Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Term Iii Mock Examination June 2019-20: Key Stage 3 (Year IX)
Uploaded by
Rashad KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Term Iii Mock Examination June 2019-20: Key Stage 3 (Year IX)
Uploaded by
Rashad KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
TERM III MOCK EXAMINATION
June 2019-20
Key Stage 3 (Year IX)
Date : 3rd June 2020
:
Name of the Candidate Rashad khan
_________________________________________________________
Subject : Chemistry
Total Maximum Marks : 30
Instructions to the candidate:
The Exam is for 40 minutes.
Read the instructions carefully.
Please make sure you have a blank paper to write down your name, question number and answers.
Write in dark blue or black pen.
You may use a soft pencil for any diagrams, graphs or rough working.
Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid.
Answer all questions.
At the end of the examination, scan your paper and send back at Google Classroom Classwork within
15 minutes. Do NOT post at the Class Stream.
A copy of the periodic table is attached on the last page.
Electronic calculators may be used.
The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question.
Section Maximum Marks
Marks Obtained
A 5
B 15
C 10
Checked by : ____________________________
TOTAL 30
Rechecked by : ____________________________
Section A
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 1 of 10 Term III (2019 – 2020)
1. A student adds a small amount of ammonium chloride to a beaker of water. The
temperature of the water decreases from 21 °C to 17 °C.
Which type of reaction has occurred and why?
type of reaction reason
A exothermic heat is released
B exothermic heat is absorbed
C endothermic heat is released
D endothermic heat is absorbed
[1]
2. Which of the following processes is endothermic?
A Reacting sodium with water.
B The use of petrol in an engine.
C Distilling crude oil.
D Burning fossil fuels [1]
3. The energy level diagram below shows the relative energies of the reactants and
products in a reaction.
Which row correctly describes the type of reaction and corresponding energy change?
type of reaction reason
A endothermic heat is released
B endothermic heat is absorbed
C exothermic heat is released
D exothermic heat is absorbed
[1]
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 2 of 9 Term III (2019 – 2020)
4. A student was investigating the rate of reaction between a solid base and a solution of
sulfuric acid. Two experiments were performed, S and T, in which the mass of the
reaction flask was recorded as shown in the graph.
Which of the following changes could explain the difference in results between S and
T?
A The sulfuric acid is less concentrated in T.
B The sulfuric acid is more concentrated in T.
C A higher temperature is used in S.
D Larger sized particles are used in T.
[1]
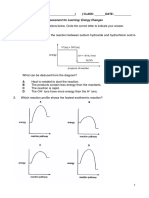
5. Which graph correctly shows the effect of increasing the temperature on the rate of
reaction between magnesium and sulfuric acid in which neither reactant runs out?
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 3 of 9 Term III (2019 – 2020)
[1]
[Total Marks: 5]
Section B
1. Ammonia is used to make nitrogen trifluoride, NF3.
Nitrogen trifluoride is essential to the electronics industry. It is made by the following
reaction.
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 4 of 9 Term III (2019 – 2020)
Determine if the above reaction is exothermic or endothermic using the following
bond energies and by completing the following table. The first line has been done as
an example. Bond energy is the amount of energy, in kJ/mole, needed to break or
make one mole of the bond.
bond bond energy in kJ/mol
N-H 390
F-F 155
N-F 280
H-F 565
bonds broken energy change in kJ/mol
N-H (3 x 390) = 1170
F-F (3 x 155) = 465
Total 1635
bonds formed energy change in kJ/mol
N-F (3 X 280) =840
H-F (3 X 565) = 1695
Total 2535 1635 – 2535 = -900kj/mol
Show your working.
………………exothermic……………………………………………………………………
………..…[5]
2. (a) Calculate the overall energy change for the reaction between iodine and chlorine
using the bond energy values shown.
I2 + Cl2 2ICl
bond energy/ kJ per mol
I-I 151
Cl-Cl 242
I-Cl 208
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 5 of 9 Term III (2019 – 2020)
bonds energy change in kJ/mol
broken
I-I 1X 151 = 151
1 X 242 = 242
Total 393
bonds energy change in kJ/mol
formed
I-Cl 2 x 208 = 416
Total 416
Show your working.
