Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paper 4 - 2
Uploaded by
andryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Paper 4 - 2
Uploaded by
andryCopyright:
Available Formats
2
1 (a) In a cycling club, the number of members are in the ratio males : females = 8 : 3.
The club has 342 females.
(i) Find the total number of members.
.................................................... [2]
(ii) Find the percentage of the total number of members that are female.
................................................ % [1]
(b) The price of a bicycle is $1020.
Club members receive a 15% discount on this price.
Find how much a club member pays for this bicycle.
$ ................................................... [2]
(c) In 2019, the membership fee of the cycling club is $79.50 .
This is 6% more than last year.
Find the increase in the cost of the membership.
$ ................................................... [3]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
3
(d) Asif cycles a distance of 105 km.
On the first part of his journey he cycles 60 km in 2 hours 24 minutes.
On the second part of his journey he cycles 45 km at 20 km/h.
Find his average speed for the whole journey.
........................................... km/h [4]
(e) Bryan invested $480 in an account 4 years ago.
The account pays compound interest at a rate of 2.1% per year.
Today, he uses some of the money in this account to buy a bicycle costing $430.
Calculate how much money remains in his account.
$ ................................................... [3]
1
(f) The formula s = at 2 is used to calculate the distance, s, travelled by a bicycle.
2
When a = 3 and t = 10 , each correct to the nearest integer, calculate the lower bound of the distance, s.
.................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
4
2 (a) The diagram shows a triangle and a quadrilateral.
All angles are in degrees.
NOT TO
3a + 2b SCALE
3b + 10 8a
a + 2b 2a b + 50 4b - 2a
(i) For the triangle, show that 3a + 5b = 170 .
[1]
(ii) For the quadrilateral, show that 9a + 7b = 310 .
[1]
(iii) Solve these simultaneous equations.
Show all your working.
a = ...................................................
b = ................................................... [3]
(iv) Find the size of the smallest angle in the triangle.
.................................................... [1]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
5
(b) Solve the equation 6x - 3 =-12 .
x = ................................................... [2]
(c) Rearrange 2 (4x - y) = 5x - 3 to make y the subject.
y = ................................................... [3]
(d) Simplify. 2
(27x 9) 3
.................................................... [2]
(e) Simplify.
x 2 + 5x
x 2 - 25
.................................................... [3]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
6
3 The table shows some values for y = x 3 + x 2 - 5x .
x -3 -2 -1.5 -1 0 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
y -3 6 6.4 0 -1.9 2 9.4
(a) Complete the table. [3]
(b) On the grid, draw the graph of y = x 3 + x 2 - 5x for - 3 G x G 3.
y
25
20
15
10
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 x
-5
[4]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
7
(c) Use your graph to solve the equation x 3 + x 2 - 5x = 0 .
x = ..................... or x = ..................... or x = ..................... [2]
(d) By drawing a suitable tangent, find an estimate of the gradient of the curve at x = 2 .
.................................................... [3]
(e) Write down the largest value of the integer, k, so that the equation x 3 + x 2 - 5x = k has three solutions
for - 3 G x G 3.
k = ................................................... [1]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
8
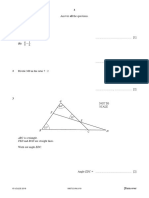
4
B
107 m
C
NOT TO
SCALE
158 m 132 m 86 m
North
116°
D
The diagram shows a field, ABCD, on horizontal ground.
(a) There is a vertical post at C.
From B, the angle of elevation of the top of the post is 19°.
Find the height of the post.
................................................ m [2]
(b) Use the cosine rule to find angle BAC.
Angle BAC = ................................................... [4]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
9
(c) Use the sine rule to find angle CAD.
Angle CAD = ................................................... [3]
(d) Calculate the area of the field.
............................................... m2 [3]
(e) The bearing of D from A is 070°.
Find the bearing of A from C.
.................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
10
5 The cumulative frequency diagram shows information about the distance, d km, travelled by each
of 60 male cyclists in one weekend.
60
50
40
Cumulative
frequency 30
20
10
0 d
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Distance (km)
(a) Use the cumulative frequency diagram to find an estimate of
(i) the median,
.............................................. km [1]
(ii) the lower quartile,
.............................................. km [1]
(iii) the interquartile range.
