Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Angle of Elevation and Depression
Uploaded by
Tania ChoudharyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Angle of Elevation and Depression
Uploaded by
Tania ChoudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
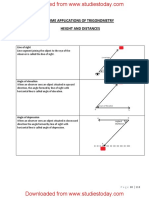
Angle of elevation and depression
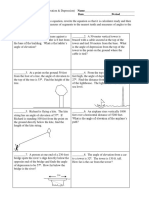
A helicopter is hovering at an altitude of 250 metres. The angle of elevation from the helipad to
the helicopter is 35°. Find the horizontal distance of the helicopter from the helipad, to the
nearest centimetre.
A bird is hovering at an altitude of 100 m. The angle of elevation from the observation point to
the bird is 55°. Find the horizontal distance of the bird from the observation point, to the nearest
centimetre.
Two vertical buildings 57 metres apart are 158 metres and 237 metres high. Find the angle of
elevation from the top of the shorter building to the top of the taller building, correct to two
decimal places.
Two vertical poles 32 metres apart are 62 metres and 79 metres high. Find the angle of elevation
from the top of the shorter pole to the top of the taller pole, correct to two decimal places.
The altitude of an aeroplane is 500 metres, and the angle of elevation from the runway to the
aeroplane is 15°. Find the horizontal distance from the aeroplane to the runway, to the nearest
centimetre.
The distance between two buildings is 24.5 metres. Find the height of the taller building, to the
nearest metre, if the angle of elevation from the top of the shorter building to the top of the taller
building is 85° and the height of the shorter building is 40 m.
The angle of depression from one mountain summit to another is 15.9°. If the two mountains
differ in height by 430 metres, find the horizontal distance between the two summits, to the
nearest centimetre.
Two vertical buildings positioned 91 metres apart are 136 metres and 192 metres tall,
respectively. Find the angle of elevation from the top of the shorter building to the top of the
taller building, to the nearest degree.
An L-shaped veranda has dimensions as shown. Find the width, to the nearest centimetre, of the
veranda for the following sides of the house:
a north side
b east side.
You might also like
- Assignment - Application of TrigonometryDocument2 pagesAssignment - Application of TrigonometryISHAAN GOYALNo ratings yet
- Ws - Sohcahtoa Word ProblemsDocument4 pagesWs - Sohcahtoa Word Problemsapi-320180050No ratings yet
- Angles of ElevationDocument25 pagesAngles of ElevationAngelu bonaganNo ratings yet
- Angle of Elevation & Depression Trig WorksheetDocument3 pagesAngle of Elevation & Depression Trig WorksheetJannah Tabura SolisNo ratings yet
- Cbse X Assignment Applications of Trigonometry PDFDocument3 pagesCbse X Assignment Applications of Trigonometry PDFrajanenihrNo ratings yet
- MLA APPLICATION OF TrigonometryDocument1 pageMLA APPLICATION OF Trigonometryanshu aroraNo ratings yet
- Angle of Elevation & DepressionDocument2 pagesAngle of Elevation & DepressionCollin DosunmuNo ratings yet
- Important Applicatins of TrigonometryDocument4 pagesImportant Applicatins of Trigonometrysohalsingh1No ratings yet
- #02 Applications of Trigonometry - Board QuestionsDocument2 pages#02 Applications of Trigonometry - Board QuestionsTeereg VINo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Height and DistanceDocument8 pagesClass 10 Maths Height and Distancemail.atharvsingh01No ratings yet
- Angle of Elevation - Depression (FAM)Document1 pageAngle of Elevation - Depression (FAM)Supriti SarkerNo ratings yet
- Most Important Questions (Class 10 Maths) Some Applications of TrigonometryDocument10 pagesMost Important Questions (Class 10 Maths) Some Applications of TrigonometryRohith SaiNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument1 pageTrigonometryPranati MishraNo ratings yet
- Trig Ratio Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesTrig Ratio Word ProblemsEmpires Allies100% (1)
- #01 Applications of Trigonometry - Board QuestionsDocument2 pages#01 Applications of Trigonometry - Board QuestionsTeereg VINo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRY: Word ProblemsDocument5 pagesTRIGONOMETRY: Word ProblemsMae SocialNo ratings yet
- 10th Math Height and DistanceDocument1 page10th Math Height and Distancesandeep_sihag07No ratings yet
