Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orchestra Training Material
Uploaded by
AdewaleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orchestra Training Material
Uploaded by
AdewaleCopyright:
Available Formats
ORCHESTRA TRAINING MATERIAL
Prepared by: Adewale Samuel Adebayo (DLBC, Rivers State Orchestra Leader)
This material gives summarized information about the various categories of
instruments. Please note that some instruments are discussed in this material
(not all). Details can be gotten from the attached documents to this material.
The above is the picture of the orchestra setting or seating arrangement.
There are five categories of instruments in the orchestra:
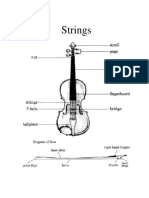
Strings
Brass
Woodwinds
Keyboards
Percussions
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
String Instruments
These are instruments that have set of strings arranged on them. They can be
plucked with fingers or played with the Bow.
There are some instruments in this category:
Violin family (Violin, Viola, Cello and Double Bass),
Harp
Guitar, etc.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
The Violin Family
The violin family is unique set of instruments that are similar in some ways:
They all have 4 strings each; they all use the Bow; they use the Bridge; f-holes;
etc.
THE VIOLIN
The violin has 4 strings:
E – String (1st String. This is the slimmest string)
A – String (2nd String)
D – String (3rd String)
G – String (4th String. It is the thickest string among the four strings).
The Violin is tuned in perfect 5th. For instance, if open G-string is doh; counting
the sulfas, we will have open D-string as ‘soh’. Then, counting 5 notes from ‘soh’,
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
we will have the next string as upper ‘ray’; and the E-String as ‘la’. This is how to
tune the Violin without the use of a tuning pipe (pitch pipe) or the Piano.
There are different sizes of the Violin:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
The Violin is a Treble Stave instrument. It can be used to play the Soprano/Treble
part (i.e. Violin I), and the Alto part (i.e. Violin II).
There are different tutors for the violin instrument. For the purpose of this
training, we are recommending “A Tune A Day”.
Some graded Tutors that can be used to systematically study the Violin are:
The posture of a Violinist can be seen below:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE VIOLA
This is very similar to the Violin instrument sine they are of the same family. The
Viola instrument is a little bit bigger than the Violin in size.
The Viola has 4 strings which are:
A – String (This is the 1st and the slimmest string)
D – String (2nd String)
G – String (3rd String)
C – String (4th String. It is the thickest string among the four strings).
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
From the picture above, you will observe that the Viola looks exactly like the
Violin, except for the different strings and size of instrument.
The Viola is a tenor instrument. Due to its note range, it can also be used in a solo
performance. So, a Violist should learn how to read the Treble Stave, Bass Stave
and Tenor Stave (where the C-Clef is used).
The Viola tutor “A Tune A Day” will also be used for the purpose of training.
Picture of a Violist can be seen below:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE CELLO
The cello (/ˈtʃɛloʊ/ CHEL-oh; plural cellos or celli) or violoncello (/ˌvaɪələnˈtʃɛloʊ/
VY-ə-lən-CHEL-oh; Italian pronunciation: *vjolonˈtʃɛllo]) is a bowed, and
sometimes plucked, string instrument with four strings tuned in perfect fifths.
From the above picture, we notice that the Viola and the Cello have the same
arrangement of strings.
Some Cello tutors are shown here:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
This instrument is played sitting down while the tail spike is on the floor. A picture
of a Cellist is shown below.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE DOUBLE BASS
The double Bass is also a Bass instrument like the Cello. The difference is that, it
has far deeper sound than the Cello, but the Cello has a wider range of notes than
it.
This is instrument is usually played standing due to its height and width. The
double bass has four strings like the previous instruments we have discussed. The
G, D, A, E strings, just like in Violin, but they are arranged in reverse order here.
They are displayed in the image below:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Double Bass tutors displayed below:
Picture of a Double Bassist can be found below:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
BRASS INSTRUMENTS
A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by sympathetic
vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the
player's lips. Brass instruments are also called labrosones, literally meaning "lip-
vibrated instruments". – Wikipedia definition.
The Brass instruments are a set of metallic instruments that uses the mouthpiece.
They are either gold or silver plated. They are played by ‘buzzing’ the lips into the
mouthpiece.
The Brass instruments are divided into two:
Valved Brass Instruments (Trumpet, Cornet, Euphonium, Tuba,
Sousaphone, etc.)
Slide Brass Instruments (Trombones, Sackbut, and Bazooka).
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE TRUMPET
The trumpet is a tri-valve instrument like most valve instruments. It is a high
pitched instrument that plays the Treble Stave. It plays the treble or soprano part
as Trumpet I, while the Alto part as Trumpet II.
The trumpet is a tone higher than the concert pitch or Piano pitch. If the piano
plays key C, it will be key D on the trumpet. To avoid this stress or transposing
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
instruments, we have decided to rewrite the fingering charts for all the
transposing instruments for easy learning. This was done due to the fact that song
pieces are not commonly written on the various keys of the different instruments.
They are rather written together on the concert keys.
Trumpet Fingering Chart
VALVES FINGERS NOTE/KEY
0 B flat
123 B
1, 3 or 1 C
2, 3 C sharp or D flat
1, 2 D
1 D sharp or E flat
2 E
1, 3 or 0 F
2, 3 F sharp or G flat
1, 2 G
1 G sharp or A flat
2 A
0 A sharp or B flat
SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES TRUMPET CHART
In order to correctly play the above, the pressures (lower, middle and higher
pressures) must be played accordingly. Posture of a trumpeter playing below:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE TROMBONE
The trombone is a musical instrument in the brass family. Like all brass
instruments, sound is produced when the player's vibrating lips (embouchure)
cause the air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones have a
telescoping slide mechanism that varies the length of the instrument to change the
pitch. Many modern trombone models also utilize a rotary valve as a means to
lower pitch of the instrument. Variants such as the valve trombone and superbone
have three valves like those on the trumpet.
The word trombone derives from Italian tromba (trumpet) and -one (a suffix
meaning "large"), so the name means "large trumpet". The trombone has a
predominantly cylindrical bore like its valved counterpart the baritone and in
contrast to its conical valved counterparts, the euphonium and the horn. The most
frequently encountered trombones are the tenor trombone and bass trombone. The
most common variant, the tenor, is a non-transposing instrument pitched in B♭, an
octave below the B♭ trumpet and an octave above the B♭ tuba. The once
common E♭ alto trombone became less widely used as improvements in
technique extended the upper range of the tenor, but it is now enjoying a
resurgence due to its lighter sonority which is appreciated in many classical and
early romantic works. Trombone music, along with music for euphonium and tuba,
is typically written in concert pitch in either bass or tenor clef, although exceptions
do occur, notably in British brass-band music where tenor trombone is presented as
a B♭ transposing instrument, written in treble clef.
A person who plays the trombone is called a trombonist or trombone player.
- From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The trombone is a slide instrument which is very unique in its design.
There are seven (7) slide positions on a trombone. See the image of a labeled
trombone:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Trombone Slide Chart
SLIDE POSITION NOTE/KEY
1 B flat
7 B
6 or 3 C
5 or 2 C sharp or D flat
4 D
3 D sharp or E flat
2 E
6 or 1 F
5 F sharp or G flat
4 G
3 G sharp or A flat
2 A
1 or 5 A sharp or B flat
SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES TROMBONE CHART
Below is the picture of a trombonist with the right posture:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
The Woodwind
Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the more
general category of wind instruments. There are two main types of woodwind
instruments: flutes and reed instruments (otherwise called reed pipes). What
differentiates these instruments from other wind instruments is the way in which
they produce their sound. All woodwinds produce sound by splitting an exhaled
air stream on a sharp edge, such as a reed or a fipple. A woodwind may be made
of any material, not just wood. Common examples include brass, silver, and cane,
as well as other metals including gold and platinum. Examples are a saxophone, a
bassoon and a piccolo.
- From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Some of these instruments are played on the concert pitch, while others like
Saxophone and Clarinet are usually transposed.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE FLUTE
The flute is a family of musical instruments in the woodwind group. Unlike
woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is an aerophone or reedless wind
instrument that produces its sound from the flow of air across an opening.
The flute is a soprano instrument whose sound is based on the concert pitch. This
means that, Flute is not a transposing instrument.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Fingering Charts for Flute:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Fingering Chart 2
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Picture of a flutist performing:
Flute tutors are shown below:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE CLARINET
The clarinet is a musical-instrument family belonging to the group known as the
woodwind instruments. It has a single-reed mouthpiece, a straight cylindrical
tube with an almost cylindrical bore, and a flared bell. A person who plays a
clarinet is called a clarinetist (sometimes spelled clarinettist).
- From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The regular Clarinet is an Alto instrument. The Clarinet Chart written on the
concert pitch will be added as part of the training materials when the students
have started the training.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Below is the regular Clarinet chart:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Clarinet tutors that can be used to train on the instrument are:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Picture of people playing the Clarinet:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE SAXOPHONE
The saxophone (also referred to as the sax) is a family of woodwind instruments.
Saxophones are usually made of brass and played with a single-reed mouthpiece
similar to that of the clarinet. Like the clarinet, saxophones have holes in the
instrument which the player closes using a system of key mechanisms. When the
player presses a key, a pad either covers a hole or lifts off a hole, lowering or
raising the pitch, respectively.
The saxophone family was invented by the Belgian instrument maker Adolphe Sax
in 1840. Adolphe Sax wanted to create a group or series of instruments that would
be the most powerful and vocal of the woodwinds, and the most adaptive of the
brass instruments, that would fill the vacant middle ground between the two
sections. Sax patented the saxophone on June 28, 1846, in two groups of seven
instruments each. Each series consisted of instruments of various sizes in
alternating transposition. The series pitched in B♭ and E♭, designed for military
bands, have proved popular and most saxophones encountered today are from this
series. Instruments from the so-called "orchestral" series, pitched in C and F, never
gained a foothold, and the B♭ and E♭ instruments have now replaced the C and
F instruments when the saxophone is used in an orchestra.
The saxophone is used in classical music (such as concert bands, chamber music,
solo repertoire, and, occasionally, orchestras), military bands, marching bands, and
jazz (such as big bands and jazz combos). The saxophone is also used as a soloing
and melody instrument or as a member of a horn section in some styles of rock and
roll and popular music. Saxophone players are called saxophonists.
- From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Basically, we have Soprano, Alto, Tenor and Baritone and Bass Saxophones. Each
of these is to be learnt or played using the sulfas and the stave notation. The
Soprano Saxophone is a tone higher than the concert pitch; while the Alto
Saxophone is 3 semitones lower than the concert pitch. All these will be clearly
explained in the class to avoid confusion, as Saxophone is a transposing
instrument like the Clarinet and the Trumpet.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
See the picture of a well-labeled Saxophone below:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
The fingering chart of the saxophone is usually not written on the concert pitch. In
the course of this training, trainees will be introduced to learning with the concert
pitch. Below is the original fingering chart.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Saxophone posture while playing:
Saxophone tutors include but not limited to the following:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
THE KEYBOARD
A musical keyboard is the set of adjacent depressible levers or keys on a musical
instrument. Keyboards typically contain keys for playing the twelve notes of the
Western musical scale, with a combination of larger, longer keys and smaller,
shorter keys that repeats at the interval of an octave. Depressing a key on the
keyboard causes the instrument to produce sounds, either by mechanically
striking a string or tine (piano, electric piano, clavichord), plucking a string
(harpsichord), causing air to flow through a pipe (organ), striking a bell (carillon),
or, on electric and electronic keyboards, completing a circuit (Hammond organ,
digital piano, synthesizer). Since the most commonly encountered keyboard
instrument is the piano, the keyboard layout is often referred to as the "piano
keyboard".
- From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Figure XX: The Keyboard drawn and labeled with all 12 keys (from C to B)
Figure Xxi: The Keyboard on a Piano Instrument
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
In summary, there are different devices on which the keyboard is found:
o Piano (Grand Piano, Mini Grand Piano and Upright Piano)
o Pipe Organ
o Electronic Keyboard.
The keyboard is the collection of the 7 white and 5 black keys repeated in a
number of times (known as octaves).