393-416 = -23kj/mol change in energy, reaction is exothermic [4]
(b) Draw a labeled energy level diagram for the reaction between iodine and
chlorine using the information in (a).
[3]
3. a. Photosynthesis is an unusual endothermic reaction.
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 6 of 9 Term III (2019 – 2020)
Where does the energy for photosynthesis come from?
………………………sun light……………………………………………………[1]
(b) Bond forming is exothermic, bond breaking is endothermic. Explain the
difference between an exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction.
In exothermic the reactants have more energy than the product
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
difference in energy is given out as heat whereas in endothermic
…………………………………………………………………………………….[2]
more energy have product than reactant and difference in energy
is taken in from the surroundings.
[Total Marks: 15]
Section C
1. One of the factors which determine the reaction rate of solids is particle size.
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 7 of 9 Term III (2019 – 2020)
(a) A mixture of finely powdered aluminium and air may explode when ignited. An
explosion is a very fast exothermic reaction. This causes alarge and sudden
increase in temperature.
Explain each of the following in terms of collisions between reacting particles.
(i) Why is the reaction between finely powdered aluminium and air very fast?
Because they have more surface area
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………….……………………....[2]
(ii)Explain why for most reactions the rate of reaction decreases with time.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Because they have same energgy
……………………………………………….……………………....[2]
(iii) Suggest an explanation why the rate of reaction in an explosion could increase
rather than decrease through time.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………….[3]
(iv) Give another example of a substance other than a metal which, when finely
powdered, might explode when ignited in air.
Bombs powder
…..………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(b) Reaction speed increases as the temperature increases.
Explain why reaction speed increases with temperature.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
When temperature increases more particle collide
when they collide then reaction becomes faster.
……………………………………………………………………………..[2]
[Total Marks: 10]
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 8 of 9 Term III (2019 – 2020)
of 10 Term III (2019 – 2020)
CHEMISTRY – Yr IX Page 9
You might also like
- Eocq Chapter 3 PDFDocument4 pagesEocq Chapter 3 PDFtylerdk80100% (2)
- Sample First Long Exam (Chem 17) : CHEM 17 (2 Sem, AY 15 - 16) UP ACME - Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesSample First Long Exam (Chem 17) : CHEM 17 (2 Sem, AY 15 - 16) UP ACME - Page 1 of 5Jasper DumalaogNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument16 pagesQuestionsTee Xin RuiNo ratings yet
- (DragonVision) Chemistry 5090 Variant2 s18 PDFDocument16 pages(DragonVision) Chemistry 5090 Variant2 s18 PDFDragonVisionNo ratings yet
- Answers 10 NSA3 ChemistryDocument4 pagesAnswers 10 NSA3 ChemistryshamooNo ratings yet
- WS Grade 10 IG Chemistry 23-24 - Energy ChangesDocument5 pagesWS Grade 10 IG Chemistry 23-24 - Energy ChangesSiyaNo ratings yet
- Anglo-Chinese Junior College Department of Chemistry Preliminary ExaminationDocument18 pagesAnglo-Chinese Junior College Department of Chemistry Preliminary ExaminationZach EganNo ratings yet
- Mock 1523Document58 pagesMock 1523Javaria AjmalNo ratings yet
- JC2 Chemistry H2 2018 MeridianDocument109 pagesJC2 Chemistry H2 2018 MeridianYao Le Titanium ChenNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Sq1 Questions Aoudi 2022Document27 pagesTopic 6 Sq1 Questions Aoudi 2022yamanfortnaimatNo ratings yet
- June 2010 CH5Document15 pagesJune 2010 CH5s5ff22mrtcNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/13Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/13chris chongNo ratings yet
- Answer Key B and D Exam Iii Dec 5TH Chem 102Document11 pagesAnswer Key B and D Exam Iii Dec 5TH Chem 102M.SNo ratings yet
- Final HSSC-I Chemistry Model Paper MergedDocument10 pagesFinal HSSC-I Chemistry Model Paper MergeddasddaNo ratings yet
