Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-331-360
New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-331-360
Uploaded by
leogerguz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views30 pagesOriginal Title
New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-up Excavator-331-360
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-331-360
New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-331-360
Uploaded by
leogerguzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fos
‘Swing pump (4, Fig. 3)
‘The swing pump is a variable displacement axial-
piston pump in tited-axis design for hydrostatic,
drives in a self-contained circuit,
‘The volumetric flow is proportional to the drive
speed and to the displacement volume and is
continuously adjustable.
With increasing deflection of the tited axis, the
flow increases from 0 to its maximum value.
If the tited axis is displayed by the zero position,
the flow changes its direction smoothly
To protect the drive system, the pump is
equipped with two pressure relief valves for the
respective high pressure side.
‘These valves act simultaneously as feed valves.
‘An integrated booster pump serves as a feed
pump.
The max. feed pressure is assured by the builtin
feed pressure relief valve.
Depending on the preselected control pressure,
the operating pressure and the pressure direction,
and thus the size and direction of the moment at
the hydraulic motor, are continuously adjustable,
This control permits virtually loss-free utilization of
the drive system, both for accelerating and for
braking procedures. No power is converted into
heat via pressure relief valves, and the drive
motor is under less pressure in'the braking op-
eration.
There are two means of braking the swinging
‘operation of the superstructure:
* Servo valve in neutral position. The superstruc-
ture is braked by an adjustable braking valve.
* Counter-rotation by servo valve. Max. braking
pressure corresponds to max. initial swinging
pressure. a
2a
73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fa
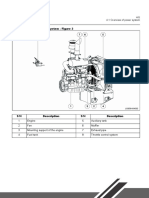
‘Twin gear pump (6, Fig. 4)
‘The pump is flange-mounted at the engine power
take-off, instead of the single gear pump, and
supplies the following circuits
~ Fan drive
= Servo control 3
73179387,00 us Cy 2
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fas
Combined oil / water cooler with fan
drive (7, Fig. 5)
‘The hydraulic oll cooler (7) cools the oll retuming
from the working and travelling hydraulics. The oi
returning trom from the fan drive also flows
‘through the oil cooler to the fiter chamber in the
reservoir.
‘The fan is driven by a gear motor with regulating
valve. A pressure-relief valve and a replenishing
valve are incorporated in the fan dive.
‘A measuring port (A, Fig. 6) on the gear motor
Permits pressure measurements. The pressures
measured are closely related to fan speed (see
also service-data 02).
Pressure-limiting valve (B) can be used to adjust
the fan speed.
Foe
73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Ea
comprises an solenoid valve with manual standby
activation and a downstream pressure relief valve
swinging output in conjunction with boom lifting. It
for the control pressure.
‘The swinging mode valve permits a reversible
‘Swinging mode valves (8 (35.1),
Fe?
Fig. 7)
73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fo.8
Filter (9, Fig. 8)
‘The filter housings with the cartridges are pres-
sure filters with a ftration rating of 20 m.
A pressure fit fiters the oil of the servo control
ump before it flows to the valve assembly (60)
and to the servo control system, The other pres-
sure fiter in the pump compartment fitters the oil
of the auxiliary or feed pump incorporated in the
swing pump before it is sent to the closed swing
circuit.
Load limit regulator PCS 3 (10)
See Technical Handbook "PCS 3"
28
73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fao
‘Switching valve (11, Fig. 9) with pressure pick-up B10, for automatic travel function
‘The switching valve (11) is controlled by switch-
ing valve (72)
It ensures that, during travel, the high pressure
keeps the controlled check valve in the 6-way
Control block past the switching valve piston by
means of shuttle valve (53).
When a 3rd function is activated, the check valve
In the control block is relieved and the oil flow of
ump 1 is divided in parallel to both travel mo-
tors.