The Grand Piano
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Pipe Organ
Electronic Keyboard
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Piano Tutors to use:
Picture of a Pianist:
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Key Signature
The 12 major keys are grouped into three (3) categories:
Sharp Keys
Flat Keys and
Natural Key C
SHARP KEYS
Table 1: Sharp Keys and their Letters
S/N KEY Number of Sharps Sharpened Letters
1 G # F
2 D ## F, C
3 A ### F, C, G
4 E #### F, C, G, D
5 B ##### F, C, G, D, A
#
6 F ###### F, C, G, D, A, E
#
7 C ####### F, C, G, D, A, E, B
FLAT KEYS
Table 2: Flat Keys and their Letters
S/N KEY Number of Sharps Flattened Letters
1 F ♭ B
b
2 B ♭♭ B, E
b
3 E ♭♭♭ B, E, A
b
4 A ♭♭♭♭ B, E, A, D
b
5 D ♭♭♭♭♭ B, E, A, D, G
b
6 G ♭♭♭♭♭♭ B, E, A, D, G, C
7 C ♭♭♭♭♭♭♭ B, E, A, D, G, C, F
NATURAL KEY C is denoted with no sign of either flats or sharps on the music
stave.
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Playing Musical Notes/Pieces
Each musical instrument is designed to be able to play on the 12 major keys and
12 minor keys. You can achieve this in two ways namely:
i. Playing Sulfa and
ii. Playing Letters
PLAYING SULFA
This is the use of tonic sulfa (d r m f s l t d’) to play a piece of music. This is
achieved by sight reading the musical notes or transcribing them into sulfa
notation before playing. An instrumentalist who sings in the choir can easily play
sulfa notes if given the fingering/position chart of a particular key. For example,
Mary Had A Little Lamb
m r d r mmm rrr mss
m r d r mmm drr mrd
PLAYING LETTERS
Playing letters has to do with playing the keys which relates to the same sulfa
notes depending on the key chosen. For instance on key C major, we have the
scale as follows:
d r m f s l t d’
C D E F G A B C
Example:
Mary Had A Little Lamb
E D C D EEE DDD EGG
E D C D EEE CDDEDC
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Exercises on playing letters and sulfa:
Sulfa Notation Letters
Twinkle, twinkle Little Star
d d s s l l s— f f m m r r d C C G G A A G— F F E E D D C—
s s f f m m r— s s f f m m r— G G F F E E D— G G F F E E D—
d d s s l l s— ffmmrrd C C G G A A G— F F E E D D C—
Old Mac Donald Had A Farm
d d d s l l s— m m r r d— CCCGAAG EEDDC
s d d d s l l s— m m r r d— GCCCGAAG EEDDC
s d d d s d d d, d d d d d d d d GCCCGCCC CCCCCCCC
d d d s l l s— m m r r d CCCGAAG EEDDC
Constructing Scales with Letters
We are going to construct the 12 major scales by matching the sulfa to the
corresponding letters following the example of key C major given above. A good
knowledge of Key Signature as seen in Table 1, Table 2 and the Keyboard in figure
XX are required to achieve this.
Key G has only one sharp (sharpened letter is F). This means in key G major, we
have F# as one of the letters on its scale while the other letters are without
accidental (No sharp no flat attached to them except for F).