- June 2013 (v1) QPDocument16 pagesJune 2013 (v1) QPmahtabsilvercraftNo ratings yet
- June 2020 (v1) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry GCSEDocument16 pagesJune 2020 (v1) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry GCSEZwe Min HtetNo ratings yet
- 0620 - s18 - 1 - 1 - QP Chem Paper 0292938384Document16 pages0620 - s18 - 1 - 1 - QP Chem Paper 0292938384Aaa IiiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationShounik JoshiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 - 2018-2003 - QP PDFDocument539 pagesChemistry Paper 1 - 2018-2003 - QP PDFal_helu26No ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument16 pagesMark SchemeSadman SameerNo ratings yet
- 9701 m19 QP 12 PDFDocument16 pages9701 m19 QP 12 PDFAnonymous PqNB7YamNo ratings yet
- G19 Paper 1 Summative 2019Document14 pagesG19 Paper 1 Summative 2019Nur Dinah Alesha Mohd Ali ZarNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Sq1 Topic 6 Energetics Answered Aoudi 2022Document27 pagesTopic 6 Sq1 Topic 6 Energetics Answered Aoudi 2022yamanfortnaimatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/12Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/12spandan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- !2014 Excel G-12 Chemistry Model - 2Document11 pages!2014 Excel G-12 Chemistry Model - 2henotech HDNo ratings yet
- Answer ALL The Following Questions Below. Circle The Correct Letter To Indicate Your AnswerDocument4 pagesAnswer ALL The Following Questions Below. Circle The Correct Letter To Indicate Your AnswerTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- J1 Promos 2015 Paper 1Document11 pagesJ1 Promos 2015 Paper 1aliciaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U CertificateDocument16 pagesCambridge Pre-U Certificatelaksh bissoondialNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/13Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/13Tamer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chem HSSC 1 Model PaperDocument8 pagesChem HSSC 1 Model PaperPikoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelaaaNo ratings yet
- Pahang NEW STPM 2012 Chemistry PDFDocument15 pagesPahang NEW STPM 2012 Chemistry PDFNorbert LimNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23Yau Yee LeungNo ratings yet
- 0620 m23 QP 22-MinDocument14 pages0620 m23 QP 22-Minjelani17fNo ratings yet
- 2023 HCI H2 Chem Prelim Paper 1 Question PaperDocument14 pages2023 HCI H2 Chem Prelim Paper 1 Question PaperMinh LukeNo ratings yet
- As Level Test - 1Document16 pagesAs Level Test - 1zafarchem_iqbal0% (1)
- Chemistry Mock Paper 1 2021Document6 pagesChemistry Mock Paper 1 2021Nattrillion TNo ratings yet
- June 2022 (9-1) (v2) QP - Paper 1 CAIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument16 pagesJune 2022 (9-1) (v2) QP - Paper 1 CAIE Chemistry IGCSEsharma_anshu_b_techNo ratings yet
- 2020 JPJC H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 1Document13 pages2020 JPJC H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 1clarissa yeo0% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12Tamer AhmedNo ratings yet
- November 2022 (9701 - 13) QPDocument16 pagesNovember 2022 (9701 - 13) QPHung Mang ThiNo ratings yet
- TSSM 2019 ExamDocument28 pagesTSSM 2019 ExamSwastikaNo ratings yet
- November 2015 (v3) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry A-LevelDocument16 pagesNovember 2015 (v3) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry A-LevelAnirudh BansalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SSC II Paper I-2Document8 pagesChemistry SSC II Paper I-2Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- 2015 Promo - Section ADocument9 pages2015 Promo - Section AMelissa0% (1)
- 2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Document16 pages2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Chow Kim WanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12zoyaNo ratings yet
- 9185 s13 QP 13 PDFDocument16 pages9185 s13 QP 13 PDFsarahNo ratings yet
- November 2017 (v3) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry A-LevelDocument16 pagesNovember 2017 (v3) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry A-LevelSalman Farsi TaharatNo ratings yet