.............................................. km [1]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
11
(b) For the same weekend, the interquartile range for the distances travelled by a group of female cyclists
is 40 km.
Make one comment comparing the distribution of the distances travelled by the males with the
distribution of the distances travelled by the females.
............................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(c) A male cyclist is chosen at random.
Find the probability that he travelled more than 50 km.
.................................................... [2]
(d) (i) Use the cumulative frequency diagram to complete this frequency table.
Distance (d km) Number of male cyclists
0 1 d G 40 18
40 1 d G 50 9
50 1 d G 60
60 1 d G 70
70 1 d G 90
90 1 d G 120 2
[2]
(ii) Calculate an estimate of the mean distance travelled.
.............................................. km [4]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
12
6 (a)
A D
NOT TO
128° SCALE
28°
C
O 30°
In the diagram, A, B, C and D lie on the circle, centre O.
Angle ADC = 128°, angle ACD = 28° and angle BCO = 30°.
(i) Show that obtuse angle AOC = 104°.
Give a reason for each step of your working.
[3]
(ii) Find angle BAO.
Angle BAO = ................................................... [2]
(iii) Find angle ABD.
Angle ABD = ................................................... [1]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
13
(iv) The radius, OC, of the circle is 9.6 cm.
Calculate the total perimeter of the sector OADC.
.............................................. cm [3]
(b)
NOT TO
SCALE
The diagram shows two mathematically similar solid metal prisms.
The volume of the smaller prism is 648 cm3 and the volume of the larger prism is 2187 cm3.
The area of the cross-section of the smaller prism is 36 cm2.
(i) Calculate the area of the cross-section of the larger prism.
............................................. cm2 [3]
(ii) The larger prism is melted down into a sphere.
Calculate the radius of the sphere.
4
[The volume, V, of a sphere with radius r is V = rr 3 .]
3
.............................................. cm [3]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
14
7
y
8
2
A
1
x
-8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
-1
-2
-3
B
-4
-5
-6
(a) Describe fully the single transformation that maps shape A onto shape B.
............................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(b) On the grid, draw the image of
-3
(i) shape A after a translation by the vector e o , [2]
4
(ii) shape A after a rotation through 180° about (0, 0), [2]
(iii) shape A after an enlargement, scale factor 2, centre (-7, 0). [2]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
15
8 (a) A bag contains 4 red marbles and 2 yellow marbles.
Behnaz picks two marbles at random without replacement.
Find the probability that
(i) the marbles are both red,
.................................................... [2]
(ii) the marbles are not both red.
.................................................... [1]
(b) Another bag contains 5 blue marbles and 2 green marbles.
Bryn picks one marble at random without replacement.
If this marble is not green, he picks another marble at random without replacement.
He continues until he picks a green marble.
Find the probability that he picks a green marble on his first, second or third attempt.
.................................................... [4]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
16
9 f (x) = 2x - 3 g (x) = 9 - x 2 h (x) = 3 x
(a) Find
(i) f (4) ,
.................................................... [1]
(ii) hg (3) ,
.................................................... [2]
(iii) g (2x) in its simplest form,
.................................................... [1]
(iv) fg (x) in its simplest form.
.................................................... [2]
(b) Find f -1 (x) .
f -1 (x) = ................................................... [2]
(c) Find x when 5f (x) = 3.
x = ................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
17
(d) Solve the equation gf (x) =-16 .
x = .................... or x = .................... [4]
(e) Find x when h -1 (x) =- 2 .
x = ................................................... [1]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19 [Turn over
18
10 Solve.
1 2
- =3
x x+1
Show all your working and give your answers correct to 2 decimal places.
x = .......................... or x = .......................... [7]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
19
11
A B
C
Q
NOT TO
P SCALE
OAB is a triangle and ABC and PQC are straight lines.
P is the midpoint of OA, Q is the midpoint of PC and OQ : QB = 3 : 1.
OA = 4a and OB = 8b .
(a) Find, in terms of a and/or b, in its simplest form
(i) AB,
AB = ................................................... [1]
(ii) OQ,
OQ = ................................................... [1]
(iii) PQ.
PQ = ................................................... [1]
(b) By using vectors, find the ratio AB : BC.
