0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesATP and ADP Structure and Cycle
The document discusses the ATP-ADP cycle. It contains 4 parts:
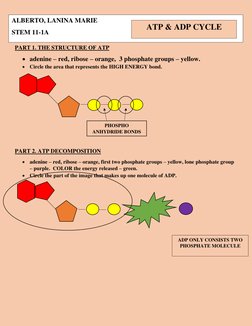
1. The structure of ATP contains adenine, ribose, and 3 phosphate groups, with the high energy bond located in the phosphoanhydride bonds.
2. ATP decomposition releases energy (green), forming ADP which contains adenine, ribose, and 2 phosphate groups.
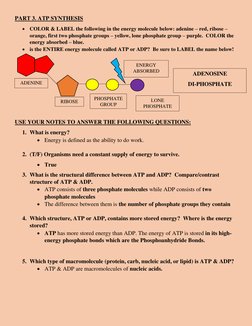
3. ATP synthesis absorbs energy (blue) to reform ATP from ADP by adding a phosphate group.
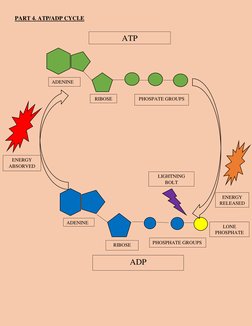
4. A diagram shows the ATP-ADP cycle with ATP breaking down to release energy and reforming from ADP by absorbing energy through biological processes.
Uploaded by
Laniña Marie AlbertoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesATP and ADP Structure and Cycle
The document discusses the ATP-ADP cycle. It contains 4 parts:
1. The structure of ATP contains adenine, ribose, and 3 phosphate groups, with the high energy bond located in the phosphoanhydride bonds.
2. ATP decomposition releases energy (green), forming ADP which contains adenine, ribose, and 2 phosphate groups.
3. ATP synthesis absorbs energy (blue) to reform ATP from ADP by adding a phosphate group.
4. A diagram shows the ATP-ADP cycle with ATP breaking down to release energy and reforming from ADP by absorbing energy through biological processes.
Uploaded by
Laniña Marie AlbertoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd