Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH - 5 Forms of Market
Uploaded by
kalynOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH - 5 Forms of Market
Uploaded by
kalynCopyright:
Available Formats
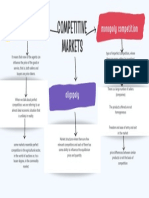
FORMS OF MARKET
An arrangement through which buyers and
sellers come in contact with each other Market is a network of dealings between potential buyers and
directly or indirectly and exchange of goods potential sellers. At any point of time, a market will exist if there are :
and services takes place among them. 1) Buyers and sellers
2) A product or service to be bought and sold
3) Price of the product
Market 4) Close contact between buyers and sellers
5) Knowledge about market
"Economists understand the term market, not any
A place where goods and services
particular market place in which things are bought
are purchased
and sold, but the whole of any region in which
a. Local
buyers and sellers are in such a close contact with
one another that the prices of the same goods tend Place b. National
to equality easily and quickly".
c. International
Classification of Market a. Very short Period
a. Perfect Competition
Monopoly Competition b. Short Period
Time 自由主題
Oligopoly b. Imperfect Competition c. Long Period
Monopolistic competition d. Very Long Period
◆◇PERFECT COMPETITION◇◆
Price determination under Perfect Competition
Features
Perfect mobility of Factors of Production 8 Meaning The interaction of demand and supply determine price
of the commodity in perfect competition. This is known
No Government Intervention 7 A perfectly competitive market is one in which as ‘equilibrium price.’
the number of Buyers and Sellers is very large.
Absence of transport cost 6
Perfect knowledge of Market 5 Definition
Single Price 4 1 By Mrs.Jan Robinson
Large entry and exit 3 " Perfect competition prevails when the
2 demand for the output of each Producer
Homogeneous product 2 is perfectly elastic ".
Large numbers of Sellers and Buyers 1
◆◇◆◇◆◇◆◇ IMPERFECT COMPETITION ◇◆◇◆◇◆◇◆
MONOPOLY
Prof. E. H. Chamberlin coined this
concept in his book “Theory of
Introduction
Meaning Monopolistic Competition” which
was published in 1933.
Derived from Greek work 'Mono' = ' “Monopolistic competition refers to competition
Single' and 'Poly' = 'Seller' . among a large number of sellers producing close but
not perfect substitutes.”
Definition
There is only one seller who controls the
MONOPOLISTIC
entire market supply for a product which 3 Mixed features of Perfect Competition and Monopoly
has no close substitute. COMPETITION
Fairly large no. of sellers
Definition
Fairly large no. of buyers
Product Differentiation
According to E. H. Chamberlin, “Monopoly
refers to a single firm which has control
Features Free Entry and Exit
over the supply of a product which has no
close substitute.”
Selling cost
Features
Close Substitutes
Concept of Group
Single seller 2
No close substitute
Barriers to entry Derived from the Greek words
‘Oligo’ which means few and
Complete control over the market supply ‘poly’ which means sellers.
Meaning
Price maker There are a few firms (sellers) in the
market producing either a homogeneous
Price discrimination
product or a differentiated product
No distinction between firm and industry
OLIGOPOLY Few firms or sellers
Private
Interdependence
Public
Advertising
Legal Features
Entry barriers
Natural Types
Lack of uniformity
Simple
Uncertainty
Discriminating
Voluntary
You might also like
- (BL.2) SM0117057 - Uditanshu MemoDocument43 pages(BL.2) SM0117057 - Uditanshu MemojffhNo ratings yet
- Break Even AnalysisDocument6 pagesBreak Even AnalysishmarcalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Price DeterminationDocument16 pagesPrice DeterminationMD. TasneemNo ratings yet
- Markets EcoDocument16 pagesMarkets EcoPrathika JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- UNIT2Document90 pagesUNIT2siriusblack3159No ratings yet
- Industry: EquilibriumDocument13 pagesIndustry: EquilibriumKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Forms of MarketDocument17 pagesForms of Marketdil preetNo ratings yet
- 12EfficiencyandEquity LectureDocument3 pages12EfficiencyandEquity LecturechinazapiusogbuehiNo ratings yet
- Perfect CompetetionDocument8 pagesPerfect Competetionwandering.17.freeNo ratings yet
- Review AgeconmktgDocument24 pagesReview AgeconmktgShieldon BulawanNo ratings yet
- Ch10 - Price and Output Under Pure MonopolyDocument8 pagesCh10 - Price and Output Under Pure MonopolyNabh GargNo ratings yet