The pressure pick-up (B10) converts the pres-
sures generated during traveling into electrical
signals,
‘These signals are transmitted to the control panel
where they are evaluated:
= When the automatic travel unit is on, the travel
cll motors (101) are automatically switched over
from fast speed to normal speed and the other
way round depending on the pump pressure val-
ve.
73179387,00 us
2
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
ig. 10
Switching valve (12 (66.2), Fig. 10)
‘The switching valve is used for the regenerative
"boom lowering" function (see also description of
system sections).
When the boom is lowered without pressure, the
solenoid valve is activated. This closes the con-
trolled check-valve in port STS of the control
block (0) by means of the instantaneous pump
pressure.
When the boom is raised, the solenoid valve (12)
Is deactivated and the controlled check-valve in
port STS without pressure. The oil from the pump
flows through the check-valve to the boom cyl-
Inder rod-side.
30
73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
I
Fatt
‘Swing gearbox (15, Fig. 11)
‘The swing gearbox is a 2-stage planetary gear-
box whose drive pinion engages in the swing
ring.
An integrated wet multiple-disk brake serves as a
holding brake for the superstructure,
‘Swing motor (Fig. 11)
‘The swing motor is a 40° axial-piston unit with a
constant intake volume. The drive speed Is pro-
portional to the incoming oil flow. The torque
supplied grows with the pressure drop between
high-pressure and low-pressure side.
‘Speed sensor (17, Fig. 11)
‘The sensor serves as a zoro-speed relay. It con-
trols the holding brake in the swing gearbox (15)
bby means of solenoid valve (61). When the sen-
sor detects zero speed, the holding brake is bloc-
ked. The brake remains released as long as the
‘superstructure is swinging, a
73179387,00 us
a
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fe 2
Hydraulic reservoir, complete
(20, Fig. 12)
Reservoir for the hydraulle il with the following
components:
~ 9 return flow fiters (21)
= 9 bypass valves (22)
+ 1 iter contamination switch $15 (28)
= 1 thermal sensor R14 (24)
Return flow filters (21, Fig. 12)
The relum flow fiters iter the oll lowing back
from the consumers. The oil flows through the
filer elements from inside to outside.
Bypass valve (22, Fig. 12)
‘The bypass valve prevents the return flow fiters
(11) from bursting. It opens at a pressure of more
than 1.5 bars. The oil then flows unfiltered into
the reservoir.
Filter contamination switch
(23 (S15), Fig. 12)
This switches on a warning light and an acoustic
warming signal in the cab when the return flow
filters are contaminated,
Thermal sensor (24 (R14), Fig. 12)
The thermal sensor registers the temperature of
the hydraulic oll and informs the load limit regula-
tor.
2
73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fe
Right servo control valve (30, Fig. 13)
The boom cylinder and the stick cylinder are
controlled by means of the 4-way servo control
valve with cross connection.
Left servo control valve (31, Fig. 13)
‘The stick cylinder and the swinging function are
controlled by means of the 4-way servo control
valve with cross connection.
Travel pedals (32, Fig. 13)
The hydraulic travel motors are controlled by
means of the 2-way servo control valves.
‘The servo control pressure ports for forward and
reverse travel are equipped with pressure switch-
es (S 7.1-7.4) ensuring the activation of the Trav-
‘1 Alarm function.
All servo control valves (30, 31, 32) are propor-
tional valves. The control valves in the 6-way
control block (50) are adjusted according to the
lever or pedal deflection.
73179387,00 us
33
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fig. t
Servo-control valve - additional
‘equipment (32, Fig. 14) (option)
The servo-control valve is used to adjust the
control spool for additional equipment in control
block (60).
Adgitional equipment:
= boom adjusting cylinder or
- hydraulic hammer or
- shears
A boom adjust cylinder can be moved with servo-
control valve (82, Fig. 14) continuously and in
different directions,
It a hydraulic hammer is installed, the hammering
rate can be controlled proprotionally to the deflec-
tion of the servo valve pedal
A pair of shears can be opened and closed.