- For Examiner's Use A B16 B17 C18 C19 C20Document8 pagesFor Examiner's Use A B16 B17 C18 C19 C20Muhd FaiZNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument6 pagesEnergeticsAmmar AbiddNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationMaameama FrempongNo ratings yet
- SRJC Promo 2009 Paper 1Document16 pagesSRJC Promo 2009 Paper 1gretchen92No ratings yet
- 2019 H2 Chem Prelim P3 QPDocument12 pages2019 H2 Chem Prelim P3 QPFaith SeahNo ratings yet
- 2019 TJC H2 Chem Prelim P1 QPDocument16 pages2019 TJC H2 Chem Prelim P1 QPaliciaNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC2 H2 Chemistry Prelim Temasek Junior CollegeDocument67 pages2019 JC2 H2 Chemistry Prelim Temasek Junior CollegePadmalaya paloNo ratings yet
- March 2016 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument16 pagesMarch 2016 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry IGCSERedCazorlaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Levelazadaland40No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12190377964No ratings yet
- ASRJC H2 Chem 2021 P1 QPDocument20 pagesASRJC H2 Chem 2021 P1 QPantesipation ฅ'ω'ฅNo ratings yet
- Plasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryFrom EverandPlasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryD. E. JensenNo ratings yet
- Pipe Phase ManualDocument402 pagesPipe Phase ManualDarwin MarceloNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Polytetrafluoroethylene by Pulsed Electron Ablation - Deposition and Wettability AspectsDocument5 pagesPreparation of Polytetrafluoroethylene by Pulsed Electron Ablation - Deposition and Wettability AspectsOmar AlshekhliNo ratings yet
- Ultratech TDS Leaflet - FixoblockDocument1 pageUltratech TDS Leaflet - FixoblockRabish ANo ratings yet
- CANDU Safety Function and Shutdown SystemsDocument47 pagesCANDU Safety Function and Shutdown Systemsanpuselvi125No ratings yet
- Density of KOH SolutionsDocument1 pageDensity of KOH SolutionsjohnihaasNo ratings yet
- Raised FloorDocument9 pagesRaised FloorSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- EcosystemsDocument2 pagesEcosystemsapi-332204622No ratings yet
- Van de Graaff GeneratorDocument8 pagesVan de Graaff GeneratorTanmoy BarikNo ratings yet
- Gaussian 03 HelpDocument1,011 pagesGaussian 03 Helpsuresh.waghmodeNo ratings yet
- Fractography AluminiumDocument21 pagesFractography AluminiumFazry NurokhmanNo ratings yet
- Glossary: PAC-3 Technical ManualDocument24 pagesGlossary: PAC-3 Technical ManualAlwi MahbubiNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Elementary ParticlesDocument5 pagesShort Notes On Elementary ParticlesJeffrey ChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document39 pagesChapter 2Sohail SakhaniNo ratings yet
- Evolution of CSIDocument19 pagesEvolution of CSItailor100% (2)
- Rust Protection by Metal Preservatives in The Humidity CabinetDocument9 pagesRust Protection by Metal Preservatives in The Humidity CabinettoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Xenon-Arc Accelerated ExposureDocument4 pagesXenon-Arc Accelerated ExposureSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Gelest - Silane Coupling AgentsDocument60 pagesGelest - Silane Coupling AgentsEugene PaiNo ratings yet
- CH6504Document7 pagesCH6504RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Fixoblock PDFDocument2 pagesFixoblock PDFRohan BagadiyaNo ratings yet
- 7557 - Lubricants Brochure PDFDocument6 pages7557 - Lubricants Brochure PDFrachitmailNo ratings yet
- A Review of Evaporative Cooling TechnologiesDocument9 pagesA Review of Evaporative Cooling TechnologiesDavid DonosoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5Document3 pagesChemistry 5Ronak JoshiNo ratings yet
- HLBDocument4 pagesHLBbobgallowayNo ratings yet
- D 6284 - 02 - RdyyodqDocument5 pagesD 6284 - 02 - RdyyodqHoem ITNo ratings yet
- Dcet Paper 2017 PDFDocument31 pagesDcet Paper 2017 PDFNanda kumarNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Dairy Chemistry PDFDocument208 pagesA Textbook of Dairy Chemistry PDFOner Altınsoy75% (4)
- Buried Pipe Design FinalDocument10 pagesBuried Pipe Design FinalDipesh100% (1)
- Air Pollution: Ozone's Travels Create Scientific Puzzle, Political MuddleDocument28 pagesAir Pollution: Ozone's Travels Create Scientific Puzzle, Political MuddleRey Bautista CeriloNo ratings yet
- NEB IlluminaDocument13 pagesNEB IlluminaLei Zi DuNo ratings yet