If in key C major, we have the scale as follows:
d r m f s l t d’
C D E F G A B C
Key G major will be:
d r m f s l t d’
G A B C D E F# G
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
Key D major will be: F and C are sharpened
d r m f s l t d’
D E F# G A B C# D
Key A major will be: F, C, and G are sharpened
d r m f s l t d’
A B C# D E F# G# A
Key F major will be: B is flattened
d r m f s l t d’
F G A B♭ C D E F
Key Bb major will be: B and E are flattened
d r m f s l t d’
B♭ C D E♭ F G A B♭
Key Eb major will be: B, E and A are flattened
d r m f s l t d’
E♭ F G A♭ B♭ C D E♭
Complete the remaining keys as an assignment…
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
EXERCISES
1. Mary Had A Little Lamb
2. Twinkle, twinkle Little Star
3. Old Mac Donald Had a Farm
4. National Anthem
5. Canon in D
6. Ode to Joy
7. Ave Maria
8. Pastorial Symphony (from Handel’s Messiah)
9. Jesu Joy of man’s Desiring
10.The Trumpet Shall Sound
11.Overture (from Handel’s Messiah) - Orchestra
12.Eine Kleine Nachtmusik, K. 525 - Orchestra
13.Handel’s Royal Fire Works - Orchestra
14.Handel’s Water Music - Orchestra
15.Symphony No.5 (by Van L. Beethoven) - Orchestra
16.Symphony No.40 (by W.A. Mozart) - Orchestra
17.Turkish March (by Van L. Beethoven) – Violin & Piano
Other Works
1. Give the World A Smile
2. Jesus Needs You to Scatter Sunshine
3. I’ll Sail Up High
4. Glory Special
5. Wonderful
6. Where Could I Go
7. Peace Be Still (GHS 96)
8. Amazing Grace (Solo Trombone & Accompaniment)
9. Finiculli Funiculla
10.Take Five (Irregular timing)
Prepared by SWAP-TECHNOLOGIES: 08063599862
You might also like
- Supervisory Plan 2022 2023Document4 pagesSupervisory Plan 2022 2023Jesieca Bulauan100% (12)
- Partitur Alvamar Ouverture PDFDocument32 pagesPartitur Alvamar Ouverture PDFÓscarEmanuelVilhenaGonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Learn the Basics of Bass Guitar Strings and NotesDocument4 pagesLearn the Basics of Bass Guitar Strings and NotesMatt WeiserNo ratings yet
- String BasicsDocument7 pagesString Basicslocrian54100% (4)
- Trash TV Trance PDFDocument20 pagesTrash TV Trance PDFJames100% (1)
- Scale Book for the Violin - Containing a Systematic Method of Fingering, Whereby all Scales and Arpeggios are Easily AcquiredFrom EverandScale Book for the Violin - Containing a Systematic Method of Fingering, Whereby all Scales and Arpeggios are Easily AcquiredRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- A Practical Guide to Selected Trios and Quartets for Trombone, Euphonium and Tuba: Practical Guide, #3From EverandA Practical Guide to Selected Trios and Quartets for Trombone, Euphonium and Tuba: Practical Guide, #3No ratings yet
- O & M Manual TemplateDocument11 pagesO & M Manual Templatesooriya_82No ratings yet
- Epic Orchestra 2.0 GuideDocument17 pagesEpic Orchestra 2.0 GuideQuasiNo ratings yet
- Altissimo fingerings for contrabass clarinetDocument10 pagesAltissimo fingerings for contrabass clarinetLucius ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- William Told Too MuchDocument12 pagesWilliam Told Too MuchhliasNo ratings yet
- Double Reed InstrumentsDocument17 pagesDouble Reed InstrumentsJohnNo ratings yet
- Music - Form 2eDocument23 pagesMusic - Form 2egabbycakes789No ratings yet
- List of Brass Instruments - Normans Music Blog PDFDocument9 pagesList of Brass Instruments - Normans Music Blog PDFLina Syazana Md RadziNo ratings yet
- Range of InstrumentsDocument10 pagesRange of InstrumentstbiancolinoNo ratings yet
- Charango Instrumental TuningsDocument17 pagesCharango Instrumental TuningsBill RobNo ratings yet
- Grade 8: and Adagio (1st and 2ndDocument10 pagesGrade 8: and Adagio (1st and 2ndPeterNo ratings yet
- Accord Luths, Guitares, EtcDocument10 pagesAccord Luths, Guitares, EtcTICLO50100% (1)
- Strings PDFDocument14 pagesStrings PDFSandro Costa100% (2)
- Trumpet Overtones and ValvesDocument2 pagesTrumpet Overtones and ValvesMarcel CelayaNo ratings yet