34
73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Fa.t8
Solenoid vaive (34 (Y113), Fig. 15)
‘This valves blocks off the servo control pressure
to the servo control valves and the hammer /
shears pedal when the left control console is
raised. In the lower locked position of the con-
sole, the solenoid valve is open and the servo
contro! pressure is applied at the servo control
valves and the hammer / shears pedal.
‘This valve is equipped with a manual emergency
control
In the event of an electrical malfunction, the con-
‘rol piston is opened manually with the help of the
knurled knob. Work with the excavator can then
continue,
Solenoid valve (35 (Y66.1), Fig. 15)
The valve is used to activate and deactivate the
regenerative "boom lowering" function.
During the pressureless boom lowering function,
the solenoid is activated and the servo- control
pressure for boom lowering merely adjusts the
‘control spool in control block (50)
‘At the same time, the servo pressure applied acts
‘on the stroke limiter of the control spool
During the boom pushing function, the solenoid
valve (35) is deactivated. The servo pressure for
the boom lowering function passes to the shuttle
valve cascade (70, 71)
The load-sensing pressure switch (S10.1) opens
and both pump regulators receive the pressure
demanded,
‘At the same time, the stroke limiter for the boom
control spool becomes ineffective,
73179387,00 us
3
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
F516
6-way control block (50, Fig. 16)
“The control block housing accomodates 6 control
spools which are shifted by the servo control
pressure in proportion to hand lever or pedal
deflection
‘The following travel or working movements. are
controlled with this block
1 = Control spo! travel right
2 - Control spoo! travel left
= Control spool boom with regeneration function
3
‘4 - Control spoo! stick with regeneration function
= Control spool bucket
~ Control spool auxiliary hysraulic function,
hammer or shears or adjusting cylinder
(eotion)
36 Cy 73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
This page intentionally left blank.
73179387,00 us 68
a7
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Pig 17
Valve arrangement within 6-way control block (50, Fig. 17)
A=
rimary valve with pressure cut‘in stage (2 valves) M, = 100 Nm
B = Replenishing valve for travel oil motor (4 valves), secured with Loctite 243,
C = Pressure-holding valve (8 valves) Mx = 200" Nm
D = Secondary valve (5 valves) M, = 100" Nm (6 valves with additional hydraulics)
E = Secondary valve (1 valve) with check valve My = 150" Nm
F = Secondary valve (1 valve) M, = 180"? Nm (1-stege or 2- stage)
G = Stroke limiter for boom control spool (7.5 mm resp. 1 1mm)
H = Pre-pressurizing valve for parallel travel T1 (p =2 bars)
Pre:pressurizing valve for parallel travel T2 (p
bars)
J = Double check valve for bucket parallel connection M, = 220"° Nm in ST4
K = Check valve for parallel travel M, = 80° Nm
L = Check valve regenerative function M, = 350"? Nvv in STS
38 Cy 73179387,00 us
SERVICE MANUAL EC 240
Control block (50, Fig. 17)
Primary valves with pressure cut-in stage (A, Fig.
117) limit the maximum pressures of both working
pumps,
To avoid cavitation in the travel oil motors, the
travel functions are equipped with replenishing
valves (B, Fig. 17).
Each travel function moreover has one pressure
holding valve (C, Fig. 17) making it easier to set
off uphill on a slope,
‘The check valve (K, Fig. 17) for parallel travel is
Installed between both travel valves,
For lowering, the boom function is equipped with
fa regenerative circuit, including @ stroke limiter
(G, Fig. 17), a check valve in the secondary valve
(E, Fig. 17) and a controlled check valve (L, Fig.
17),
‘The bucket parallel connection is ensured by a
double check valve (J, Fig. 17) during bucket
actuation.
For lowering, the stick function is equipped with a
regenerative circuit. For this purpose, intemal
check and pre-pressurizing valves are installed in
the stick control spools.
‘The additional hydraulics can be equipped alter-
natively with single- or double-stage pressure-
limiting valves (F, Fig. 17).
