Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Money and Credit: Economics Class-10
Uploaded by
Ankita MondalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Money and Credit: Economics Class-10
Uploaded by
Ankita MondalCopyright:
Available Formats
Session: 2019-20 Notes | By Ajeet Sir
Money and Credit
Economics
Class-10
__________________________________________________________
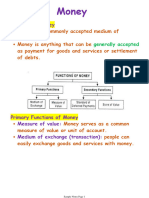
Money
Since the beginning of known history, humans have directly exchanged goods and services with one another in a
trading system called barter system. The limitations of barter system led to the evolution of currency system that is
part of modern economies today.
Barter System
• A system of buying and selling where direct exchange of goods for goods and services takes place.
• No money is involved in bartering
• Double coincidence of wants is an essential feature of barter system of exchange.
Double coincidence of wants: The situation of barter exchange in which both the parties or persons agree
and are ready to sell and buy each other’s goods.
Example of exchanging shoes for wheat: The shoe maker wants to buy wheat in exchange of shoes. Here the
two coincidences area:
(i) A person who wants to buy shoes
(ii) The same person wants to sell wheat
Money and its different forms
Money is an intermediate common measure of value that is accepted as a medium of economic exchanges by
both the sellers and the buyers. The countries have their own national currency system issued as legal tender
by their governments.
Functions of money:
• Money acts as a common measure of value for different goods and services.
• Money acts as a medium of exchange in an economic system.
• Removes the need for double coincidence
• Money has store of value
Modern Forms of money:
Currency: Board Questions:
Modern currency includes coins and paper notes. In earlier times 1. “Banks are efficient medium of
the Indians used cattle and grains as money. Later coins of gold, exchange.” Support this statement
silver and copper came into use. The problem associated with with arguments. (Delhi 2017)
metallic coins led to evolution of paper notes. 2. What are demand deposits? Explain
any three features of it. (2016)
Deposits with bank (bank money) 3. What are modern forms of money?
• People open bank accounts to deposit their surplus money (2013)
with bank.
© https://www.ncerttutorials.com Session: 2019 - 20 Twitter @ncerttutorials
Class 10 Economics Chapter: Money and credit | Ajeet Sir
• Bank pays interest on their deposits. So, depositor earns extra amount on their deposits in the form of
interest.
• The deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand and are called demand deposits.
• Along with currency, demand deposits also constitute money as they are accepted means of payment
via the following different modes.
Cheque facility:
• Cheque facility is provided by bank to the depositors to make payment without the use of cash.
• Cheque can be issued against demand deposits to transfer money from the account of the issuer of the
cheque to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Online transfer of bank money:
• The demand deposits are also used to settle payments through online transfer of bank money through
NEFT, RTGS, UPI, bank debit and credit cards.
• Online mode of transfer of demand deposits has increased since the demonetization of Indian economy
in the year 2016.
Deposits with the banks are beneficial for individual as well as for the nation
Beneficial for the individual Board Questions:
• People’s money is supposed to be safe with banks. 1. ‘How deposits with the banks
• Bank pays interest on deposits made by people are beneficial for the
individual as well as for the
• People can get loan from banks in the form of house and education nation.’ Examine the
loans or agricultural loans. statement. (2015, 2016)
2. How do bans play an
• Cheque and online transfer facilities make transaction easy and important role in the
secure without the use of cash. economy of India? (2011, 15)
Beneficial for the nation
• Banks extend loan facility at cheaper and reasonable rates for different economic development
purposes.
• Credit from banks help in the agricultural, industrial and infrastructural development of the nation.
• Banks play major role in promotion of international trade.
Modern currency as accepted medium of exchange
Board Questions:
• Modern currency is authorised by the government of a country. 1. Why is modern
currency accepted as
• In India, Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues currency notes on behalf of
medium of exchange
Central Government of India. without any use of its
own? (Delhi 2015)
• No other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency.
2. Why is rupee widely
• The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot accepted as a medium
be refused in settling transactions in India. of exchange? (2013)
• No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees in India.
2|7Pages © https://ncerttutorials.com Contact:
Class 10 Economics Chapter: Money and credit | Ajeet Sir
Loan activities of banks
Board Questions:
• Banks act as mediators between the depositors (who have surplus 1. Explain any three loan
money) and the borrowers (who need money). activities of banks in
• Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits to pay the India. (2017)
depositors who may come to withdraw money from their saving 2. How do banks mediate
accounts. between those who
• In India, banks keep about 15% of their deposits. have surplus money
and those who need
• The major portion of the deposits is used by banks to extend loans to
money? (2011)
the people for various economic needs.