- Music WorkshopDocument17 pagesMusic WorkshopKevin Drummond100% (1)
- Pomp and Circumstance: Preview OnlyDocument16 pagesPomp and Circumstance: Preview OnlyDomenico Bruno0% (1)
- Full Score: - For OrchestraDocument40 pagesFull Score: - For OrchestraDouble DreamNo ratings yet
- The Transposing Instruments PDFDocument12 pagesThe Transposing Instruments PDFCesco Nigris100% (1)
- Ariel - Grade 3Document20 pagesAriel - Grade 3lorenzo marcolina100% (1)
- Brass: The Trumpet FamilyDocument1 pageBrass: The Trumpet FamilyTom HartNo ratings yet
- Naming The Octaves Octave, Ottava (Italian F.), Oktave (German F.), Octave (French F.), Octava (Spanish F.)Document4 pagesNaming The Octaves Octave, Ottava (Italian F.), Oktave (German F.), Octave (French F.), Octava (Spanish F.)amaamawNo ratings yet
- EXE24Document40 pagesEXE24SiHyun UhmNo ratings yet
- Violin Double Triple StopsDocument14 pagesViolin Double Triple StopsAsyaNo ratings yet
- Sacred Winds Full Score v2 ALLDocument167 pagesSacred Winds Full Score v2 ALLLuis Enrique Guillermo Vilca PalominoNo ratings yet
- Prelude: Preview OnlyDocument12 pagesPrelude: Preview OnlyEmmanuel Camelo QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Latin American MelodiesDocument77 pagesLatin American MelodiesEdleJulve100% (1)
- Aza deDocument16 pagesAza derexbeyondNo ratings yet
- Tuning and Voicing The Clarinet PDFDocument10 pagesTuning and Voicing The Clarinet PDFLeko Mladenovski100% (1)
- The Abduction From The Seraglio: Preview OnlyDocument20 pagesThe Abduction From The Seraglio: Preview OnlyOrquesta Juvenil de FresiaNo ratings yet
- Syncopated Clock - BullockDocument10 pagesSyncopated Clock - Bullockjuan100% (1)
- ARMY Piano and Guitar - 1978 69 PgsDocument84 pagesARMY Piano and Guitar - 1978 69 PgsJohnConnor4235No ratings yet
- Miller, Glenn - Method For Orchestral Arranging (1943)Document124 pagesMiller, Glenn - Method For Orchestral Arranging (1943)fefefe100% (3)
- RotaryDocument0 pagesRotaryapi-238000790No ratings yet
- Transposing InstrumentsDocument5 pagesTransposing InstrumentsnorthpolebcsNo ratings yet
- Instruments Used in Music: Kimberly Ann AquinoDocument27 pagesInstruments Used in Music: Kimberly Ann AquinoAshley MendozaNo ratings yet
- 88 Drawbars & PercussionDocument60 pages88 Drawbars & PercussionthemusicusNo ratings yet
- General KnowledgeDocument14 pagesGeneral KnowledgeShir TeoNo ratings yet
- Voice Name List Liste de Sons Klangübersicht Lista de Nombres de Las VocesDocument12 pagesVoice Name List Liste de Sons Klangübersicht Lista de Nombres de Las VocesladydaladyNo ratings yet
- As Twilight Falls: Preview OnlyDocument8 pagesAs Twilight Falls: Preview OnlyERCOLE LATTARINo ratings yet
- Trumpet Excerpts 2016Document12 pagesTrumpet Excerpts 2016Jacob Morgan100% (1)
- Salsa With That_ ScoreDocument16 pagesSalsa With That_ ScoreFacundo JuárezNo ratings yet
- Renaissance: 2000 Allen Organ Company All Rights Reserved AOC P/N 033-00005 April-2000Document22 pagesRenaissance: 2000 Allen Organ Company All Rights Reserved AOC P/N 033-00005 April-2000nblartNo ratings yet
- Bend Portamento, Pitch Bend, GlissandoDocument3 pagesBend Portamento, Pitch Bend, GlissandoRogerio LimaNo ratings yet
- Altes Metodo 1Document46 pagesAltes Metodo 1koke42100% (1)
- Ii - V - I: For Solo or Two Electric GuitarsDocument5 pagesIi - V - I: For Solo or Two Electric GuitarsEricsson CastroNo ratings yet
- Drum NotationDocument4 pagesDrum NotationDiddi_86No ratings yet
- Drum Notation Guide PDFDocument4 pagesDrum Notation Guide PDFmailmanager8946No ratings yet
- How To Play The Tin WhistleDocument21 pagesHow To Play The Tin WhistleJohn Ray EnajeNo ratings yet
- 15 Etudes modernes et progressives: for FluteFrom Everand15 Etudes modernes et progressives: for FluteRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- There's More to Playing the Piano: A thorough explanation of music theory with practical keyboard activities and video links for each topicFrom EverandThere's More to Playing the Piano: A thorough explanation of music theory with practical keyboard activities and video links for each topicNo ratings yet
