Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson9 BES025
Uploaded by
dan adrian palaganas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views16 pagessadasdkia sadklnask
Original Title
Lesson9-BES025
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsadasdkia sadklnask
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views16 pagesLesson9 BES025
Uploaded by
dan adrian palaganassadasdkia sadklnask
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
. : Studont Activity Sheet #9
Name THX Ms PALACE BNAG Ef s number
Section B-ausee 10 Schedule Date z
———————
Tesson title: Analysis of Structure: Truss ( Method of Joints) Materials
Canon F-789SGA, Pen and
Lesson Objectives: Notebook
At the end of the module you will be able to: References:
1. Engineering Mechanics Statics
(Metric Edition) by Andrew Pytel &
Jaan Kiusalaas
2. Simplified Engineering
Mechanics by Dela Fuente
Racines Ocampo Siapno & Olleta
3 Engineering Mechanics by
Ferdinand Singer
4 Understanding Engineering
Mechanics Statics by A Pytel & J
Kiusalaas
5. Engineering Mechanics by
Besavilla
1. Define a simple /plane truss
2 Identify a zero- force members in a structure.
3 Determine the reactions and member forces
Productivity Tip:
A. LESSON PREVIEWIREVIEW
i) Introduction (2 mins)
Being an engineering student take note that one of the most important
lesson in statics we must learn is, how to analyze a certain structures
such as trusses and frames whose component method are welded.
riveted or bolted to a gusset plate; at the joint or node.
Structural Analysis involves the determination of the effects of the
loads on physical structures and their component members, Structures
that are subject to this type of analysis include all that must withstand
loads such as buildings and bridges, to mention a few. (see the figure)
Structural Analysis plays a key part in the engineenng”design of the
structures whose results are used to verify the fitness and stability of the
structure, which oftentimes aid in saving time and money on physical
tests,
‘This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 1
tatics of Rigid sone
25: s
‘Student Activity Sheet #5 \
BES 0:
irgsia IDUCATION
_ Class number
Date:_
¢
Name
Section
Schedule
2) Activity 1: What | Know Chae. part 1 (3 mins)
What | Know ~~ Questions: ane
sane 1, What is the purpose of @ uss? |
Qurpcet Foe | |
CePA _ | i
jeceeree ~)-2 What are the methods you wil
METHOD oF use to analyze a simple truss?
Jones | i
3 Whats tues amavis? r
PARUNG THE
=z Bae ov |
Tag moe |
B.MAIN LESSON
1) Activity 2: Content Notes (13 mins)
TRUSS
Pin- connected Trusses: the internal force in a member is directed along its axis or centerline (truss
components are two-force members, that is, members held in equilibrium by only two forces
A truss is a structure which is Different Truss Types
composed completely of axial
members thal are assumed t0 be
weightless." The members. are 7
connected by pinned joints, that AED
form triangular structures within the Parker
main truss, with the external loads
applied only at the joints. The
primary concer in the structural
analysis of a truss is the
determination of the forces acting in
the members and n the joints / pins
Warren with Vials)
in the structure.
RYYYYYY
Each member of the truss is either AXON
tension: (cause forces whisir pulis
away from the joints) or in
compressic:. cause forces which
push towards the joints)
I
‘This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION is
PHINMA EDUCATION, BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
- . Student Activity Sheet #9
¢
Nam
Section
Class number
Date
ANALYSIS/ METHODS IN THE SOLUTION OF A TRUSS
METHODS OF JOINTS
As the nam ofthe methods indicates, the analysis of he structure fs through the consideration ofthe joints
~ taken as ffee bodes and the conditions of equilibrium applied (the structure being in eq
elements are also in equilibrium)
i tem in equilibrium
Thisis also based on the assumption that all members of any joint is a concurrent force syst bru
At no time should there be more than two unknown forces at a joint, indicate the force by means of an @
> A 5 b00n a
STEPS TO FOLLOW:
1. From the given loaded truss, the reactions at the supports are determined using:
ye
2. Choose a joint with at most two unknown members as the free body, and assume their force directions
(towards the joint for compression and away from the joint for tension: if a negative value results, the
force magnitude is correct but must be directed oppositely). Once the value and the type of forces have
been determined, the same should be indicated in the truss,
DF =0and YM =0
5 Is similar to the second step, with the next joint taken as free body and analyzed in a similar way. This
Procedure is repeated, until all he members have been completely analyzed and their forces determined
NOTE:
itis Suggested that the analysis stavts from tie leftinost jul
07 the truss to the middle portion, and then
from the rightmost joint to the middle portion. A check on the forces of the middle members could be
obtained in this way
BES 025: Statics of
Student Ac
Glass number
Schedule an tes
Example Problems:
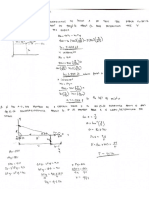
1. Determine the magnitude and the type of the forces in the members of the truss shown in the figure]
with @ horizontal force applied at the upper chord and a vertical load at the lower chord.