......................... : ........................ [3]
© UCLES 2019 0580/43/O/N/19
You might also like
- 0580 w19 QP 43 PDFDocument20 pages0580 w19 QP 43 PDFneelam goelNo ratings yet
- Math PracticeDocument16 pagesMath PracticeSwara TendulkarNo ratings yet
- Paper 3Document10 pagesPaper 3yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Homework P4Document7 pagesHomework P4yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Class 11C - Maths P2Document20 pagesClass 11C - Maths P2St. Andrew's High School KarachiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationBara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- Tafadzwa WorkDocument5 pagesTafadzwa WorkffgfgfgffgNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Write Down The Temperature That Is 7: 0580/23/O/N/19 © UCLES 2019Document11 pages2 1 Write Down The Temperature That Is 7: 0580/23/O/N/19 © UCLES 2019YashodhaNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument85 pagesCombinepdfDhrisha GadaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Educationtaslima nasreenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics O1p1Document10 pagesMathematics O1p1Umar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Math Paper 4Document14 pagesMath Paper 4SREYASH KALALNo ratings yet
- 0607 s19 QP 21Document4 pages0607 s19 QP 21Yakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- 0580 w17 4 3 QPDocument16 pages0580 w17 4 3 QPLetuka SelloNo ratings yet
- 2019 SolvedDocument9 pages2019 SolvedJenna HanyNo ratings yet
- Yr11 - Monthly Revision WorksheetDocument10 pagesYr11 - Monthly Revision WorksheetOmar WaheedNo ratings yet
- 0580 Practice Test 3 2024 (Paper 4)Document22 pages0580 Practice Test 3 2024 (Paper 4)AFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- 0580 m18 QP 42 PDFDocument16 pages0580 m18 QP 42 PDFRichie TangNo ratings yet
- Math - Core IG02 S2T1 QP - P2Document19 pagesMath - Core IG02 S2T1 QP - P2Su YongshengNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41mandaramade9111No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/43Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/43kdebipershadNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Class 9 - PagenumberDocument41 pagesMid Term Class 9 - PagenumberAnay PatelNo ratings yet
- 2020 Paper 2Document12 pages2020 Paper 2Linh TranNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test (April) - Igcse Maths: Marks %Document6 pagesMonthly Test (April) - Igcse Maths: Marks %Aqilah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 0580 s20 QP 42 PDFDocument19 pages0580 s20 QP 42 PDFLearn TodayNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam Review Pack 2Document15 pagesMock Exam Review Pack 2Aman WaniyaNo ratings yet
- Num 2016Document15 pagesNum 2016Tala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2015Document18 pagesMaths Paper 2015aminathNo ratings yet
- A Plus 03.02 fm20 - 22 - 42Document17 pagesA Plus 03.02 fm20 - 22 - 42chinkhuslen1225No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Mathematics 0580/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Mathematics 0580/42Haron HarveyNo ratings yet
- AayanDocument11 pagesAayanZunaira SafdarNo ratings yet
- 0580 Practice Test 2 2024 (Paper 4)Document20 pages0580 Practice Test 2 2024 (Paper 4)AFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- 0580 w20 QP 43Document15 pages0580 w20 QP 43Gigi WangNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/41AbdullaNo ratings yet
- P4s Maths CIE IGCSE (Compilation)Document358 pagesP4s Maths CIE IGCSE (Compilation)uwizewe.kezaNo ratings yet
- 0580 m19 QP 22Document12 pages0580 m19 QP 22Richie TangNo ratings yet
- Practice Que BBDocument18 pagesPractice Que BBpetriNo ratings yet
- 2 1 "We Eat More Ice Cream As The Temperature Rises."Document11 pages2 1 "We Eat More Ice Cream As The Temperature Rises."andryNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document27 pagesAlgebra 2S.V. CREATIONSNo ratings yet
- (A) A Cube NumberDocument17 pages(A) A Cube NumberHarizZaimNo ratings yet
