Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SQL employee book loan queries
Uploaded by
35Ramya MOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SQL employee book loan queries
Uploaded by
35Ramya MCopyright:
Available Formats
1 .Create a Table as workers and the details are { S.
No, Name, Designation,
Branch }
Perform the following commands:
create table employee(SNo number,Name varchar(20),Designation varchar(20),Branch
varchar(20));
insert into employee values(1,'AAA','Professor','cse');
insert into employee values(2,'BBB','technician','cse');
insert into employee values(3,'CCC','HOD','civil');
Alter the table by adding a column Salary
alter table employee add(Salary number);
Alter the table modifying the column Name
alter table employee modify ( Name varchar(20));
Describe the table employee
desc employee;
Copy the table employee as emp
create table emp as select * from employee;
Truncate the table
truncate table employee;
Delete the Second row from the table
delete employee where name='BBB';
Drop the table
drop table employee;
2. Create the following tables
student_details {register_no, student_name, DOB, address, city}
mark_details {register_no, mark1, mark2, mark3, total }
create table student_details(register_nonumber,student_namevarchar(20),DOB
number,addressvarchar(20),city varchar(10));
insert into student_details values(161,'Anu',10-3-1998,'VOCnagar','Tuty');
insert into student_details values(162,'Banu',11-7-1999,'Annanagar','Chennai');
insert into student_details values(163,'Abi',20-6-1997,'Balajinagar','Tcr');
create table mark_details(register_no number,mark1 number,mark2 number,mark3
number,total number);
insert into mark_details values(161,89,90,88,267);
insert into mark_details values(162,70,80,75,225);
insert into mark_details values(163,80,90,87,257);
? Display only those rows whose total ranges between 250 and 300.
select * from mark_details where total between 250 and 300;
? Drop the table mark_details and Delete the row whose register_no=161.
delete mark_details where register_no=161;
drop table mark_details;
? Display all details whose names begins with 'a'.
select * from student_details where student_name like 'A%';
6. (a). Create a table as book (sl.no, book_name, author_name,price,
edition,publisher_name ).
create table book(s1.no number,book_namevarchar(10),author_namevarchar(10),price
number,editionnumber,publisher_namevarchar(10));
Perform the following operations:
? Insert minimum ten tuples in book table
insert into book values(1,'java','Silber',250,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(2,'python','Silber',275,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(3,'C','Silber',250,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(4,'C++','Silber',250,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(5,'html','Silber',250,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(6,'poni','kalki',250,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(7,'paathip','Silber',250,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(8,'thenali','Silber',125,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(9,'good','barathi',190,6,'AAA');
insert into book values(10,'alpha','barath',195,6,'AAA');
? Commit the table book
commit;
? Create a save point for the table book as B
savepoint B;
? Rollback the table book after inserting 4 & 5 row
rollback B;
? Define Grant & Revoke
Definition of Grant:
The command is use to give user access privileges to a database.
Syntax: GRANT SELECT ,UPDATE ON MY_TABLE TO SOME_USER,ANOTHER_USER
example:GRANT SELECT ON USER TO 'Tom' @ Local cost:
Definition of Revoke:
It is useful to back permission from to user.
Syntax: REVOKE privilege_name on object_name from{user_name/PUBLIC role_name}
example:REVOKE SELECT,UPDATE ON STUDENT,FROM BCA MCA
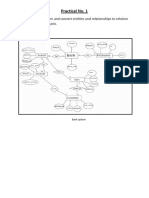
Consider the following relational schema:
Employee( empno, name, office, age )
Books ( isbn, title, authors, publisher )
Loan ( empno, isbn, date )
Write the following queries in SQL:
create table employee (empno number primary,name varchar(20),office varchar(20),age
number);
insert into employee values(1,'AAA','XXX',30);
insert into employee values (2,'BBB','YYY',45);
insert into employee values (3,'CCC','ZZZ',56);
insert into employee values (4,'ddd','ZZY',57);
create table book(isbn varchar(13) primary,title varchar(10),author
varchar(10),publisher varchar(10));
insert into book values(1234,'barbie','jimmy','jack');
insert into book values(5678,'ben','sam','McGraw-Hill ');
insert into book values(1256,'dora','buji','thara');
create table loan(empno int ,isbn varchar(13),sdate number,foreign key(empno,isbn)
references employee(empno),book_i(isbn);
insert into loan values(1,1234,12);
insert into loan values(2,5678,13);
insert into loan values(2,1234,13);
insert into loan values(3,1256,14);
insert into loan values(3,1234,13);
insert into loan values(4,5678,13);
Print the names of employees who have borrowed any books published by McGraw-Hill
select name from employee e,book b,loan l where e.empno=l.empno and l.isbn=b.isbn
and b.publisher='McGrawHill';
Print the names of employees who have borrowed all books published by McGraw-Hill.