50 KN, Cc
Ra 20 kN
|
} 1.00 m
| (Angles BAF = CDE = BEF = 33.7°)
SOLUTION
(1) Determine the support reactions
(a) £ (Mee = 0, Ral4.5) — 50(1) — 2063) = 0
4SRq= 110, or Ra = 2444 KN
| (b) YFL= 0. Ro ~ 50-0 oF Rix = SOKN
| (2 SF=8. By 2 RS, =0 or By, -244t-20
Rp) = 444 kN
From which, Ro= V Rov + Roy
This document is the property OF PHINMTA EDUCATION a
50.20 kN
+ ne AREF
Name
Section: _
Nye
‘This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION
PHINMA EDUCATION
Schedule
Ra = 24.44 kN
(2). Take joint A as the tree body (trom the leftmost joint)
(a) LEy=0. Ra~Faasin33.7 = 0
4.44 | 0.5548 = 44.05 KN (compression)
or Fal
(b) SF,=0, Far ~ Fag cos 33,7° = 0
or Fay = 44.05(0,8319) = 36.65 kN (tension)
Fie
Fay = 36.65 KN
20 kN
(3). Take joint F as the free body,
By observation. Fry = 20 KN (tension)
Fre = Far = 36.65 KN (tension)
BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
‘Student Activity Sheet #9
Class number:
Date
I
|
|
: BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
re con eno Student Activity Sheet #9
Name
50kN
33.79 NB: re
Fay = 44.05 kN Ey
Section _
Fre = 20 kN
Class number
(4) Take joint B as the tree body
(a) DF, =O, Fagsin 33.7° - Fy sin 33.7°- Fy <0
Fe(0.5548) = 44.05(0.5548) - 20
Far =8 KN (tension)
(0) 2 Fx=0. Fac + Fan cos 33.7°- 50+ Fyeeos 33.7° = 0.
Fu
0 - 6.66 ~ 36.65 = 6.69 KN (tension)
Roy = 50 kN
Roy = 4.44 kN
(5) Take joint D as the free body (from the rightmost joint),
(a) SF, =0. Feosin 33.7°-4.44=0 or Feo =8kN
(tension)
(b) DF.=0. 50- Fey cos 33.7°- Fo. = 0
or For: = 50 ~ 8 (0.8319) = 43.34 KN (tension)
Nye
InaInwia EDUCATION BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
: ‘Student Activity Sheet #9
Class number: _
Name
Date as
Section _ ‘Schedule’
does
Fep = 8 KN
For
(6) Take joint Cas the Iree body.
(a) SF, =0, Fee~Feosin 33.7°=0 or Fee = 4.44 KN
(compression)
(b) DF. =0, - Fepcos 33.7° + Fuc = 0
of Fac = 8(0.8319) = 6.66 KN (tension
CHECK!
(See Number 4)
Fee = 4.44 kN
Fep = 43.34 KN
(7) Take joint & as the free body,
(a) EF) =0, Foe~Foesin 33.7°=0 or Fue =8 KN
(tension)
CHECK!
(See Number 4)
(b) LF. =O, 43.34 - Fagcos 32.7° - Fer = 0.
6.68 KN (tension)
CHECK!