- 4024 w19 QP 12 PDFDocument20 pages4024 w19 QP 12 PDFIbrahim MAnshaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-25 at 10.57.41 PMDocument17 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-25 at 10.57.41 PMViha GaliaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42spotifysubs250No ratings yet
- 0580 w14 QP 42Document20 pages0580 w14 QP 42Bobby SNo ratings yet
- 0580 s19 QP 11 PDFDocument12 pages0580 s19 QP 11 PDFMajed AlIraqiNo ratings yet
- Mensuration New 23 CombineDocument24 pagesMensuration New 23 CombineAshbeela rashdiNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test (April) - Igcse Maths: Marks %Document6 pagesMonthly Test (April) - Igcse Maths: Marks %Aqilah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 4024 w08 QP 1Document16 pages4024 w08 QP 1mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Friday 2nd October TestDocument11 pagesFriday 2nd October Testcarolinethami13No ratings yet
- My TestDocument6 pagesMy Testenock chilufyajrNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document7 pagesHomework 2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- 0580 w19 QP 23Document12 pages0580 w19 QP 23neelam goelNo ratings yet
- IGCSEDocument9 pagesIGCSEBalasubramaniam GauthamanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Maths Paper 2 Model AnswersDocument18 pagesIGCSE Maths Paper 2 Model AnswersraksnghNo ratings yet
- Mock Maths QPDocument21 pagesMock Maths QPArman JavedNo ratings yet
- Mocktest 10Document11 pagesMocktest 10KIEN NGUYENDACCHINo ratings yet
- Igcse MathsDocument20 pagesIgcse MathsMiesha AmyshaNo ratings yet
- Review Paper - Nonlinear Control Theory - E. Andry Dwi Kurniawan (20123007)Document5 pagesReview Paper - Nonlinear Control Theory - E. Andry Dwi Kurniawan (20123007)andryNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations CDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations CandryNo ratings yet
- Will or Be Going ToDocument2 pagesWill or Be Going ToVanusa100% (1)
- Chapter 4 CirclesDocument9 pagesChapter 4 CirclesandryNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations eDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations eandryNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations DDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations DandryNo ratings yet
- Momentum and EnergyDocument9 pagesMomentum and EnergyandryNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations ADocument3 pagesGrade 5 Word Problems Fractions Mixed Operations AandryNo ratings yet
- Physics 8 - EnergyDocument54 pagesPhysics 8 - EnergyandryNo ratings yet
- Fractions Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesFractions Worksheet AnswersandryNo ratings yet
- Adding Negative Numbers 1Document2 pagesAdding Negative Numbers 1andryNo ratings yet
- Fractions WorksheetDocument2 pagesFractions WorksheetandryNo ratings yet
- Physics - PowerDocument16 pagesPhysics - PowerandryNo ratings yet
- Xin Zhong Secondary School SCHOOL YEAR 2021-2022 Mathematics Topical Test Semester 2 - Grade 9BDocument2 pagesXin Zhong Secondary School SCHOOL YEAR 2021-2022 Mathematics Topical Test Semester 2 - Grade 9BandryNo ratings yet
- Matrix Fundamentals: Cambridge IGCSE™Document32 pagesMatrix Fundamentals: Cambridge IGCSE™andryNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document6 pagesWeek 1Anonymous ushTkrG133% (3)
- Chapter 1: Sets: Cambridge IGCSE™Document19 pagesChapter 1: Sets: Cambridge IGCSE™andryNo ratings yet
- 2 1 "We Eat More Ice Cream As The Temperature Rises."Document11 pages2 1 "We Eat More Ice Cream As The Temperature Rises."andryNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency 10CDocument15 pagesCumulative Frequency 10CandryNo ratings yet
- R. Compr. 5 PDFDocument6 pagesR. Compr. 5 PDFIvana Troshanska100% (1)
- Practice BookDocument13 pagesPractice Booku_funfNo ratings yet
- Reading 2Document6 pagesReading 2Mary Grace CernechezNo ratings yet