• Banks charge higher rate of interest on loans and pays comparatively less interest on deposits. The
difference between the interest received from borrowers and the interest paid to the depositors is the
income of the bank.
Credit (loan) arrangements
Credit refers to agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return
for the promise of future payment. Credit arrangements can differ in different situations of lending and
borrowing.
Two different credit situations
Vital and positive role of credit
Board Questions:
• Credit helps people in establishing and running their business. 1. Explain with examples
the role of loan in
• It helps in promoting agricultural production and small-scale industries. business. (2017)
• House loans and education loans help people in construction of houses
2. What is credit?
and promoting education of their children. Describe the vital and
positive role of credit.
• In rural areas, farmers need credit to buy seeds, fertilizers, pesticides
(2015, 16)
etc. They take loan in the beginning of the crop season and repay the
3. ‘Credit has its unique
loan after harvest. role in for
development.’ Justify
• Credit is supposed to increase income and raise standard of living.
the statement with
• Example: Salim (in textbook) obtained loans from two sources to meet arguments. (2016)
the expenses of production and completed the production in time. This
way he increased his earnings. Credit made his life better off than before.
Bad and debt-trap effect of credit
Board Questions:
Describe the bad effects
• Usefulness of credit depends on the risk in the situation and may worsen
of informal sources of
the condition. There should be some support in cases of loss. credit on borrowers.
• Farmers in rural areas take loan mostly from informal sources like money (2019)
lenders.
• Loans from informal sources are costly and eats up larger part of income of the borrowers.
• Crop failure or inability to repay loan worsens the situation and the borrower has to sell his or her
assets like land.
3|7Pages © https://ncerttutorials.com Contact:
Class 10 Economics Chapter: Money and credit | Ajeet Sir
• Example from textbook: Swapna had to sell part of her land to pay off the loan she had taken from the
moneylender because the debt had grown over the year into a large amount. Credit left Swapna worse
off than before.
Terms of credit
• Terms of credit refers to conditions and requirements that need to be fulfilled to obtain loan.
• A specified rate of interest that the borrower must pay along with the principal amount.
• Lender may demand collateral as security against loan.
• The formalities of formal sector loans require proper documents to sanction loan.
• Mode of payment of loan is also a part of credit arrangement in which the loan is being sanctioned.
• The terms of credit are not always same and vary depending upon the nature of lender and the
borrower.
Collateral and its importance
Board Questions:
• Collateral is asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building,
1. Explain the importance of
vehicle, livestock, deposits with bank. collateral. (2019)
2. Why do banks and lender
• Collateral is demanded by the lender because collateral acts as
demand collateral? (2016, 19)
security against loan.
• Collateral helps in ensuring that the borrower is financially strong to repay the loan.
• If the borrower fails to repay the loan then the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to
recover the due amount.
Formal and informal sectors of credit (loan)
Formal Sector Credit Informal Sector Credit Board Questions:
1. Why are service
1. No proper formal process and
1. Formal process is required like conditions of
collateral may not be a condition for
collateral and proper documents. formal sector
loan
loans better
2. Unreasonably hight rate of interest
2. A reasonable rate of interest is than informal
is charged and may lead the
charged. sector? Explain.
borrower into debt trap.
(2019)
3. Objective of social welfare is a part 3. Maximisation of profit is the motive 2. Mention three
of formal loaning points of
difference
4. Reserve Bank of India supervises the 4. Reserve Bank of India does not between
functioning of banks supervise the informal sector formal and
informal sector
5. Rich urban households mostly seek 5. Poor households depend mostly on loan. (2012,
loan in formal sector. informal sector 2016)
6. Example: Moneylenders, traders,
6. Example: Banks and cooperatives
employers, friends and relatives.
4|7Pages © https://ncerttutorials.com Contact:
Class 10 Economics Chapter: Money and credit | Ajeet Sir
Supervision of banks by Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
• RBI monitors and ensure that minimum cash balance is maintained by banks.
• RBI sees that banks distribute credit not only to big businessmen but also to small cultivators and
small-scale industry.
• Banks have to periodically submit report regarding their lending, their borrowers and rate of interests
charged.