- Forms of MarketDocument22 pagesForms of Marketkenguvamanojkumar013No ratings yet
- Fase2-Natalia Cano - Estudio Sobre Las GeneralidadesDocument1 pageFase2-Natalia Cano - Estudio Sobre Las GeneralidadesIsabella SotoNo ratings yet
- Perfect MarketDocument7 pagesPerfect MarketAlit AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Maam Nario Eco 1 Module 4Document6 pagesMaam Nario Eco 1 Module 4Kier Arven SallyNo ratings yet
- Eco - Module 1 - Unit 3Document8 pagesEco - Module 1 - Unit 3Kartik PuranikNo ratings yet
- 318 Economics Eng Lesson21Document12 pages318 Economics Eng Lesson21Kirankumar AriNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 9: Forms of Market: Lilavatibai Podar High School. ISCDocument12 pagesChapter No. 9: Forms of Market: Lilavatibai Podar High School. ISCStephine BochuNo ratings yet
- Perfect CompetitionDocument11 pagesPerfect CompetitionRekha BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Econ311 LBCDocument9 pagesModule 3 Econ311 LBCItsss ClarizzaNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Types of MarketsDocument66 pagesMeaning and Types of MarketsVrinda TayadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.1 and 7.2 Group 1 ManEconDocument3 pagesChapter 7.1 and 7.2 Group 1 ManEconfrancheskaarcederaNo ratings yet
- Market Structure: Extreme Cases ofDocument10 pagesMarket Structure: Extreme Cases ofRockyNo ratings yet
- Market: Subject: Business Economics Subject Code: SBAA1103Document19 pagesMarket: Subject: Business Economics Subject Code: SBAA1103ushna ahmedNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 EconomicsDocument22 pagesUnit-4 Economicsrakshit konchadaNo ratings yet
- Name of The Course: Business Economics Name of The Course: Business Economics Course Code: Course CodeDocument33 pagesName of The Course: Business Economics Name of The Course: Business Economics Course Code: Course CodeVIVA MANNo ratings yet
- Ch2 - Basic Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument2 pagesCh2 - Basic Demand and Supply AnalysisNabh GargNo ratings yet
- Actividad 8, Fundamentos de MatematicasDocument4 pagesActividad 8, Fundamentos de MatematicasNina Tovar PaezNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Market PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 4. Market PDFЕвгения ПантелейNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Demand Supply and Market Equilibrium PDFDocument30 pagesSilo - Tips - Demand Supply and Market Equilibrium PDFSZANo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 Updated Core Notes 2022 Paper 2Document55 pagesGRADE 10 Updated Core Notes 2022 Paper 2cyonela5No ratings yet
- Applied Econ Week 5Document4 pagesApplied Econ Week 5Coleen Heart Migue PortonNo ratings yet
- Ma Eco Pre Pap1 bl3Document95 pagesMa Eco Pre Pap1 bl3gopalNo ratings yet
- CE 132 Engineering Economics Basic Terms and Principles of EconomicsDocument3 pagesCE 132 Engineering Economics Basic Terms and Principles of EconomicsMa Aaron Gwyneth BalisacanNo ratings yet
- Rem 116 - 456Document2 pagesRem 116 - 456Michael Talento CobillaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1567149977 SmsDocument31 pagesAssignment 1567149977 SmsdipanajnNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 U1 A4 PLUSDocument12 pagesChap 4 U1 A4 PLUSshadmaanNo ratings yet
- Activity 21 Table of Structure Regarding To M.S.Document2 pagesActivity 21 Table of Structure Regarding To M.S.Kerby Geroza AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 08 Seatwork 2MANECODocument1 page08 Seatwork 2MANECOMhaiel EscalNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document11 pagesModule 2thelmaNo ratings yet
- ME - Price Output Determination (Perfect Competition)Document3 pagesME - Price Output Determination (Perfect Competition)soubhagya_babuNo ratings yet
- Appeco Lecture 7Document13 pagesAppeco Lecture 7Isabella EgeNo ratings yet
- Week 10, Group 4Document10 pagesWeek 10, Group 4Pam SicatNo ratings yet
- Project For First Semester: MarketDocument22 pagesProject For First Semester: MarketShravan SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- I T & D (E) : Mportant Erms Efinitions ConomicsDocument10 pagesI T & D (E) : Mportant Erms Efinitions ConomicskulsumNo ratings yet
- ECo9.Lesson10 MarketsDocument34 pagesECo9.Lesson10 Marketsgavinlaxamana2021No ratings yet
- TA Unit 9Document24 pagesTA Unit 9THẢO KHIẾU THỊ THANHNo ratings yet
- ApuntesDocument1 pageApuntesainhoa puenteNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument45 pagesMarket StructuresbonduamrutharaoNo ratings yet