(See Number 3)
Student Activity Sheet #8
Name
- Sass number
Section —— Cla aoe
Date
SUMMARY
50 k,
20 kN
Member Force Magnitude
(kN)
AB 44.05
AF 36.65
BF 20.00 Tension
BC 6.69 Tension
BE 8.00 Tension
cD 8.00 Tension
CE 4.44 Compression
DE 43.34 Tension
EF 36.65 Tension
Force Type
Compression
Tension
~~
: 8
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION
Name
Section
At point A:
BFy=0
‘AB Sin 30° = 1000 Sin 60°
AB= 1732 KN
AtpointB:
BF y = O.BE Cos 30° = 1000
BE= 1155 kN
At point F:
oF
oF
point O:
DE Sin 60° = 1000
DE = 1155 kN.
BD
Ae
yao
=0
EF
DF i
,
we DG
D,
oyar SPF
DE
‘of PHINMA EDUCATION
BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
Student Activity Sheet #9
Class number
Date __ in
AC = 1000 Cos 60" - AB Cos 30°
AC = 1000 Cos 60° + 1732 Cos 30°
‘AC = 2000 KN CB
BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
Student Activity Sheet #9
$
Name
Section
Glass number
Schedule —— Oate:_______
2) Activity 3. Skill-bullding Act
les (with answer key) (18 mins + 2 mins checking)
Exercise:
Solve the following problems then place and show your complete solution in a short coupon bond in a
landscape orientation without erasures
1. The truss has 5 equilateral triangles. 3m on a side (all vertex angles are 60’). With the given load.
find the forces ( magnitude and type) in the members
25.kN 10 kN
Ro
/— 3 panels @ 3.0m = 9.0 m —4
2. The cantilever truss shown in the figure is hinged at D and E. Find the force in each member.
Trndocomen sine pope er neo CeO
10
2 Prunana LOUCATION BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
‘Student Activity Sheet #9
Name
Section _ aa e lass number ___
: Schedule a Date ae
3) Activity 4: What | Know Chart, part 2 (2 mins)
What Know Ouestions ‘What F Learned (Activity 4)
| 1 Whatis the purpose of Wis? [surgoex fOr
| | Stenowee ANP
- 7 Pees [exxerne foes |
3 What are the methods you wil |
ise toanalyze a simpietuss? (PAC THOD OF WIN
[cera sececee —15 Whats wuss analysis? ——~S*CdRaU zie “THE Fotas
| GR russe owe
fesceeeeeeeeeeees JESS eerseeees J
4) Activity 5: Check for Understanding (5 mins)
5)
‘Student Engagement (SE) Think-Pair-Share
Problem Solving:
Rea eithe problem with complete solution in landscape orientation by placing itin a short coupon bond
and avoid erasures.
Shown below is a triangular truss with members that are symmetrical withthe vertical middle merbers
Rreta W(N) acts atthe middle joint in the lower chord. Show that their is no force in the members
behacen the upper and the lower chords except in the middle vertical member. Draw a conclusion
from the result
y
t
GH = DE= L/4 (m)
DEI2 = L/8 (m)
45°; Angle BAC = 26.6°)
SAX EDUCATION BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
eens Student Activity Sheet #9
Name ___ Class number
Section __ ‘Schedule: Date
5)_Activity 6 Assessment for Student Learning
Classroom Assessment Technique (CAT) 3-2-1
Three things you leamed : ae
1, TARTHOD OF SotnTs
2 AMA TANG Wer poeceS
3_SOWE ERM foRCRS peri OM DAE
Two things that you would like to learn more about |
T pero of Forces
Teassee
2_ MAH ZUM vo)
‘Ore question you stil
1 pene
LESSON WRAP-UP
1) Activity 6: Thinking about Leaming (5 mins)
_You are done with the session! Lers track your progress
Period 1
revod? ras
PPEB EP RMP] a= [s [elo] =] |e [ala [as ]x [ola s[ a]
1. \What is important or necessary in our lesson?
2. How do you intend to use the acquired knowledge from our lesson?
FAQs
Q:What is the easiest way to determine whether a truss is stable or not?
A: The easiest way to distinguish a stable truss is to remember the triangular bull
violates this rule will be unstable.
ing blocks. A truss that
Q:Are the bars ina real truss structure pinned at each joint?
in most truss-like structures, the bars are held together by being bolted or welded to gusset plates or simply
gussets (Fig. a). Since the axial forces in members at a common joint form a concurrent force system, itis
permissible to idealize the truss joints as simple pin connections (Fig. b).
N
exams?