• RBI also sees that banks also consider the welfare of public and provide cheaper and affordable credits.
Loans in informal sources should be discouraged
• Around 85% of poor households in urban areas take loan from Board Questions:
‘The credit activities of informal
informal sources like moneylenders, traders, employers, friends
sector should be discouraged’.
and relatives. Support this statement with
arguments. (2016)
• Borrowings from informal sources are costly because the informal
sector charges high rate interests.
• Most part of the borrowers goes in paying off debt and they are left with less income.
• In certain cases, amount to be repaid is greater is greater than the income of the borrower. Such a
situation leads to debt trap and painful conditions.
• Example from textbook: Swapna had to sell part of her land to pay off the loan she had taken from the
moneylender because the debt had grown over the year into a large amount.
Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development
• The high cost of borrowing in informal sector exploits the poor Board Questions:
people and their earnings. Inability to pay loans lands the 1. Describe the importance of formal
sources of credit in the economic
borrower in debt trap and they have to sell their asset to pay off development. (2019)
the debt. 2. Why is it necessary to increase
large number of banks in mainly in
• To prevent people from seeking loans from informal sector, rural areas? Explain. (2019)
3. Explain any three reasons for
formal sector banks and cooperative societies should be banks and cooperative societies to
accessible to people and need to lend more and more increase their lending facilities in
rural areas. (2019)
particularly in rural areas. 4. How can the formal sector loan be
made beneficial for poor farmers
• It would reduce dependence on informal sources of credit.
and workers? Suggest any five
• The people could borrow cheaply for variety of needs. People measures. (2016)
5. Why is it necessary that banks and
could grow crops, do business, setup industries or trade in cooperatives increase their
goods. All this ultimately contribute to infrastructure and lending in rural areas? Explain.
(2012, 16)
economic development of the country.
• Formal credit sector need to expand so that everyone receives the loans and credit is distributed
equally to provide benefits of cheap credit to small borrowers also.
5|7Pages © https://ncerttutorials.com Contact:
Class 10 Economics Chapter: Money and credit | Ajeet Sir
• The income of people would rise as they will not have to pay high rate of interests as they have to do for
informal sector loans.
• We can say that the formal sector of credit goes well with the concept of welfare government and helps
in the economic development of the country.
Poor households are still dependent on informal sources of credit
• Banks are not present everywhere in rural India whereas informal Board Questions:
sources are present everywhere in the form of moneylenders, ‘Most of the poor households are
still dependent on informal
traders, employers, friends and relatives. sources of credit.’ Explain the
• Getting loan from banks is comparatively much more difficult than statements. (2012)
taking loan from informal sources.
• Absence of collateral is a major reason that prevents people from approaching banks to apply for loan.
In formal sector the lender knows the borrower and is ready to give loan without collateral.
• The borrowers in formal sector have to clear due amounts before applying for fresh loans while
borrowers can ask for repeated loans even before paying off the earlier loans. Example: Swapna took
another loan from the moneylender before repaying the earlier loan.
• Moneylenders exploit the exigencies of people by charging high rate of interests on their loans and also
harass the poor borrowers.
Self Help Groups (SHGs)
Self Help Groups (SHGs) are the building blocks of organisations of poor people particularly women who come
together to pool their savings, provide loans to borrowers at reasonable rates and make women self-reliant and
generate employment opportunities for women.
Organisation of SGHs
• Women in near neighbourhood areas organise themselves into small Self Help Groups.
• A typical membership of a SHG ranges from 15 to 20.
• Regular saving of group members ranges from Rs 25 to 100 or more depending on the ability to save.
• Meeting of the group is held regularly.
Loan system in SGHs
• The SGHs help borrowers overcome the problem of collateral by Board Questions:
giving loan to its members but the interest rate is less than the “‘Self help Groups’ help
borrowers overcome the problem
charge of moneylenders. of lack of collateral.” Examine the
• Regular savings increase the credibility and eligibility of the statements. (Delhi 2016)
groups to avail loan from bank.
• Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group to create self-employment opportunities for members.
6|7Pages © https://ncerttutorials.com Contact:
Class 10 Economics Chapter: Money and credit | Ajeet Sir
• Borrowers can use small loans from the banks for releasing mortgaged land, meeting working capital
needs (e.g. buying seeds, fertilisers, raw materials like bamboo and cloth), for housing construction
materials, for acquiring assets like sewing machines, handlooms, cattle etc.