select name from employee where empno in (select emp_no from book_i natural join
loan where publisher ='jam');
For each publishers, print the names of employees who have borrowed more than five
books of that publisher.
select name from employee where empno in (select emp_no from book_i natural join
loan where publisher in (select publisher from book_i natural join loan group by
publisher having count (publisher)>5));
You might also like
- DBS Week2Document12 pagesDBS Week2BhavikNo ratings yet
- DBMS lab fileDocument14 pagesDBMS lab fileanyt6126No ratings yet
- SqlnotesDocument17 pagesSqlnotesManasa ReddyNo ratings yet
- Practical 3 & 4 DDL Commands & ConstraintsDocument22 pagesPractical 3 & 4 DDL Commands & ConstraintsAnshNo ratings yet
- Rdbms Lab-5: Jenma Maria Binoy Rollno 34Document6 pagesRdbms Lab-5: Jenma Maria Binoy Rollno 34Jenma Maria BinoyNo ratings yet
- SQL ComandDocument4 pagesSQL Comandrati islamNo ratings yet
- Create PKs, FKs, Views and Indexes on HR TablesDocument5 pagesCreate PKs, FKs, Views and Indexes on HR TablesIndrid Gomez SolisNo ratings yet
- DBMS Practice Questions-SQLDocument10 pagesDBMS Practice Questions-SQLshivaniNo ratings yet
- Exp 8 DbmsDocument8 pagesExp 8 DbmsmadhanNo ratings yet
- SubqueriesDocument25 pagesSubqueriesdubeypratistha913No ratings yet
- Lab SQLDocument3 pagesLab SQLSinan KNo ratings yet
- DBMS AssignmnetDocument13 pagesDBMS AssignmnetRiya LoveNo ratings yet
- Database System II Lab ManualDocument13 pagesDatabase System II Lab ManualElias Petros100% (1)
- MySQL 04 With AnswersDocument5 pagesMySQL 04 With AnswersRocketNo ratings yet
- Top 50 SQL QuestionsDocument15 pagesTop 50 SQL QuestionsRavi Chandra Reddy MuliNo ratings yet
- Da 20bce0647Document13 pagesDa 20bce0647Nikitha JohnNo ratings yet
- Practice 1Document2 pagesPractice 1Masood MughalNo ratings yet
- ADBTLab Manua115-16Document45 pagesADBTLab Manua115-16EdenNo ratings yet
- DBMS DocumentationDocument18 pagesDBMS DocumentationMrunali KudtarkarNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document5 pagesSession 2midhilesh sagarNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument60 pagesDatabase Management SystemÐipänzän 'rocky' ZärkärNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab-1 Submitted By-Saurav Majoka (B19CSE079) : 1.connect The Database and Create The TableDocument11 pagesDbms Lab-1 Submitted By-Saurav Majoka (B19CSE079) : 1.connect The Database and Create The TableSarthak Kumar Singh (B19CSE077)No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 17bcs2733Document22 pagesAssignment 1 17bcs2733Singh NaviNo ratings yet
- 21BCS7870 DBMS1.1Document13 pages21BCS7870 DBMS1.1innovator mindNo ratings yet
- Practice Question CHP 1Document3 pagesPractice Question CHP 1op gamerNo ratings yet
- Using DDL Statements To Create and Manage TablesDocument34 pagesUsing DDL Statements To Create and Manage TablesMuhammad Bilal AyubNo ratings yet
- SQL Commands - 1Document4 pagesSQL Commands - 1veerajghalyanNo ratings yet
- SQL PracticeDocument10 pagesSQL PracticeGopala Krishna VankayalapatyNo ratings yet
- Data Base (SQL) : Creating TablesDocument24 pagesData Base (SQL) : Creating TablesShaji kahoutNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 5 DBMSDocument3 pagesExperiment No 5 DBMSabhishek.ap2003No ratings yet
- S Another NotesDocument2 pagesS Another NotesKrishna MakwanaNo ratings yet
- SQL QueryDocument16 pagesSQL QueryMastanNo ratings yet
- SQL Date Functions, Table Creation, and Data ManipulationDocument41 pagesSQL Date Functions, Table Creation, and Data ManipulationSwarup Uriti100% (1)
- CSE2031 - Principle of Database Management Systems Lab Fall Semester 2021 - 2022 Lab Assignment - 1Document10 pagesCSE2031 - Principle of Database Management Systems Lab Fall Semester 2021 - 2022 Lab Assignment - 1Priyanka BVSNo ratings yet