- 2 TrigonometryDocument24 pages2 TrigonometryJuan Miguel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Angle of Elevation and DepressionDocument27 pagesAngle of Elevation and DepressionNica BasanalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry PracticeDocument1 pageTrigonometry PracticeKamlesh MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Trigo Previous Year QuestionsDocument2 pagesApplications of Trigo Previous Year QuestionsRITU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Mithi Gobind Ram Public School: Work SheetDocument2 pagesMithi Gobind Ram Public School: Work SheetHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- OME Pplications of RigonometryDocument1 pageOME Pplications of RigonometryJunaid PalangadNo ratings yet
- Maths Application of Trignometry NewDocument2 pagesMaths Application of Trignometry NewSUBHAM DUBEYNo ratings yet
- Day 4 Angle of Elevation-Depression WS PDFDocument2 pagesDay 4 Angle of Elevation-Depression WS PDFAnonymous jYuDy8QcCNo ratings yet
- Applications of TrigonometryDocument4 pagesApplications of TrigonometryRaamu RavuriNo ratings yet
- 2b SampleDocument22 pages2b SampleMichelle HsiehNo ratings yet
- PP APPLICATIONOFTRIGONOMETRY - D05 Oct 2023Document12 pagesPP APPLICATIONOFTRIGONOMETRY - D05 Oct 2023vyom.jatindpsvNo ratings yet
- Angle of Elevation & Depression Trig WorksheetDocument3 pagesAngle of Elevation & Depression Trig WorksheetkaelynNo ratings yet
- MCR3U Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry AssignmentDocument1 pageMCR3U Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Assignmentapi-22661649No ratings yet
- 9.some Applications of TrigonometryDocument6 pages9.some Applications of TrigonometryDROZON GAMING YTNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument15 pagesTrigonometryJhon Christian CabintoyNo ratings yet
- 10th Application of Trigonometry Test Paper - 2Document3 pages10th Application of Trigonometry Test Paper - 2Adarsh BhushanNo ratings yet
- Maths CH10 SumsDocument3 pagesMaths CH10 Sumspurvesh2510No ratings yet
- Trigonometry WorkbookDocument74 pagesTrigonometry WorkbookBeatixe CanumayNo ratings yet
- ElevationDocument1 pageElevationPromise SalvatieraNo ratings yet
- Angles of Depression and Elevation WorksheetDocument2 pagesAngles of Depression and Elevation WorksheetJohn Philip Reyes100% (1)
- XMqfsby 6 P 7 y GH PV ZDG Q1Document27 pagesXMqfsby 6 P 7 y GH PV ZDG Q1ujjwalan2109No ratings yet
- 9 Applications of TrigonometryDocument2 pages9 Applications of TrigonometryJeswin RajNo ratings yet
- Prism Academy CBSE 10 Worksheet AOTDocument3 pagesPrism Academy CBSE 10 Worksheet AOTHarsh LambeNo ratings yet
- U4L2 Angle of Elevation - Depression HWDocument4 pagesU4L2 Angle of Elevation - Depression HWShirin JaswalNo ratings yet
- A.O.T. Class XDocument4 pagesA.O.T. Class Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Trig Word Problems 2Document2 pagesTrig Word Problems 2Romel0% (1)
- Word Problems Ch15Document3 pagesWord Problems Ch15Boolean TypeNo ratings yet
- ITT (Topic 1) Form 4Document1 pageITT (Topic 1) Form 4Sawakita EijiNo ratings yet
- Primary Trig Ratios - Part 2Document5 pagesPrimary Trig Ratios - Part 2Shaun PattersonNo ratings yet
- 10th - Maths - Apps of Trigo - Assignment 2 - STPDFDocument1 page10th - Maths - Apps of Trigo - Assignment 2 - STPDFjai gopalNo ratings yet
- AnglesDepressionElevation WorksheetDocument1 pageAnglesDepressionElevation Worksheetcaroline_amideast8101100% (1)
- Geometry Advanced WorksheetDocument2 pagesGeometry Advanced WorksheetdevikaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Trigo Class 10Document3 pagesAssignment 1 Trigo Class 10anshu aroraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Application Worksheet-2Document2 pagesTrigonometry Application Worksheet-2IWAN SETIAWANNo ratings yet
- A Man On A 135Document2 pagesA Man On A 135Jensen Ryan LimNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Word Problems Part 1-Corrected Version - dszc-Vegyipari#762433#Tanulo#77365#CsatolmanyDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Word Problems Part 1-Corrected Version - dszc-Vegyipari#762433#Tanulo#77365#CsatolmanyFruzsi SzatmáriNo ratings yet
- 10th - Maths - Apps of Trigo - Assignment 3 - STPDFDocument4 pages10th - Maths - Apps of Trigo - Assignment 3 - STPDFjai gopalNo ratings yet
- Application of TrigoDocument3 pagesApplication of Trigohackerboy99356No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Angle of Elevation DepressionDocument21 pagesLesson 7 Angle of Elevation DepressionParadox Hans AgravanteNo ratings yet