Decision process and disciplined repayment of loans in SGHs
• The group as a whole decides as on matters like – which loans to be granted, purpose and amount of the
loan, rate of interest and schedule of repayment of loans etc.
• Group members have to strictly follow the schedule of repayment. Any case of non-repayment of loans
by any member is seriously followed up by other group members.
• Banks consider the discipline of repayment record of SGHs and are willing to lend more even in the
absence of collateral as such.
Advantages of SGHs
• SGHs are the building blocks of organisations of the rural poor and women in particular.
• SGHs help borrowers overcome the lack of collateral.
• Members can get timely loans for variety of purposes and at reasonable interest rate.
• SGHs are an example of organisational and collective efforts toward their self-reliance.
• Regular meetings also provide a platform to discuss and decide some action on different social issues
such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc.
You can visit us at the following links
https://www.ncerttutorials.com
7|7Pages © https://ncerttutorials.com Contact:
You might also like
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Study Notes on Money and Credit ChapterDocument6 pagesClass 10 Study Notes on Money and Credit ChapterAavy MishraNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument12 pagesMoney and CreditthinkiitNo ratings yet
- MONEY X EconomicsDocument7 pagesMONEY X EconomicsAvika SinghNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit Class 10 Notes CBSE Economics Chapter 3 (PDF)Document9 pagesMoney and Credit Class 10 Notes CBSE Economics Chapter 3 (PDF)jangdesarthakNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument2 pagesMoney and CreditChris JudeNo ratings yet
- Why Modern Currency is Accepted as a Medium of ExchangeDocument13 pagesWhy Modern Currency is Accepted as a Medium of ExchangeRengavadivelammaal .CNo ratings yet
- December-10-Eco-Ch-3 Money & Credit-NotesDocument36 pagesDecember-10-Eco-Ch-3 Money & Credit-Notesananyamishra11122007No ratings yet
- Money and Credit Question and AnswersDocument12 pagesMoney and Credit Question and AnswersAashi Ranjan100% (1)
- Money ND CreditDocument28 pagesMoney ND CreditSanchita JianNo ratings yet
- 3 - Money & CreditDocument3 pages3 - Money & CreditsonurazadNo ratings yet
- 21-22 /I Sri Sri Ravishankar Vidya Mandir NOTES STD: X Topic: Money and Credit Subject: ECONOMICS Date:15-04-21Document3 pages21-22 /I Sri Sri Ravishankar Vidya Mandir NOTES STD: X Topic: Money and Credit Subject: ECONOMICS Date:15-04-21Lammichand ViraNo ratings yet
- 5fb8aa157f899075e8d880ef 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341 1636704765310Document11 pages5fb8aa157f899075e8d880ef 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341 1636704765310ZULNo ratings yet
- Banking CH 1 Power PointDocument24 pagesBanking CH 1 Power PointYoseph KassaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsDocument4 pagesNotes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 Money and Credit (Economics-X)Document11 pagesCh.3 Money and Credit (Economics-X)Ayush ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Money and CreditDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Money and CreditKiran shukla100% (1)
- 3 Money N Credit NotesDocument15 pages3 Money N Credit NotesAbhay100% (1)
- Notes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsDocument9 pagesNotes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit Class-X MoneyDocument9 pagesMoney and Credit Class-X MoneyAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 Money and CreditDocument5 pages3 Money and CreditRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 - Money and Credit PDFDocument7 pagesChapter-1 - Money and Credit PDFAnonymous qIs8cBbNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Eco Chap 3 Money and CreditDocument42 pagesClass 10 Eco Chap 3 Money and CreditDNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Questions and Answers Money and CreditDocument11 pagesClass 10 Economics Chapter 3 Questions and Answers Money and Credithimanshu mangalNo ratings yet
- Economics, Chapter 3 Money and CreditDocument3 pagesEconomics, Chapter 3 Money and CreditshambhaviNo ratings yet
