increase The Efficiency of Ivf by Lifestyle ChangesjanisthaapharmaNo ratings yet