- Basic SQL: (Tool: MYSQL Workbench)Document25 pagesBasic SQL: (Tool: MYSQL Workbench)Muhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Creating Tables and Performing CRUD OperationsDocument4 pagesCreating Tables and Performing CRUD OperationsAdityaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Practical Example For StudentsDocument33 pagesDBMS Practical Example For Studentslilwani aniketNo ratings yet
- Extrea Queries For PracticeDocument7 pagesExtrea Queries For Practicerajvaibhav nimbalkarNo ratings yet
- Overview SQLDocument5 pagesOverview SQLSarung SubnaniNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Anant KajrolkarDocument18 pagesDBMS - Anant Kajrolkarkulkarnivishal907No ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document11 pagesWa0003.competitionclasses94No ratings yet
- Simple and Complex QueriesDocument31 pagesSimple and Complex QueriesHar JadNo ratings yet
- Creating DatabaseDocument52 pagesCreating DatabaseAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab 1 Sarthak Kumar Singh B19CSE077: Q1. Create A Table: Employee - Info (Emp - Id, Emp - Name, Dept, Salary)Document12 pagesDbms Lab 1 Sarthak Kumar Singh B19CSE077: Q1. Create A Table: Employee - Info (Emp - Id, Emp - Name, Dept, Salary)Sarthak Kumar Singh (B19CSE077)No ratings yet
- SQL DDL and DML Statements SummaryDocument17 pagesSQL DDL and DML Statements SummaryPal BootsNo ratings yet
- SQL Day3Document5 pagesSQL Day3ziad akramanNo ratings yet
- Saurabh Tariyal Sec:J 1918677Document66 pagesSaurabh Tariyal Sec:J 1918677Divesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Alok DbmsDocument36 pagesAlok DbmsKeshav LekhwarNo ratings yet
- DBMS Aggignment ManualDocument12 pagesDBMS Aggignment ManualprogramNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 DBDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 DBKashfa MahmoodNo ratings yet
- DBMS Question Bank and Lab PracticalsDocument12 pagesDBMS Question Bank and Lab PracticalsSujal PatelNo ratings yet
- Dbmslab 2Document17 pagesDbmslab 2HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Creating and Altering Tables: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesCreating and Altering Tables: ObjectivedramaNo ratings yet
- SampDocument7 pagesSampAhamedNo ratings yet
- Queries - Class of DBDocument32 pagesQueries - Class of DBsyma masoodNo ratings yet
- Aima DBMS BCE7A Lab MidDocument13 pagesAima DBMS BCE7A Lab MidMian Muhammad Ashar HussnainNo ratings yet
- Dbms Record1Document61 pagesDbms Record1Johnpaul JohnNo ratings yet
- (Exercise On Retrieving Records From The Table)Document19 pages(Exercise On Retrieving Records From The Table)TIHCBBA 2023No ratings yet
- 21BCB0241 VL2023240101046 Ast01Document24 pages21BCB0241 VL2023240101046 Ast01Sathvik MuppidiNo ratings yet
- S.No Date Name of The Experiment NO SignatureDocument83 pagesS.No Date Name of The Experiment NO Signature35Ramya MNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument29 pagesStress Management35Ramya MNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 12: Database Design, Creation of Table, Data Program / Queries Output Viva-Voce Record Total 30 50 10 10 100Document12 pagesPage 1 of 12: Database Design, Creation of Table, Data Program / Queries Output Viva-Voce Record Total 30 50 10 10 10035Ramya MNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Dbms-PrintoutDocument23 pagesDokumen - Tips Dbms-Printout35Ramya MNo ratings yet
- Sap BW On Hana (Lesson1-3)Document18 pagesSap BW On Hana (Lesson1-3)Azfar RazaNo ratings yet
- Day15 PLSQL-1Document44 pagesDay15 PLSQL-1Kundan KumarNo ratings yet