‘All cylinder functions have secondary pressure
limiting valves (D, Fig. 17) with integrated replen-
ishing valves.
In addition, there are pressure-holding valves (C,
Fig. 17) maintaining the load pressure in the oyl-
inder against the pressure in the pump line. The
pressure-holding valves are also needed to com-
bine (double admission) or to separate (single
admission) the pump flows.
Both outlets of the tank line are equipped with
pre-pressurizing valves (H and |, Fig. 18).
‘The upper and lower servo-control caps are per-
manently flushed from the pre- pressurized tank
line of the control block when the engine is run-
ning.
‘Any existing air bubbles are thus transported via
the servo-control valves (30, 31, 32) to the hy-
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Manual de Partes RT-160Document622 pagesManual de Partes RT-160leogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-301-330Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-301-330leogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-691-720Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-691-720leogerguzNo ratings yet
- 7inch RT Crane Instruction ManualDocument20 pages7inch RT Crane Instruction ManualleogerguzNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookDocument30 pagesSodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookleogerguz100% (1)
- Touch Display - Programme Update InstructionDocument3 pagesTouch Display - Programme Update InstructionleogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-541-570Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-541-570leogerguzNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookDocument30 pagesSodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookleogerguzNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookDocument30 pagesSodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookleogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-661-690Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-661-690leogerguzNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookDocument30 pagesSodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookleogerguz100% (1)
- R Tranmicion 3Document2 pagesR Tranmicion 3leogerguzNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookDocument30 pagesSodaPDF Splitted LG856H.bookleogerguzNo ratings yet
- R Tranmicion 1Document3 pagesR Tranmicion 1leogerguzNo ratings yet
- R Tramicion 4Document2 pagesR Tramicion 4leogerguzNo ratings yet
- R TranmicionDocument3 pagesR TranmicionleogerguzNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Assy - Brake MasterDocument2 pagesCylinder Assy - Brake MasterleogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-421-450Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-421-450leogerguzNo ratings yet
- Axle, Front Drive - MountingDocument3 pagesAxle, Front Drive - MountingleogerguzNo ratings yet
- R Tranmicion 2Document3 pagesR Tranmicion 2leogerguzNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Cancel Calibration: CanceledDocument14 pages7.4 Cancel Calibration: CanceledleogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-91-120Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-91-120leogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-391-420Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-391-420leogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-241-270Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-241-270leogerguzNo ratings yet
- Ec240 - Crawler Excavator (05/00 - 12/04) 05 - Superstructure 31.051 (002) - Electrical Compon. I.circuit Diagram Page 02 (S/N 724002-Up)Document4 pagesEc240 - Crawler Excavator (05/00 - 12/04) 05 - Superstructure 31.051 (002) - Electrical Compon. I.circuit Diagram Page 02 (S/N 724002-Up)leogerguzNo ratings yet
- Ec240 - Crawler Excavator (05/00 - 12/04) 05 - Superstructure 31.051 (004) - Electrical Compon. I.circuit Diagram Page 04 (S/N 724002-Up)Document4 pagesEc240 - Crawler Excavator (05/00 - 12/04) 05 - Superstructure 31.051 (004) - Electrical Compon. I.circuit Diagram Page 04 (S/N 724002-Up)leogerguzNo ratings yet
- Ec240 - Crawler Excavator (05/00 - 12/04) 05 - Superstructure 31.051 (010) - Electrical Compon. I.circuit Diagram Page 10 (S/N 724002-Up)Document4 pagesEc240 - Crawler Excavator (05/00 - 12/04) 05 - Superstructure 31.051 (010) - Electrical Compon. I.circuit Diagram Page 10 (S/N 724002-Up)leogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-151-180Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-151-180leogerguzNo ratings yet
- New Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-121-150Document30 pagesNew Holland EC240 Excavator SN 724002-Up Excavator-121-150leogerguzNo ratings yet