- Applied EconomicsDocument21 pagesApplied EconomicsDanica LlamazaresNo ratings yet
- Perfect Ion 1Document8 pagesPerfect Ion 1Vijay100% (1)
- Market StructureDocument7 pagesMarket StructureMuhammad AbrarrNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocument5 pagesMonopolistic Competitionvinay535No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1Likitha GangaramNo ratings yet
- Project EconomicsDocument12 pagesProject EconomicsBoomNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document65 pagesUnit 4M ChandruNo ratings yet
- Market and Revenue Curves of Firms - Ch12Document17 pagesMarket and Revenue Curves of Firms - Ch12LeenaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Market Structures: Managerial Economics and Financial AnalysisDocument27 pagesUnit-Iii Market Structures: Managerial Economics and Financial AnalysisAnusha EnigallaNo ratings yet
- Eco Finals - Lesson 1Document6 pagesEco Finals - Lesson 1Rodessa CacayuranNo ratings yet
- Colombia's Forward Energy Market: Figure 1. Two Products, One MarketDocument63 pagesColombia's Forward Energy Market: Figure 1. Two Products, One MarketJUAN SEBASTIAN HERNANDEZ PEÑANo ratings yet
- BDA AuctionDocument51 pagesBDA Auctions dNo ratings yet
- BelleflammePeitz IOMS2 ToCDocument11 pagesBelleflammePeitz IOMS2 ToCCARMEN ADRIANA CONTRERAS REYESNo ratings yet
- Extra Oligopolio PDFDocument17 pagesExtra Oligopolio PDFkako_1984No ratings yet
- Welfare Effects of Perfect CompetitionDocument7 pagesWelfare Effects of Perfect CompetitionBoi NonoNo ratings yet
- Market Structure TableDocument2 pagesMarket Structure TableJohn Jeric Ramos DacioNo ratings yet
- Share Monopoly and Oligopoly in Market StructureDocument33 pagesShare Monopoly and Oligopoly in Market Structurekatariya vatsalNo ratings yet
- Imperfect Competition: Economics 302 - Microeconomic Theory II: Strategic BehaviorDocument11 pagesImperfect Competition: Economics 302 - Microeconomic Theory II: Strategic BehaviorNikanon AvaNo ratings yet
- S Snip Test KK Sharma 260711Document5 pagesS Snip Test KK Sharma 260711Nikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Monopoly: Lipsey & Chrystal Economics 12EDocument28 pagesMonopoly: Lipsey & Chrystal Economics 12EAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Organization 02: OligopolyDocument42 pagesIndustrial Organization 02: Oligopolyheh92No ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document31 pagesChapter 15Shiela MaeaNo ratings yet
- Marketstructure PDFDocument15 pagesMarketstructure PDFmihir kumarNo ratings yet
- A Study of Single Economic Entity Doctrine in Context of IndiaDocument9 pagesA Study of Single Economic Entity Doctrine in Context of IndiaChirag AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Economics - Chapter 7Document59 pagesFundamentals of Economics - Chapter 7Jai ToneExcelNo ratings yet
- 3036-Article Text-14751-2-10-20210316Document6 pages3036-Article Text-14751-2-10-20210316claraNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument20 pagesFinalMaryamNo ratings yet
- OligopolyDocument16 pagesOligopolySaagar MengarNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Basic Oligopoly Models: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy Baye Prince 9 EditionDocument28 pagesCh. 9 Basic Oligopoly Models: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy Baye Prince 9 EditionLivia Indriyani Lasria InnonchykaNo ratings yet
- Vertical - Relations 2023Document90 pagesVertical - Relations 2023Eva MorinNo ratings yet
- Last Assignment ECODocument3 pagesLast Assignment ECOU-Sri JupriNo ratings yet
- Floyds PM CheatsheetDocument4 pagesFloyds PM CheatsheetHyung Su Cheong (MaSsanSC)No ratings yet
- Unit-12.pdf OligoolyDocument23 pagesUnit-12.pdf OligoolyYeniezemen MuluNo ratings yet
- Survey of Economics 8th Edition Tucker Test BankDocument31 pagesSurvey of Economics 8th Edition Tucker Test Bankamandabinh1j6100% (27)
- Competition Law PrinciplesDocument15 pagesCompetition Law PrinciplesAhmad FaiqNo ratings yet
- Tdrbpconf9l1 enDocument17 pagesTdrbpconf9l1 enKanita Imamovic-CizmicNo ratings yet
- Microeconomic PresentationDocument18 pagesMicroeconomic PresentationFara AraNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Quarter 1Document12 pagesApplied Economics - Quarter 1Gladys Angela ValdemoroNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 UK Competition LegislationsDocument25 pagesUNIT 2 UK Competition LegislationsDEEPANJALI K SNo ratings yet