- Z4Nu868oQ7mjnCJKWOvg - Using - SQLite - With - QT - Squeeze - Every - CPU - Clock - To - Get - Faster - Gianbattista - GualeniDocument48 pagesZ4Nu868oQ7mjnCJKWOvg - Using - SQLite - With - QT - Squeeze - Every - CPU - Clock - To - Get - Faster - Gianbattista - Gualeniyoni zerbibNo ratings yet
- MSU Lab Report Database Design and DevelopmentDocument17 pagesMSU Lab Report Database Design and Developmentprofessor dubeNo ratings yet
- Project 2 Database Design and ETL: 1 Introduction: What Is This Project All About?Document16 pagesProject 2 Database Design and ETL: 1 Introduction: What Is This Project All About?EllenNo ratings yet
- Asm 2 DatabaseDocument35 pagesAsm 2 DatabaseHoàng Trung KiênNo ratings yet
- Query Examples in Relational Algebra and SQLDocument3 pagesQuery Examples in Relational Algebra and SQLPranab DasNo ratings yet
- Event Driven 6Document26 pagesEvent Driven 6dawitzeganeNo ratings yet
- DB211 - Unit 7 Assignment ADocument7 pagesDB211 - Unit 7 Assignment ATim Williams0% (1)
- New 8Document31 pagesNew 8vikram chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Multi Level User Login and Registration System in PHP and MySQLDocument14 pagesMulti Level User Login and Registration System in PHP and MySQLVirgo Virgo100% (1)
- Relational Languages and Relational ModeDocument68 pagesRelational Languages and Relational ModetechtechNo ratings yet
- Respuestas Oracle PL-SQL Practica 2Document2 pagesRespuestas Oracle PL-SQL Practica 2Ezequiel Hernán VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Run Liquibase As Part of A Java SE Application: Integrate Liquibase Into Hibernate's Bootstrapping ProcessDocument4 pagesRun Liquibase As Part of A Java SE Application: Integrate Liquibase Into Hibernate's Bootstrapping ProcessAdolfNo ratings yet
- Student Marklist Application: ProgramDocument10 pagesStudent Marklist Application: ProgramLavanya KvNo ratings yet
- SQL Fundamentals III - AssignmentDocument2 pagesSQL Fundamentals III - AssignmentFree For meNo ratings yet
- CRUD OperationsDocument7 pagesCRUD OperationsK Ganesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Database Programming With SQL 13-2: Using Data Types Practice ActivitiesDocument2 pagesDatabase Programming With SQL 13-2: Using Data Types Practice ActivitiesFlorin CatalinNo ratings yet
- Database Constraints and Keys ExplainedDocument8 pagesDatabase Constraints and Keys ExplainedHeman SetiaNo ratings yet
- Databases Sde SheetDocument34 pagesDatabases Sde SheetSuyash SinghNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Oracle 10g Program With PLSQLDocument1 pageSyllabus - Oracle 10g Program With PLSQLAfif Kamal FiskaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Oracle FormsDocument7 pagesBasics of Oracle FormstiwarialokNo ratings yet
- EXAM 000-302: DB2 9 Database and Application Fundamentals - Academic InitiativeDocument71 pagesEXAM 000-302: DB2 9 Database and Application Fundamentals - Academic InitiativePreeti Julian D'souzaNo ratings yet
- JDBC Driver and Its TypesDocument8 pagesJDBC Driver and Its Typespraty888No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Swasti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Relational Schema Exercises Answer KeyDocument5 pagesRelational Schema Exercises Answer KeySa SyNo ratings yet
- CrateDB PostgreSQL Query BenchmarkDocument12 pagesCrateDB PostgreSQL Query BenchmarkakukurtNo ratings yet
- Oracle Supple LoggingDocument16 pagesOracle Supple Loggingabilash0011253No ratings yet
- Data Modeling, SQL, and PL/SQL ( ) Systems Programming and Computer Architecture Computer Repairs Database Performance TuningDocument4 pagesData Modeling, SQL, and PL/SQL ( ) Systems Programming and Computer Architecture Computer Repairs Database Performance TuningAndre SeptianNo ratings yet
- SQL LAB Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesSQL LAB Assignment PDFDrShashikant Dargar50% (2)