- SST - Revision (Economics)Document45 pagesSST - Revision (Economics)RSNo ratings yet
- 1.money and CreditDocument18 pages1.money and CreditNandita KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Ch3. Money and CreditDocument30 pagesCh3. Money and CreditGarima GoelNo ratings yet
- Bank, Banking and Banking Regulations PresentationDocument7 pagesBank, Banking and Banking Regulations PresentationApekshaNo ratings yet
- 10-Money and Credit NotesDocument6 pages10-Money and Credit NotesNagulan MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument7 pagesMoney and Creditraimaali220077No ratings yet
- Banking Types and FunctionsDocument13 pagesBanking Types and FunctionsGemechis BussaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Meaning and Definition of BankDocument6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Meaning and Definition of BankdineshNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit NotesDocument14 pagesClass 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit Notesmexeb28867No ratings yet
- Essential Role of Banks in SocietyDocument8 pagesEssential Role of Banks in SocietyDarshan M MNo ratings yet
- Banking LawDocument13 pagesBanking Lawprithvi yadavNo ratings yet
- 5 Tiwxm MR Be 8 RKAk T0 UsgDocument28 pages5 Tiwxm MR Be 8 RKAk T0 Usgshanmuga Priya (Shan)No ratings yet
- Money and Credit Class 10 Extra Questions Economics Chapter 3Document5 pagesMoney and Credit Class 10 Extra Questions Economics Chapter 3AaravNo ratings yet
- All Types of Bank Report SumeshDocument30 pagesAll Types of Bank Report Sumeshsumesh894No ratings yet
- What is Banking? A Brief HistoryDocument26 pagesWhat is Banking? A Brief HistoryShikha KumariNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument4 pagesMoney and Creditvibrantbhabha7No ratings yet
- Sample NotesDocument20 pagesSample NotesKenpin EteNo ratings yet
- Business Services Part 2Document11 pagesBusiness Services Part 2Santa GlenmarkNo ratings yet
- Banking SystemDocument12 pagesBanking SystemDilip RCNo ratings yet
- 0 - Retail Banking Doc2Document8 pages0 - Retail Banking Doc2Niyati BagweNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Banking BasicsDocument97 pagesIntroduction to Banking Basicsraj731No ratings yet
- STD X CH 3 Money and Credit Notes (21-22)Document6 pagesSTD X CH 3 Money and Credit Notes (21-22)Dhwani ShahNo ratings yet
- Micro Finance-Lessons From International Experience: Lecture - 19811Document102 pagesMicro Finance-Lessons From International Experience: Lecture - 19811dipu jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking SystemDocument67 pagesIndian Banking SystemTejas MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Self PPT On Money and CreditDocument15 pagesSelf PPT On Money and CreditTripti SinghaNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMoney and Credit Practice QuestionsARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Attachment Video 3 - Supply of Money Lyst9092 PDFDocument30 pagesAttachment Video 3 - Supply of Money Lyst9092 PDFSaumyaNo ratings yet
- Sant Atulanand Convent School Koirajpur, Varanasi Class:-10 (Economics) Lesson: - Money and CreditDocument12 pagesSant Atulanand Convent School Koirajpur, Varanasi Class:-10 (Economics) Lesson: - Money and CreditVaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument14 pagesMoney and CreditAbhimanyu Chauhan72% (57)
- Money and Credit-Ncert SolutionsDocument4 pagesMoney and Credit-Ncert SolutionsSafwa KhasimNo ratings yet
- MONEY & CREDIT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-MapDocument49 pagesMONEY & CREDIT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-Mapnimit jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit: Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesMoney and Credit: Practice QuestionsAshok MukhijaNo ratings yet
- Economics FinalDocument36 pagesEconomics FinalPratham PrahaladkaNo ratings yet
- Research TopDocument20 pagesResearch Tophari.vyas1946No ratings yet
- Indian Banking System: An IntroductionDocument67 pagesIndian Banking System: An IntroductionamitNo ratings yet
- FT-04 OYMR Code-A 13.06.2019 SolutionDocument5 pagesFT-04 OYMR Code-A 13.06.2019 SolutionAnkita MondalNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 ElectrostaticDocument280 pagesUNIT - 1 ElectrostaticAnkita MondalNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and The Indian Economy: Political Science Class-10Document7 pagesGlobalisation and The Indian Economy: Political Science Class-10Ankita MondalNo ratings yet