CATION 2
‘This document is the property of PHINMA
Seca BES 025: Statics of Rigid Bodies
Student Activity Sheet #9
Name
Name Class number
Section Schedule ~ Date
KEY TO CORRECTIONS
Activity 3
1. AB=16.36 KN (compression)
‘AC=8.18 KN (tension)
BC=16.36 KN (tension)
BI
ct
16.36 KN (compression)
16.36 KN (compression)
4.54 KN (tension)
DE=12.50 KN (compression)
FG=24.05 KN (compression)
EG=12.03 KN (tension)
2.50 KN (tension)
DF =18.29 KN (compression)
DE=12.50 KN (compression)
CE=24.53 KN (tension)
2
2. AB=2000 KN (tension)
‘AC=1732 KN (compression)
CB=866 KN (compression)
CD=2020 KN (tension)
EC=3175 KN (compression)
BD=2500 KN (tension
Activity 5
1 Rae Rie
12 W (compression)
AC=W (tension)
412. W (compression)
‘CE=W (tension)
DE=W (tension)
EG= W (tension) -
CE= W (tension) ~
DG=0
FG=0
TT aTTINMATDUCATION : een 3
| er
VAN forming MM PaCAGAHAS
Al-resce -t0
howe a
Cae VERTEY AAILES. AEE Go)
A Sie
COUIATERAL THAHGLES ary Ot
Wo The reser wer 6
5
iy THe orCeS LidactrtUoe ¥ Tee)
We easy HS
Wi THE Gweth OAD, FH
ase (OEH
4 Avs IG 2SA EH (> pee ia Soaee ©)
noe g L7H CTY pe = (6 HH ©)
peri BS AUC we = (20M cr)
d= la- SAW gos 3Req tn (o>
pes We3sa EN OCD 52 2a.0satle?
Ge = \a-3sa ten (CD
fa
eee
74.000 EH ED)
sryee
4
Vl + Aw sings =o /° KO?
Gara.
4B We -3sa eu
Agee IG-25akN (O c
Fy so
Be
« ad OPN
6 t wey -
erro
py Nnad + BCSMGD=e
©
BLE ~1G-9S49 Pe
oe s
gee LL. 9s4H\ (1) sty =o : u
° =O Singo EEFSIO=
Pe (Bs te senea 7
poeesc@H 1-354 WS (U0) = BD=-Keseqee oe
Be Meseqe (CY perso FEFOSGO EGrO
a
CNT ue
rwuss,
)
SINT A
&
Sk
6
oor
Ey =0
~lo60 4 KEGIngO= ©
ly
AC - AMIg 39 =6
Joint
_ | eco
PR Le
2
& ze
sry=0
BO - foceeys Bo" =o
\ Be = Faq ovr en (©)
Gee =o
~BY + 1000 S36 4 BAe
Ie WE Flee
x= §.qu0
6
po= 200 ka Cy)
he = 1ys2 eH (0)
Me = Fe-ors eH C)
B= egoo EN CD
cH = 2070-72@ EN (TD
See ZirS. 336 EK CD
Jeti
oii
© oo
%
\ 000
sfy 20
ensmao ~ Be SiKGO ADCO =°
efyeo
-Ee i
WINWEO AT) BD
&
ww os
Abe Lew CO
RCZ (Wor w(t
Ce zw Crd
Fae | Fe
ice,
§a=0
Td
No
geye? a °
weno cin tee =O
ww eitirs (CD :
ero v «
i= ABE x2
= oer
J he= we or w © ce UH =o
eH= Ww
aecies
Tony #
&
yy
Wo
eae
y — ERC eG
eK = Ve AEe ©)
You might also like
- Problem StatementDocument1 pageProblem Statementdan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- AeroponicDocument9 pagesAeroponicdan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- Different Units in SI and English of The Different Quantities Involved in Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsDocument2 pagesDifferent Units in SI and English of The Different Quantities Involved in Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulicsdan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- EDA Reviewer FEDocument11 pagesEDA Reviewer FEdan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- MemaDocument2 pagesMemadan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- Engg Econ P1 ExamDocument2 pagesEngg Econ P1 Examdan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-BES025Document10 pagesAssignment 2-BES025dan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 BES025Document6 pagesAssignment1 BES025dan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- Breakout Group3Document4 pagesBreakout Group3dan adrian palaganasNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)