- Human Ear and Role of Hearing in HCIDocument4 pagesHuman Ear and Role of Hearing in HCIrafia0% (1)
- Use of Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesUse of Passive VoiceLuciana DicieroNo ratings yet
- CV of Dr. Mohammad TahirDocument12 pagesCV of Dr. Mohammad TahirMuhammad FayyazNo ratings yet
- Senior Power Apps Engineer JobDocument3 pagesSenior Power Apps Engineer JobMichałNo ratings yet
- Central Bank Digital Currency:: The Future of Payments For CorporatesDocument29 pagesCentral Bank Digital Currency:: The Future of Payments For CorporatesknwongabNo ratings yet
- The University of QueenslandDocument2 pagesThe University of Queenslandimmanuel nauk elokpereNo ratings yet
- Listado 2 4ghzDocument4 pagesListado 2 4ghzRogerNo ratings yet
- Imeko WC 2012 TC21 O10Document5 pagesImeko WC 2012 TC21 O10mcastillogzNo ratings yet
- Environmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingDocument20 pagesEnvironmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingHitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Power Over Ethernet - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesPower Over Ethernet - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitNo ratings yet
- New Product Performance Advantages For Extending Large, Established Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) BrandsDocument18 pagesNew Product Performance Advantages For Extending Large, Established Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) Brandssmart_kidzNo ratings yet
- Studi Kasus Pada PT Damar Bandha Jaya Corp. BogorDocument10 pagesStudi Kasus Pada PT Damar Bandha Jaya Corp. BogorMayHan13No ratings yet
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For 9957W Automatic Balancing ValveDocument2 pagesInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For 9957W Automatic Balancing ValveManuel Molina CamposNo ratings yet
- WRBS Quarter 1 Modules WEEK-1-8Document32 pagesWRBS Quarter 1 Modules WEEK-1-8Sir Kindred VillaruzNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Setting Procedure Evs HMF Tech Procedure Evs 11 16pdf Setting ProcedureDocument37 pagesVdocuments - MX Setting Procedure Evs HMF Tech Procedure Evs 11 16pdf Setting ProcedureKrum Kashavarov100% (1)
- Resume-Mariam Abdul AzizDocument2 pagesResume-Mariam Abdul Azizmaryam cookNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Pidilite IndustriesDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Pidilite IndustriesAbhijit DharNo ratings yet
- Intro To Rizal LawDocument61 pagesIntro To Rizal Lawnicachavez030No ratings yet
- AGN PresentationDocument119 pagesAGN PresentationNikki GarlejoNo ratings yet
- The Impact of COVID-19 On The Steel IndustryDocument25 pagesThe Impact of COVID-19 On The Steel IndustryAyesha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Office Call About Infected Foot InjuryDocument5 pagesDoctor's Office Call About Infected Foot InjuryNur annisa HarahapNo ratings yet
- Kwame Ture InterviewDocument8 pagesKwame Ture InterviewSumayya K AliNo ratings yet
- HW3 - Chapter 9-2Document3 pagesHW3 - Chapter 9-2Zachary MedeirosNo ratings yet
- RIZAL: INSPIRATION FOR A NEW GENERATIONDocument11 pagesRIZAL: INSPIRATION FOR A NEW GENERATIONErica B. DaclanNo ratings yet
- CSB 211102 1 FCT EMS 702 Upgrade Process With Security FeaturesDocument2 pagesCSB 211102 1 FCT EMS 702 Upgrade Process With Security FeaturesCedric NkongoNo ratings yet
- Rubber Conveyor Belt Wear ResistanceDocument5 pagesRubber Conveyor Belt Wear ResistanceBelt Power LLCNo ratings yet
- Rapid Web Development With Python/Django: Julian HillDocument37 pagesRapid Web Development With Python/Django: Julian Hilljppn33No ratings yet
- Participation RubricDocument2 pagesParticipation RubricCarmen Ibañez AlvarezNo ratings yet