- Assessing Democracy Through Its OutcomesDocument7 pagesAssessing Democracy Through Its OutcomesAnkita MondalNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need Political Parties?Document9 pagesWhy Do We Need Political Parties?Ankita MondalNo ratings yet
- Cebu Oxygen Acetylene Co., vs. Drilon, G.R. No. 82849, August 2, 1989Document6 pagesCebu Oxygen Acetylene Co., vs. Drilon, G.R. No. 82849, August 2, 1989JemNo ratings yet
- Bayes Slides1Document146 pagesBayes Slides1Panagiotis KarathymiosNo ratings yet
- GUEST REGISTRATION CARDDocument1 pageGUEST REGISTRATION CARDRasmi Ranjan Kar100% (1)
- Pengembangan Lembar Kegiatan Siswa Berbasis Online Berbantuan Geogebra Book Untuk Siswa SMA Kelas X Pada Materi TrigonometriDocument15 pagesPengembangan Lembar Kegiatan Siswa Berbasis Online Berbantuan Geogebra Book Untuk Siswa SMA Kelas X Pada Materi TrigonometriNovita Rizki YustianiNo ratings yet
- 11 Ways To Encourage Stakeholder Participation:: Writing Good Consultation QuestionsDocument1 page11 Ways To Encourage Stakeholder Participation:: Writing Good Consultation QuestionsLuz Alinsunurin DulogNo ratings yet
- OPTION STRATEGIES PAYOFF CALCULATOR v2Document9 pagesOPTION STRATEGIES PAYOFF CALCULATOR v2Jay KewatNo ratings yet
- Mushroom Storage and ProcessingDocument5 pagesMushroom Storage and ProcessingKho Siong Thong80% (5)
- Document - University Admission SystemDocument100 pagesDocument - University Admission SystemNaresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Distributor AgreementDocument10 pagesDistributor Agreementsanket_hiremathNo ratings yet
- Digest Office of The Ombudsman V Samaniego 2008Document3 pagesDigest Office of The Ombudsman V Samaniego 2008Lea Gabrielle FariolaNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document4 pagesSet 1insan biasaNo ratings yet
- Odoo JS Framework Rewrite Brings New Views and TestingDocument68 pagesOdoo JS Framework Rewrite Brings New Views and TestingglobalknowledgeNo ratings yet
- Manual Micro DNC 2dDocument31 pagesManual Micro DNC 2dDiego GarciaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics d201Document185 pagesThermodynamics d201Rentu PhiliposeNo ratings yet
- Java Programming: Lab Assignment 2Document17 pagesJava Programming: Lab Assignment 2Sanjana chowdary50% (4)
- Iwan Lab Guide v1.1 FinalDocument63 pagesIwan Lab Guide v1.1 FinalRicardo SicheranNo ratings yet
- SQL Server Management Studio Database Engine Query Editor Window - Microsoft DocsDocument6 pagesSQL Server Management Studio Database Engine Query Editor Window - Microsoft DocsAchamyeleh TamiruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Earth WorkDocument39 pagesChapter 4 Earth WorkYitbarek BayieseNo ratings yet
- No or Islamic Bank OurStory EnglishDocument45 pagesNo or Islamic Bank OurStory EnglishTalib ZaidiNo ratings yet
- ISLAND SAILING CLUB COWES 2012 ROUND THE ISLAND RACE RESULTSDocument64 pagesISLAND SAILING CLUB COWES 2012 ROUND THE ISLAND RACE RESULTSmatthias_25No ratings yet
- MB1 - The Australian Economy PA 7092016Document8 pagesMB1 - The Australian Economy PA 7092016ninja980117No ratings yet
- JBNBNBNBNBNBDocument4 pagesJBNBNBNBNBNBmaheshNo ratings yet
- D20 Q12Document7 pagesD20 Q12Luca PitocchiNo ratings yet
- Nasrullah March23Document11 pagesNasrullah March23Angellin JoiceNo ratings yet
- Sjzl20061019-ZXC10 BSCB (V8.16) Hardware ManualDocument69 pagesSjzl20061019-ZXC10 BSCB (V8.16) Hardware ManualAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- Inspection & Testing of Elastic Rail Clips PDFDocument5 pagesInspection & Testing of Elastic Rail Clips PDFfiemsabyasachi0% (1)
- The Future of Retail in Asia-Pacific: How To Thrive at High SpeedDocument12 pagesThe Future of Retail in Asia-Pacific: How To Thrive at High SpeedPhạm Thanh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- CIMA Introduction To NLPDocument4 pagesCIMA Introduction To NLPsambrefoNo ratings yet
- Indian Railway Bridge Design ProcessDocument18 pagesIndian Railway Bridge Design ProcessCivil Engineer100% (1)
- Tourism and Development Planning: Slide 9.1Document19 pagesTourism and Development Planning: Slide 9.1English TimeNo ratings yet