- Ratios and Proportions: You May Use Calculators in This Chapter!!Document14 pagesRatios and Proportions: You May Use Calculators in This Chapter!!Joceme B. CaloniaNo ratings yet
- Review Exercise CHP 4,5 and 6Document2 pagesReview Exercise CHP 4,5 and 6andryNo ratings yet
- Standard Deviation: Chapter 3: Statistical Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesStandard Deviation: Chapter 3: Statistical Data AnalysisandryNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following Questions. Show All Your Workings. 1.: School Year 2021 - 2022Document6 pagesAnswer The Following Questions. Show All Your Workings. 1.: School Year 2021 - 2022andryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Sets (Continuation ) : Cambridge IGCSE™Document17 pagesChapter 1: Sets (Continuation ) : Cambridge IGCSE™andryNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency 10CDocument15 pagesCumulative Frequency 10CandryNo ratings yet
- Adding Fractions 2Document2 pagesAdding Fractions 2arlidaNo ratings yet
- VT Directed Io SpecDocument297 pagesVT Directed Io SpechobomanNo ratings yet
- STR ReportDocument30 pagesSTR ReportrahulNo ratings yet
- Astar - 23b.trace - XZ Bimodal Next - Line Next - Line Next - Line Next - Line Drrip 1coreDocument4 pagesAstar - 23b.trace - XZ Bimodal Next - Line Next - Line Next - Line Next - Line Drrip 1corevaibhav sonewaneNo ratings yet
- VP5 Datasheet Infusion Pump PDFDocument2 pagesVP5 Datasheet Infusion Pump PDFsafouen karrayNo ratings yet
- OPTICast BrochureDocument2 pagesOPTICast BrochureIndra Pratap SengarNo ratings yet
- C++ NotesDocument11 pagesC++ NotesVedant AmonkarNo ratings yet
- Visit Braindump2go and Download Full Version 350-801 Exam DumpsDocument4 pagesVisit Braindump2go and Download Full Version 350-801 Exam DumpsArsic AleksandarNo ratings yet
- ElcometerDocument228 pagesElcometerMohammedMudassirNo ratings yet
- Hofman NotesDocument114 pagesHofman NotesNoelia PizziNo ratings yet
- BMTC 132Document16 pagesBMTC 132Deepak Chaudhary JaatNo ratings yet
- Rockschool Popular Music Theory Syllabus 2015 18Document33 pagesRockschool Popular Music Theory Syllabus 2015 18Archit AnandNo ratings yet
- JVR Fingerprint Attendance User ManualDocument30 pagesJVR Fingerprint Attendance User ManualDomingo MonteroNo ratings yet
- Ashtakvarga KAS SystemDocument4 pagesAshtakvarga KAS Systemdakudkm0% (1)
- Classification of ConvertersDocument1 pageClassification of ConvertersJon BNo ratings yet
- DNV RP F401Document23 pagesDNV RP F401Christopher BlevinsNo ratings yet
- 2021 SEM 4 CC 9 OrganicDocument3 pages2021 SEM 4 CC 9 OrganicGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Ratio Worksheet AKDocument12 pagesRatio Worksheet AKChika AuliaNo ratings yet
- Ap T240 13Document92 pagesAp T240 13mehdiNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 3: Room AcousticsDocument11 pagesBuilding Utilities 3: Room AcousticsIzzah LNo ratings yet
- Grade Sheet BlankDocument50 pagesGrade Sheet BlankCarlo Troy AcelottNo ratings yet
- Zipato MQTTCloudDocument34 pagesZipato MQTTClouddensasNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 6 NotesDocument5 pagesBiology Paper 6 NotesbNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Utility Impact Assessment For Local Roads in Developed Areas MME 2012 Cross-SectionDocument81 pagesGuidelines For Utility Impact Assessment For Local Roads in Developed Areas MME 2012 Cross-Sectionirfan mohammedNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems: Lecture - 5Document37 pagesDatabase Management Systems: Lecture - 5harisNo ratings yet
- TMS Advanced TreeViewDocument64 pagesTMS Advanced TreeViewDanilo CristianoNo ratings yet
- Chameleon ChipDocument2 pagesChameleon ChipChetan KumarNo ratings yet
- IV Dam Outlet Work1Document33 pagesIV Dam Outlet Work1hailish100% (1)
- Amta5 8 Applying Tungsten Inert Gas Tig Welding TechniquesDocument115 pagesAmta5 8 Applying Tungsten Inert Gas Tig Welding TechniquesAbu RectifyNo ratings yet
- Flyback Converter DesignDocument8 pagesFlyback Converter DesignLullaby summerNo ratings yet